spark源码分析, 任务提交及序列化
简易基本流程图如下
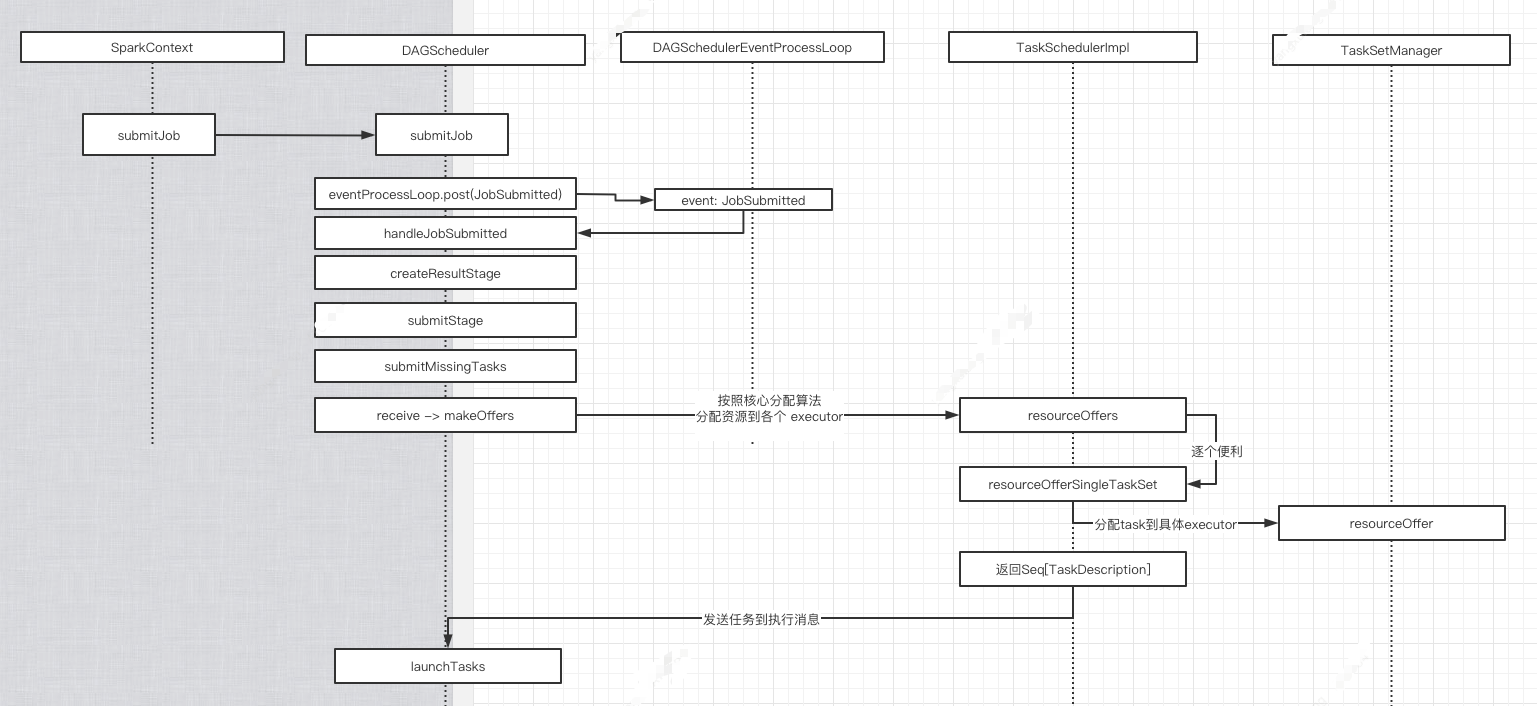
1. org.apache.spark.scheduler.DAGScheduler#submitMissingTasks
2. => org.apache.spark.scheduler.TaskSchedulerImpl#submitTasks
// First figure out the indexes of partition ids to compute.
val partitionsToCompute: Seq[Int] = stage.findMissingPartitions() // Use the scheduling pool, job group, description, etc. from an ActiveJob associated
// with this Stage
val properties = jobIdToActiveJob(jobId).properties runningStages += stage
// SparkListenerStageSubmitted should be posted before testing whether tasks are
// serializable. If tasks are not serializable, a SparkListenerStageCompleted event
// will be posted, which should always come after a corresponding SparkListenerStageSubmitted
// event.
stage match {
case s: ShuffleMapStage =>
outputCommitCoordinator.stageStart(stage = s.id, maxPartitionId = s.numPartitions - 1)
case s: ResultStage =>
outputCommitCoordinator.stageStart(
stage = s.id, maxPartitionId = s.rdd.partitions.length - 1)
}
val taskIdToLocations: Map[Int, Seq[TaskLocation]] = try {
stage match {
case s: ShuffleMapStage =>
partitionsToCompute.map { id => (id, getPreferredLocs(stage.rdd, id))}.toMap
case s: ResultStage =>
partitionsToCompute.map { id =>
val p = s.partitions(id)
(id, getPreferredLocs(stage.rdd, p))
}.toMap
}
} //序列化 RDD
// TODO: Maybe we can keep the taskBinary in Stage to avoid serializing it multiple times.
// Broadcasted binary for the task, used to dispatch tasks to executors. Note that we broadcast
// the serialized copy of the RDD and for each task we will deserialize it, which means each
// task gets a different copy of the RDD. This provides stronger isolation between tasks that
// might modify state of objects referenced in their closures. This is necessary in Hadoop
// where the JobConf/Configuration object is not thread-safe.
var taskBinary: Broadcast[Array[Byte]] = null
var partitions: Array[Partition] = null
try {
// For ShuffleMapTask, serialize and broadcast (rdd, shuffleDep).
// For ResultTask, serialize and broadcast (rdd, func).
var taskBinaryBytes: Array[Byte] = null
// taskBinaryBytes and partitions are both effected by the checkpoint status. We need
// this synchronization in case another concurrent job is checkpointing this RDD, so we get a
// consistent view of both variables.
RDDCheckpointData.synchronized {
taskBinaryBytes = stage match {
case stage: ShuffleMapStage =>
JavaUtils.bufferToArray(
closureSerializer.serialize((stage.rdd, stage.shuffleDep): AnyRef))
case stage: ResultStage =>
JavaUtils.bufferToArray(closureSerializer.serialize((stage.rdd, stage.func): AnyRef))
} partitions = stage.rdd.partitions
} taskBinary = sc.broadcast(taskBinaryBytes)
} //生成 taskset
val tasks: Seq[Task[_]] = try {
val serializedTaskMetrics = closureSerializer.serialize(stage.latestInfo.taskMetrics).array()
stage match {
case stage: ShuffleMapStage =>
stage.pendingPartitions.clear()
partitionsToCompute.map { id =>
val locs = taskIdToLocations(id)
val part = partitions(id)
stage.pendingPartitions += id
new ShuffleMapTask(stage.id, stage.latestInfo.attemptNumber,
taskBinary, part, locs, properties, serializedTaskMetrics, Option(jobId),
Option(sc.applicationId), sc.applicationAttemptId, stage.rdd.isBarrier())
} case stage: ResultStage =>
partitionsToCompute.map { id =>
val p: Int = stage.partitions(id)
val part = partitions(p)
val locs = taskIdToLocations(id)
new ResultTask(stage.id, stage.latestInfo.attemptNumber,
taskBinary, part, locs, id, properties, serializedTaskMetrics,
Option(jobId), Option(sc.applicationId), sc.applicationAttemptId,
stage.rdd.isBarrier())
}
}
} //最终提交 taskset
if (tasks.size > 0) {
logInfo(s"Submitting ${tasks.size} missing tasks from $stage (${stage.rdd}) (first 15 " +
s"tasks are for partitions ${tasks.take(15).map(_.partitionId)})")
taskScheduler.submitTasks(new TaskSet(
tasks.toArray, stage.id, stage.latestInfo.attemptNumber, jobId, properties))
}
3. => org.apache.spark.scheduler.cluster.CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend#reviveOffers ,发送消息
def reviveOffers() {
// 类型 CoarseGrainedClusterMessage
driverEndpoint.send(ReviveOffers) }
4. => 自己处理消息org.apache.spark.scheduler.cluster.CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend.DriverEndpoint#receive
override def receive: PartialFunction[Any, Unit] = {
case StatusUpdate(executorId, taskId, state, data) =>
.....
case ReviveOffers =>
makeOffers()
case KillTask(taskId, executorId, interruptThread, reason) =>
....
case KillExecutorsOnHost(host) =>
.....
case UpdateDelegationTokens(newDelegationTokens) =>
.....
case RemoveExecutor(executorId, reason) =>
...
removeExecutor(executorId, reason)
}
5.=> org.apache.spark.scheduler.cluster.CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend.DriverEndpoint#makeOffers
// Make fake resource offers on all executors
private def makeOffers() {
// Make sure no executor is killed while some task is launching on it
val taskDescs = withLock {
// Filter out executors under killing
val activeExecutors = executorDataMap.filterKeys(executorIsAlive)
val workOffers = activeExecutors.map {
case (id, executorData) =>
new WorkerOffer(id, executorData.executorHost, executorData.freeCores,
Some(executorData.executorAddress.hostPort))
}.toIndexedSeq
scheduler.resourceOffers(workOffers)
}
if (!taskDescs.isEmpty) {
launchTasks(taskDescs)
}
}
6.=> org.apache.spark.scheduler.TaskSchedulerImpl#resourceOffers. 按照核心分配算法分配各 task 到 executor 上.
// Take each TaskSet in our scheduling order, and then offer it each node in increasing order
// of locality levels so that it gets a chance to launch local tasks on all of them.
// NOTE: the preferredLocality order: PROCESS_LOCAL, NODE_LOCAL, NO_PREF, RACK_LOCAL, ANY
for (taskSet <- sortedTaskSets) {
var launchedAnyTask = false
// Record all the executor IDs assigned barrier tasks on.
val addressesWithDescs = ArrayBuffer[(String, TaskDescription)]()
for (currentMaxLocality <- taskSet.myLocalityLevels) {
var launchedTaskAtCurrentMaxLocality = false
do {
launchedTaskAtCurrentMaxLocality = resourceOfferSingleTaskSet(taskSet,
currentMaxLocality, shuffledOffers, availableCpus, tasks, addressesWithDescs)
launchedAnyTask |= launchedTaskAtCurrentMaxLocality
} while (launchedTaskAtCurrentMaxLocality)
}
}
=>org.apache.spark.scheduler.TaskSchedulerImpl#resourceOfferSingleTaskSet
=>org.apache.spark.scheduler.TaskSchedulerImpl#resourceOfferSingleTaskSet private def resourceOfferSingleTaskSet(
taskSet: TaskSetManager,
maxLocality: TaskLocality,
shuffledOffers: Seq[WorkerOffer],
availableCpus: Array[Int],
tasks: IndexedSeq[ArrayBuffer[TaskDescription]],
addressesWithDescs: ArrayBuffer[(String, TaskDescription)]) : Boolean = {
var launchedTask = false //分配任务
for (i <- 0 until shuffledOffers.size) {
val execId = shuffledOffers(i).executorId
val host = shuffledOffers(i).host
if (availableCpus(i) >= CPUS_PER_TASK) { for (task <- taskSet.resourceOffer(execId, host, maxLocality)) {
tasks(i) += task
val tid = task.taskId
taskIdToTaskSetManager.put(tid, taskSet)
taskIdToExecutorId(tid) = execId
executorIdToRunningTaskIds(execId).add(tid)
availableCpus(i) -= CPUS_PER_TASK launchedTask = true
} }
}
return launchedTask
} ==> org.apache.spark.scheduler.TaskSetManager#resourceOffer
@throws[TaskNotSerializableException]
def resourceOffer(
execId: String,
host: String,
maxLocality: TaskLocality.TaskLocality)
: Option[TaskDescription] =
{
val offerBlacklisted = taskSetBlacklistHelperOpt.exists { blacklist =>
blacklist.isNodeBlacklistedForTaskSet(host) ||
blacklist.isExecutorBlacklistedForTaskSet(execId)
}
if (!isZombie && !offerBlacklisted) {
val curTime = clock.getTimeMillis() var allowedLocality = maxLocality if (maxLocality != TaskLocality.NO_PREF) {
allowedLocality = getAllowedLocalityLevel(curTime)
if (allowedLocality > maxLocality) {
// We're not allowed to search for farther-away tasks
allowedLocality = maxLocality
}
} dequeueTask(execId, host, allowedLocality).map { case ((index, taskLocality, speculative)) =>
// Found a task; do some bookkeeping and return a task description
//找到一个任务,然后封装task的信息,包括序列化
val task = tasks(index)
//原子自增
val taskId = sched.newTaskId()
// Do various bookkeeping
copiesRunning(index) += 1
val attemptNum = taskAttempts(index).size
val info = new TaskInfo(taskId, index, attemptNum, curTime,
execId, host, taskLocality, speculative)
taskInfos(taskId) = info
taskAttempts(index) = info :: taskAttempts(index) // Serialize and return the task
val serializedTask: ByteBuffer = try {
ser.serialize(task)
}
//添加到运行Map中
addRunningTask(taskId) sched.dagScheduler.taskStarted(task, info)
new TaskDescription(
taskId,
attemptNum,
execId,
taskName,
index,
task.partitionId,
addedFiles,
addedJars,
task.localProperties,
serializedTask)
}
} else {
None
}
}
7.=> org.apache.spark.scheduler.cluster.CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend.DriverEndpoint#launchTasks
// Launch tasks returned by a set of resource offers
private def launchTasks(tasks: Seq[Seq[TaskDescription]]) {
for (task <- tasks.flatten) {
val serializedTask = TaskDescription.encode(task)
...
executorData.executorEndpoint.send(LaunchTask(new SerializableBuffer(serializedTask)))
}
8. => org.apache.spark.scheduler.TaskDescription#encode TaskDescription作为 message 发送给 executor
def encode(taskDescription: TaskDescription): ByteBuffer = {
val bytesOut = new ByteBufferOutputStream(4096)
val dataOut = new DataOutputStream(bytesOut)
dataOut.writeLong(taskDescription.taskId)
dataOut.writeInt(taskDescription.attemptNumber)
dataOut.writeUTF(taskDescription.executorId)
dataOut.writeUTF(taskDescription.name)
dataOut.writeInt(taskDescription.index)
dataOut.writeInt(taskDescription.partitionId)
// Write files.
serializeStringLongMap(taskDescription.addedFiles, dataOut)
// Write jars.
serializeStringLongMap(taskDescription.addedJars, dataOut)
// Write properties.
dataOut.writeInt(taskDescription.properties.size())
taskDescription.properties.asScala.foreach { case (key, value) =>
dataOut.writeUTF(key)
// SPARK-19796 -- writeUTF doesn't work for long strings, which can happen for property values
val bytes = value.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)
dataOut.writeInt(bytes.length)
dataOut.write(bytes)
}
// Write the task. The task is already serialized, so write it directly to the byte buffer.
Utils.writeByteBuffer(taskDescription.serializedTask, bytesOut)
dataOut.close()
bytesOut.close()
bytesOut.toByteBuffer
}
spark源码分析, 任务提交及序列化的更多相关文章
- Spark源码分析之四:Stage提交
各位看官,上一篇<Spark源码分析之Stage划分>详细讲述了Spark中Stage的划分,下面,我们进入第三个阶段--Stage提交. Stage提交阶段的主要目的就一个,就是将每个S ...
- spark 源码分析之十九 -- Stage的提交
引言 上篇 spark 源码分析之十九 -- DAG的生成和Stage的划分 中,主要介绍了下图中的前两个阶段DAG的构建和Stage的划分. 本篇文章主要剖析,Stage是如何提交的. rdd的依赖 ...
- Spark源码分析之七:Task运行(一)
在Task调度相关的两篇文章<Spark源码分析之五:Task调度(一)>与<Spark源码分析之六:Task调度(二)>中,我们大致了解了Task调度相关的主要逻辑,并且在T ...
- Spark源码分析之六:Task调度(二)
话说在<Spark源码分析之五:Task调度(一)>一文中,我们对Task调度分析到了DriverEndpoint的makeOffers()方法.这个方法针对接收到的ReviveOffer ...
- Spark源码分析之三:Stage划分
继上篇<Spark源码分析之Job的调度模型与运行反馈>之后,我们继续来看第二阶段--Stage划分. Stage划分的大体流程如下图所示: 前面提到,对于JobSubmitted事件,我 ...
- spark 源码分析之二十一 -- Task的执行流程
引言 在上两篇文章 spark 源码分析之十九 -- DAG的生成和Stage的划分 和 spark 源码分析之二十 -- Stage的提交 中剖析了Spark的DAG的生成,Stage的划分以及St ...
- spark源码分析以及优化
第一章.spark源码分析之RDD四种依赖关系 一.RDD四种依赖关系 RDD四种依赖关系,分别是 ShuffleDependency.PrunDependency.RangeDependency和O ...
- 【转】Spark源码分析之-deploy模块
原文地址:http://jerryshao.me/architecture/2013/04/30/Spark%E6%BA%90%E7%A0%81%E5%88%86%E6%9E%90%E4%B9%8B- ...
- Spark源码分析:多种部署方式之间的区别与联系(转)
原文链接:Spark源码分析:多种部署方式之间的区别与联系(1) 从官方的文档我们可以知道,Spark的部署方式有很多种:local.Standalone.Mesos.YARN.....不同部署方式的 ...
随机推荐
- 牛客网数据库SQL实战解析(21-30题)
牛客网SQL刷题地址: https://www.nowcoder.com/ta/sql?page=0 牛客网数据库SQL实战解析(01-10题): https://blog.csdn.net/u010 ...
- day38:MySQL数据库之约束&索引&外键&存储引擎
目录 part1:数据类型 part2:约束 part3:主键索引 PRI &唯一索引 UNI &普通索引 MUL part4:外键:foreign key part5:在外键中设置联 ...
- Linux磁盘分区、挂载、查看文件大小
快速查看系统文件大小命令 du -ah --max-depth=1 后面可以添加文件目录 ,如果不添加默认当前目录. 下面进入正题~~ 磁盘分区.挂载 引言: ①.分区的方式 a)mbr分区: 最多支 ...
- 8.深入k8s:资源控制Qos和eviction及其源码分析
转载请声明出处哦~,本篇文章发布于luozhiyun的博客:https://www.luozhiyun.com,源码版本是1.19 又是一个周末,可以愉快的坐下来静静的品味一段源码,这一篇涉及到资源的 ...
- nginx配置过程中出现的问题
在安装nginx时我们先创建用户useradd -s /sbin/nologin -M nginx 不然会报nginx: [emerg] getpwnam("nginx") fai ...
- 解决Oracle12cr2自创建用户无法登录的问题
说明: 下面创建是创建CDB本地用户,不是PDB应用程序用户,如果是PDB应用程序创建语法会不一样.下面介绍创建CDB本地用户. 创建表空空间 CREATE TABLESPACE YH datafil ...
- Android开发之SDCardUtils工具类。java工具详细代码,附源代码。判断SD卡是否挂载等功能
package com.xiaobing.zhbj.utils; import java.io.BufferedInputStream; import java.io.BufferedOutputSt ...
- LoadRunner回放脚本遇到的问题(遇到就补上)
问题一:Error-26612:HTTP Status-code=500(Internal Server Error) 解决过程:google找到了关于这个错误有多种解决的方法,但是都不是我要的,最重 ...
- 【python】装饰器听了N次也没印象,读完这篇你就懂了
装饰器其实一直是我的一个"老大难".这个知识点就放在那,但是拖延症... 其实在平常写写脚本的过程中,这个知识点你可能用到不多 但在面试的时候,这可是一个高频问题. 一.什么是装饰 ...
- MyBatis动态SQL(使用)整理
MyBatis 令人喜欢的一大特性就是动态 SQL.在使用 JDBC 的过程中, 根据条件进行 SQL 的拼接是很麻烦且很容易出错的.MyBatis 动态 SQL 的出现, 解决了这个麻烦. MyBa ...
