Apache Hadoop YARN – ResourceManager--转载
原文地址:http://zh.hortonworks.com/blog/apache-hadoop-yarn-resourcemanager/
ResourceManager (RM) is the master that arbitrates all the available cluster resources and thus helps manage the distributed applications running on the YARN system. It works together with the per-node NodeManagers (NMs) and the per-application ApplicationMasters (AMs).
- NodeManagers take instructions from the ResourceManager and manage resources available on a single node.
- ApplicationMasters are responsible for negotiating resources with the ResourceManager and for working with the NodeManagers to start the containers.
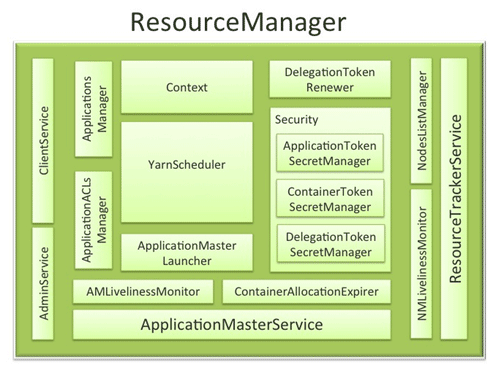
ResourceManager Components
The ResourceManager has the following components (see the figure above):
- Components interfacing RM to the clients:
- ClientService: The client interface to the Resource Manager. This component handles all the RPC interfaces to the RM from the clients including operations like application submission, application termination, obtaining queue information, cluster statistics etc.
- AdminService: To make sure that admin requests don’t get starved due to the normal users’ requests and to give the operators’ commands the higher priority, all the admin operations like refreshing node-list, the queues’ configuration etc. are served via this separate interface.
- Components connecting RM to the nodes:
- ResourceTrackerService: This is the component that responds to RPCs from all the nodes. It is responsible for registration of new nodes, rejecting requests from any invalid/decommissioned nodes, obtain node-heartbeats and forward them over to the YarnScheduler. It works closely with NMLivelinessMonitor and NodesListManager described below.
- NMLivelinessMonitor: To keep track of live nodes and specifically note down the dead nodes, this component keeps track of each node’s its last heartbeat time. Any node that doesn’t heartbeat within a configured interval of time, by default 10 minutes, is deemed dead and is expired by the RM. All the containers currently running on an expired node are marked as dead and no new containers are scheduling on such node.
- NodesListManager: A collection of valid and excluded nodes. Responsible for reading the host configuration files specified via
yarn.resourcemanager.nodes.include-pathandyarn.resourcemanager.nodes.exclude-pathand seeding the initial list of nodes based on those files. Also keeps track of nodes that are decommissioned as time progresses.
- Components interacting with the per-application AMs:
- ApplicationMasterService: This is the component that responds to RPCs from all the AMs. It is responsible for registration of new AMs, termination/unregister-requests from any finishing AMs, obtaining container-allocation & deallocation requests from all running AMs and forward them over to the YarnScheduler. This works closely with AMLivelinessMonitor described below.
- AMLivelinessMonitor: To help manage the list of live AMs and dead/non-responding AMs, this component keeps track of each AM and its last heartbeat time. Any AM that doesn’t heartbeat within a configured interval of time, by default 10 minutes, is deemed dead and is expired by the RM. All the containers currently running/allocated to an AM that gets expired are marked as dead. RM schedules the same AM to run on a new container, allowing up to a maximum of 4 such attempts by default.
- The core of the ResourceManager – the scheduler and related components:
- ApplicationsManager: Responsible for maintaining a collection of submitted applications. Also keeps a cache of completed applications so as to serve users’ requests via web UI or command line long after the applications in question finished.
- ApplicationACLsManager: RM needs to gate the user facing APIs like the client and admin requests to be accessible only to authorized users. This component maintains the ACLs lists per application and enforces them whenever an request like killing an application, viewing an application status is received.
- ApplicationMasterLauncher: Maintains a thread-pool to launch AMs of newly submitted applications as well as applications whose previous AM attempts exited due to some reason. Also responsible for cleaning up the AM when an application has finished normally or forcefully terminated.
- YarnScheduler: The Scheduler is responsible for allocating resources to the various running applications subject to constraints of capacities, queues etc. It performs its scheduling function based on the resource requirements of the applications such as memory, CPU, disk, network etc. Currently, only memory is supported and support for CPU is close to completion.
- ContainerAllocationExpirer: This component is in charge of ensuring that all allocated containers are used by AMs and subsequently launched on the correspond NMs. AMs run as untrusted user code and can potentially hold on to allocations without using them, and as such can cause cluster under-utilization. To address this, ContainerAllocationExpirer maintains the list of allocated containers that are still not used on the corresponding NMs. For any container, if the corresponding NM doesn’t report to the RM that the container has started running within a configured interval of time, by default 10 minutes, the container is deemed as dead and is expired by the RM.
- TokenSecretManagers (for security):ResourceManager has a collection of SecretManagers which are charged with managing tokens, secret-keys that are used to authenticate/authorize requests on various RPC interfaces. A future post on YARN security will cover a more detailed descriptions of the tokens, secret-keys and the secret-managers but a brief summary follows:
- ApplicationTokenSecretManager: To avoid arbitrary processes from sending RM scheduling requests, RM uses the per-application tokens called ApplicationTokens. This component saves each token locally in memory till application finishes and uses it to authenticate any request coming from a valid AM process.
- ContainerTokenSecretManager: SecretManager for ContainerTokens that are special tokens issued by RM to an AM for a container on a specific node. ContainerTokens are used by AMs to create a connection to the corresponding NM where the container is allocated. This component is RM-specific, keeps track of the underlying master and secret-keys and rolls the keys every so often.
- RMDelegationTokenSecretManager: A ResourceManager specific delegation-token secret-manager. It is responsible for generating delegation tokens to clients which can be passed on to unauthenticated processes that wish to be able to talk to RM.
- DelegationTokenRenewer: In secure mode, RM is Kerberos authenticated and so provides the service of renewing file-system tokens on behalf of the applications. This component renews tokens of submitted applications as long as the application runs and till the tokens can no longer be renewed.
Conclusion
In YARN, the ResourceManager is primarily limited to scheduling i.e. only arbitrating available resources in the system among the competing applications and not concerning itself with per-application state management. Because of this clear separation of responsibilities coupled with the modularity described above, and with the powerful scheduler API discussed in the previous post, RM is able to address the most important design requirements – scalability, support for alternate programming paradigms.
To allow for different policy constraints, the scheduler described above in the RM is pluggable and allows for different algorithms. In a future post of this series, we will dig deeper into various features of CapacityScheduler that schedules containers based on capacity guarantees and queues.
The next post will dive into details of the NodeManager, the component responsible for managing the containers’ life cycle and much more.
Apache Hadoop YARN – ResourceManager--转载的更多相关文章
- Apache Hadoop YARN: 背景及概述
从2012年8月开始Apache Hadoop YARN(YARN = Yet Another Resource Negotiator)成了Apache Hadoop的一项子工程.自此Apache H ...
- hadoop错误org.apache.hadoop.yarn.exceptions.YarnException Unauthorized request to start container
错误: 14/04/29 02:45:07 INFO mapreduce.Job: Job job_1398704073313_0021 failed with state FAILED due to ...
- Apache Hadoop YARN – NodeManager--转载
原文地址:http://zh.hortonworks.com/blog/apache-hadoop-yarn-nodemanager/ The NodeManager (NM) is YARN’s p ...
- spark 笔记 4:Apache Hadoop YARN: Yet Another Resource Negotiator
spark支持YARN做资源调度器,所以YARN的原理还是应该知道的:http://www.socc2013.org/home/program/a5-vavilapalli.pdf 但总体来说, ...
- 记录一次 hadoop yarn resourceManager无故切换的故障
某日 收到告警 线上集群rm切换 观察resourcemanager 日志报错如下 这行不明显 再看看其他日志报错 在 app attempt_removed 时候发生了空指针错误 break; ca ...
- spark on yarn 动态资源分配报错的解决:org.apache.hadoop.yarn.exceptions.InvalidAuxServiceException: The auxService:spark_shuffle does not exist
组件:cdh5.14.0 spark是自己编译的spark2.1.0-cdh5.14.0 第一步:确认spark-defaults.conf中添加了如下配置: spark.shuffle.servic ...
- org.apache.hadoop.yarn.exceptions.InvalidAuxServiceException: The auxService: mapreduce_shuffle do
在yarn-site.xml 配置文件中增加: <property> <name>yarn.nodemanager.aux-services</name> < ...
- Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: org/apache/hadoop/yarn/exceptions/YarnException
这个是Flink 1.11.1 使用yarn-session 出现的错误:原因是在Flink1.11 之后不再提供flink-shaded-hadoop-*” jars 需要在yarn-sessio ...
- Caused by:java.lang.ClassNotFoundException:org.apache.hadoop.yarn.util.Apps
错误原因 缺少hadoop-yarn.jar包. 导入jar包就好了~-~
随机推荐
- sql语句-6-更新数据
- MySql Host is blocked because of many connection errors; unblock with 'mysqladmin flush-hosts' 的解决方法
解决方法如下: 方法 1.在线修改提高允许的max_connection_errors数量: A. 登录Mysql数据库查看max_connection_errors: mysql>show ...
- 学习HTML 第五节.简单交互 加个按钮
学习HTML 第五节.简单交互 也许你和我一样,对页面排版的兴趣小于网页交互,那么我们就先略过一些章节,直接先学一下简单交互. 前面点击图片打开链接的网址,已经是最简单的交互方式了,复杂的方式则需要用 ...
- Jmeter直连postgresql数据库进行压测
关于Jmeter直连数据库进行压测,网上有好多教程了,pg数据库的相对少一些,今天自己测试了下,还是挺简单的,有个别需要注意的地方.相较于Loadrunner这么全面庞大的压测工具,Jmeter在数据 ...
- [转]git学习------>git-rev-parse命令初识
git学习------>git-rev-parse命令初识 2017年06月13日 10:04:13 阅读数:2172 一.准备工作 第一步:在d盘git test目录下,新建工作区根目录dem ...
- application/x-www-urlencoded与multipart/form-data
学习ajax时,学到了GET与POST两种HTTP方法,于是去W3C看了二者的区别,里面提到了二者的编码类型不同,就在网上查阅了相关资料, 在这里把我查阅到的相关结果记录在此,方便以后学习,详细了解一 ...
- 获取一个数组里面第K大的元素
如何在O(n)内获取一个数组比如{9, 1, 2, 8, 7, 3, 6, 4, 3, 5, 0, 9, 19, 39, 25, 34, 17, 24, 23, 34, 20}里面第K大的元素呢? 我 ...
- win2003系统网络安装——基于linux+pxe+dhcp+tftp+samba+ris
原文发表于:2010-09-16 转载至cu于:2012-07-21 一.原理简介 PXE(preboot execute environment)工作于Client/Server的网络模式,支持工作 ...
- #Ubuntu 18.04 安装tensorflow-gpu 1.9
参考 https://tensorflow.google.cn/install/install_linux http://nvidia.com/cuda http://developer.nvidia ...
- Scrum立会报告+燃尽图(Beta阶段第七次)
此作业要求参见:https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/nenu/2018fall/homework/2388 项目地址:https://coding.net/u/wuyy694 ...
