《Java Spring框架》Spring切面(AOP)配置详解
1. Spring 基本概念
AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming)称为面向切面编程,在程序开发中主要用来解决一些系统层面上的问题,比如日志,事务,权限等待,Struts2的拦截器设计就是基于AOP的思想,是个比较经典的例子。
在不改变原有的逻辑的基础上,增加一些额外的功能。代理也是这个功能,读写分离也能用aop来做。
2. 原理图:
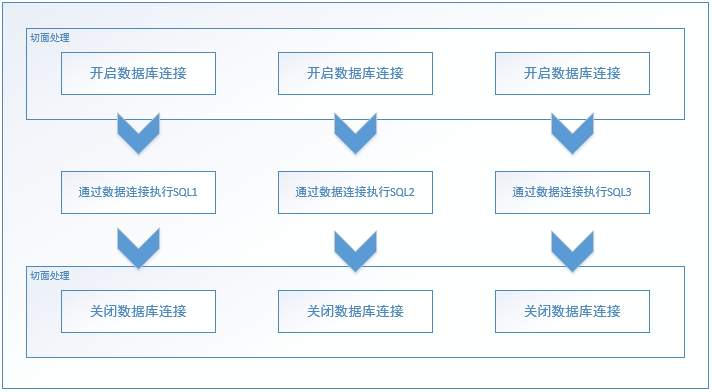
我们希望业务开发人员只关心中间部分,不再需要关系开启和关闭数据库连接的情况,同时也避免了代码重复和可能出现的问题。
3. 代码
public interface UserService {
//删
void save();
String getStr();
void setStr(String str);
}
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
private String str = "0";
public String getStr() {
return str;
}
public void setStr(String str) {
this.str = str;
}
@Override
public void save() {
System.out.println("--------- save --------------");
}
}
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint; /**
* 自定义通知类
*/
public class MyAdvice { //before 前置通知 在目标方法前调用
public void before() {
System.out.println("before");
} //after 最终通知(后置通知)在目标方法后调用,无论是否出现异常都会执行 finally
public void after() {
System.out.println("after");
} //afterReturning 成功通知(后置通知)在目标方法执行后,并且执行成功,如果方法出现异常则不调用
public void afterReturning() {
System.out.println("afterReturning");
} //afterThrowing 异常通知(后置通知)在目标方法执行出现异常的时候才会调用
public void afterThrowing() {
System.out.println("afterThrowing");
} //around 环绕通知 需要我们手动调用目标方法,并且可以设置通知
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("around before");
Object proceed = pjp.proceed();
System.out.println("around after");
return proceed;
}
}
import com.bing.aop.service.UserService;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner; import javax.annotation.Resource; @RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:applicationContext_aop.xml")
public class AopTest { @Resource(name="userService")
UserService us;
@Test
public void Test2() {
us.save();
}
}
配置文件:文件名(applicationContext_aop.xml)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.3.xsd">
<!-- 目标对象 -->
<bean name="userService" class="com.bing.aop.service.UserServiceImpl"></bean> <!-- 通知对象 -->
<bean name="myAdvice" class="com.bing.aop.MyAdvice"></bean> <aop:config>
<!-- 切入点 expression 切入点表达式 可以配置要增强的方法
public void com.bing.aop.service.UserServiceImpl.save()
* com.bing.aop.service.*ServiceImpl.*(..)
id 就是唯一标识
-->
<aop:pointcut expression="execution(* com.bing.aop.service.*ServiceImpl.*(..))" id="servicePc"/> <!-- 切面 通知+切入点 -->
<aop:aspect ref="myAdvice">
<!-- 通知类型 -->
<aop:before method="before" pointcut-ref="servicePc"/>
<!-- 最终通知 后置通知 -->
<aop:after method="after" pointcut-ref="servicePc"/>
<!-- 成功通知 后置通知 -->
<aop:after-returning method="afterReturning" pointcut-ref="servicePc"/>
<!-- 异常通知 后置通知 -->
<aop:after-throwing method="afterThrowing" pointcut-ref="servicePc"/>
<!-- 环绕通知-->
<aop:around method="around" pointcut-ref="servicePc"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
</beans>
运行结果:

到这里其实发现这个AOP没有什么实际用处,前后中间执行的东西都没有关系,并不能体现真正的AOP思想。
我们将上述代码修改一下:修改环绕通知的方法。
import com.bing.aop.service.UserService;
import com.bing.aop.service.UserServiceImpl;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint; /**
* 自定义通知类
*/
public class MyAdvice { //before 前置通知 在目标方法前调用
public void before() {
System.out.println("before");
} //after 最终通知(后置通知)在目标方法后调用,无论是否出现异常都会执行 finally
public void after() {
System.out.println("after");
} //afterReturning 成功通知(后置通知)在目标方法执行后,并且执行成功,如果方法出现异常则不调用
public void afterReturning() {
System.out.println("afterReturning");
} //afterThrowing 异常通知(后置通知)在目标方法执行出现异常的时候才会调用
public void afterThrowing() {
System.out.println("afterThrowing");
} //around 环绕通知 需要我们手动调用目标方法,并且可以设置通知
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
UserService userService = (UserServiceImpl)pjp.getTarget();
Object proceed = null;
if("1".equals(userService.getStr()) || "setStr".equals(pjp.getSignature().getName())){
proceed = pjp.proceed();
}
return proceed;
}
}
import com.bing.aop.service.UserService;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner; import javax.annotation.Resource; @RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:applicationContext_aop.xml")
public class AopTest { @Resource(name="userService")
UserService us;
@Test
public void Test2() {
System.out.println("设置前:------------Str == 0");
us.save();
us.setStr("1");
System.out.println("设置前:------------Str == 1");
us.save();
}
}
然后将配置文件的其他通知都去掉:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.3.xsd">
<!-- 目标对象 -->
<bean name="userService" class="com.bing.aop.service.UserServiceImpl"></bean> <!-- 通知对象 -->
<bean name="myAdvice" class="com.bing.aop.MyAdvice"></bean> <aop:config>
<!-- 切入点 expression 切入点表达式 可以配置要增强的方法
public void com.bing.aop.service.UserServiceImpl.save()
* com.bing.aop.service.*ServiceImpl.*(..)
id 就是唯一标识
-->
<aop:pointcut expression="execution(* com.bing.aop.service.*ServiceImpl.*(..))" id="servicePc"/> <!-- 切面 通知+切入点 -->
<aop:aspect ref="myAdvice">
<!-- 环绕通知-->
<aop:around method="around" pointcut-ref="servicePc"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
</beans>
运行效果:

把实体类和MyAdvice 结合起来,可以更加方便的写你想要处理的逻辑。
XML 用的越来越少了,现在大部分都使用注解了,下面是使用注解的Demo
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.EnableAspectJAutoProxy; @ComponentScan("com.hundsun.cop.aop")
@Configuration
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
public class AppConfig { }
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterReturning;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterThrowing;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Aspect
@Component
public class MyAdvice { //设置切点
@Pointcut("execution(public * com.hundsun.cop.aop.UserService.*(..))")
public void execution(){ } // 执行前
@Before("MyAdvice.execution()")
public void before(){ } // 执行后
@After("MyAdvice.execution()")
public void after() {
System.out.println("after");
} //afterReturning 成功通知(后置通知)在目标方法执行后,并且执行成功,如果方法出现异常则不调用
@AfterReturning("MyAdvice.execution()")
public void afterReturning() {
System.out.println("afterReturning");
} //afterThrowing 异常通知(后置通知)在目标方法执行出现异常的时候才会调用
@AfterThrowing("MyAdvice.execution()")
public void afterThrowing() {
System.out.println("afterThrowing");
} //around 环绕通知 需要我们手动调用目标方法,并且可以设置通知
@Around("MyAdvice.execution()")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("around before");
Object proceed = pjp.proceed();
System.out.println("around after");
return proceed;
}
}
public interface UserService {
void save();
String getStr();
void setStr(String str);
}
@Component
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
private String str = "0"; public String getStr() {
return str;
} public void setStr(String str) {
this.str = str;
} @Override
public void save() {
System.out.println("--------- save --------------");
}
}
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext annotationConfigApplicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
UserService userService = annotationConfigApplicationContext.getBean(UserService.class);
userService.save();
}
}
运行结果

不喜欢夸夸奇谈,实战才是真理。代码是说明原理的最可靠的方式。
总结来源:http://www.sikiedu.com/ 网站学习。
《Java Spring框架》Spring切面(AOP)配置详解的更多相关文章
- 【Spring】——声明式事务配置详解
项目中用到了spring的事务: @Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class, transactionManager = "zebraTrans ...
- spring, spring mvc, mybatis整合文件配置详解
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/wxisme/p/4924561.html 使用SSM框架做了几个小项目了,感觉还不错是时候总结一下了.先总结一下SSM整合的文件配置.其实具体的用 ...
- Spring MVC的web.xml配置详解(转)
出处http://blog.csdn.net/u010796790 1.spring 框架解决字符串编码问题:过滤器 CharacterEncodingFilter(filter-name) 2.在w ...
- Spring mvc的web.xml配置详解
1.spring 框架解决字符串编码问题:过滤器 CharacterEncodingFilter(filter-name) 2.在web.xml配置监听器ContextLoaderListener(l ...
- Spring学习(十九)----- Spring的五种事务配置详解
前段时间对Spring的事务配置做了比较深入的研究,在此之间对Spring的事务配置虽说也配置过,但是一直没有一个清楚的认识.通过这次的学习发觉Spring的事务配置只要把思路理清,还是比较好掌握的. ...
- 1、Spring MVC的web.xml配置详解(转)
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,转载请注明出处http://blog.csdn.net/u010796790 1.spring 框架解决字符串编码问题:过滤器 CharacterEncodingFilt ...
- Spring Boot 2.0 教程 - 配置详解
Spring Boot 可以通过properties文件,YAML文件,环境变量和命令行参数进行配置.属性值可以通过,@Value注解,Environment或者ConfigurationProper ...
- Spring中配置文件applicationContext.xml配置详解
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><beans xmlns="http://www.spr ...
- spring框架的定时任务cronExpression表达式详解
附:cronExpression表达式解释: 0 0 12 * * ?---------------在每天中午12:00触发 0 15 10 ? * *---------------每天上午10:15 ...
- spring boot slf4j日记记录配置详解
https://blog.csdn.net/liuweixiao520/article/details/78900779
随机推荐
- 学习完vue指令 做的一个学生信息录入系统
一.demo实现原理 输入完个人信息后 点击创建用户 数据就会显示在下面的表格中 用到了vue中的数据双向绑定 v-model v-for 还要js正则 数组的unshift splice 等方法 ...
- 都9012了,Java8中的日期时间API你还没有掌握?
一,Java8日期时间API产生的前因后果 1.1 为什么要重新定义一套日期时间API 操作不方便:java中最初的Date不能直接对指定字段进行加减操作也不支持国际化,后来新增了Calendar,但 ...
- 关于HashMap容量的初始化,还有这么多学问。
在<HashMap中傻傻分不清楚的那些概念>文章中,我们介绍了HashMap中和容量相关的几个概念,简单介绍了一下HashMap的扩容机制. 文中我们提到,默认情况下HashMap的容量是 ...
- 英语口语考试资料Food
新东方推荐文章:Food and Health The food we eat seems to have profound effects on our health. Although scien ...
- attach()与detach()的使用
attach()与detach()需要配对使用,如果使用了attach而未使用detach,再次使用attach时,会有"对象被屏蔽"的问题,如下:
- 相对和绝对路径、cd命令、创建和删除目录、rm命令 使用介绍
第2周第1次课(3月26日) 课程内容:2.6 相对和绝对路径2.7 cd命令2.8 创建和删除目录mkdir/rmdir2.9 rm命令 2.6相对和绝对路径 任何一个文件都有一个从根开始的路径,绝 ...
- 中标麒麟neokylin信息查看
中标麒麟Neokylin系统版本信息: # nkvers ############## NeoKylin Linux Version################# Release: NeoKyli ...
- react-native技术调研:react-native是什么?
如有疏漏错误,还望指正.转载不忘加上>>原链接<<哦~ react-native是什么? react-native原理 从字面意思上来看,react-native由单词reac ...
- Java学习笔记(面向对象上)
面向对象(上) 面向对象的特点:封装性(是面向对象的核心思想,将对象的属性和行为封装起来).继承性(主要描述类与类之间的关系,通过继承,可以在无需重新编写原有类的情况下,对原有类的功能进行扩展)和多态 ...
- 使用PaintCode便捷地实现动画效果
// // ViewController.m // paintCodeTestOC //gif // Created by LongMa on 2019/7/25. // #import " ...
