Vuex简介
一. 什么是Vuex?

Vuex是一个专门为Vue.js应用程序开发的状态管理模式, 它采用集中式存储管理所有组件的公共状态, 并以相应的规则保证状态以一种可预测的方式发生变化.
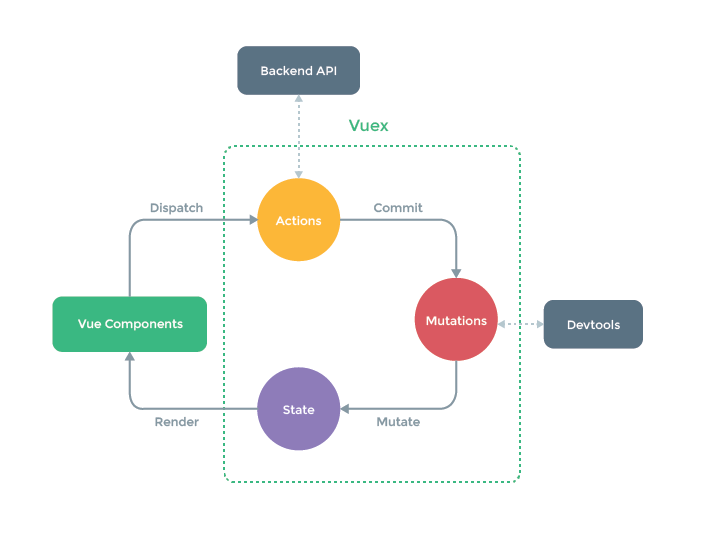
上图中绿色虚线包裹起来的部分就是Vuex的核心, state中保存的就是公共状态, 改变state的唯一方式就是通过mutations进行更改. 可能你现在看这张图有点不明白, 等经过本文的解释和案例演示, 再回来看这张图, 相信你会有更好的理解.
二. 为什么要使用Vuex?
试想这样的场景, 比如一个Vue的根实例下面有一个根组件名为App.vue, 它下面有两个子组件A.vue和B.vue, App.vue想要与A.vue或者B.vue通讯可以通过props传值的方式, 但是如果A.vue和B.vue之间的通讯就很麻烦了, 他们需要共有的父组件通过自定义事件进行实现, A组件想要和B组件通讯往往是这样的:
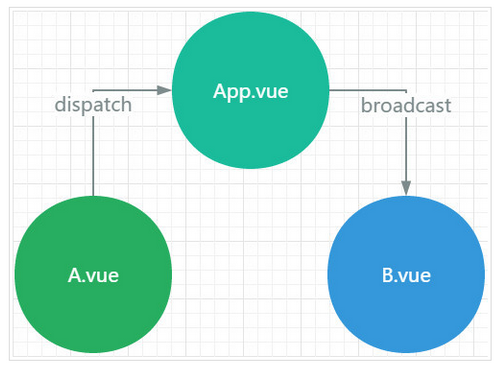
- A组件说: "报告老大, 能否帮我托个信给小弟B" => dispatch一个事件给App
- App老大说: "包在我身上, 它需要监听A组件的dispatch的时间, 同时需要broadcast一个事件给B组件"
- B小弟说: "信息已收到", 它需要on监听App组件分发的事件
这只是一条通讯路径, 如果父组件下有多个子组件, 子组件之间通讯的路径就会变的很繁琐, 父组件需要监听大量的事件, 还需要负责分发给不同的子组件, 很显然这并不是我们想要的组件化的开发体验.
Vuex就是为了解决这一问题出现的
三.如何引入Vuex?
- 下载
vuex:npm install vuex --save - 在
main.js添加:
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use( Vuex );
const store = new Vuex.Store({
//待添加
})
new Vue({
el: '#app',
store,
render: h => h(App)
})
四. Vuex的核心概念?
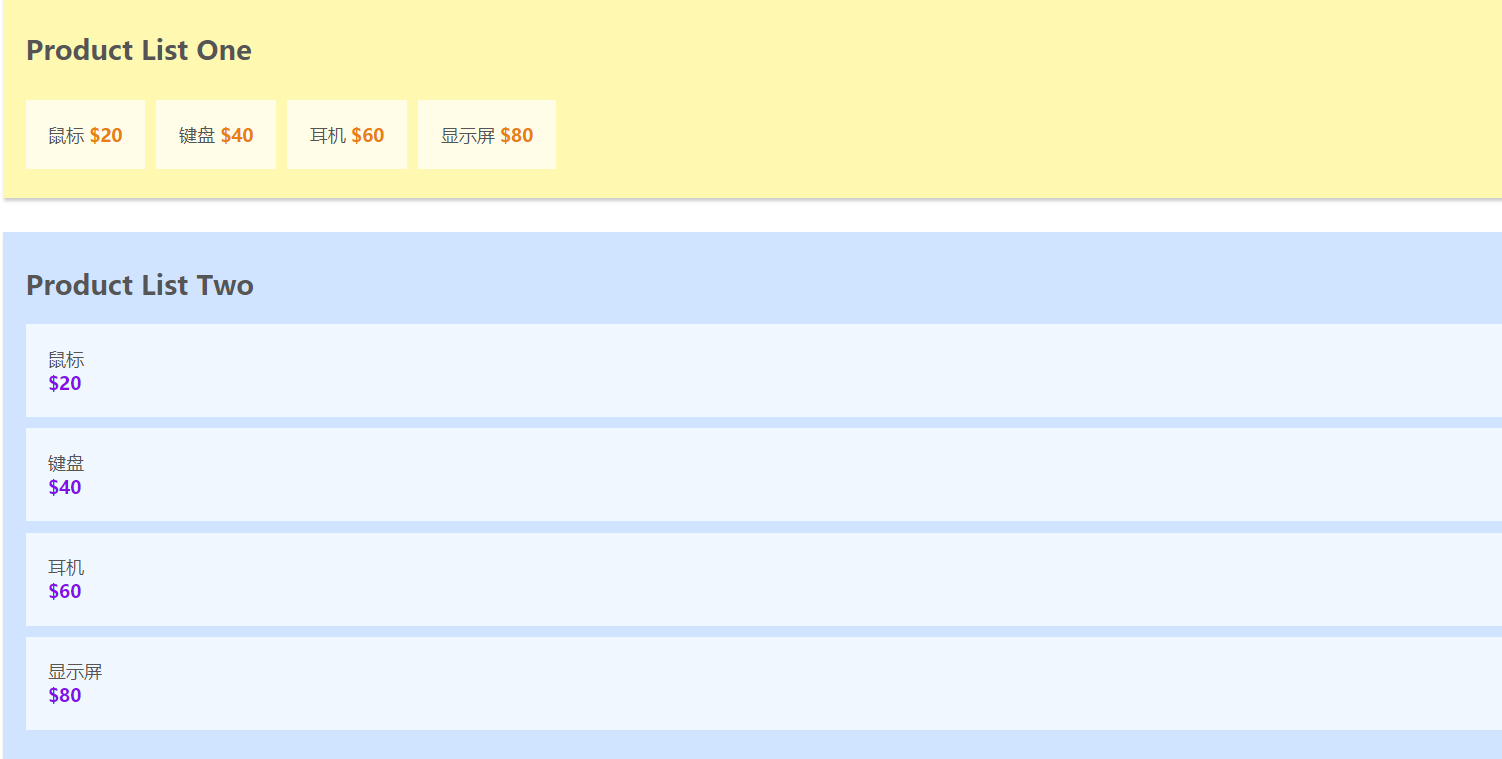
在介绍Vuex的核心概念之前, 我使用vue-cli初始化了一个demo, 准备以代码的形式来说明Vuex的核心概念, 大家可以在github上的master分支进行下载.这个demo分别有两个组件ProductListOne.vue和ProductListTwo.vue, 在App.vue的datat中保存着共有的商品列表, 代码和初始化的效果如下图所示:
//App.vue中的初始化代码
<template>
<div id="app">
<product-list-one v-bind:products="products"></product-list-one>
<product-list-two v-bind:products="products"></product-list-two>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import ProductListOne from './components/ProductListOne.vue'
import ProductListTwo from './components/ProductListTwo.vue'
export default {
name: 'app',
components: {
'product-list-one': ProductListOne,
'product-list-two': ProductListTwo
},
data () {
return {
products: [
{name: '鼠标', price: 20},
{name: '键盘', price: 40},
{name: '耳机', price: 60},
{name: '显示屏', price: 80}
]
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
body{
font-family: Ubuntu;
color: #555;
}
</style>
//ProductListOne.vue
<template>
<div id="product-list-one">
<h2>Product List One</h2>
<ul>
<li v-for="product in products">
<span class="name">{{ product.name }}</span>
<span class="price">${{ product.price }}</span>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
props: ['products'],
data () {
return {
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
#product-list-one{
background: #FFF8B1;
box-shadow: 1px 2px 3px rgba(0,0,0,0.2);
margin-bottom: 30px;
padding: 10px 20px;
}
#product-list-one ul{
padding: 0;
}
#product-list-one li{
display: inline-block;
margin-right: 10px;
margin-top: 10px;
padding: 20px;
background: rgba(255,255,255,0.7);
}
.price{
font-weight: bold;
color: #E8800C;
}
</style>
//ProductListTwo.vue
<template>
<div id="product-list-two">
<h2>Product List Two</h2>
<ul>
<li v-for="product in products">
<span class="name">{{ product.name }}</span>
<span class="price">${{ product.price }}</span>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
props: ['products'],
data () {
return {
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
#product-list-two{
background: #D1E4FF;
box-shadow: 1px 2px 3px rgba(0,0,0,0.2);
margin-bottom: 30px;
padding: 10px 20px;
}
#product-list-two ul{
padding: 0;
list-style-type: none;
}
#product-list-two li{
margin-right: 10px;
margin-top: 10px;
padding: 20px;
background: rgba(255,255,255,0.7);
}
.price{
font-weight: bold;
color: #860CE8;
display: block;
}
</style>
核心概念1: State
state就是Vuex中的公共的状态, 我是将state看作是所有组件的data, 用于保存所有组件的公共数据.
- 此时我们就可以把
App.vue中的两个组件共同使用的data抽离出来, 放到state中,代码如下:
//main.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use( Vuex )
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state:{
products: [
{name: '鼠标', price: 20},
{name: '键盘', price: 40},
{name: '耳机', price: 60},
{name: '显示屏', price: 80}
]
}
})
new Vue({
el: '#app',
store,
render: h => h(App)
})
- 此时,
ProductListOne.vue和ProductListTwo.vue也需要做相应的更改
//ProductListOne.vue
export default {
data () {
return {
products : this.$store.state.products //获取store中state的数据
}
}
}
//ProductListTwo.vue
export default {
data () {
return {
products: this.$store.state.products //获取store中state的数据
}
}
}
此时的页面如下图所示, 可以看到, 将公共数据抽离出来后, 页面没有发生变化.
 state效果
state效果
到此处的Github仓库中代码为: 分支code01
核心概念2: Getters
我将getters属性理解为所有组件的computed属性, 也就是计算属性. vuex的官方文档也是说到可以将getter理解为store的计算属性, getters的返回值会根据它的依赖被缓存起来,且只有当它的依赖值发生了改变才会被重新计算。
- 此时,我们可以在
main.js中添加一个getters属性, 其中的saleProducts对象将state中的价格减少一半(除以2)
//main.js
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state:{
products: [
{name: '鼠标', price: 20},
{name: '键盘', price: 40},
{name: '耳机', price: 60},
{name: '显示屏', price: 80}
]
},
getters:{ //添加getters
saleProducts: (state) => {
let saleProducts = state.products.map( product => {
return {
name: product.name,
price: product.price / 2
}
})
return saleProducts;
}
}
})
- 将
productListOne.vue中的products的值更换为this.$store.getters.saleProducts
export default {
data () {
return {
products : this.$store.getters.saleProducts
}
}
}
- 现在的页面中,Product List One中的每项商品的价格都减少了一半

到此处的Github仓库中代码为: 分支code02
核心概念3: Mutations
我将mutaions理解为store中的methods, mutations对象中保存着更改数据的回调函数,该函数名官方规定叫type, 第一个参数是state, 第二参数是payload, 也就是自定义的参数.
- 下面,我们在
main.js中添加mutations属性,其中minusPrice这个回调函数用于将商品的价格减少payload这么多, 代码如下:
//main.js
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state:{
products: [
{name: '鼠标', price: 20},
{name: '键盘', price: 40},
{name: '耳机', price: 60},
{name: '显示屏', price: 80}
]
},
getters:{
saleProducts: (state) => {
let saleProducts = state.products.map( product => {
return {
name: product.name,
price: product.price / 2
}
})
return saleProducts;
}
},
mutations:{ //添加mutations
minusPrice (state, payload ) {
let newPrice = state.products.forEach( product => {
product.price -= payload
})
}
}
})
- 在
ProductListTwo.vue中添加一个按钮,为其添加一个点击事件, 给点击事件触发minusPrice方法
//ProductListTwo.vue
<template>
<div id="product-list-two">
<h2>Product List Two</h2>
<ul>
<li v-for="product in products">
<span class="name">{{ product.name }}</span>
<span class="price">${{ product.price }}</span>
</li>
<button @click="minusPrice">减少价格</button> //添加按钮
</ul>
</div>
</template>
- 在
ProductListTwo.vue中注册minusPrice方法, 在该方法中commitmutations中的minusPrice这个回调函数
注意:调用mutaions中回调函数, 只能使用store.commit(type, payload)
//ProductListTwo.vue
export default {
data () {
return {
products: this.$store.state.products
}
},
methods: {
minusPrice() {
this.$store.commit('minusPrice', 2); //提交`minusPrice,payload为2
}
}
}
- 添加按钮, 可以发现, Product List Two中的价格减少了2, 当然你可以自定义
payload,以此自定义减少对应的价格. mutations效果
mutations效果
(Product List One中的价格没有发生变化,原因是getter 监听的是map方法产生的新对象)
到此处的Github仓库中代码为: 分支code03
核心概念4: Actions
actions 类似于 mutations,不同在于:
actions提交的是mutations而不是直接变更状态actions中可以包含异步操作,mutations中绝对不允许出现异步actions中的回调函数的第一个参数是context, 是一个与store实例具有相同属性和方法的对象此时,我们在
store中添加actions属性, 其中minusPriceAsync采用setTimeout来模拟异步操作,延迟2s执行 该方法用于异步改变我们刚才在mutaions中定义的minusPrice
//main.js
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state:{
products: [
{name: '鼠标', price: 20},
{name: '键盘', price: 40},
{name: '耳机', price: 60},
{name: '显示屏', price: 80}
]
},
getters:{
saleProducts: (state) => {
let saleProducts = state.products.map( product => {
return {
name: product.name,
price: product.price / 2
}
})
return saleProducts;
}
},
mutations:{
minusPrice (state, payload ) {
let newPrice = state.products.forEach( product => {
product.price -= payload
})
}
},
actions:{ //添加actions
minusPriceAsync( context, payload ) {
setTimeout( () => {
context.commit( 'minusPrice', payload ); //context提交
}, 2000)
}
}
})
- 在
ProductListTwo.vue中添加一个按钮,为其添加一个点击事件, 给点击事件触发minusPriceAsync方法
<template>
<div id="product-list-two">
<h2>Product List Two</h2>
<ul>
<li v-for="product in products">
<span class="name">{{ product.name }}</span>
<span class="price">${{ product.price }}</span>
</li>
<button @click="minusPrice">减少价格</button>
<button @click="minusPriceAsync">异步减少价格</button> //添加按钮
</ul>
</div>
</template>
- 在
ProductListTwo.vue中注册minusPriceAsync方法, 在该方法中dispatchactions中的minusPriceAsync这个回调函数
export default {
data () {
return {
products: this.$store.state.products
}
},
methods: {
minusPrice() {
this.$store.commit('minusPrice', 2);
},
minusPriceAsync() {
this.$store.dispatch('minusPriceAsync', 5); //分发actions中的minusPriceAsync这个异步函数
}
}
}
添加按钮, 可以发现, Product List Two中的价格延迟2s后减少了5
 actions效果
actions效果
到此处的Github仓库中代码为: 分支code04
核心概念5: Modules
由于使用单一状态树,应用的所有状态会集中到一个比较大的对象。当应用变得非常复杂时,store 对象就有可能变得相当臃肿。为了解决以上问题,Vuex 允许我们将 store 分割成模块(module)。每个模块拥有自己的 state、mutation、action、getter、甚至是嵌套子模块——从上至下进行同样方式的分割
const moduleA = {
state: { ... },
mutations: { ... },
actions: { ... },
getters: { ... }
}
const moduleB = {
state: { ... },
mutations: { ... },
actions: { ... }
}
const store = new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
a: moduleA,
b: moduleB
}
})
store.state.a // -> moduleA 的状态
store.state.b // -> moduleB 的状态
【相关链接】
- 本文代码地址: https://github.com/Lee-Tanghui/Vuex-Demo
- Vuex官方文档: https://vuex.vuejs.org/zh-cn/intro.html
- Vuex官方案例演示源码: https://github.com/vuejs/vuex/tree/dev/examples
.
Vuex简介的更多相关文章
- 手摸手教你在vue-cli里面使用vuex,以及vuex简介
写在前面: 这篇文章是在vue-cli里面使用vuex的一个极简demo,附带一些vuex的简单介绍.有需要的朋友可以做一下参考,喜欢的可以点波赞,或者关注一下,希望可以帮到大家. 本文首发于我的个人 ...
- vuex简介(转载)
安装.使用 vuex 首先我们在 vue.js 2.0 开发环境中安装 vuex : npm install vuex --save 然后 , 在 main.js 中加入 : import vuex ...
- vuex使用报错
1.vuex简介 最近在玩vuex,不得不说它是一个很强大的工具,它的目的就是把数据统一管理起来,方便各个组件之间来回调用 2.vuex引用报错 当我们去官网看API文档的时候,会发现官网是这么应用a ...
- Vue.js 2.x笔记:状态管理Vuex(7)
1. Vuex简介与安装 1.1 Vuex简介 Vuex是为vue.js应用程序开发的状态管理模式,解决的问题: ◊ 组件之间的传参,多层嵌套组件之间的传参以及各组件之间耦合度过高问题 ◊ 不同状态中 ...
- Vuex以及axios
Vuex 简介 vuex是一个专门为Vue.js设计的集中式状态管理架构. 状态? 我们把它理解为在data中需要共享给其他组件使用的部分. Vuex和单纯的全局对象有以下不同: 1.Vuex 的状态 ...
- 09:vuex组件间通信
1.1 vuex简介 官网:https://vuex.vuejs.org/zh/guide/ 参考博客:https://www.cnblogs.com/first-time/p/6815036.htm ...
- Vuex以及axios 看这个
vuex -- 安装 npm i vuex -- 配置 -- 导入vuex import vuex from "vuex" -- vue使用vuex ...
- 详解Vuex常见问题、深入理解Vuex
Vuex 是一个专为 Vue.js 应用程序开发的状态管理模式.它采用集中式存储管理应用的所有组件的状态,并以相应的规则保证状态以一种可预测的方式发生变化. 状态?我把它理解为在data中的属性需要共 ...
- Vuex+axios
Vuex+axios Vuex简介 vuex是一个专门为Vue.js设计的集中式状态管理架构. 状态? 我们把它理解为在data中需要共享给其他组件使用的部分. Vuex和单纯的全局对象有以下不同 ...
随机推荐
- SQL Serve里DBA要去改变的3个配置选项
用安装向导安装了全新的SQL Server,最后你点击了完成按钮.哇噢~~~现在我们可以把我们的服务器进入生产了! 抱歉,那并不是真的,因为你的全新SQL Server默认配置是未优化的,一个合格的D ...
- centos 6.9 升级glibc动态库
glibc是gnu发布的libc库,即c运行库,glibc是linux系统中最底层的api,几乎其它任何运行库都会依赖于glibc.glibc除了封装linux操作系统所提供的系统服务外,它本身也提供 ...
- Python3+Requests+Excel完整接口自动化框架
框架整体使用Python3+Requests+Excel:包含对实时token的获取 框架结构图 1.------base -------runmethond.py runmethond:对不同的请求 ...
- 手工挖掘web常见漏洞时的一些经验总结
一.前提: 漏洞挖掘原则 所有变量 所有头 cookie中的变量 逐个变量删除 漏洞的本质 数据与指令的混淆 对用户输入信息过滤不严判断失误,误将数据当指令 二.经典漏洞: 1.身份认证 常用弱口令/ ...
- Centos7升级gcc极简教程
centos7默认gcc版本为4.8,一般不满足编译需求,因此升级gcc版本为常见操作: 现有博客中,大多数教程都是基于源码重新编译安装:但是源码编译过程等待时间很长且编译麻烦. 因此,直接基于命令升 ...
- 如何查看PDF的坐标
有时候,我们明知道现状并不够科学.不够合理,但没有时间和条件去改变现状,还得硬要照着这种方式去维护,很是痛苦. 在程序生成文字报告通常使用docx,如果需要更通用.更灵活,还可以使用rtf,而前期设计 ...
- 不为人知的网络编程(九):理论联系实际,全方位深入理解DNS
本文原作者:selfboot,博客地址:selfboot.cn,Github地址:github.com/selfboot,感谢原作者的技术分享. 1.引言 对于 DNS(Domain Name Sys ...
- Java 泛型示例 - 泛型方法,类,接口
Java Genrics 是 Java 5 中引入的最重要的功能之一. 如果您一直在使用Java Collections并使用版本 5 或更高版本,那么我确定您已经使用过它. Java 中具有集合类的 ...
- Java Arrays类方法
1:概述 主要谈一谈 Java使用fork/koin类 实现的并发排序 以及对于Stream流的支持的splitetor mismatch() -> 寻找两个数组 第一次出现数据不一致的下 ...
- windows server 2008 r2 安装 vs2017 无法进入安装界面问题解决方法
在 windows server 2008 r2 版本操作系统上安装 vs2017 经常出现下载进度条结束后没有任何反应问题,一般是因为安装程序兼容性造成的,解决方案如下: 将 C:\Program ...
