Measuring & Optimizing I/O Performance
By Ilya Grigorik on June 23, 2009
 Measuring and optimizing IO performance
Measuring and optimizing IO performance
is somewhat of a black art: the tools are there, the resources and discussions are plenty, but it is also incredibly easy to get lost in the forest. I speak from recent experience. Having gone down multiple false starts with filesystem optimization, RAID tweaking,
and even app-level changes it really helped to finally step back and revisit the basics. Many man pages and discussion threads later, a few useful realizations emerged: iostat is your best friend, but it can also be incredibly deceiving; refreshing your memory
of disk latencies will go a long way; disks and filesystems are fast, but not that fast.
Monitoring IO Performance with iostat
If IO performance is suspect, iostat is your best friend. Having said that, the man pages are cryptic so don't be surprised if you find
yourself reading the source. To get started, identify the device in question and start a monitoring process:
# -k output rates in kB
# -x output extended stats
# -d monitoring single device
# sample stats every 5 seconds for device /dev/sdh
$ iostat -dxk /dev/sdi 5
Next, allocate yourself a couple of hours to understand the output or expect to find yourself down a wrong path in no time flat (been there, done that). iostat is a popular tool amongst the database crowd, so not surprisingly you'll find a lot of great discussions documenting the
use. Depending on your application you will need to focus on different metrics, but as a gentle introduction let's take a look at await, svctime and avgque:
- await - The average time (in milliseconds) for I/O requests issued to the device to be served. This includes the time spent by the requests in queue and the time spent servicing them.
- svctime - The average service time (in milliseconds) for I/O requests that were issued to the device.
- avgqu-sz - The average queue length of the requests that were issued to the device.

First off, await is a deceiving metric! Even though it claims to measure average time, it is better understood
as an aggregate function, so don't be mislead by it: avgqu-sz * svctm / (%util/100). Ideally, await should be roughly equal to your svctime, which leads us to a corollary: your average queue size is ideally
hovering around single digits. Understanding these variables alone can tell you volumes about the application generating the load.
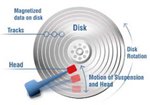
Disk Latencies Refresher & EBS Performance
 Disk access
Disk access
time is determined via the sum of several variables: spin-up, seek, rotational delay, and transfer time. Assuming your disk is not is not sleeping we can discount the spin-up
time, which leaves us with seek (time for the disk arm to find the track: ~10ms), rotational
delay (time to get the right sector under the head: depends on RPM), and the actual transfer time. Hence, in the worst case we will take ~10ms to seek, 60s/7200RPM ~= 8ms in rotational delay, plus the read time. On average, for a 7.2k RPM
disk this translates into roughly ~5ms access time (~20ms in worst case) to read the first byte!
Armed with this knowledge we can now put Amazon's EBS performance in context: on average our EBS mounts show 10~30ms svctime, which all things considered is not outrageous for a SAN. This number also dips into low single digits at nights and on weekends,
which points to the fact that as with any shared resource, the performance of EBS degrades during the day.
Having said that, a 6x performance difference based on time of day is definitely not anything to sneeze at, so let's hope Amazon is on top of this!
Average queue size (avgqu-sz) is a popular metric in the DBA circles, but do be
careful with it when
running on a SAN or any multi-spindle device. Ideally, your queue size (avgqu-sz) for a single disk should be in single digits, which means that the underlying device is well matched to the IO load generated by the application. Conversely,
if the queue size is artificially low, chances are your application code can benefit from some tuning: do less disk flushing, think about caching or buffering, or in other words, double check the assumption that IO is the bottleneck!
Disks, Filesystems and Facebook Case Study: Haystack
 Average access time on our disks places some hard
Average access time on our disks places some hard
limits on the number of IOPs - at 5ms average, we get a very optimistic 200 req/s with no read time. Hence, if you're trying to store several hundred files a second, you might want to revisit the architecture or seriously think about switching to SSD's! Databases
such as MySQL work around this constraint by minimizing the number of file handles, caching data, and using aggressive buffering techniques. Willing to potentially loose a little bit of data with InnoDB? Set flush_log_at_trx_commit
to 2 to avoid flushing on every transaction in favor of a periodic one second flush. In similar fashion, you can tweak your MyISAM key
buffers, or even place your index and data files on different drives.
Facebook team recently released the details of their Haystack photo storage system which serves as a great case study
of working around the IO bottlenecks: over 15PB of photo storage, and ~360 new photos being uploaded every second as of April '09. To meet the requirements, they dropped the POSIX filesystem semantics and went for an append only structure with a separate in-memory
index which stores the direct inode offsets for each photo. As a result, each photo access is translated into a single IO request - a huge win. Read through it, fascinating
stuffand an illustrative example of optimizing for IO.

Ilya Grigorik is a web performance engineer and developer advocate on the Make The Web Fast team
at Google, where he spends his days and nights on making the web fast and driving adoption of performance best practices.
Follow @igrigorik
Measuring & Optimizing I/O Performance的更多相关文章
- Optimizing Item Import Performance in Oracle Product Hub/Inventory
APPLIES TO: Oracle Product Hub - Version 12.1.1 to 12.1.1 [Release 12.1] Oracle Inventory Management ...
- PatentTips - Optimizing Write Combining Performance
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION The use of a cache memory with a processor facilitates the reduction of ...
- [Forward]Improving Web App Performance With the Chrome DevTools Timeline and Profiles
Improving Web App Performance With the Chrome DevTools Timeline and Profiles We all want to create h ...
- Java性能提示(全)
http://www.onjava.com/pub/a/onjava/2001/05/30/optimization.htmlComparing the performance of LinkedLi ...
- Migrating Oracle on UNIX to SQL Server on Windows
Appendices Published: April 27, 2005 On This Page Appendix A: SQL Server for Oracle Professionals Ap ...
- (转) [it-ebooks]电子书列表
[it-ebooks]电子书列表 [2014]: Learning Objective-C by Developing iPhone Games || Leverage Xcode and Obj ...
- 数据库调优过程(一):SqlServer批量复制(bcp)[C#SqlBulkCopy]性能极低问题
背景 最近一段给xx做项目,这边最头疼的事情就是数据库入库瓶颈问题. 环境 服务器环境:虚拟机,分配32CPU,磁盘1.4T,4T,5T,6T几台服务器不等同(转速都是7200r),内存64G. 排查 ...
- 跨过slf4j和logback,直接晋级log4j 2
今年一直关注log4j 2,但至今还没有出正式版.等不及了,今天正式向大家介绍一下log4j的升级框架,log4j 2. log4j,相信大家都熟悉,至今对java影响最大的logging系统,至今仍 ...
- 论文笔记:Model-Agnostic Meta-Learning for Fast Adaptation of Deep Networks
Model-Agnostic Meta-Learning for Fast Adaptation of Deep Networks ICML 2017 Paper:https://arxiv.org/ ...
随机推荐
- IOS本地日志记录方案
我们在项目中日志记录这块也算是比较重要的,有时候用户程序出什么问题,光靠服务器的日志还不能准确的找到问题. 现在一般记录日志有几种方式: 1.使用第三方工具来记录日志,如腾讯的Bugly,它是只把程序 ...
- java利用url实现网页内容的抓取
闲来无事,刚学会把git部署到远程服务器,没事做,所以简单做了一个抓取网页信息的小工具,里面的一些数值如果设成参数的话可能扩展性能会更好!希望这是一个好的开始把,也让我对字符串的读取掌握的更加熟练了, ...
- curl javaSSm框架中传入json数组的格式方法
curl与java结合传入get.post,head请求, 比如: curl的地址: curl -l 127.0.0.1:8080/spacobj/core/do?acid=100 -H " ...
- X64系统下IIS运行ASP网站HTTP500错误 【安装FoxMail Server时出现】
错误如上 解决办法 使用管理员模式运行CMD 输入cscript C:\inetpub\adminscripts\adsutil.vbs SET W3SVC/AppPools/Enable32bitA ...
- 转:Java中finally和return的执行关系
finally可以分两方面理解 1.执行时机问题.finally总会执行(除非是System.exit()),正常情况下在try后执行,抛异常时在catche后面执行 2.返回值问题.可以认为try( ...
- js,jq获取元素位置属性及兼容性写法
网页被卷起来的高度/宽度 document.documentElement.scrolltop //火狐 和 其他浏览器 document.body.scrolltop //ie,谷歌浏览器和没有 ...
- 实时消息传输协议(RTMP)详解
一.概念与摘要 RTMP协议从属于应用层,被设计用来在适合的传输协议(如TCP)上复用和打包多媒体传输流(如音频.视频和互动内容).RTMP提供了一套全双工的可靠的多路复用消息服务,类似于TCP协议[ ...
- 【Egret】Native版本 视频播放器(android)
前段时间,领导说客户要一个平板版本的视频播放器,把我们做的一些视频资源放进去,要是本地的:我们部门又没有app开发程序员,正好又前段我在实验egret的app打包功能,就说用egret做(ps:本来想 ...
- c++ 字符串去重
##### c++ 字符串去重 == 需求 == * 编写一个字符串过滤函数,若字符串出现多个相同的字符,将不是首次出现的字符过滤掉. > 输入:"apache" 输出:&q ...
- zoom动画,实现图片点击预览效果
参考:https://developer.android.google.cn/training/animation/zoom.html 1.创建Views 下面的布局包括了你想要zoom的大版本和小版 ...
