SciTech-Mathmatics-Probability+Statistics:Quantifing Uncertainty_统计数据分析:朱怀球PKU-3-Sampling Theory 统计抽样理论基础
Statistics & Data Analysis
— Zhu Huaiqiu, Peking University
《统计与数据分析》, 朱怀球, 北京大学
7 Steps
§3 统计抽样理论基础
"\(\large \text{ Get your facts first, then you can distort them as you please.}\)"
— \(\large Mark\ Twin\)
"\(\large \text{ Our behavior, attitudes, and sometimes actions are based on samples.}\)"
— \(\large Elements\ of\ Sampling\ Theory\ and\ Methods\)
3.1 统计抽样的基本概念
\bm{ Statistical\ Inference }\ Theory \begin{cases} \bm{ Hypothesis\ Testing }\ Theory \\
\bm{ Parameter\ Estimation } \ Theory \\ \bm{ Statistical\ Sampling }\ Theory \\ \bm{ Probability\ }\ Theory \\
\end{cases} \\
\end{array} \]
Comparing: Statistics 和 Probability

Statistics基本思想( 总体 — 样本 — 总体 )
\(\large \begin{array}{rl} \\
X :& \bm{ Population },\ Statistics: \mu,\ \tau, \sigma, \ \sigma^2 \\
\Theta :& \bm{ Parameter\ Space } \\
\theta :& \bm{ Parameter } \\
\{X_i\}:& \bm{Sample} ,\ Statistics: \overset{-}{x}, \ \\
\overset{\sim}{\Theta}:& \bm{ Parameter\ Estimation } \\
\end{array}\)
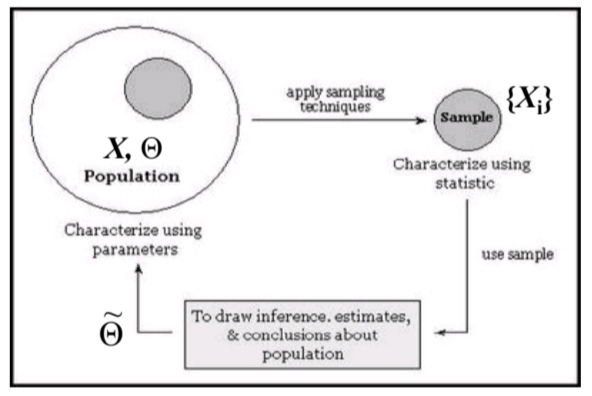
Sampling Concept(抽样 的 概念)
For \(\large \text{ one existing }\) \(\large \bm{Measuring\ Population }\) (named \(\large \bm{\text{Simple Population}}\)),
sample \(\large \bm{Measuring\ Sample}\) (named \(\large \bm{\text{Simple Sample}}\) ) from the \(\large \bm{\text{Simple Population}}\)), using specific sort of \(\large \bm{\text{Inference Method}}\).
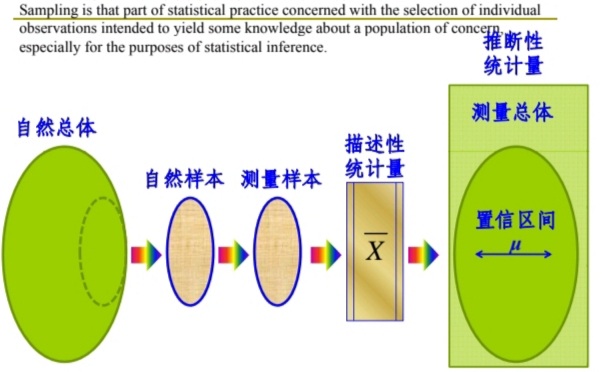
\(\large \begin{array} {lll} \\
\bm{ Population(Natural) } &\Rightarrow \bm{ Sample(Natural) } &\Rightarrow \bm{ Sample(Measuring) } \\
\bm{ Sample(Measuring) } &\Rightarrow \bm{ Descriptive\ Statistics } &\Rightarrow \bm{ Population(Measuring) } \end{array}\)
Sampling & Statistics
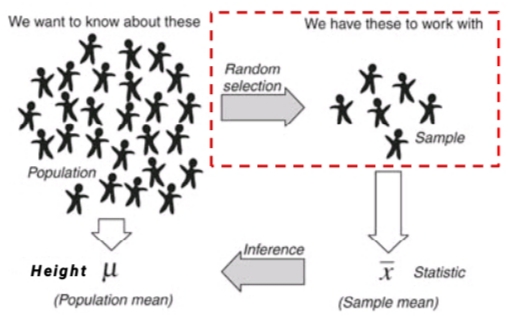
Parameters & Statistics
Parameters(of Population) and Statistics(of Sample)
\bm{ Statistical\ Theory } & \begin{cases} \bm{ Center\ Tendency } & \rightarrow \bm {Mean} \\
\bm{ Variation\ Tendency } & \rightarrow \bm {Variance, \ STD} \\
\end{cases} \\
\bm{ Probability\ Theory } & \begin{cases} \bm{ Center\ Tendency } & \rightarrow \bm {Expectation} \\
\bm{ Variation\ Tendency } & \rightarrow \bm {Variance} \\
\end{cases} \\
\end{array} \]
1.4.1 Statistics(统计变量) 和 Observation(观测) of Statistical Resources(统计资料)
Statistics(统计变量):
研究对象的、可测量的特征
且对于一组对象中的不同对象可以取不同的值。Observation Value(观测值): 变量的每一个测量值(x,x)
- Quanlitative Variable(定性变量): Non-Rankable观测值, 特征的 量值不能排序
- Quantitative Variable(定量变量): Rankable 观测值, 特征的 数量可以排序
- Discrete Variable
- Continuous Variable
Statistical Function:
- 函数关系,运用统计方法确定的,自变量和因变量之间的,
- 只需要定义域、值域和两个变量间的对应关系,
并不总是需要等式表达式
Statistical Resources(统计资料):
观测结果组成的集合
- 定性统计资料、定量统计资料
- 连续统计资料、离散统计资料
- 有效数字: 在观测尺度(或科学计算)中实际能够得到的所有数字
常见问题:- \(\large 102个细胞\)
- \(\large 10,100个细菌(精确到100) \ \rightarrow\ 10,050 \text{ ~ } 10,150\)
- \(\large 23.4\%(23.437201\%?)\)
- \(\large 4.15 \text{ ~ } 4.25\ \times\ 10^{-3}\)
Observation of Statistics(统计变量的观测)
统计资料测量值, 受各种随机因秦的影响
System Error(系统误差)
System Error(系统误差)的大小,
- 稳定(观测过程不变),
- 可预测(用计算或实验方法可求得),
- 可补偿(可修正或调整使其减少).
Random Error(随机误差):
在相同条件下, 对同一Statistic的多次观测,
由于各种 Random Factors, 会出现测量值时而偏大、时而偏小的误差现象, 这种类型的误差叫Random Error。
在确定的测量条件, 对同一Statistic多次测量并用它的算术平均值, 作为它的测量结果, 能够比较好地减少Random Error。Statistical Rules of Random Error
- 绝对值相等的 正的与负的 误差 出现的机会相同
- Variance: 绝对值小的误差 比 绝对值大的误差 出现的机会多
- Range: 误差 不会超出 一定的范围。
Descriptive Statistics(of Samples)
\text {Samples Data} \begin{cases} \\
\bm{ Center\ Tendency } \overset{ \bm {Mean} }{ \rightarrow } & \begin{cases}
& \bm{ Mean } \\ & \bm{ Median } \\ & \bm{ Mode } \\
\end{cases} \\
\bm{ Variation\ Tendency } & \begin{cases}
& \overset{ \bm{Range} }{ \rightarrow } & \begin{cases}
\bm{ Max } \\ \bm{ Min } \\
\end{cases} \\
& \overset{ \bm{Quartiles} }{ \rightarrow } & \begin{cases}
\bm{ Up Quartile } \\ \bm{ Down Quartile } \\
\end{cases} \\
\end{cases} \\
\end{cases} \\
\end{array} \]
Population Parameters
设总体 \(\large X\) 容量为 \(\large N\), 个体取值为\(\large \{x _i \},\ i \in [1, N]\), 定义:
\(\large \begin{array}{ll} \\
\text{ population }mean : & \mu = \dfrac{1}{N} \overset{N}{\underset{i =1}{\sum}}{ x_i } \\
\text{ population }total : & \tau = \dfrac{1}{N} \overset{N}{\underset{i =1}{\sum}}{ x_i } = N \cdot \mu \\
\text{ population }variance : & \sigma^2 = \dfrac{1}{N} \overset{N}{\underset{i =1}{\sum}}{ (x_i - \mu)^2 } \\
\text{ population }standard\ deviation : & s = \sqrt{ \sigma^2 } \\
\end{array}\)
3.1.1 Statistical Model and Statistical Sampling Model
- Statistical Model:
- 设 \(\large \{\Omega, F_{\Omega}\} \ 为可定义\ p.\ f.\ 的\ Measurable\ Space\),
- \(\large \Omega\ is \text{ Sample Space }\)
- \(\large F_{\Omega}\ is \text{ p. f.(Probability Function) }\)
$\large \text{ for measuring the } \bm{Likelyhood} \text{ of the each } \bm{Outcome} $
- \(\large \Phi \text{ 为其上的一个} \bm{ Distribution\ Cluster(概率分布族) }\),
- 设 \(\large \{\Omega, F_{\Omega}\} \ 为可定义\ p.\ f.\ 的\ Measurable\ Space\),
\(\large 则三元组\{\Omega, F_{\Omega}, \Phi \}为\bm{ Statistical\ Model },\ 按是否取决于参数变量分两类\)
- \(\large \bm{ 参数统计模型 }:若 \bm{ 概率分布族 \Phi } \text{ 取决于某一} \ \bm{ \theta(Parameter\ Variable) }\)
$\large \Phi =\{ P(\theta) | \theta \in \Theta,\ where\ \Theta \text{ is the }\ \bm{ Parameter\ Space }\} $ - \(\large \bm{ 非参数统计模型 }:\ \bm{ 概率分布族 \Phi } \text{ 不取决于任何} \ \bm{Parameter\ Variable}\)
- 乘积模型 和 重复抽样模型
\(\large 设\ \{\Omega, F_{\Omega}, \Phi \}\ 和 \ \{\Omega', F_{\Omega}', \Phi' \}\ 为两个\ Statistical\ Model\),
$\large 则\bm{ 乘积模型 } \{ \Omega \bigotimes \Omega', F_{\Omega} \bigotimes F_{\Omega}', \Phi \bigotimes \Phi' \} 记作 \{ \Omega, F_{\Omega}, \Phi \} \bigotimes \{\Omega', F_{\Omega}', \Phi' \} \ $- $\large n\ 个\bm{等同}的\ \{\Omega, F_{\Omega}, \Phi \}\ 的\bm{乘积模型}称 \bm{ 重复抽样模型 },记为\{ \Omega, F_{\Omega}, \Phi \}^n $
- \(\large \bm{乘积模型} \text{ 实际等于 }\bm{独立观察系统}\)
- $\large \bm{重复抽样模型} \text{ 等于 }\bm{对一个观测对象} \text{ 进行 }\bm{有限次独立抽样结果} \text{ 的 }\bm{描述} $。
3.1.2 Sampling Design
\(\large \text{ Results from } \bm{probability\ theory} \text{ and } \bm{statistical\ theory} \text{ are } ,\)
\(\large employed\ to\ \bm{guide\ practice\ of\ sampling}.\)
\(\large Random\ Sampling\)(随机抽样, 简称抽样):
\(\large \text{ for } \bm{observing\ the\ elements\ of\ Population\ X },\)
\(\large 由其 \text{ 按照 } \bm{一定的概率} 抽取 \bm{\ Some\ Individuals}\).
\(\large Random\ Sample\)(随机样本, 简称样本):
\(\large 按照\bm{一定的概率}由Population \ \bm{X} =\{ x_i \},\ i \in [1, N] 抽取\bm{作为总体代表}\ 的\)
\(\large \bm{\ Some\ Individuals\ 的集合} \ \\{ X_1, X_2, \dots , X_n \\},\ n<N,\)
\(\large\ 称为\ \bm{ 容量为\ n\ 的Sample\ X} \ \\{ X_i \\}, \ i \in [1, n]\)
讨论
- 构成某一样本的每一个体都必须取自某一特定的统计总体,
不允许该总体之外的个体计入该总体的样本; - 样本个体的抽取应是按一定的概率进行的,而具体样本的产生应是随机的,
因此必须排除 人的主观因素 对 样本个体、抽取 和 样本生成 的干扰; - Sample是Population的代表,带有其 Distribution 信息;
- 因而, 能够 推断Population的Distribution规律;
- 然而,Sample只是Population的一个subset, 有随机性;
因此,由Sample推断Population, 会产生 代表性误差。
\(\large Random\ Sampling\)的优点
\(\large Random\ Sampling\)是按照 Probability 来进行的,
即 Population 的任一 Individual 都按照 某一特定的Probability 有可能被选择,
产生的 Sample 的组成 因此是 随机的。
- 客观: 可避免抽样者有意或无意的偏好;
- 经济: 以尽可能小容量的Sample 来实现对Population 尽可能客观的Statistical Inference;
- 容差: 可较好地估计出由Sampling Method带来的Error;
- 可控: 可根据对Sampling Error的要求来设计Sample Size。
- 工业化革命的直接产物: 大规模制造要求标准化设计和制造,
对制造过程的质量控制, 直接诞生了统计抽样思想和技术.
根据 Statistics of Samples 对 Parameters of Population 进行 Estimation估计
\(\large \begin{array}{ll} \\
\text{ based on Statics of Samples estimate Parameters of Population } \\
\text{ hypothesis, } Population\ Size = N, \\
\text{ a }Simple\ Random\ Sample \text{ is } (X_1,\ X_2,\ \cdots,\ X_n), \\
Statistics\ of\ Samples \text{ as } estimate\ value \text{ of } Parameters\ of\ Population. \\
\\
\text{ Some }\ usually\ used\ estimations \text{ are }: \\
\end{array}\)
\(\large (1)\ Sample\ mean \text{ estimate } Population\ mean\)
\(\large \begin{array}{ll} \bm{ \overset{-}{X} } = \dfrac{1}{n} \overset{n}{\underset{i=1}{\sum}} {X_i} & \sim & \bm{ \mu } = \dfrac{1}{N} \overset{N}{\underset{i=1}{\sum}} {x_i} \end{array}\)
\(\large (2)\ Sample\ variance \text{ estimate } Population\ variance\)
\(\large \begin{array}{ll} \bm{ s^2 } = \dfrac{1}{n-1} \overset{n}{\underset{i=1}{\sum}} { ( X_i - \overset{-}{X} )^2 } & \sim & \bm{ \sigma^2 } = \dfrac{1}{N} \overset{N}{\underset{i=1}{\sum}} { (x_i - \mu)^2 } \end{array}\)
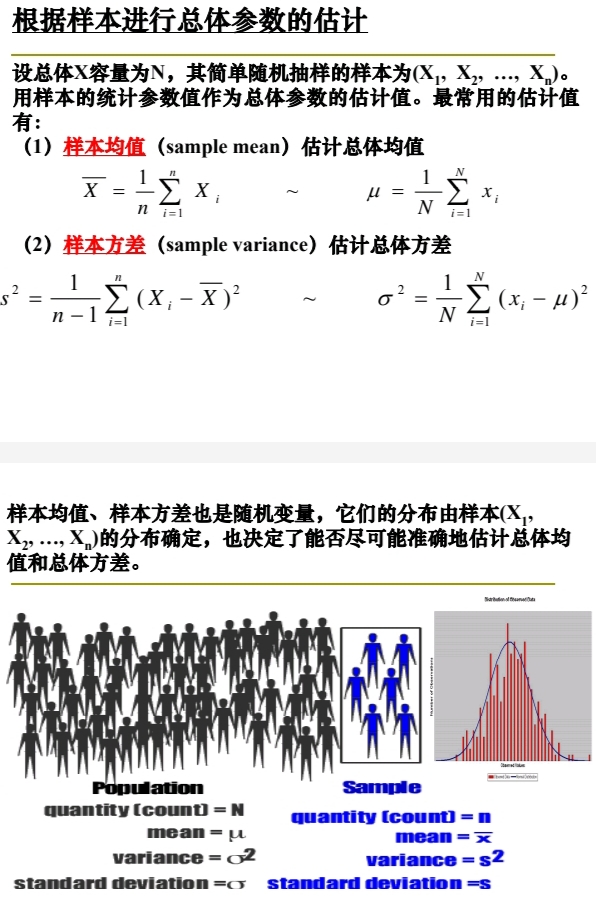
\(\large Sample\ mean\) and \(\large Sample\ variance\) are also \(\large Random\ Variables\),
their $\large Distribution $ are determined by the $\large Distribution $ of \(\large Sample\ (X_1,\ X_2,\ \cdots,\ X_n)\) that also determines if we can estimate the \(\large Population\ mean\) and \(\large Population\ variance\) as accurate as possible。
\(\large \begin{array}{rrll} \\
\bm{ Population } & \bm{ Parameters } & \bm{ Statistics } & \bm{ Sample } \\
quantity(count)\ =& \bm{ N } & \bm{ n } &=\ quantity (count) \\
mean\ =& \bm{ \mu } & \bm{ \overset{-}{x} } &=\ mean \\
variance \ =& \bm{ \sigma^2 } & \bm{ s^2 } &=\ variance \\
standard\ deviation \ =& \bm{ \sigma } & \bm{ s } &=\ standard\ deviation \\
\end{array}\)
Example:
- \(\large X_{\theta_1} \sim {\mathcal {N}}(\mu_1 ,\sigma_1 ^{2})\)
- \(\large X_{\theta_2} \sim {\mathcal {N}}(\mu_2 ,\sigma_2 ^{2})\)
- parameter vector is \(\large \theta = [\mu, \sigma^{2}]\)
SciTech-Mathmatics-Probability+Statistics:Quantifing Uncertainty_统计数据分析:朱怀球PKU-3-Sampling Theory 统计抽样理论基础的更多相关文章
- 号外号外:9月21号关于Speed-BI 《全国人口统计数据分析》开讲了
引言:如何快速分析纷繁复杂的数据?如何快速做出老板满意的报表?如何快速将Speed-BI云平台运用到实际场景中? 本课程将通过各行各业案例背景,将Speed-BI云平台运用到实际场景中,通 ...
- 第十二章——SQLServer统计信息(2)——非索引键上统计信息的影响
原文:第十二章--SQLServer统计信息(2)--非索引键上统计信息的影响 前言: 索引对性能方面总是扮演着一个重要的角色,实际上,查询优化器首先检查谓词上的统计信息,然后才决定用什么索引.一般情 ...
- 从键盘输入一个字符串(长度不超过30),统计字符串中非数字的个数,并将统计的结果显示在屏幕上,用EXE格式实现。
问题 从键盘输入一个字符串(长度不超过30),统计字符串中非数字的个数,并将统计的结果显示在屏幕上,用EXE格式实现. 源程序 data segment hintinput db "plea ...
- Python数据分析之路(一)查询和统计
0. 如何入门数据分析 关注沙漠之鹰的同学一定看过沙漠君写得很多篇数据分析文章,比如分析房价,车价,预测机动车摇号这些话题.其实文章中所有的分析都使用了Python和它非常强大的数据分析库Pandas ...
- Apache Lens —— 统计数据分析查询接口
Lens 提供了一个统一数据分析接口.通过提供一个跨多个数据存储的单一视图来实现数据分析任务切分,同时优化了执行的环境.无缝的集成 Hadoop 实现类似传统数据仓库的功能. 该项目主要特性: 简单元 ...
- Probability&Statistics 概率论与数理统计(1)
基本概念 样本空间: 随机试验E的所有可能结果组成的集合, 为E的样本空间, 记为S 随机事件: E的样本空间S的子集为E的随机事件, 简称事件, 由一个样本点组成的单点集, 称为基本事件 对立事件/ ...
- HotApp小程序统计,第一个专业的微信第三方小程序统计工具
1.什么是HotApp小程序统计 HotApp小程序统计是第一个微信第三方小程序统计工具,就像做android 和 ios开发的人知道友盟统计一样,小程序也需要有个统计工具. 通过这个工具,可以知道小 ...
- B2C经典查询,统计 绝对用的上,根据日期分组统计当天各种支付方式的销售数量和销售额
declare @sql varchar(8000) set @sql = 'select CONVERT(varchar(10), OrderDate, 120) as 日期' select @sq ...
- 如何把百度统计代码放入JS文件中?百度统计的JS脚本原理分析
<script> var _hmt = _hmt || []; (function() { var hm = document.createElement("script&quo ...
- bash 统计在线时长最长的十个玩/统计一天内一直处于不活跃状态的玩家的百分比
1.某游戏的客户端每隔5分钟会向服务端报告一次玩家的账户积分,如果两次报告的时间间隔不大于5分钟,认为该玩家在这5分钟内在线,假设报告数据的格式如下: IP Dat ...
随机推荐
- js--弹出对话框、改变控件内容、验证输入邮箱的合法性
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title> ...
- Java Objects.equals(a,b)的说明
一:值是null的情况: a.equals(b), a 是null, 抛出NullPointException异常. a.equals(b), a不是null, b是null, 返回false Obj ...
- 高性能深度学习推理引擎 -- OpenPPL
OpenPPL OpenPPL是商汤基于自研高性能算字库的开源深度学习推理平台,能够让人工智能应用高效可靠地运行在现有的CPU/GPU等计算平台上,为云端场景提供人工智能推理服务 OpenPPL基于全 ...
- ASP.NET Core Razor融合JS库Demo
cshtml.cs using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc; using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.RazorPages; namespace Razor ...
- 玩转代码:深入GitHub,高效管理我们的“shou学”平台源代码
玩转代码:深入GitHub,高效管理我们的"shou学"平台源代码 在当今快节奏的开发世界中,有效地管理代码不仅仅是一种良好实践,更是一种必需.无论您是独立开发者还是大型团队的一员 ...
- 聊一聊 .NET Dump 中的 Linux信号机制
一:背景 1. 讲故事 当 .NET程序 在Linux上崩溃时,我们可以配置一些参考拿到对应程序的core文件,拿到core文件后用windbg打开,往往会看到这样的一句信息 Signal SIGAB ...
- 聊聊@Autowired注解的Field injection is not recommended提示问题
1. 前言 在我接触过的大部分Java项目中,经常看到使用@Autowired注解进行字段注入: import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation ...
- HarmonyOS运动开发:精准估算室内运动的距离、速度与步幅
前言 在室内运动场景中,由于缺乏 GPS 信号,传统的基于卫星定位的运动数据追踪方法无法使用.因此,如何准确估算室内运动的距离.速度和步幅,成为了运动应用开发中的一个重要挑战.本文将结合鸿蒙(Harm ...
- java原生链利用
java原生链利用 在上一个文章中我们利用Java原生链进行shiro的无依赖利用; 针对在没有第三方库的时候,我们该如何进行java反序列化; 确实存在一条不依赖第三方库的java反序列化利用链;但 ...
- Docker拉取镜像时的疑惑
Docker拉取镜像时的疑惑 不知道你在拉取镜像的时候会不会有这样的疑惑--我不是只拉取了一个镜像嘛,为什么会出现这么多的东西 Docker中Layer(层)的概念 在 Docker 中,镜像(Ima ...
