java package 命名空间
原文: http://www.studytonight.com/java/package-in-java.php
创建一个简单的maven 项目的命令是: mvn archetype:generate -DgroupId=com.tellidea.run -DartifactId=go -DarchetypeArtifactId=maven-archetype-quickstart -DinteractiveMode=false
成功后,项目结构如下:

pom.xml中自己加了一段:
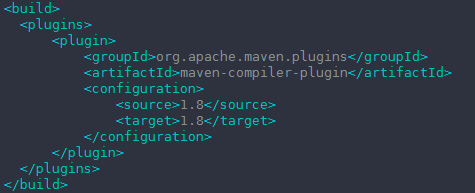
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/maven-v4_0_0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.tellidea.run</groupId>
<artifactId>go</artifactId>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>go</name>
<url>http://maven.apache.org</url>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>3.8.1</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<source>1.8</source>
<target>1.8</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
执行编译:mvn compile 后,结构目录如下:
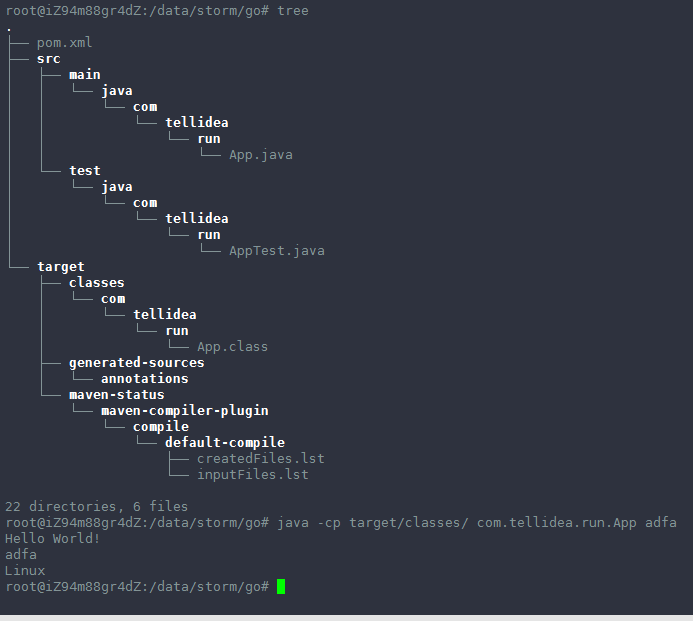
这两种方式都可以跑起来:
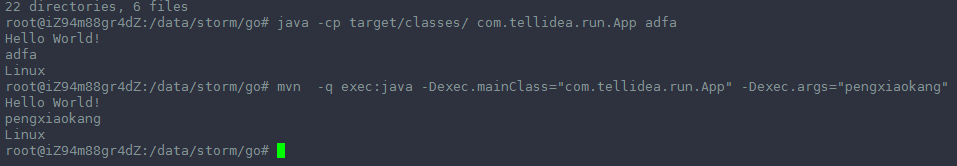
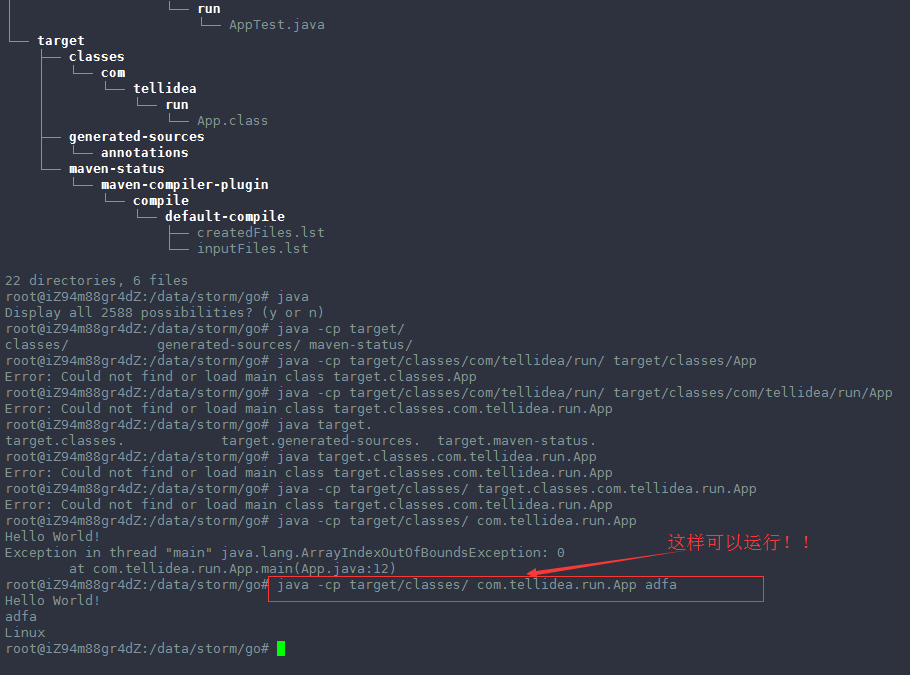
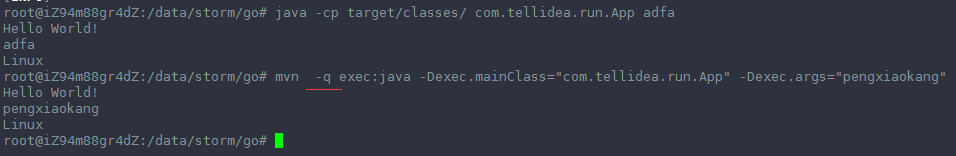
上面两种方式都可以运行 App.class成功!!

-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Java Package
Package are used in Java, in-order to avoid name conflicts and to control access of class, interface and enumeration etc. A package can be defined as a group of similar types of classes, interface, enumeration and sub-package. Using package it becomes easier to locate the related classes.
Package are categorized into two forms
- Built-in Package:-Existing Java package for example
java.lang,java.utiletc. - User-defined-package:- Java package created by user to categorized classes and interface
Creating a package
Creating a package in java is quite easy. Simply include a package command followed by name of the package as the first statement in java source file.
package mypack;
public class employee
{
...statement;
}
The above statement create a package called mypack.
Java uses file system directory to store package. For example the .class for any classes you define to be part of mypack package must be stored in a directory called mypack.
Additional points on package:
- A package is always defined in a separate folder having the same name as a package name.
- Define all classes in that package folder.
- All classes of the package which we wish to access outside the package must be declared public.
- All classes within the package must have the package statement as its first line.
- All classes of the package must be compiled before use (So that its error free)
Example of java package
//save as FirstProgram.java
package LearnJava;
public class FirstProgram{
public static void main(String args[]){
System.out.println("Welcome to package");
}
}
How to compile java package?
If you are not using any IDE, you need to follow the syntax given below:
javac -d directory javafilename
Example:
javac -d . FirstProgram.java
The -d switch specifies the destination where to put the generated class file. You can use any directory name like d:/abc (in case of windows) etc. If you want to keep the package within the same directory, you can use . (dot).
How to run java package program?
You need to use fully qualified name e.g. LearnJava.FirstProgram etc to run the class.
To Compile: javac -d . FirstProgram.java
To Run: java LearnJava.FirstProgram
Output: Welcome to package
The -d is a switch that tells the compiler where to put the class file i.e. it represents destination. The . represents the current folder.
import keyword
import keyword is used to import built-in and user-defined packages into your java source file so that your class can refer to a class that is in another package by directly using its name.
There are 3 different ways to refer to class that is present in different package
- Using fully qualified name(But this is not a good practice.)
If you use fully qualified name then only declared class of this package will be accessible. Now there is no need to import. But you need to use fully qualified name every time when you are accessing the class or interface.
It is generally used when two packages have same class name e.g. java.util and java.sql packages contain Date class.
Example :
//save by A.java
package pack;
public class A{
public void msg(){System.out.println("Hello");}
}
//save by B.java
package mypack;
class B{
public static void main(String args[]){
pack.A obj = new pack.A();//using fully qualified name
obj.msg();
}
}Output:
Hello
- import the only class you want to use(Using packagename.classname)
If you import package.classname then only declared class of this package will be accessible.
Example :
//save by A.java
package pack;
public class A{
public void msg(){
System.out.println("Hello");
}
}
//save by B.java
package mypack;
import pack.A;
class B{
public static void main(String args[]){
A obj = new A();
obj.msg();
}
}Output:
Hello
- import all the classes from the particular package(Using packagename.*)
If you use package.* then all the classes and interfaces of this package will be accessible but not subpackages.
The import keyword is used to make the classes and interface of another package accessible to the current package.
Example :
//save by First.java
package LearnJava;
public class First{
public void msg(){System.out.println("Hello");}
}
//save by Second.java
package Java;
import Learnjava.*;
class Second{
public static void main(String args[]){
First obj = new First();
obj.msg();
}
}Output:
Hello
Points to remember
- When a package name is not specified , a class is defined into the default package (the current working directory) and the package itself is given no name. Hence you were able to execute assignments earlier.
- While creating a package, care should be taken that the statement for creating package must be written before any other import statements.
// not allowed
import package p1.*;
package p3;
//correct syntax
package p3;
import package p1.*;
java package 命名空间的更多相关文章
- Atitit.软件命名空间 包的命名统计 及命名表(2000个名称) 方案java package
Atitit.软件命名空间 包的命名统计 及命名表(2000个名称) 方案java package 1. 统计的lib jar 列表1 2. Code3 3. 常用包名按找字母排序(2000个)4 ...
- 从零认识Java Package
Java Package为何被设计?如果你没想过,我这里或许可以提供一种视角. 想象一下,作为一个语言的设计者,你一定会考虑一个问题:变量名的冲突.为了解决这个问题,C++引入了命名空间(namesp ...
- JAVA package与import机制
JAVA package与import机制 http://files.cnblogs.com/files/misybing/JAVA-package-and-import.pdf import org ...
- java package(包)的用法
一般来说都用eclipse自动化图形工具搞定,我用的是ubuntu,所以需要自己打包引入. 什么是包? 这是对java源代码的组织和管理的一种方式,比如:当操作系统某个目录的文件非常多的时候,我们一般 ...
- Java package 包的命名规范。
Java的包名都有小写单词组成,类名首字母大写:包的路径符合所开发的 系统模块的 定义,比如生产对生产,物资对物资,基础类对基础类.以便看了包名就明白是哪个模块,从而直接到对应包里找相应的实现. 由于 ...
- java package 包 学习笔记
编译命令示例: javac -d . Main.java 注:带参数-d自动建立文件目录, 只使用javac 则需要手工创建目录 把 class文件打包 jar命令 jar cvf T.jar *; ...
- JAVA - package与import解析(一)
一.为什么要引入package和import?这个问题和c++中引入命名空间是一样的,也是为了解决重名问题.java通过包机制来解决重名问题,也就相当于给重名的代码加一系列前缀,从而达到唯一标识的作用 ...
- Java package详解
Java引入包(package)机制,提供了类的多层命名空间,用于解决类的命名冲突.类文件管理等问题.Java允许将一组功能相关的类放在同一个package下,从而组成逻辑上的类库单元.如果希望把一个 ...
- Java——package与import
[package] <1>为了解决类的命名冲突问题,Java引入包(package)机制,提供类的多重类命名空间. <2>package作为源文件的第一条语句(缺省时指定为 ...
随机推荐
- 分享一些对IT人员非常好用的资源
前言 分享一下本人工作至今整理的一些好用的资源,这些资源主要是一些工作和生活中用到的文档.软件和网站. 文档主要是面试相关的文档和技术文档,其中面试文档主要是Java这块的,技术文档就有很多,除了Ja ...
- Aspose Cells dll 实现数据简单下载
Workbook workbook = new Workbook(); //工作簿 Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[ ...
- 题解报告:hdu 1285 确定比赛名次
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1285 Problem Description 有N个比赛队(1<=N<=500),编号依次 ...
- cocos2d-x 不规则碰撞检测 【转载】
原文:http://www.2cto.com/kf/201401/272331.html //判断有没有点到有材质的部分, p_point相对, CCSprite坐标 (p_point是相对 Spr ...
- c# winform控件dock属性停造位置、摆放顺序详解
dock : [英文释义- 码头.依靠][winform释义- 获取或设置当前控件依靠到父容器的哪一个边缘.] 用途:多数控件都有这个属性,主要用来设置控件的布局. 但对于不太了解这个属性的朋友来说有 ...
- Educational Codeforces Round 42 (Rated for Div. 2)
A. Equator(模拟) 找权值的中位数,直接模拟.. 代码写的好丑qwq.. #include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #include< ...
- [原创]Toolbar setNavigationIcon无效
最近在做一个Toolbar,setNavigationIcon()这个方法一直无效,说什么的都有,什么getSupportActionBar().setNavigationIcon()的,说设置sty ...
- c++ 以二进制和以文本方式读写文件的区别
在c++项目开发中,时常涉及到文件读写操作.因此在这里先简单梳理和回顾一下文本模式和二进制模式在进行文件读写上的区别. 1.linux平台下文本文件和二进制文件的读写 在linux平台下进行文件读写时 ...
- js基本类型的包装对象
var test = "test"; test.a = "hello"; console.log(test.a); 在JavaScript中,“一切皆对象”,数 ...
- 一个好玩的 屏蔽别人审查元素F12 右键及其他复制粘贴等
有的时候自己写的私下的个人小页面 里面有些自己的小秘密 或者别的东西 不想人别人审查元素看见 所以我提供了一段不让别人审查元素的代码(我个人比较喜欢弄有意思的东西 喜欢玩 ) //屏蔽右键菜单doc ...
