1.springboot启动流程
SpringBoot版本:2.1.2.RELEASE
1.maven
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.1.2.RELEASE</version>
</parent> <dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
2.主程序入口,两种方式
- SpringApplication.run(Application.class);
- new SpringApplication(Application.class).run(args);可以通过设置springApplication的defaultProperties等属性,设置一些配置参数信息
2.1. 初始化springApplication对象
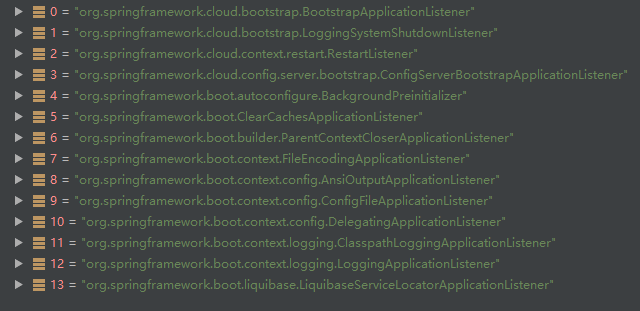
listeners.starting(); EventPublishingRunListener
发布一个ApplicationStartingEvent事件
- LoggingApplicationListener
- BackgroundPreinitializer
- DelegatingApplicationListener
- LiquibaseServiceLocatorApplicationListener
2.2. 准备环境变量 Environment
2.2.1.org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication#prepareEnvironment
org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication#getOrCreateEnvironment
new StandardServletEnvironment() ->new StandardEnvironment() ->new AbstractEnvironment()
public AbstractEnvironment() {
this.propertyResolver = new PropertySourcesPropertyResolver(this.propertySources);
this.customizePropertySources(this.propertySources);
}
#StandardServletEnvironment
protected void customizePropertySources(MutablePropertySources propertySources) {
propertySources.addLast(new StubPropertySource("servletConfigInitParams"));
propertySources.addLast(new StubPropertySource("servletContextInitParams"));
if (JndiLocatorDelegate.isDefaultJndiEnvironmentAvailable()) {
propertySources.addLast(new JndiPropertySource("jndiProperties"));
}
super.customizePropertySources(propertySources);
}
#StandardEnvironment
protected void customizePropertySources(MutablePropertySources propertySources) {
propertySources.addLast(new MapPropertySource("systemProperties", this.getSystemProperties()));
propertySources.addLast(new SystemEnvironmentPropertySource("systemEnvironment", this.getSystemEnvironment()));
}
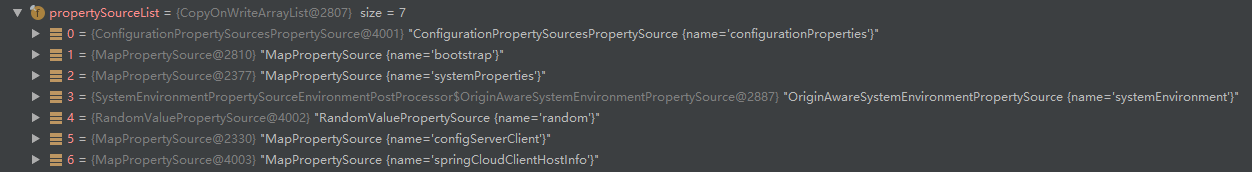
此时,environment中的propertySources包含servletConfigInitParams,servletContextInitParams,jndiProperties(存在的话,spring.properties中配置spring.jndi.ignore=true,且...待定),systemProperties,systemEnvironment
org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication#configureEnvironment
protected void configurePropertySources(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, String[] args) {
MutablePropertySources sources = environment.getPropertySources();
if (this.defaultProperties != null && !this.defaultProperties.isEmpty()) {
sources.addLast(new MapPropertySource("defaultProperties", this.defaultProperties));
}
if (this.addCommandLineProperties && args.length > 0) {
String name = "commandLineArgs";
if (sources.contains(name)) {
PropertySource<?> source = sources.get(name);
CompositePropertySource composite = new CompositePropertySource(name);
composite.addPropertySource(new SimpleCommandLinePropertySource("springApplicationCommandLineArgs", args));
composite.addPropertySource(source);
sources.replace(name, composite);
} else {
sources.addFirst(new SimpleCommandLinePropertySource(args));
}
}
}
org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListeners#environmentPrepared
发布一个ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent

- ConfigServerBootstrapApplicationListener
private PropertySource<?> propertySource = new MapPropertySource("configServerClient", Collections.singletonMap("spring.cloud.config.enabled", "false")); public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent event) {
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = event.getEnvironment();
if (!environment.resolvePlaceholders("${spring.cloud.config.enabled:false}").equalsIgnoreCase("true") && !environment.getPropertySources().contains(this.propertySource.getName())) {
environment.getPropertySources().addLast(this.propertySource);
} } - BootstrapApplicationListener
- LoggingSystemShutdownListener
- ConfigFileApplicationListener
- AnsiOutputApplicationListener
- LoggingApplicationListener
- BackgroundPreinitializer
- ClasspathLoggingApplicationListener
- DelegatingApplicationListener
- FileEncodingApplicationListener
2.3. 初始化ApplicatonContext
org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication#createApplicationContext
创建一个AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication#prepareContext
发布一个ApplicationContextInitializedEvent
org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication#refreshContext
发布一个ContextRefreshedContext,初始化所有的Bean
1.springboot启动流程的更多相关文章
- SpringBoot启动流程解析
写在前面: 由于该系统是底层系统,以微服务形式对外暴露dubbo服务,所以本流程中SpringBoot不基于jetty或者tomcat等容器启动方式发布服务,而是以执行程序方式启动来发布(参考下图ke ...
- SpringBoot启动流程分析(五):SpringBoot自动装配原理实现
SpringBoot系列文章简介 SpringBoot源码阅读辅助篇: Spring IoC容器与应用上下文的设计与实现 SpringBoot启动流程源码分析: SpringBoot启动流程分析(一) ...
- SpringBoot启动流程分析(六):IoC容器依赖注入
SpringBoot系列文章简介 SpringBoot源码阅读辅助篇: Spring IoC容器与应用上下文的设计与实现 SpringBoot启动流程源码分析: SpringBoot启动流程分析(一) ...
- SpringBoot启动流程分析(一):SpringApplication类初始化过程
SpringBoot系列文章简介 SpringBoot源码阅读辅助篇: Spring IoC容器与应用上下文的设计与实现 SpringBoot启动流程源码分析: SpringBoot启动流程分析(一) ...
- SpringBoot启动流程分析(二):SpringApplication的run方法
SpringBoot系列文章简介 SpringBoot源码阅读辅助篇: Spring IoC容器与应用上下文的设计与实现 SpringBoot启动流程源码分析: SpringBoot启动流程分析(一) ...
- SpringBoot启动流程分析(三):SpringApplication的run方法之prepareContext()方法
SpringBoot系列文章简介 SpringBoot源码阅读辅助篇: Spring IoC容器与应用上下文的设计与实现 SpringBoot启动流程源码分析: SpringBoot启动流程分析(一) ...
- SpringBoot启动流程分析(四):IoC容器的初始化过程
SpringBoot系列文章简介 SpringBoot源码阅读辅助篇: Spring IoC容器与应用上下文的设计与实现 SpringBoot启动流程源码分析: SpringBoot启动流程分析(一) ...
- SpringBoot启动流程及其原理
Spring Boot.Spring MVC 和 Spring 有什么区别? 分别描述各自的特征: Spring 框架就像一个家族,有众多衍生产品例如 boot.security.jpa等等:但他们的 ...
- springboot启动流程(一)构造SpringApplication实例对象
所有文章 https://www.cnblogs.com/lay2017/p/11478237.html 启动入口 本文是springboot启动流程的第一篇,涉及的内容是SpringApplicat ...
- SpringBoot 启动流程
SpringBoot 启动流程 加载 resources/META-INF/spring.factories 中配置的 ApplicationContextInitializer 和 Applicat ...
随机推荐
- 关于iReport5.6.0无法正常启动或者闪退或者JDK8不兼容的解决方案
参考网址: https://blog.csdn.net/erlian1992/article/details/76359191?locationNum=6&fps=1 说白了 ,即 jaspe ...
- Unexpected token '...'. Expected a property name.
原因:浏览器不支持 es6 扩展运算符 结论: 1.不用 ... 2. babel-polyfill对扩展运算符...搞的不是太好,要单独安装一个 plugin-proposal-object-re ...
- 如何使用cgdb(一)——窗口切换
cgdb是一个轻量级的基于控制台的多窗口gdb调试界面.除了标准的gdb控制台之外,cgdb还提供了一个分屏视图,可以在执行的时候显示具备语法高亮的源代码.键盘控制是仿照vim设计的,所以vim用户使 ...
- 《数据结构与算法之美》 <02>复杂度分析(下):浅析最好、最坏、平均、均摊时间复杂度?
上一节,我们讲了复杂度的大 O 表示法和几个分析技巧,还举了一些常见复杂度分析的例子,比如 O(1).O(logn).O(n).O(nlogn) 复杂度分析.掌握了这些内容,对于复杂度分析这个知识点, ...
- ffmpeg 命令行 杂记
输入mp4文件中的音频每一帧的信息 ffprobe -show_streams -select_streams a -show_format -show_frames .\HYUNDAIMOBIS.m ...
- 12_Redis_服务器命令
一:Redis 服务器:Redis 服务器命令主要是用于管理 redis 服务
- linux 设备驱动与应用程序异步通知
一.异步通知机制简介 异步通知机制的意思:一旦设备准备就绪,可以主动的通知应用程序进行相应的操作,从而使得应用程序不必去查询设备的状态. 异步通知比较准确的称谓是"信号驱动的异步IO&quo ...
- mysql 数据库常见的一些基本操作 !详不详细你说了算!
在日常应用中可能一时想不起来,所以有必要整理一份 指令相关的笔记,以是个人比较满意,也比较全面的一份笔记,希望能帮到你,适用初级小白,大神可略过! MYSQL常用命令: 数据备份与还原·注意:不要打分 ...
- 关于join() 是否会释放锁的一些思考
# 首先从一个很有意思的问题开始: - 问 : Thread 的join() 方法是否会释放锁? - 答: 会! # 如果一切到这里就结束了,那可能也就没有这篇小记了,但是我的脑子却冒出了一些奇怪的想 ...
- okhttp拦截器之ConnectInterceptor解析
主流程分析: 继续分析okhttp的拦截器,继上次分析了CacheInterceptor缓存拦截器之后,接下来到连接拦截器啦,如下: 打开看一下它的javadoc: 而整个它的实现不长,如下: 也就是 ...
