POJ 2442 - Sequence - [小顶堆][优先队列]
题目链接:http://poj.org/problem?id=2442
Time Limit: 6000MS Memory Limit: 65536K
Description
Given m sequences, each contains n non-negative integer. Now we may select one number from each sequence to form a sequence with m integers. It's clear that we may get n ^ m this kind of sequences. Then we can calculate the sum of numbers in each sequence, and get n ^ m values. What we need is the smallest n sums. Could you help us?
Input
The first line is an integer T, which shows the number of test cases, and then T test cases follow. The first line of each case contains two integers m, n (0 < m <= 100, 0 < n <= 2000). The following m lines indicate the m sequence respectively. No integer in the sequence is greater than 10000.
Output
For each test case, print a line with the smallest n sums in increasing order, which is separated by a space.
Sample Input
1
2 3
1 2 3
2 2 3
Sample Output
3 3 4
题意:
给出 $m$ 个长度为 $n$ 的序列,在每一个序列中挑选一个数求和,可知有 $n^m$ 个结果,要求给出这些结果中前 $n$ 小的。
题解(参考《算法竞赛进阶指南》):
首先考虑当 $M=2$ 时的做法,记这两个序列为 $a,b$,先对所有的序列进行升序排序,并且用两个指针 $p,q$ 分别指向这两个序列的头部 $a[0],b[0]$,显然此时就是第 $1$ 小的和 $S_1 = a[0] + b[0]$。
那么,第 $2$ 小的和 $S_2 = \min (a[1] + b[0], a[0] + b[1])$,
如果第 $2$ 小和是 $S_2 = a[1] + b[0]$,那么此时竞争的第 $3$ 小的候选者,除了上面已经存在的 $a[0] + b[1]$ 外还应当再增加 $a[2] + b[0], a[1] + b[1]$,也就是序列一的指针 $ptr_1++$ 或者序列二的指针 $ptr_2++$。
不难想到,可以用一个小顶堆(或者STL的优先队列)来维护所有候选者,不断地扔进去新晋的候选者,再取出堆顶作为答案之一,再由该堆顶求出新的候选者插入堆中,再取出堆顶,反复如此……
候选方案产生方式如图:
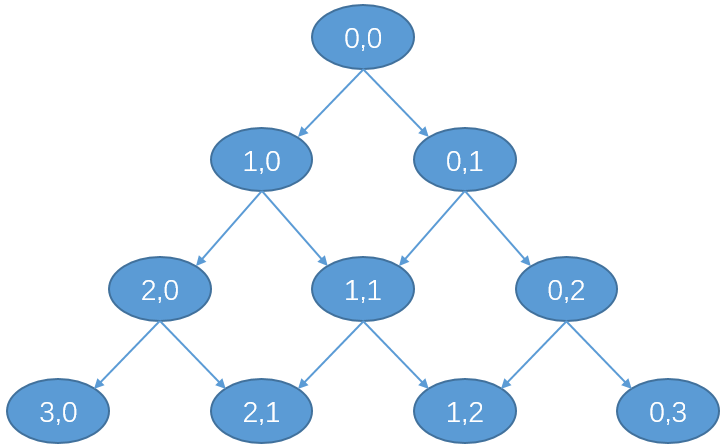
不过,有一点需要注意,例如我们在上述例子中已得 $S_2 = a[1] + b[0]$,那么入堆两个新的候选者之后堆中有三个节点: $a[0] + b[1], a[2] + b[0], a[1] + b[1]$;此时如果 $S_3 = a[0] + b[1]$,会发现又一次产生了候选者 $a[1] + b[1]$,这样就产生了重复,具体表现就是在上图中,就是绝大部分候选方案从 $(0,0)$ 出发可以有多条路径到达。重复方案多次入堆显然是影响正确性的,因此要避免这种情况发生。
不妨增加限定,如果当前选中的方案所产生新的候选者是 $ptr_2++$,那么以后都只能 $ptr_2++$,不能再回到 $ptr_1++$。换句话说,$a[0]+b[0]$ 要走到任何候选方案 $a[i]+a[j]$,必须先移动 $ptr_1 = 0 \sim i$,再移动 $ptr_2 = 0 \sim j$,使得到达备选方案 $a[i]+a[j]$ 的路径的唯一性,这样即可避免产生同一个候选方案重复入队的情况。
增加限定条件后的候选方案产生方式如图(不难看出,已经变为了一棵树):

考虑到添加了该限定条件后,是否影响到算法的正确性:
考虑原算法在选定 $a[i] + b[j]$ 成为第 $k$ 小之后,原本会产生 $a[i+1] + b[j]$ 和 $a[i] + b[j+1]$ 两个新的候选者。那么增加限定条件后,是否会发生本来第 $k+1$ 小应当是 $a[i+1] + b[j]$ 但是现在却没有生成该候选方案的情况?
根据限定条件,可知 $a[i] + b[j]$ 该方案成为第 $k$ 小,必然是由于 $a[i] + b[j-1]$ 产生了它,往前依次类推必然是在某一时刻选择了 $a[i] + b[0]$,而 $a[i] + b[0]$ 会产生两个候选者 $a[i+1] + b[0]$ 和 $a[i] + b[1]$,由此可知选中方案 $a[i] + b[j]$,只要 $j \ge 1$,那么此时队列里必然曾经出现过 $a[i+1] + b[0]$。
因此,如果说选定 $a[i] + b[j]$ 成为第 $k$ 小同时堆中没有 $a[i+1] + b[j]$,那么此时堆中必然存在 $a[i+1] +b[0],a[i+1] +b[1], \cdots ,a[i+1] +b[j-1]$ 中的某一个。显然,存在比 $a[i+1] + b[j]$ 还小的方案,肯定不会选到 $a[i+1] + b[j]$,因此增加该限定条件不影响算法正确性。
时间复杂度:
由于我们每次获取并删除一个堆顶,最多往堆中插入两个新的元素,因此每一次堆的大小最多增加 $1$,又因为最多只有 $N$ 次出堆操作且堆初始为空,因此堆的规模最大为 $O(n)$。
因此每次push和pop都是 $O(\log n)$ 的复杂度,而最多做 $O(n)$ 次push和pop,因此 $O(n \log n)$ 就能求得两个序列的前 $n$ 小的和。
而对于 $M>2$ 的情况,可以先求出第一个序列和第二个序列的前 $n$ 小的和,作为一个新序列再去和第三个序列求前 $n$ 小的和,以此类推总的时间复杂度为 $O(mn \log n)$。
AC代码:
手写二叉堆版本(500ms):
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int,int> pii; const int maxm=+;
const int maxn=+; int m,n;
vector<int> a[maxm];
struct Plan{
pii ptr;
bool last; //记录本方案是否是由ptr2++得到的
int sum;
Plan(){}
Plan(int i,int j,pii _ptr,bool _last)
{
ptr=_ptr;
last=_last;
sum=a[i][ptr.first]+a[j][ptr.second];
}
}init; struct Heap
{
int sz;
Plan heap[*maxn];
void up(int now)
{
while(now>)
{
int par=now>>;
if(heap[now].sum<heap[par].sum) //子节点小于父节点,不满足小顶堆性质
{
swap(heap[par],heap[now]);
now=par;
}
else break;
}
}
void push(const Plan &x) //插入权值为x的节点
{
heap[++sz]=x;
up(sz);
}
inline Plan top(){return heap[];}
void down(int now)
{
while((now<<)<=sz)
{
int nxt=now<<;
if(nxt+<=sz && heap[nxt+].sum<heap[nxt].sum) nxt++; //取左右子节点中较小的
if(heap[now].sum>heap[nxt].sum) //子节点小于父节点,不满足小顶堆性质
{
swap(heap[now],heap[nxt]);
now=nxt;
}
else break;
}
}
void pop() //移除堆顶
{
heap[]=heap[sz--];
down();
}
void del(int p) //删除存储在数组下标为p位置的节点
{
heap[p]=heap[sz--];
up(p), down(p);
}
inline void clr(){sz=;}
}h; int main()
{
int T;
cin>>T;
while(T--)
{
scanf("%d%d",&m,&n);
for(int i=;i<=m;i++)
{
a[i].clear();
for(int j=,x;j<=n;j++)
{
scanf("%d",&x);
a[i].push_back(x);
}
sort(a[i].begin(),a[i].end());
} int i=;
for(int j=;j<=m;j++,i^=)
{
init=Plan(i,j,make_pair(,),);
h.clr();
h.push(init);
a[i^].clear();
while(h.sz)
{
Plan now=h.top(); h.pop(); a[i^].push_back(now.sum);
if(a[i^].size()>=n) break; if(!now.last && now.ptr.first<n-)
h.push(Plan(i,j,make_pair(now.ptr.first+,now.ptr.second),));
if(now.ptr.second<n-)
h.push(Plan(i,j,make_pair(now.ptr.first,now.ptr.second+),));
}
}
for(int k=;k<a[i].size();k++) printf("%d ",a[i][k]);
printf("\n");
}
}
优先队列版本(563ms):
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int,int> pii; const int maxm=+;
const int maxn=+; int m,n;
vector<int> a[maxm];
struct Plan{
pii ptr;
bool last; //记录本方案是否是由ptr2++得到的
int sum;
Plan(){}
Plan(int i,int j,pii _ptr,bool _last)
{
ptr=_ptr;
last=_last;
sum=a[i][ptr.first]+a[j][ptr.second];
}
bool operator<(const Plan& oth)const{return sum>oth.sum;}
}init; priority_queue<Plan> Q; int main()
{
int T;
cin>>T;
while(T--)
{
scanf("%d%d",&m,&n);
for(int i=;i<=m;i++)
{
a[i].clear();
for(int j=,x;j<=n;j++)
{
scanf("%d",&x);
a[i].push_back(x);
}
sort(a[i].begin(),a[i].end());
} int i=;
for(int j=;j<=m;j++,i^=)
{
init=Plan(i,j,make_pair(,),);
while(!Q.empty()) Q.pop();
Q.push(init);
a[i^].clear();
while(!Q.empty())
{
Plan now=Q.top(); Q.pop(); a[i^].push_back(now.sum);
if(a[i^].size()>=n) break; if(!now.last && now.ptr.first<n-)
Q.push(Plan(i,j,make_pair(now.ptr.first+,now.ptr.second),));
if(now.ptr.second<n-)
Q.push(Plan(i,j,make_pair(now.ptr.first,now.ptr.second+),));
}
}
for(int k=;k<a[i].size();k++) printf("%d ",a[i][k]);
printf("\n");
}
}
POJ 2442 - Sequence - [小顶堆][优先队列]的更多相关文章
- POJ 1456 - Supermarket - [贪心+小顶堆]
题目链接:http://poj.org/problem?id=1456 Time Limit: 2000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Description A supermarke ...
- HDU 4006The kth great number(K大数 +小顶堆)
The kth great number Time Limit:1000MS Memory Limit:65768KB 64bit IO Format:%I64d & %I64 ...
- poj 1442 Black Box(堆 优先队列)
题目:http://poj.org/problem?id=1442 题意:n,m,分别是a数组,u数组的个数,u[i]w为几,就加到a几,然后输出第i 小的 刚开始用了一个小顶堆,超时,后来看了看别人 ...
- CodeForces - 867E Buy Low Sell High (贪心 +小顶堆)
https://vjudge.net/problem/CodeForces-867E 题意 一个物品在n天内有n种价格,每天仅能进行买入或卖出或不作为一种操作,可以同时拥有多种物品,问交易后的最大利益 ...
- 堆排序(大顶堆、小顶堆)----C语言
堆排序 之前的随笔写了栈(顺序栈.链式栈).队列(循环队列.链式队列).链表.二叉树,这次随笔来写堆 1.什么是堆? 堆是一种非线性结构,(本篇随笔主要分析堆的数组实现)可以把堆看作一个数组,也可以被 ...
- 大顶堆与小顶堆应用---寻找前k小数
vector<int> getLeastNumber(vector<int>& arr,int k){ vector<int> vec(k,); if(== ...
- heap c++ 操作 大顶堆、小顶堆
在C++中,虽然堆不像 vector, set 之类的有已经实现的数据结构,但是在 algorithm.h 中实现了一些相关的模板函数.下面是一些示例应用 http://www.cplusplus.c ...
- python 基于小顶堆实现随机抽样
起因:之前用蓄水池抽样,算法精简,但直观性很差. 所以这次采用了简单的,为没一个行,赋值一个随机值,然后取 最大的K个作为,随机样本. 基本思路:为每一个行(record,记录,实体) 赋一个rand ...
- Python使用heapq实现小顶堆(TopK大)、大顶堆(BtmK小)
Python使用heapq实现小顶堆(TopK大).大顶堆(BtmK小) | 四号程序员 Python使用heapq实现小顶堆(TopK大).大顶堆(BtmK小) 4 Replies 需1求:给出N长 ...
随机推荐
- 解决《UNIX环境高级编程》(APUE)示例代码的编译问题
转自 http://cunsheng.sinaapp.com/?p=360 APUE中示例很多, 把这些源码拿来跑跑调调对学习理解有着莫大的帮助, 随书网站就提供了源码下载, 不过我自己在Linux和 ...
- linux每日命令(8):mv命令
mv命令是move的缩写,可以用来移动文件或者将文件改名(move (rename) files),是Linux系统下常用的命令,经常用来备份文件或者目录. 一.命令格式: mv [选项] 源文件或目 ...
- 【九天教您南方cass 9.1】 11 方格网土方计算
同学们大家好,欢迎收看由老王测量上班记出品的cass9.1视频课程 我是本节课主讲老师九天. 我们讲课的教程附件也是共享的,请注意索取测量空间中. [点击索取cass教程]5元立得 (给客服说暗号:“ ...
- pyenv BUILD FAILED解决方法
在本机mac上安装pyenv安装成功后,用pyenv来安装python 3.5.0又出现了如下的问题: -> pyenv install 3.5.0 Downloading Python-3.5 ...
- Git 推送操作
Jerry 修改了他的最后一次提交的修改操作,他已经准备好将更改.推操作的数据永久存储的 Git 仓库.推操作成功后,其他开发人员可以看到Jerry 的变化. 他执行的git日志命令来查看提交的细节. ...
- c#.net基础
值类型:值类型的实例一般在线程的栈上分配 引用类型:引用类型的实例在线程的托管堆上分配 引用类型变量的Equals比较的是二者的引用地址而不是内部的值,值类型变量的Equals方法比较的是二者的值. ...
- volatile内存语义
全面理解Java内存模型(JMM)及volatile关键字 volatile的内存语义 Volatile读写所建立的happens-before关系Volatile读写的内存语义 锁: 获取和释放Vo ...
- 关于spring boot自动注入出现Consider defining a bean of type 'xxx' in your configuration问题解决方案
搭建完spring boot的demo后自然要实现自动注入来体现spring ioc的便利了,但是我在实施过程中出现了这么一个问题,见下面,这里找到解决办法记录下来,供遇到同样的问题的同僚参考 Des ...
- Spring注解开发之Spring常用注解
https://blog.csdn.net/Adrian_Dai/article/details/80287557主要的注解使用: 本文用的Spring源码是4.3.16@Configuration ...
- 避免在构造函数中调用虚方法(Do not call overridable methods in constructors)
CLR中说道,不要在构造函数中调用虚方法,原因是假如被实例化的类型重写了虚方法,就会执行派生类型对虚方法的实现.但在这个时候,尚未完成对继承层次结构中所有字段的初始化.所以,调用虚方法会导致不可预测的 ...
