C++ TrieTree(字典树)容器的实现
最近研究了一下C++线程池,在网上看了一下别人的代码,写的很不错,参见:http://www.cnblogs.com/lidabo/p/3328646.html
其中,他用了STL的set容器管理线程池中的线程,在线程池运行的过程中需要频繁的进行插入、查找和删除的操作,我个人觉得这些操作会是线程池中的很大的时间开销,想起了大学老师讲过的一个TireTree(字典树)的数据结构,利用多叉树
可以快速的实现元素的插入、查找和删除,稍加改动也可以支持自动排序,唯一的缺点就是多叉树的结构空间开销较大,所以要控制好内存操作,防止内存泄露。
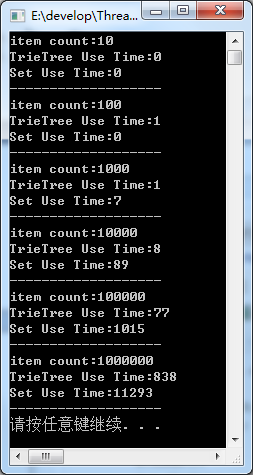
经测试,再插入元素和删除元素的方面,TrieTree比set有明显优势,在相同的元素数量下,内存开销也不过是set的1.5~2倍,时间却是1/10左右。
#ifndef _MY_TRIE_TREE
#define _MY_TRIE_TREE template<class T,class K>
class TrieTree{
public:
TrieTree();
virtual ~TrieTree();
bool insert(T *data,K key,bool overwrite = false);
bool remove(K key,bool free_memory = false);
bool find(K key,T *& pData);
private:
enum
{
Dimension = ,
};
typedef struct tagNode
{
tagNode *child[Dimension];
T *data;
tagNode()
{
for(int i = ;i < Dimension;i++)
{
child[i] = NULL;
}
data = NULL;
}
~tagNode()
{
if(child == NULL)
{
delete[] child;
}
if(data != NULL)
{
delete data;
}
}
}Node;
Node *m_pHead;
unsigned int m_nElementCnt;
unsigned int m_nNodeCnt;
void destory(Node *p_head);
public:
void free();
void dump();
void trival( Node *pNode,int &nodeCnt );
}; template<class T,class K>
bool TrieTree<T, K>::find( K key,T *& pData )
{
int m = ;
Node **p_find = NULL;
if(m_pHead == NULL)
{
return false;
}
p_find = &m_pHead;
while( key > )
{
m = key%;
if((*p_find) != NULL)
{
p_find = &(*p_find)->child[m];
}
else
{
break;
}
key /= ;
}
if((*p_find) != NULL)
{
// 数据为空
if((*p_find)->data == NULL)
{
return false;
}
pData = (*p_find)->data;
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
} template<class T,class K>
void TrieTree<T, K>::free()
{
destory(m_pHead);
} template<class T,class K>
void TrieTree<T, K>::destory( Node *p_head )
{
if(p_head != NULL)
{
for(int i = ;i < Dimension;i++)
{
destory(p_head->child[i]);
}
delete p_head;
m_nNodeCnt--;
}
} template<class T,class K>
void TrieTree<T, K>::trival( Node *pNode,int &nodeCnt )
{
if(pNode != NULL)
{
nodeCnt++;
if(pNode->data != NULL)
{
//cout<<*(pNode->data)<<" ";
}
for(int i = ;i < Dimension;i++)
{
trival(pNode->child[i],nodeCnt);
}
}
} template<class T,class K>
void TrieTree<T, K>::dump()
{
int nodeCnt = ;
trival(m_pHead,nodeCnt);
cout<<endl;
//cout<<endl<<"size = "<<sizeof(Node)<< " * "<<nodeCnt<<" = "<<sizeof(Node)*nodeCnt<<endl;
//cout<<endl<<"data = "<<sizeof(T)<< " * "<<m_nElementCnt<<" = "<<sizeof(T)*m_nElementCnt<<endl;
//cout<<endl<<"rate = "<<((double)sizeof(T) * m_nElementCnt)/(sizeof(Node)*nodeCnt)<<endl;
cout<<"m_nNodeCnt = "<<m_nNodeCnt;
cout<<",m_nElementCnt = "<<m_nElementCnt;
cout<<",nodeCnt = "<<nodeCnt<<endl;
} template<class T,class K>
TrieTree<T,K>::TrieTree()
{
m_pHead = new Node();
m_nElementCnt = ;
m_nNodeCnt = ;
} template<class T,class K>
TrieTree<T,K>::~TrieTree()
{
destory(m_pHead);
} template<class T,class K>
bool TrieTree<T, K>::remove( K key ,bool free_memory)
{
int m = ;
Node **p_find = NULL;
if(m_pHead == NULL)
{
return false;
}
p_find = &m_pHead;
while( key > )
{
m = key%;
if((*p_find) != NULL)
{
p_find = &(*p_find)->child[m];
}
else
{
break;
}
key /= ;
}
if((*p_find) != NULL)
{
// 不释放节点空间
if( free_memory == false )
{
if((*p_find)->data == NULL)
{
return false;
}
delete (*p_find)->data;
(*p_find)->data = NULL;
m_nElementCnt--;
return true;
}
// 释放节点空间
else
{
//并不是所有节点都能释放,没有子节点的节点才能释放
bool hasChild = false;
for(int i = ;i < Dimension;i++)
{
if((*p_find)->child[i] != NULL)
{
hasChild = true;
}
}
// 释放节点,直接delete
if(hasChild == false)
{
delete (*p_find);
(*p_find) = NULL;
m_nElementCnt--;
m_nNodeCnt--;
}
// 不能释放节点,释放data,data = NULL
else
{
if((*p_find)->data == NULL)
{
return false;
}
T *pData = (*p_find)->data;
(*p_find)->data = NULL;
delete pData;
pData = NULL;
m_nElementCnt--;
return true;
}
}
}
else
{
return false;
}
} template<class T,class K>
bool TrieTree<T, K>::insert( T *data,K key,bool overwrite)
{
int m = ;
Node **p_find = NULL;
if(m_pHead == NULL)
{
return false;
}
p_find = &m_pHead;
while( key > )
{
m = key%;
if((*p_find) == NULL)
{
(*p_find) = new Node();
m_nNodeCnt++;
}
p_find = &(*p_find)->child[m];
key /= ;
}
if((*p_find) == NULL)
{
(*p_find) = new Node();
(*p_find)->data = data;
m_nNodeCnt++;
m_nElementCnt++;
return true;
}
else
{
if((*p_find)->data == NULL)
{
(*p_find)->data = data;
m_nElementCnt++;
return true;
}
else
{
if(overwrite == false)
{
return false;
}
else
{
(*p_find)->data = data;
m_nElementCnt++;
return true;
}
}
}
} #endif
测试代码:
void test1()
{
int cnt = ;
time_t s,e;
int n = ,m = ;
TrieTree<R,int> a;
set<R*> b;
for(m = ;m < ;m++)
{
cout<<"item count:"<<n<<endl;
s = clock();
for(int i = ;i < n;i++)
{
R *r = new R(i);
a.insert(r,i);
}
//a.dump();
for(int i = ;i < n/;i++)
{
a.remove(i,true);
}
e = clock();
cout<<"TrieTree Use Time:"<<e-s<<endl;
s = clock();
for(int i = ;i < n;i++)
{
R *r = new R(i);
b.insert(r);
}
b.clear();
e = clock();
cout<<"Set Use Time:"<<e-s<<endl;
cout<<"-------------------"<<endl;
n*=;
}
}
int main()
{
test1();
system("pause");
return ;
}
测试结果:
以上仅是我个人的观点,代码也仅仅是练练手而已,不保证理论和实现完全正确,仅供参考。
C++ TrieTree(字典树)容器的实现的更多相关文章
- 剑指Offer——Trie树(字典树)
剑指Offer--Trie树(字典树) Trie树 Trie树,即字典树,又称单词查找树或键树,是一种树形结构,是一种的单词.对于每一个单词,我们要判断他出没出现过,如果出现了,求第一次出现在第几个位 ...
- 初级字典树查找在 Emoji、关键字检索上的运用 Part-2
系列索引 Unicode 与 Emoji 字典树 TrieTree 与性能测试 生产实践 在有了 Unicode 和 Emoji 的知识准备后,本文进入编码环节. 我们知道 Emoji 是 Unico ...
- BestCoder Round #92 1001 Skip the Class —— 字典树 or map容器
题目链接:http://bestcoder.hdu.edu.cn/contests/contest_showproblem.php?cid=748&pid=1001 题解: 1.trie树 关 ...
- 012-数据结构-树形结构-哈希树[hashtree]、字典树[trietree]、后缀树
一.哈希树概述 1.1..其他树背景 二叉排序树,平衡二叉树,红黑树等二叉排序树.在大数据量时树高很深,我们不断向下找寻值时会比较很多次.二叉排序树自身是有顺序结构的,每个结点除最小结点和最大结点外都 ...
- trie字典树详解及应用
原文链接 http://www.cnblogs.com/freewater/archive/2012/09/11/2680480.html Trie树详解及其应用 一.知识简介 ...
- 字典树(Trie Tree)
在图示中,键标注在节点中,值标注在节点之下.每一个完整的英文单词对应一个特定的整数.Trie 可以看作是一个确定有限状态自动机,尽管边上的符号一般是隐含在分支的顺序中的.键不需要被显式地保存在节点中. ...
- 算法导论:Trie字典树
1. 概述 Trie树,又称字典树,单词查找树或者前缀树,是一种用于快速检索的多叉树结构,如英文字母的字典树是一个26叉树,数字的字典树是一个10叉树. Trie一词来自retrieve,发音为/tr ...
- [数据结构]字典树(Tire树)
概述: Trie是个简单但实用的数据结构,是一种树形结构,是一种哈希树的变种,相邻节点间的边代表一个字符,这样树的每条分支代表一则子串,而树的叶节点则代表完整的字符串.和普通树不同的地方是,相同的字符 ...
- Trie树/字典树题目(2017今日头条笔试题:异或)
/* 本程序说明: [编程题] 异或 时间限制:1秒 空间限制:32768K 给定整数m以及n个数字A1,A2,..An,将数列A中所有元素两两异或,共能得到n(n-1)/2个结果,请求出这些结果中大 ...
随机推荐
- 使用C#导出MSSQL表数据Insert语句,支持所有MSSQL列属性
在正文开始之前,我们先看一下MSSQL的两张系统表sys.objects . syscolumnsMSDN中 sys.objects表的定义:在数据库中创建的每个用户定义的架构作用域内的对象在该表中均 ...
- HDU3987 Harry Potter and the Forbidden Forest(边数最少的最小割)
方法1:两遍最大流.一遍最大流后,把满流边容量+1,非满流边改为INF:再求最小割即为答案. 我大概想了下证明:能构成最小割的边在第一次跑最大流时都满流,然后按那样改变边容量再求一次最小割,就相当于再 ...
- ural 1268. Little Chu
1268. Little Chu Time limit: 0.25 secondMemory limit: 64 MB The favorite occupation of Little Chu is ...
- Machine Schedule
Machine Schedule Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others) ...
- 首发 手把手教你制作 Windows8 应用程序内部的 hubtile (动态瓷砖控件) MetroStyle(转)
http://blog.csdn.net/wangrenzhu2011/article/details/8175492 (转) 在metro 风格中 动态磁贴是他的精髓 在wp7 的开发中 我们可以使 ...
- android环境安装之android4.2安装(转)
准备学习android,着手安装android时听说很麻烦,在网上看了很多android安装说明,都是android比较早的版本,我这里安装了android4.2,简单记录一下. 安装分为几步,首先申 ...
- 【BZOJ】1043: [HAOI2008]下落的圆盘(计算几何基础+贪心)
http://www.lydsy.com/JudgeOnline/problem.php?id=1043 唯一让我不会的就是怎么求圆的周长并QAAQ... 然后发现好神!我们可以将圆弧变成$[0, 2 ...
- 【BZOJ】1049: [HAOI2006]数字序列(lis+特殊的技巧)
http://www.lydsy.com/JudgeOnline/problem.php?id=1049 题意:给一个长度为n的整数序列.把它变成一个单调严格上升的序列.但是不希望改变过多的数,也不希 ...
- POJ 2948 Martian Mining(DP)这是POJ第200道,居然没发现
题目链接 两种矿石,Y和B,Y只能从从右到左,B是从下到上,每个空格只能是上下或者左右,具体看图.求左端+上端最大值. 很容易发现如果想最优,分界线一定是不下降的,分界线上面全是往上,分界线下面都是往 ...
- Google Code Jam 2010 Round 1C Problem B. Load Testing
https://code.google.com/codejam/contest/619102/dashboard#s=p1&a=1 Problem Now that you have won ...
