python之路函数
1、函数参数,引用
2、lambda表达式
lambda表达式
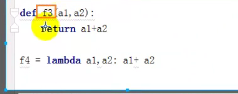
f1 = lambda a1,a2: a1+a2
3、python的内置函数
abs(),绝对值
all(),循环参数,如果每个元素都为真,那么all返回值为真
0是假的,None 是假,“”,[],(),{},空值都是假的
any() 只要有一个是真则为真
ascii(对象),去对象的类中找_repr_,获取返回值
bin(),二进制
oct(),八进制
int(),十进制
hex(),十六进制


bool(), 判断真假,把一个对象转换成bool值,None,“”,【】,{}
bytes 字节
bytearray 字节列表
字节转字符串
bytes(“xxx”, encoding=‘utf-8’)
chr(),把数字转换成asc码,对应的字符
ord(),把字符转化成数字
实例:生成一个随机验证码
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import random temp = ""
for i in range(6):
# 生成0-4的随机数
num = random.randrange(0, 4)
# 如果随机数是1或3,那么就在验证码中生成一个0-9的随机数字
# 否则,验证码中生成一个随机字母
if num == 3 or num == 1:
rad2 = random.randrange(0, 10)
temp = temp + str(rad2)
else:
rad1 = random.randrange(65, 91)
c1 = chr(rad1)
temp = temp + rad1
print(temp)
验证码代码
callable(),能不能执行
compile(),编译
complex(),
dir(),看看函数提供的功能
divmod(),计算需要多少页

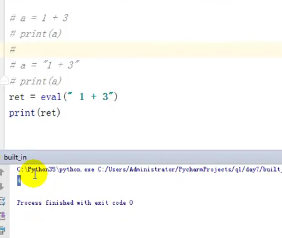
eval(),可以执行一个字符串形式的字符串,有返回值
exec(),执行python代码

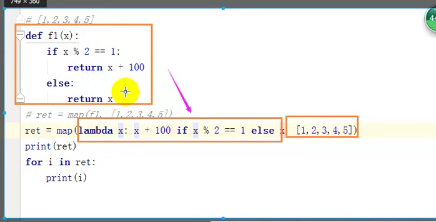
一、 map(函数,可迭代的对象),让所有的数统一做个操作

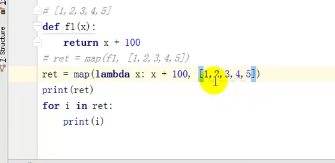
li = [11, 22, 33] new_list = map(lambda a: a + 100, li)
li = [11, 22, 33]
sl = [1, 2, 3]
new_list = map(lambda a, b: a + b, li, sl)
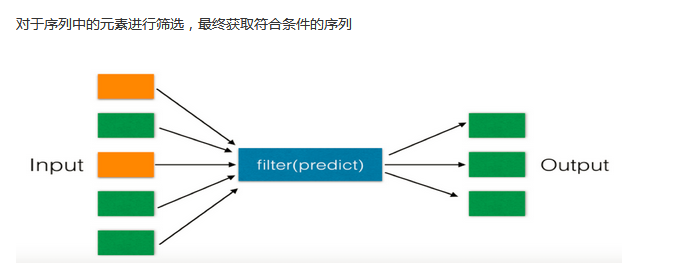
二、filter(函数,可迭代的对象),过滤,循环可迭代的对象,获取每一个参数,
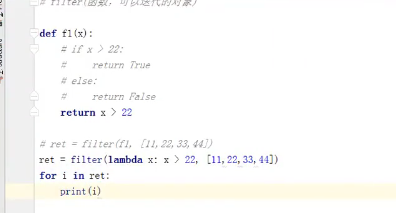
li = [11, 22, 33] new_list = filter(lambda arg: arg > 22, li) #filter第一个参数为空,将获取原来序列
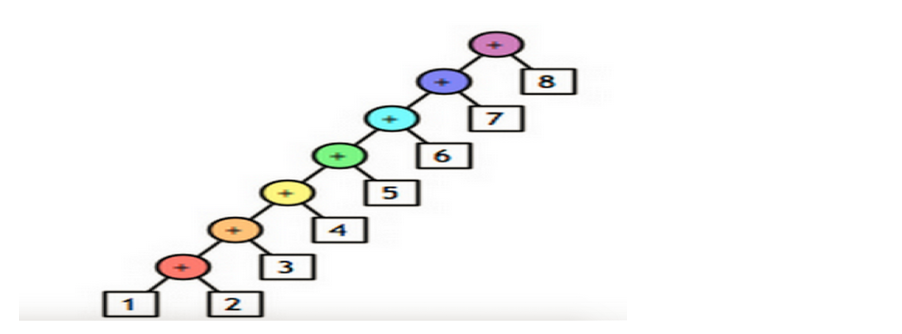
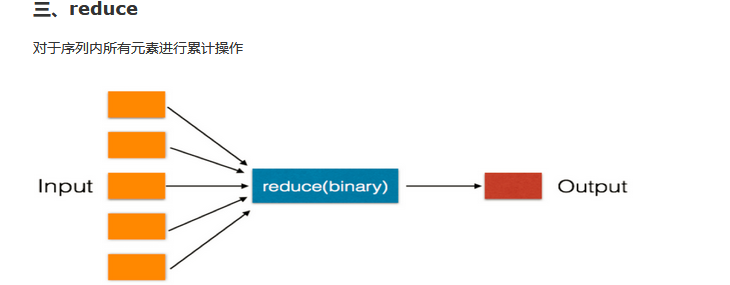
li = [11, 22, 33] result = reduce(lambda arg1, arg2: arg1 + arg2, li) # reduce的第一个参数,函数必须要有两个参数
# reduce的第二个参数,要循环的序列
# reduce的第三个参数,初始值
format()字符串格式化
globals()获取所有的全局变量
locals()获取所有的局部变量
hash()算哈希值
isinstance(),判断某个对象是否有某个类创建的
issubclass(),是不是子类
open()打开文件
pow(),求指数
repr()====ascii(),
round()四舍五入
silce(),去对象的索引
vars()一个对象有的变量
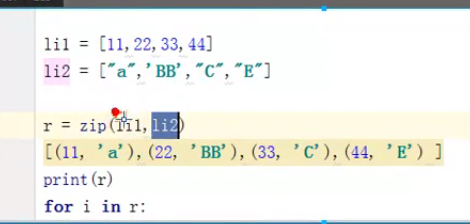

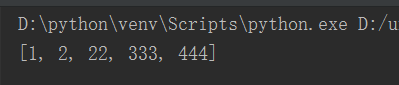
字符串不能排序
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- li = [1, 2, 22, 333, 444]
new_li = sorted(li)
print(new_li)
文件操作
一、打开文件
open(文件名,模式,编码)
默认是只读模式
打开文件时,需要指定文件路径和以何等方式打开文件,打开后,即可获取该文件句柄,日后通过此文件句柄对该文件操作。
打开文件的模式有:
- r,只读模式(默认)。
- w,只写模式。【不可读;不存在则创建;存在则删除内容;】
- a,追加模式。【可读; 不存在则创建;存在则只追加内容;】
"+" 表示可以同时读写某个文件
- r+,可读写文件。【可读;可写;可追加】
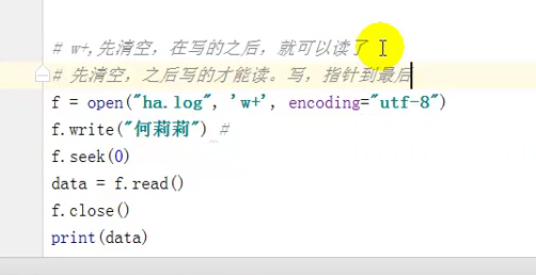
- w+,写读
- a+,同a
"U"表示在读取时,可以将 \r \n \r\n自动转换成 \n (与 r 或 r+ 模式同使用)
- rU
- r+U
"b"表示处理二进制文件(如:FTP发送上传ISO镜像文件,linux可忽略,windows处理二进制文件时需标注)
- rb
- wb
- ab

以字节的方式打开
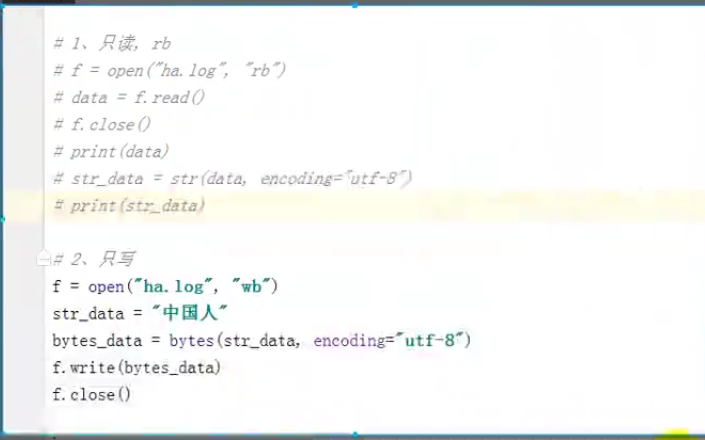
1、只读 rb
二、操作文件
class file(object):
def close(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
关闭文件
"""
close() -> None or (perhaps) an integer. Close the file.
Sets data attribute .closed to True. A closed file cannot be used for
further I/O operations. close() may be called more than once without
error. Some kinds of file objects (for example, opened by popen())
may return an exit status upon closing.
"""
def fileno(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
文件描述符
"""
fileno() -> integer "file descriptor".
This is needed for lower-level file interfaces, such os.read().
"""
return 0
def flush(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
刷新文件内部缓冲区
""" flush() -> None. Flush the internal I/O buffer. """
pass
def isatty(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
判断文件是否是同意tty设备
""" isatty() -> true or false. True if the file is connected to a tty device. """
return False
def next(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
获取下一行数据,不存在,则报错
""" x.next() -> the next value, or raise StopIteration """
pass
def read(self, size=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
读取指定字节数据
"""
read([size]) -> read at most size bytes, returned as a string.
If the size argument is negative or omitted, read until EOF is reached.
Notice that when in non-blocking mode, less data than what was requested
may be returned, even if no size parameter was given.
"""
pass
def readinto(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
读取到缓冲区,不要用,将被遗弃
""" readinto() -> Undocumented. Don't use this; it may go away. """
pass
def readline(self, size=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
仅读取一行数据
"""
readline([size]) -> next line from the file, as a string.
Retain newline. A non-negative size argument limits the maximum
number of bytes to return (an incomplete line may be returned then).
Return an empty string at EOF.
"""
pass
def readlines(self, size=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
读取所有数据,并根据换行保存值列表
"""
readlines([size]) -> list of strings, each a line from the file.
Call readline() repeatedly and return a list of the lines so read.
The optional size argument, if given, is an approximate bound on the
total number of bytes in the lines returned.
"""
return []
def seek(self, offset, whence=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
指定文件中指针位置
"""
seek(offset[, whence]) -> None. Move to new file position.
Argument offset is a byte count. Optional argument whence defaults to
0 (offset from start of file, offset should be >= 0); other values are 1
(move relative to current position, positive or negative), and 2 (move
relative to end of file, usually negative, although many platforms allow
seeking beyond the end of a file). If the file is opened in text mode,
only offsets returned by tell() are legal. Use of other offsets causes
undefined behavior.
Note that not all file objects are seekable.
"""
pass
def tell(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
获取当前指针位置
""" tell() -> current file position, an integer (may be a long integer). """
pass
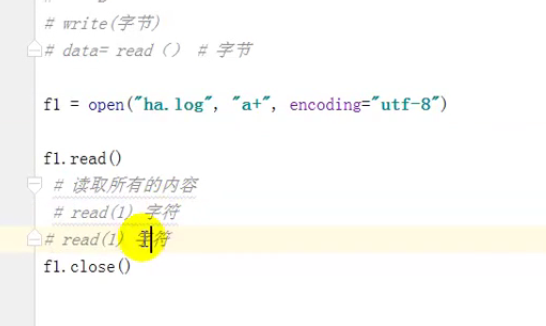
def truncate(self, size=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
截断数据,仅保留指定之前数据
"""
truncate([size]) -> None. Truncate the file to at most size bytes.
Size defaults to the current file position, as returned by tell().
"""
pass
def write(self, p_str): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
写内容
"""
write(str) -> None. Write string str to file.
Note that due to buffering, flush() or close() may be needed before
the file on disk reflects the data written.
"""
pass
def writelines(self, sequence_of_strings): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
将一个字符串列表写入文件
"""
writelines(sequence_of_strings) -> None. Write the strings to the file.
Note that newlines are not added. The sequence can be any iterable object
producing strings. This is equivalent to calling write() for each string.
"""
pass
def xreadlines(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
可用于逐行读取文件,非全部
"""
xreadlines() -> returns self.
For backward compatibility. File objects now include the performance
optimizations previously implemented in the xreadlines module.
"""
pass

 ‘
‘
f.tell()# 获取指针的位置
f.seek(num)#调整指针的位置

truncate()截取数据,仅保留指定之前的数据
要掌握的内容
三、关闭文件

with open('log','r') as f:
...

自动关闭

with支持同时打开两个文件


python之路函数的更多相关文章
- Python之路-函数
一.函数是什么: python中函数定义:函数是逻辑结构化和过程化的一种编程方法.定义函数的方法为: def function(): ""The function definiti ...
- python之路——函数进阶
阅读目录 楔子 命名空间和作用域 函数嵌套及作用域链 函数名的本质 闭包 本章小结 楔子 假如有一个函数,实现返回两个数中的较大值: def my_max(x,y): m = x if x> ...
- 百万年薪python之路 -- 函数的动态参数
1.函数的动态参数 1.1 动态接收位置参数 在参数位置用*表示接受任意参数 def eat(*args): print('我想吃',args) eat('蒸羊羔','蒸熊掌','蒸鹿尾儿','烧花鸭 ...
- Python之路-函数基础&局部变量与全局变量&匿名函数&递归函数&高阶函数
一.函数的定义与调用 函数:组织好的.可重复使用的.用户实现单一或者关联功能的代码段.函数能够提高应用的模块性和代码的重复利用率.Python提供了很多内置的函数,比如len等等,另外也可以根据自己的 ...
- 百万年薪python之路 -- 函数名的第一类对象及使用
函数名是一个变量, 但它是一个特殊的变量, 与括号配合可以执行函数的变量 1.1.函数名的内存地址 def func(): print("呵呵") print(func) 结果: ...
- 百万年薪python之路 -- 函数的动态参数练习
1.继续整理函数相关知识点. 2.写函数,接收n个数字,求这些参数数字的和.(动态传参) def func(*args,**kwargs): num_sum = 0 num_dic = [] num ...
- 百万年薪python之路 -- 函数初始
1.函数 1.1 认识函数 定义一个事情或者是功能,等到需要的时候直接去用就好了.那么这里定义东西就是一个函数 函数:对代码块和功能的封装和定义 函数的好处: 减少代码的重复性 代码可读性高 将功能进 ...
- 百万年薪python之路 -- 函数初始练习
1.整理函数相关知识点 2.写函数,检查获取传入列表或元组对象的所有奇数位索引对应的元素,并将其作为新列表返回给调用者. def func(lst): lst = lst[1::2] return l ...
- 09-Python之路---函数进阶
Python之路---函数进阶️ 程序员三大美德: 懒惰 因为一直致力于减少工作的总工作量. 缺乏耐性 因为一旦让你去做本该计算机完成的事,你将会怒不可遏. 傲慢 因为被荣誉感冲晕头的你会把程序写得让 ...
随机推荐
- 返回一个整数数组中最大子数组的和——java程序设计
一.题目要求 1.输入一个整形数组,数组里有正数也有负数.2.数组中连续的一个或多个整数组成一个子数组,每个子数组都有一个和.3.求所有子数组的和的最大值.要求时间复杂度为O(n) 二.设计思想 解决 ...
- Linux高性能服务器编程:Linux服务器程序规范
Linux服务器程序一般以后台进程形式运行,后台进程又称守护进程.它没有控制终端,不会接收到用户输入.守护进程的父进程通常是init进程(PID为1). Linux服务器程序有一套日志系统 Linux ...
- string_random
1.随机数 import random 0-1间的随机浮点数,random.random() 指定区间随机浮点数,random.uniform(a,b) 指定区间随机整数(闭区间),random.ra ...
- 逻辑卷管理(LVM)-快照
1.需要在逻辑卷相同的卷组中创建逻辑卷快照.-s :表示快照 -p r:表示只读 /dev/vg0/mysql 为那个卷的快照 2.查看快照卷信息. 3.快照恢复,必须先取消挂载,还原成功之后,快 ...
- node post 大数据无响应超时
使用 express 框架,post 较大数据量(富文本,里面包含了图片base64数据,大约300k)时,node 无响应,把数据内容减少后能顺利提交. 是因为数据量大过body post 的限制导 ...
- Unbuntu--安装VMware Tools
实现虚拟机Ubuntu窗口自适应,以及与本地主机粘贴复制 一.安装VMware Tools 1.首先在虚拟机点击安装VMware tools,会在个人home目录下生成VMwareTools-10.3 ...
- 使用 VMware Workstation Pro 安装新的虚拟机
一.连接服务器 (1)“文件”右键 (2)输入用户名.密码连接服务器 二.创建新的虚拟机 (1) (2) (3) (4) (5) (6) (7) (8) 三.配置服务器 配置文档 - 链接:htt ...
- Keras高层API之Metrics
在tf.keras中,metrics其实就是起到了一个测量表的作用,即测量损失或者模型精度的变化.metrics的使用分为以下四步: step1:Build a meter acc_meter = m ...
- sublime—text终端无法输入,不支持scanf、input等语法问题的解决
sublimetext是个很好用的轻量编辑器,,支持多语言语法高亮,自动补全,快捷键编译运行,而且ui也不错挺简洁,我一直在用.我之前浏览帖子时候看到有些人也在用这个编辑器. 但是吧,这个编辑器的的编 ...
- STM32学习笔记 —— 0.1 Keil5安装和DAP仿真下载器配置的相关问题与注意事项
Keil5安装的注意事项 安装细节在此不再做过多赘述,主要介绍一下注意事项: 安装路径中不能有中文. ARM的Keil的路径不能与51的Keil的有冲突,必须将目录分开. Keil5中不会自动添加芯片 ...