基于Arduino的音乐动感节奏灯
1、音乐动感节奏灯是个什么东西?
前段时间听音乐觉得无聊,便想着音乐光听也没意思啊,能不能 “看见” 音乐呢?于是谷歌了一番,发现还真有人做了将音乐可视化的东西,那就是音乐节奏灯。说的简单点就是LED灯光颜色亮度等随着音乐的节奏而发生变化,看了下他们的实现方法有很多,不过大都比较复杂,而且灯只能够做节奏灯也比较浪费,于是我便动手做了一个既可以当作普通台灯使用,又可以随着音乐而闪烁的动感节奏灯,一举两得。
2、做这个东西需要准备哪些材料?
工欲善其事,必先利其器。那么做这样一个音乐动感节奏等需要准备哪些材料呢?
- Arduino UNO 开发板
- 声音传感器(最好买Arduino专用的)
- BLE蓝牙4.0模块
- WS2812B彩色灯带
- 灯罩
- 3D打印底座
- 电源线和杜邦线若干
以上材料可以在淘宝买到,灯罩和3D打印的底座可以按照自己的实际需求来进行自己选择,为了防止打广告的嫌疑我就不放购买链接了,可以自行设计打印~
3、做这个东西需该怎么做?
准备好上述的材料之后,我们就可以开始进行灯的制作啦~,节奏灯的主要结构如下图:
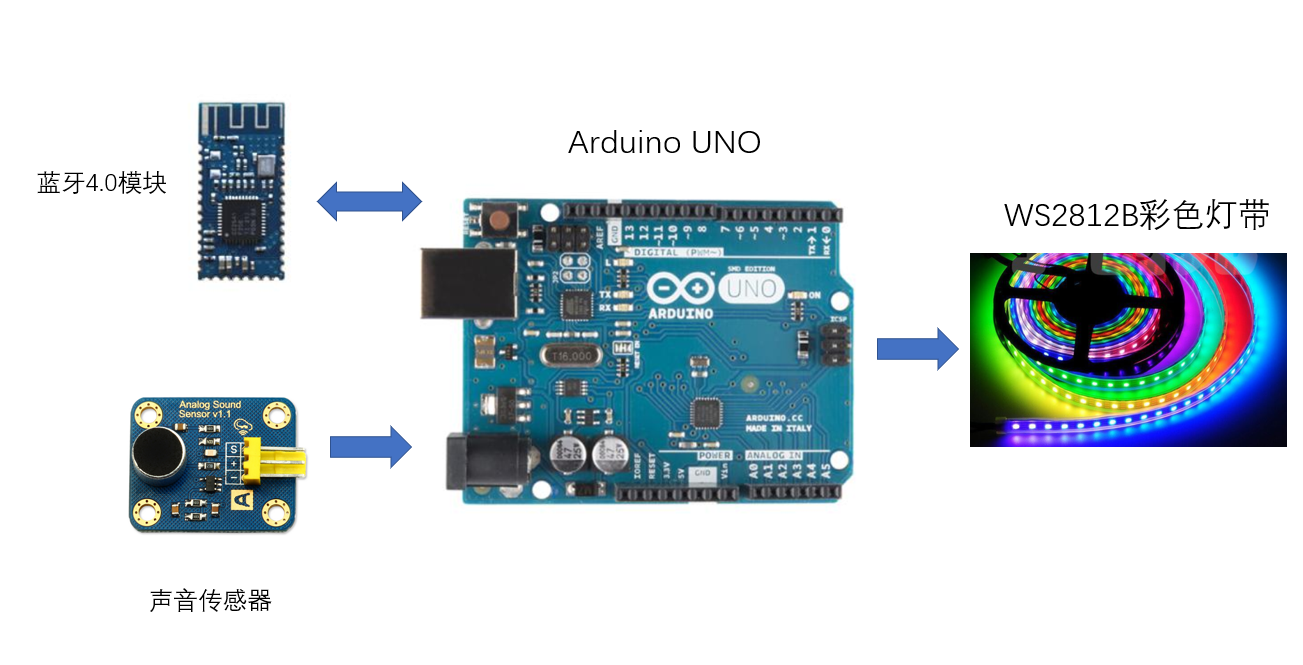
我们使用Arduino UNO作为主要的计算和处理模块,蓝牙4.0模块和手机进行通信,利用手机APP来选择模式(后续会讲),在节奏灯的模式下,通过声音传感器来采集声音,通过得到的声音来控制灯带的颜色和闪烁,在彩色灯的模式下,利用手机来控制灯的颜色,理论上的有160万可调颜色。接下来介绍下详细的步骤。
3.1 安装开发环境
Arduino UNO 开发的环境为Arduino IDE,软件下载地址为 https://www.arduino.cn/thread-5838-1-1.html ,默认安装为最新版即可。安装完IDE之后还需要安装第三方的库。
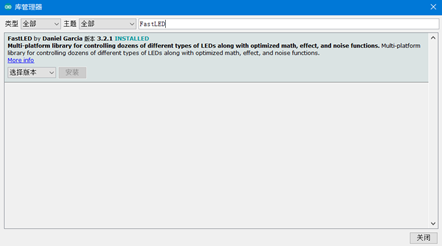
1) WS2812B的库 FastLED, 选择 项目->加载库->管理库,然后在输入栏输入FastLED,选择最新的版本安装,FastLED库的更多使用方法可以参考 http://www.taichi-maker.com/homepage/reference-index/arduino-library-index/fastled-library/
2) 物联网开发平台库 Blinker, 在Blinker 官网https://doc.blinker.app 页面下载最新的Blinker库,然后:
Window:将下载好的blinker库解压到 我的电脑>文档>Arduino>libraries 文件夹中
Mac OS:将下载好的blinker库解压到
文稿>Arduino>libraries 文件夹中
可以在文件->示例 查看库是否安装成功。
3.2 连接线路
具体的线路图由于时间原因没有画,所以直接按照后续的代码可以找到每个模块的连接方式,当然这些连接方式都可以自定义,然后在代码内做简单修改即可。需要注意的是蓝牙模块采用软串口连接,即RX,TX连接在ARDUINO UNO的2 和 3 号脚,而不是0和1 号脚,这个在BLINKER的网站上会说明,如果你代码烧录不了,查查是不是这个原因。
3.3 代码编写
#define BLINKER_PRINT Serial
#define BLINKER_BLE #include <FastLED.h>
#include <Blinker.h> /** BASIC CONFIGURATION **/ //The amount of LEDs in the setup
#define NUM_LEDS 100
//The pin that controls the LEDs
#define LED_PIN 6
//The pin that we read sensor values form
#define ANALOG_READ 0 //Confirmed microphone low value, and max value
#define MIC_LOW 0.0
#define MIC_HIGH 300.0
/** Other macros */
//How many previous sensor values effects the operating average?
#define AVGLEN 5
//How many previous sensor values decides if we are on a peak/HIGH (e.g. in a song)
#define LONG_SECTOR 20 //Mneumonics
#define HIGH 3
#define NORMAL 2 //How long do we keep the "current average" sound, before restarting the measuring
#define CYCLES 30 * 1000 float fscale( float originalMin, float originalMax, float newBegin, float newEnd, float inputValue, float curve);
void insert(int val, int *avgs, int len);
int compute_average(int *avgs, int len);
void visualize_music(); //How many LEDs to we display
int curshow = NUM_LEDS; /*Not really used yet. Thought to be able to switch between sound reactive
mode, and general gradient pulsing/static color*/
int mode = ; //Showing different colors based on the mode.
int songmode = NORMAL; //Average sound measurement the last CYCLES
unsigned long song_avg; //The amount of iterations since the song_avg was reset
int iter = ; //The speed the LEDs fade to black if not relit
float fade_scale = 1.2; //Led array
CRGB leds[NUM_LEDS]; /*Short sound avg used to "normalize" the input values.
We use the short average instead of using the sensor input directly */
int avgs[AVGLEN] = {-}; //Longer sound avg
int long_avg[LONG_SECTOR] = {-}; // LED Model 1/Music LED 2/Color LED
int LED_Model = ; //Keeping track how often, and how long times we hit a certain mode
struct time_keeping {
unsigned long times_start;
short times;
}; //How much to increment or decrement each color every cycle
struct color {
int r;
int g;
int b;
}; struct time_keeping high;
struct color Color;
// when you use the MusicLED as a Color LED
CRGB LEDColor(,,);
uint8_t Bright = ; // declare the button
BlinkerRGB RGB1("RGBKey");
BlinkerButton Button1("switch"); // rgb1_callback
void rgb1_callback(uint8_t r_value, uint8_t g_value, uint8_t b_value, uint8_t bright_value)
{
// change the color of strip by your set on Blinker
LEDColor.r = r_value;
LEDColor.g = g_value;
LEDColor.b = b_value;
Bright = bright_value;
fill_solid(leds,NUM_LEDS,LEDColor); FastLED.show();
} void button1_callback(const String & state) {
if(LED_Model == )
{
LEDColor.r = ;
LEDColor.g = ;
LEDColor.b = ;
Bright = ;
fill_solid(leds,NUM_LEDS,LEDColor);
BLINKER_LOG2("strip_state: ","OFF");
LED_Model = ;
}
else if(LED_Model == )
{
LED_Model = ;
}
FastLED.show();
} void setup() {
Serial.begin();
//Set all lights to make sure all are working as expected
FastLED.addLeds<NEOPIXEL, LED_PIN>(leds, NUM_LEDS);
for (int i = ; i < NUM_LEDS; i++)
leds[i] = CRGB(, , );
FastLED.show();
delay(); //bootstrap average with some low values
for (int i = ; i < AVGLEN; i++) {
insert(, avgs, AVGLEN);
} //Initial values
high.times = ;
high.times_start = millis();
Color.r = ;
Color.g = ;
Color.b = ; Blinker.begin();
//attach the RGB1 SlidersRGB
RGB1.attach(rgb1_callback);
Button1.attach(button1_callback);
} /*With this we can change the mode if we want to implement a general
lamp feature, with for instance general pulsing. Maybe if the
sound is low for a while? */
void loop() {
Blinker.run(); if(LED_Model == )
visualize_music(); delay(); // delay in between reads for stability
} /**Funtion to check if the lamp should either enter a HIGH mode,
or revert to NORMAL if already in HIGH. If the sensors report values
that are higher than 1.1 times the average values, and this has happened
more than 30 times the last few milliseconds, it will enter HIGH mode.
TODO: Not very well written, remove hardcoded values, and make it more
reusable and configurable. */
void check_high(int avg) {
if (avg > (song_avg/iter * 1.1)) {
if (high.times != ) {
if (millis() - high.times_start > 200.0) {
high.times = ;
songmode = NORMAL;
} else {
high.times_start = millis();
high.times++;
}
} else {
high.times++;
high.times_start = millis(); }
}
if (high.times > && millis() - high.times_start < 50.0)
songmode = HIGH;
else if (millis() - high.times_start > ) {
high.times = ;
songmode = NORMAL;
}
} //Main function for visualizing the sounds in the lamp
void visualize_music() {
int sensor_value, mapped, avg, longavg; //Actual sensor value
sensor_value = analogRead(ANALOG_READ);
Serial.println(sensor_value); //If 0, discard immediately. Probably not right and save CPU.
if (sensor_value == )
return; //Discard readings that deviates too much from the past avg.
mapped = (float)fscale(MIC_LOW, MIC_HIGH, MIC_LOW, (float)MIC_HIGH, (float)sensor_value, 2.0);
avg = compute_average(avgs, AVGLEN); if (((avg - mapped) > avg*0.8)) //|| ((avg - mapped) < -avg*0.8))
return; //Insert new avg. values
insert(mapped, avgs, AVGLEN);
insert(avg, long_avg, LONG_SECTOR); //Compute the "song average" sensor value
song_avg += avg;
iter++;
if (iter > CYCLES) {
song_avg = song_avg / iter;
iter = ;
} longavg = compute_average(long_avg, LONG_SECTOR); //Check if we enter HIGH mode
check_high(longavg); if (songmode == HIGH) {
fade_scale = ;
Color.r = ;
Color.g = ;
Color.b = -;
}
else if (songmode == NORMAL) {
fade_scale = ;
Color.r = -;
Color.b = ;
Color.g = ;
} //Decides how many of the LEDs will be lit
curshow = fscale(MIC_LOW, MIC_HIGH, 0.0, (float)NUM_LEDS, (float)avg, -); /*Set the different leds. Control for too high and too low values.
Fun thing to try: Dont account for overflow in one direction,
some interesting light effects appear! */
for (int i = ; i < NUM_LEDS; i++)
//The leds we want to show
if (i < curshow) {
if (leds[i].r + Color.r > )
leds[i].r = ;
else if (leds[i].r + Color.r < )
leds[i].r = ;
else
leds[i].r = leds[i].r + Color.r; if (leds[i].g + Color.g > )
leds[i].g = ;
else if (leds[i].g + Color.g < )
leds[i].g = ;
else
leds[i].g = leds[i].g + Color.g; if (leds[i].b + Color.b > )
leds[i].b = ;
else if (leds[i].b + Color.b < )
leds[i].b = ;
else
leds[i].b = leds[i].b + Color.b; //All the other LEDs begin their fading journey to eventual total darkness
} else {
leds[i] = CRGB(leds[i].r/fade_scale, leds[i].g/fade_scale, leds[i].b/fade_scale);
}
FastLED.show();
}
//Compute average of a int array, given the starting pointer and the length
int compute_average(int *avgs, int len) {
int sum = ;
for (int i = ; i < len; i++)
sum += avgs[i]; return (int)(sum / len); } //Insert a value into an array, and shift it down removing
//the first value if array already full
void insert(int val, int *avgs, int len) {
for (int i = ; i < len; i++) {
if (avgs[i] == -) {
avgs[i] = val;
return;
}
} for (int i = ; i < len; i++) {
avgs[i - ] = avgs[i];
}
avgs[len - ] = val;
} //Function imported from the arduino website.
//Basically map, but with a curve on the scale (can be non-uniform).
float fscale( float originalMin, float originalMax, float newBegin, float
newEnd, float inputValue, float curve){ float OriginalRange = ;
float NewRange = ;
float zeroRefCurVal = ;
float normalizedCurVal = ;
float rangedValue = ;
boolean invFlag = ; // condition curve parameter
// limit range if (curve > ) curve = ;
if (curve < -) curve = -; curve = (curve * -.) ; // - invert and scale - this seems more intuitive - postive numbers give more weight to high end on output
curve = pow(, curve); // convert linear scale into lograthimic exponent for other pow function // Check for out of range inputValues
if (inputValue < originalMin) {
inputValue = originalMin;
}
if (inputValue > originalMax) {
inputValue = originalMax;
} // Zero Refference the values
OriginalRange = originalMax - originalMin; if (newEnd > newBegin){
NewRange = newEnd - newBegin;
}
else
{
NewRange = newBegin - newEnd;
invFlag = ;
} zeroRefCurVal = inputValue - originalMin;
normalizedCurVal = zeroRefCurVal / OriginalRange; // normalize to 0 - 1 float // Check for originalMin > originalMax - the math for all other cases i.e. negative numbers seems to work out fine
if (originalMin > originalMax ) {
return ;
} if (invFlag == ){
rangedValue = (pow(normalizedCurVal, curve) * NewRange) + newBegin; }
else // invert the ranges
{
rangedValue = newBegin - (pow(normalizedCurVal, curve) * NewRange);
} return rangedValue;
}
上述代码编译无误后上传到Arduino UNO即可。
3.4 下载并使用Blinker软件连接
Blinker软件的安装包可以在官网上找到:

安装好之后注册账号,登陆,在主页面右上角选择-->添加设备-->Arduino-->蓝牙接入,然后会自动发现我们的蓝牙,连接上之后,如图。

上面表示是否已经连接,现在表示已连接。然后添加上面的两个组件,编辑组件参数如下:
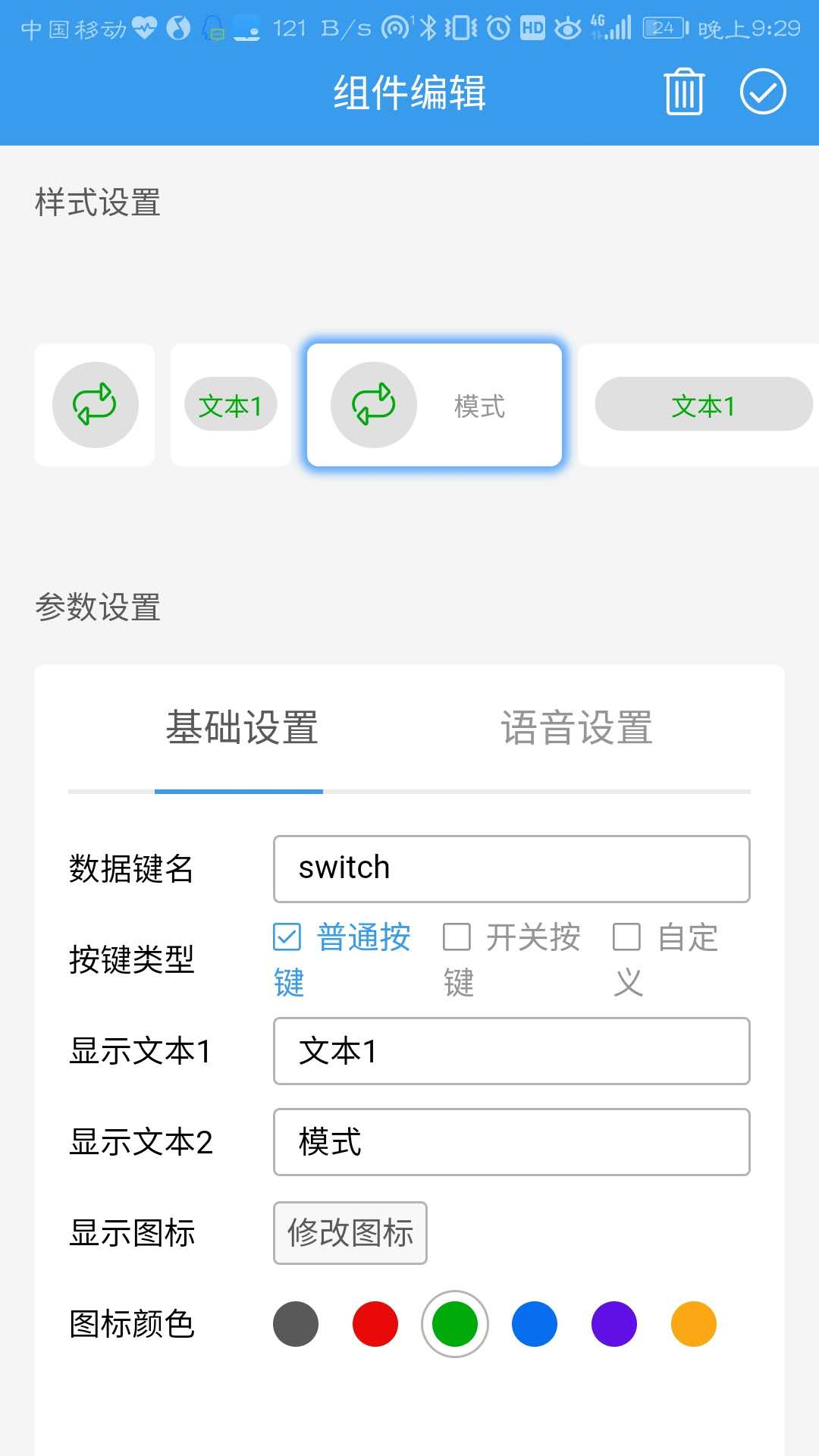

完成之后便可以通过RGB滑条来控制颜色,通过模式按钮来控制灯的模式。
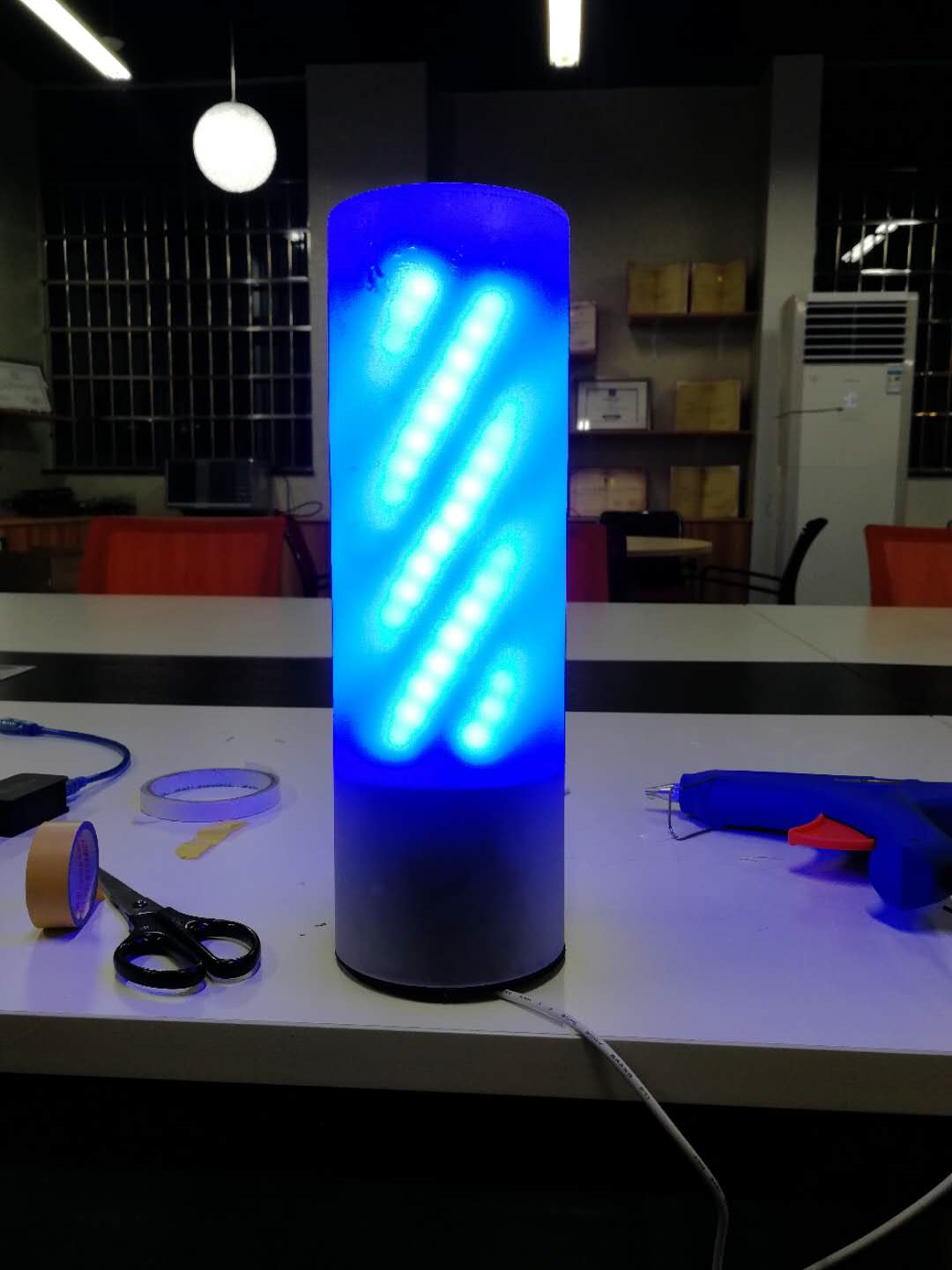
3.5 灯的组装
我是自己在网上买的灯罩,然后根据自己的需求3D打印的底座,大家可以发挥自己的想象力来创作出不一样的外观~
然后来一波安装完成的照片:

最后更新一波实测视频(由于不能同时录像和控制,所以只放了节奏灯效果):
地址:https://www.bilibili.com/video/av38471827/
基于Arduino的音乐动感节奏灯的更多相关文章
- arduino 蓝牙控制RGB LED灯
/* 日期:2016.9.2 功能:arduino 蓝牙控制RGB LED灯 元件: 跳线公公头 * 8 rgbled, 220欧电阻 蓝牙模块 接线: 蓝牙模块VCC,GND分别接5V,GND;TX ...
- Recommending music on Spotify with deep learning 采用深度学习算法为Spotify做基于内容的音乐推荐
本文参考http://blog.csdn.net/zdy0_2004/article/details/43896015译文以及原文file:///F:/%E6%9C%BA%E5%99%A8%E5%AD ...
- Android基于发展Service音乐播放器
这是一个基于Service组件的音乐播放器,程序的音乐将会由后台的Service组件负责播放,当后台的播放状态改变时,程序将会通过发送广播通知前台Activity更新界面:当用户单击前台Activit ...
- 基于jQuery虾米音乐播放器样式代码
分享一款基于jQuery虾米音乐播放器样式代码.这是一款基于jquery+html5实现的虾米音乐播放器源码下载.效果图如下: 在线预览 源码下载 实现的代码. html代码: <div c ...
- 基于 Arduino 开发板,这款插座是可编程且开源的
基于 Arduino 开发板,这款插座是可编程且开源的 https://www.oschina.net/news/74861/open-source-socket https://github.com ...
- 基于Arduino开发的智能蓝牙小车
基于Arduino的智能蓝牙小车 材料准备: Arduino开发板一块.四驱小车底板及相关配件一套.L298N驱动模块一个.HC-05/06蓝牙模块一块,九伏电源一块(用于主板供电).12V锂电池一块 ...
- 基于arduino的红外传感系统
一.作品背景 在这个科技飞速发展的时代,物联网已经成为了我们身边必不可少的技术模块,我这次课程设计做的是一个基于arduino+树莓派+OneNet的红外报警系统,它主要通过识别人或者动物的运动来判断 ...
- 基于arduino UNO R3+ESP8266控制LED灯的开关(无USB转TTL工具实现)
最近由于项目要求,需要开发物联网云平台,而本人对硬件和通信技术一窍不通,故而选择arduino这一简单单片机来实现学习掌握基础的硬件和通信技术. 下面就是本人通过查阅大佬资料做的一个整合版本的通过手机 ...
- 基于 Arduino 的 RFID 识别实验
http://www.it165.net/embed/html/201512/3287.html 2015年12月04日(周五) 上午 博士的智能卡实验--RFID识别实验,基于51单片机: 我们的 ...
随机推荐
- Eclipse导入外部项目问题总结
此次在项目开发过程中导入从oksvn下载的共享项目时出现几个项目在不同的IDE导入导出时的问题,为免忘记做例如以下笔记: 1 类路径问题 在Java开发中大多数的开发人员使用的IDE是MyEcl ...
- POJ 题目2761 Feed the dogs(主席树||划分树)
Feed the dogs Time Limit: 6000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions: 16860 Accepted: 5273 De ...
- MySQL hash分区(四)
具体描写叙述总结请看MySQL分区(一) 样例:该样例为本人个人学习总结分享->具体说明-->有问题欢迎前来交流 watermark/2/text/aHR0cDovL2Jsb2cuY3Nk ...
- 一个APP爆炸的时代,假设没有wifi
我们每天都离不开的微信,又传来了一个新消息.你造?微信公众平台新增了设备功能.眼下可支持可穿戴设备,将来呢,前景不可限量!能够想象,"后果"是我们越来越离不开微信,依附于它.这样的 ...
- Selenium中配置链接使用FTP服务
Enable the default report solution Step1: Create a suite listener and add codes into it, please watc ...
- TeeChart绘图控件 - 之三 - 提高绘图的效率 .
TeeChart是个很强大的控件,其绘图能力之强,其他控件难以比拟,但是有个问题就是他的绘图速度,其实TeeChart绘图速度还是很快的,只是大家一直都没正确运用其功能所以导致绘图速度慢的假象. 下面 ...
- 【WIP】客户端JavaScript DOM
创建: 2017/10/12 初步完成: 2017/10/15 更新: 2017/10/14 标题加上[WIP],继续完成 [TODO] 补充暂略的, 搜[略] DOM树 概要 基本 ...
- Codeforces 771C
我的树形dp果然是渣... 题意:给一棵树,共n(0<n<=15e4)个节点,可在树上进行跳跃,每次跳的最大距离为k(0<k<=5),定义f(s,t)为(dis(s,t)+k) ...
- ACM_堆箱子咯(栈)
堆箱子咯 Time Limit: 2000/1000ms (Java/Others) Problem Description: 双十一大家都在买买买,可忙坏了快递小哥了.zl和皮卡鸡在大伙在剁手的时候 ...
- 题解报告:hdu 1233 还是畅通工程
Problem Description 某省调查乡村交通状况,得到的统计表中列出了任意两村庄间的距离.省政府“畅通工程”的目标是使全省任何两个村庄间都可以实现公路交通(但不一定有直接的公路相连,只要能 ...
