object detection[NMS]
非极大抑制,是在对象检测中用的较为频繁的方法,当在一个对象区域,框出了很多框,那么如下图:
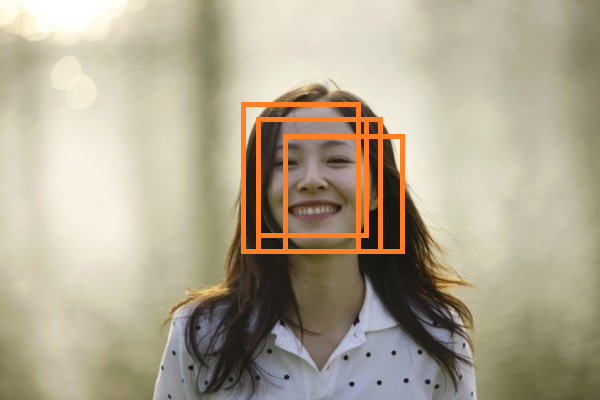
上图来自这里
目的就是为了在这些框中找到最适合的那个框.有以下几种方式:
- 1 nms
- 2 soft-nms
- 3 softer-nms
1. nms
主要就是通过迭代的形式,不断的以最大得分的框去与其他框做iou操作,并过滤那些iou较大(即交集较大)的框
IOU也是一种Tanimoto测量方法[见模式识别,希腊,书609页]
按照github上R-CNN的matlab代码,改成py的,具体如下:
def iou(xminNp,yminNp,xmaxNp,ymaxNp,areas,lastInd,beforeInd,threshold):
# 将lastInd指向的box,与之前的所有存活的box做比较,得到交集区域的坐标。
# np.maximum([3,1,4,2],3) 等于 array([3,3,4,3])
xminNpTmp = np.maximum(xminNp[lastInd], xminNp[beforeInd])
yminNpTmp = np.maximum(yminNp[lastInd], yminNp[beforeInd])
xmaxNpTmp = np.maximum(xmaxNp[lastInd], xmaxNp[beforeInd])
ymaxNpTmp = np.maximum(ymaxNp[lastInd], ymaxNp[beforeInd])
#计算lastInd指向的box,与存活box交集的,所有width,height
w = np.maximum(0.0,xmaxNpTmp-xminNpTmp)
h = np.maximum(0.0,ymaxNpTmp-yminNpTmp)
#计算存活box与last指向box的交集面积
# array([1,2,3,4]) * array([1,2,3,4]) 等于 array([1,4,9,16])
inter = w*h
iouValue = inter/(areas[beforeInd]+areas[lastInd]-inter)
indexOutput = [item[0] for item in zip(beforeInd,iouValue) if item[1] <= threshold ]
return indexOutput
def nms(boxes,threshold):
'''
boxes:n by 5的矩阵,n表示box个数,每一行分别为[xmin,ymin,xmax,ymax,score]
'''
assert isinstance(boxes,numpy.ndarray),'boxes must numpy object'
assert boxes.shape[1] == 5,'the column Dimension should be 5'
xminNp = boxes[:,0]
yminNp = boxes[:,1]
xmaxNp = boxes[:,2]
ymaxNp = boxes[:,3]
scores = boxes[:,4]
#计算每个box的面积
areas = (xmaxNp-xminNp)*(ymaxNp-yminNp)
#对每个box的得分按升序排序
scoresSorted = sorted(list(enumerate(scores)),key = lambda item:item[1])
#提取排序后数据的原索引
index = [ item[0] for item in scoresSorted ]
pick = []
while index:
#将当前index中最后一个加入pick
lastInd = index[-1]
pick.append(lastInd)
#计算最后一个box与之前所有box的iou
index = iou(xminNp,yminNp,xmaxNp,ymaxNp,areas,lastInd,index[:-1],threshold)
return pick
if __name__ == '__main__':
nms(boxes,threshold)
2. soft-nms
import copy
def iou(xminNp,yminNp,xmaxNp,ymaxNp,scores,areas,remainInds,maxGlobalInd,Nt,sigma,threshold, method):
remainInds = np.array(remainInds)
# 将maxGlobalInd指向的box,与所有剩下的box做比较,得到交集区域的坐标。
# np.maximum([3,1,4,2],3) 等于 array([3,3,4,3])
xminNpTmp = np.maximum(xminNp[maxGlobalInd], xminNp[remainInds])
yminNpTmp = np.maximum(yminNp[maxGlobalInd], yminNp[remainInds])
xmaxNpTmp = np.maximum(xmaxNp[maxGlobalInd], xmaxNp[remainInds])
ymaxNpTmp = np.maximum(ymaxNp[maxGlobalInd], ymaxNp[remainInds])
# 计算box交集所有width,height
w = np.maximum(0.0,xmaxNpTmp-xminNpTmp)
h = np.maximum(0.0,ymaxNpTmp-yminNpTmp)
#计算IOU
# array([1,2,3,4]) * array([1,2,3,4]) 等于 array([1,4,9,16])
inter = w*h
iouValue = inter/(areas[remainInds]+areas[maxGlobalInd]-inter)
# 依据不同的方法进行权值更新
weight = np.ones_like(iouValue)
if method == 'linear': # linear
# 实现1 - iou
weight = weight - iouValue
weight[iouValue <= Nt] = 1
elif method == 'gaussian':
weight = np.exp(-(iouValue*iouValue)/sigma)
else: # original NMS
weight[iouValue > Nt] = 0
# 更新scores
scores[remainInds] = weight*scores[remainInds]
# 删除低于阈值的框
remainInds = remainInds[scores[remainInds] > threshold]
return remainInds.tolist(),scores
def soft_nms(boxes, threshold, sigma, Nt, method):
'''
boxes:n by 5的矩阵,n表示box个数,每一行分别为[xmin,ymin,xmax,ymax,score]
# 1 - 先找到最大得分的box,放到结果集中;
# 2 - 然后将最大得分的box与剩下的做对比,去更新剩下的得分权值
# 3 - 删除低于最小值的框;
# 4 - 再找到剩下中最大的,循环
# 5 - 返回结果集
'''
assert isinstance(boxes,numpy.ndarray),'boxes must numpy object'
assert boxes.shape[1] == 5,'the column Dimension should be 5'
pick = []
copyBoxes = copy.deepcopy(boxes)
xminNp = boxes[:,0]
yminNp = boxes[:,1]
xmaxNp = boxes[:,2]
ymaxNp = boxes[:,3]
scores = copy.deepcopy(boxes[:,4]) # 会不断的更新其中的得分数值
remainInds = list(range(len(scores))) # 会不断的被分割成结果集,丢弃
#计算每个box的面积
areas = (xmaxNp-xminNp)*(ymaxNp-yminNp)
while remainInds:
# 1 - 先找到最大得分的box,放到结果集中;
maxLocalInd = np.argmax(scores[remainInds])
maxGlobalInd = remainInds[maxLocalInd]
pick.append(maxGlobalInd)
# 2 - 丢弃最大值在索引中的位置
remainInds.pop(maxLocalInd)
if not remainInds: break
# 3 - 更新scores,remainInds
remainInds,scores = iou(xminNp,yminNp,xmaxNp,ymaxNp,scores,areas,remainInds,maxGlobalInd,Nt,sigma,threshold, method)
return pick
if __name__ == '__main__':
soft_nms(boxes, 0.001, 0.5, 0.3, 'linear')
3. softer-nms
参考资料:
- 非极大抑制
- [首次提出nms] Rosenfeld A, Thurston M. Edge and curve detection for visual scene analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on computers, 1971 (5): 562-569.
- Theodoridis.S.,.Koutroumbas.K..Pattern.Recognition,.4ed,.AP,.2009
- [soft-nms] Bodla N, Singh B, Chellappa R, et al. Soft-nms—improving object detection with one line of code[C]//Computer Vision (ICCV), 2017 IEEE International Conference on. IEEE, 2017: 5562-5570. 【code】
- [fitness nms] Tychsen-Smith L, Petersson L. Improving Object Localization with Fitness NMS and Bounded IoU Loss[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:1711.00164, 2017.
- [learning NMS] J. H. Hosang, R. Benenson, and B. Schiele. Learning nonmaximum suppression. In CVPR, pages 6469–6477, 2017
- [softer-nms] He Y, Zhang X, Savvides M, et al. Softer-NMS: Rethinking Bounding Box Regression for Accurate Object Detection[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:1809.08545, 2018.)
object detection[NMS]的更多相关文章
- Object Detection · RCNN论文解读
转载请注明作者:梦里茶 Object Detection,顾名思义就是从图像中检测出目标对象,具体而言是找到对象的位置,常见的数据集是PASCAL VOC系列.2010年-2012年,Object D ...
- [Arxiv1706] Few-Example Object Detection with Model Communication 论文笔记
p.p1 { margin: 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px; font: 13.0px "Helvetica Neue"; color: #042eee } p. ...
- 论文阅读笔记五十五:DenseBox: Unifying Landmark Localization with End to End Object Detection(CVPR2015)
论文原址:https://arxiv.org/abs/1509.04874 github:https://github.com/CaptainEven/DenseBox 摘要 本文先提出了一个问题:如 ...
- 论文阅读笔记五十二:CornerNet-Lite: Efficient Keypoint Based Object Detection(CVPR2019)
论文原址:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1904.08900.pdf github:https://github.com/princeton-vl/CornerNet-Lite 摘要 基 ...
- 论文阅读笔记四十八:Bounding Box Regression with Uncertainty for Accurate Object Detection(CVPR2019)
论文原址:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1809.08545.pdf github:https://github.com/yihui-he/KL-Loss 摘要 大规模的目标检测数据集在 ...
- 论文阅读笔记四十六:Feature Selective Anchor-Free Module for Single-Shot Object Detection(CVPR2019)
论文原址:https://arxiv.org/abs/1903.00621 摘要 本文提出了基于无anchor机制的特征选择模块,是一个简单高效的单阶段组件,其可以结合特征金字塔嵌入到单阶段检测器中. ...
- 论文阅读笔记四十四:RetinaNet:Focal Loss for Dense Object Detection(ICCV2017)
论文原址:https://arxiv.org/abs/1708.02002 github代码:https://github.com/fizyr/keras-retinanet 摘要 目前,具有较高准确 ...
- Adversarial Examples for Semantic Segmentation and Object Detection 阅读笔记
Adversarial Examples for Semantic Segmentation and Object Detection (语义分割和目标检测中的对抗样本) 作者:Cihang Xie, ...
- 论文阅读笔记三十五:R-FCN:Object Detection via Region-based Fully Convolutional Networks(CVPR2016)
论文源址:https://arxiv.org/abs/1605.06409 开源代码:https://github.com/PureDiors/pytorch_RFCN 摘要 提出了基于区域的全卷积网 ...
随机推荐
- python地理处理包——geopy使用之地理编码与反地理编码
由于专业需要,经常接触一些地理处理的工具包,文档都是英文的,自己看的同时将其翻译一下,一方面自己学习的同时有个记录,要是能同时给一起的学习的童鞋们一些帮助,想想也是极好的.以下的文档内容主要翻译自官方 ...
- DAY3(PYTHON)字符串切片
字符串调整: capitalize() #首字母大写 upper() #全大写 lower() #全小写 swapcase() #大小写翻转 字符串切片: 顾头不顾尾!!! ...
- (后端)Mybatis中#{}和${}传参的区别及#和$的区别小结(转)
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/zqr99/p/8094234.html 最近在用mybatis,之前用过ibatis,总体来说差不多,不过还是遇到了不少问题,再次记录下, ...
- SQL SERVER数据库级的触发器
CREATE TRIGGER [Object_Change_Trigger_DDL] ON database FOR DROP_TABLE AS DECLARE @EventData AS xml; ...
- 暂别SQL Server,转战MySQL和Redis
机缘巧合下找到一个愿意提供学习MySQL和Redis机会的岗位,于是要暂别SQL Server了. 后续一段时间会陆续总结三年来SQL Server相关的工作经验,当做是暂别前的总结.
- C# 中将月份格式化为英语缩写格式
在测试Android 系统的时候,日期输入框需要输入英语短格式,如下. 考虑到系统日期格式和地域的关系紧密,地域不同,日期格式不同,所以经过查找,找到下面的解决方法. date.ToString(&q ...
- Python - 判断list是否为空
Python中判断list是否为空有以下两种方式: 方式一: list_temp = [] if len(list_temp): # 存在值即为真 else: # list_temp是空的 方式二: ...
- Python爬虫之Urllib库的基本使用
# get请求 import urllib.request response = urllib.request.urlopen("http://www.baidu.com") pr ...
- AI学习---基于TensorFlow的案例[实现线性回归的训练]
线性回归原理复习 1)构建模型 |_> y = w1x1 + w2x2 + -- + wnxn + b 2)构造损失函数 | ...
- PHP中生产不重复随机数的方法
PHP内置函数不重复随机数 需求:要生成一个数组,这个数组里面有10个元素,都是整形,并且是1-60之间不重复的随机数. 代码: 代码示例: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 ...
