[Unit Testing] Fundamentals of Testing in Javascript
In this lesson, we’ll get the most fundamental understanding of what an automated test is in JavaScript. A test is code that throws an error when the actual result of something does not match the expected output.
Tests can get more complicated when you’re dealing with code that depends on some state to be set up first (like a component needs to be rendered to the document before you can fire browser events, or there needs to be users in the database). However, it is relatively easy to test pure functions (functions which will always return the same output for a given input and not change the state of the world around them).
Base file to test against:
math.js
const sum = (a, b) => a - b;
const subtract = (a, b) => a - b; const sumAsync = (...args) => Promise.resolve(sum(...args));
const subtractAsync = (...args) => Promise.resolve(subtract(...args)); module.exports = { sum, subtract, sumAsync, subtractAsync };
index.js
const { sum, subtract } = require("./math");
let result, expected;
result = sum(, );
expected = ;
if (actual !== expected) {
throw new Error(`${result} is not equal to ${expected}`);
}
result = subtract(, );
expected = ;
if (actual !== expected) {
throw new Error(`${result} is not equal to ${expected}`);
}
Let’s add a simple layer of abstraction in our simple test to make writing tests easier. The assertion library will help our test assertions read more like a phrase you might say which will help people understand our intentions better. It will also help us avoid unnecessary duplication.
const { sum, subtract } = require("./math");
let result, expected;
result = sum(, );
expected = ;
expect(result).toBe(expected);
result = subtract(, );
expected = ;
expect(result).toBe(expected);
function expect(actual) {
return {
toBe(expected) {
if (actual !== expected) {
throw new Error(`${actual} is not equal to ${expected}`);
}
}
};
}
This is also a common way to write a assetion library, expect() function take a actual value and return an object contains 'toBe', 'toEqual'... functions.
One of the limitations of the way that this test is written is that as soon as one of these assertions experiences an error, the other tests are not run. It can really help developers identify what the problem is if they can see the results of all of the tests.
Let’s create our own test function to allow us to encapsulate our automated tests, isolate them from other tests in the file, and ensure we run all the tests in the file with more helpful error messages.
const { sum, subtract } = require("./math");
let result, expected;
test("sum adds numbers", () => {
result = sum(, );
expected = ;
expect(result).toBe(expected);
});
test("subtract substracts numbers", () => {
result = subtract(, );
expected = ;
expect(result).toBe(expected);
});
function test(title, cb) {
try {
cb();
console.log(`%c ✔︎ ${title}`, "color: green");
} catch (err) {
console.error(`✘ ${title}`);
console.error(err);
}
}
Our testing framework works great for our synchronous test. What if we had some asynchronous functions that we wanted to test? We could make our callback functions async, and then use the await keyword to wait for that to resolve, then we can make our assertion on the result and the expected.
Let’s make our testing framework support promises so users can use async/await.
const { sumAsync, subtractAsync } = require("./math");
let result, expected;
test("sum adds numbers", async () => {
result = await sumAsync(3, 7);
expected = 10;
expect(result).toBe(expected);
});
test("subtract substracts numbers", async () => {
result = await subtractAsync(7, 3);
expected = 4;
expect(result).toBe(expected);
});
function test(title, cb) {
try {
cb();
console.log(`%c ✔︎ ${title}`, "color: green");
} catch (err) {
console.error(`✘ ${title}`);
console.error(err);
}
}
function expect(actual) {
return {
toBe(expected) {
if (actual !== expected) {
throw new Error(`${actual} is not equal to ${expected}`);
}
}
};
}
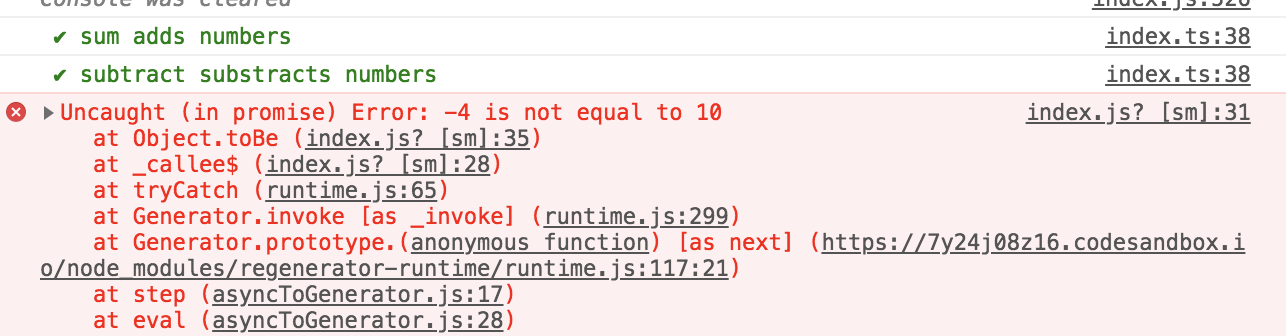
To fix the problem, we can make our testing lib async / await.
async function test(title, cb) {
try {
await cb();
console.log(`%c ✔︎ ${title}`, "color: green");
} catch (err) {
console.error(`✘ ${title}`);
console.error(err);
}
}
Not it works normal again.
These testing utilities that we built are pretty useful. We want to be able to use them throughout our application in every single one of our test files.
Some testing frameworks provide their helpers as global variables. Let’s implement this functionality to make it easier to use our testing framework and assertion library. We can do this by exposing our test and expect functions on the global object available throughout the application.
setup-global.js:
async function test(title, cb) {
try {
await cb();
console.log(`%c ✔︎ ${title}`, "color: green");
} catch (err) {
console.error(`✘ ${title}`);
console.error(err);
}
}
function expect(actual) {
return {
toBe(expected) {
if (actual !== expected) {
throw new Error(`${actual} is not equal to ${expected}`);
}
}
};
}
global.test = test;
global.expect = expect;
Run:
node --require ./setup-global.js src/index.js
Up to this point we’ve created all our own utilities. As it turns out, the utilities we’ve created mirror the utilities provided by Jest perfectly! Let’s install Jest and use it to run our test!
npx jest
[Unit Testing] Fundamentals of Testing in Javascript的更多相关文章
- 【Android Api 翻译1】Android Texting(2)Testing Fundamentals 测试基础篇
Testing Fundamentals The Android testing framework, an integral part of the development environment, ...
- Android Texting(2)Testing Fundamentals 测试基础篇
Testing Fundamentals The Android testing framework, an integral part of the development environment, ...
- Unit Testing, Integration Testing and Functional Testing
转载自:https://codeutopia.net/blog/2015/04/11/what-are-unit-testing-integration-testing-and-functional- ...
- Android测试:Fundamentals of Testing
原文地址:https://developer.android.com/training/testing/fundamentals.html 用户在不同的级别上与你的应用产生交互.从按下按钮到将信息下载 ...
- Difference Between Performance Testing, Load Testing and Stress Testing
http://www.softwaretestinghelp.com/what-is-performance-testing-load-testing-stress-testing/ Differen ...
- Go testing 库 testing.T 和 testing.B 简介
testing.T 判定失败接口 Fail 失败继续 FailNow 失败终止 打印信息接口 Log 数据流 (cout 类似) Logf format (printf 类似) SkipNow 跳过当 ...
- [Testing] Config jest to test Javascript Application -- Part 1
Transpile Modules with Babel in Jest Tests Jest automatically loads and applies our babel configurat ...
- [Testing] Config jest to test Javascript Application -- Part 3
Run Jest Watch Mode by default locally with is-ci-cli In CI, we don’t want to start the tests in wat ...
- [Testing] Config jest to test Javascript Application -- Part 2
Setup an afterEach Test Hook for all tests with Jest setupTestFrameworkScriptFile With our current t ...
随机推荐
- Verilog学习笔记基本语法篇(一)·········数据类型
Verilog中共有19种数据类型. 基本的四种类型: reg型.wire型.integer型.parameter型. 其他类型:large型.medium型.small型.scalared型.tim ...
- python图像插值
最近邻:选择离它所映射到的位置最近的输入像素的灰度值为插值结果. 最临近插值 图像的缩放很好理解,就是图像的放大和缩小.传统的绘画工具中,有一种叫做“放大尺”的绘画工具,画家常用它来放大图画.当然,在 ...
- centos中python2替换为python3,并解决yum出错
这里采用安装python3.6版本. 安装python3.6可能使用的依赖 yum install openssl-devel bzip2-devel expat-devel gdbm-devel r ...
- WordPress登录框显示/隐藏输入的密码
直接让用户自行根据需要选择是全部隐藏输入的密码,还是全部显示输入的密码. 在全部显示密码框的内容时,用户输错的可能性就大大降低,这也是微软推荐的一种密码框处理方式.效果如下: 今天,我将给大家介绍,在 ...
- [uiautomator篇] uiautoviewer 定位不到元素
定位工具: Uiautomatorviewer 在我们的APP中,只有这一个页面,元素无法加载出来,其它的都没有什么问题. 提示的错误:Error while obtaining UI hiera ...
- HDU-3065 病毒侵袭持续中 AC自动机又是一板子!
病毒侵袭持续中 上一题是求出现多少病毒输出病毒序号,而这题输出每个病毒出现的次数.这题有字典树基础都能做出来,把叶子节点用相应的编号标记起来,匹配的时候遍历到叶子节点用一个数组把次数存起来就行了. 有 ...
- vue 自定义日历组件
<template> <div class=""> <div class="calendarTraffic" name=" ...
- 【bzoj4383】[POI2015]Pustynia 线段树优化建图+差分约束系统+拓扑排序
题目描述 给定一个长度为n的正整数序列a,每个数都在1到10^9范围内,告诉你其中s个数,并给出m条信息,每条信息包含三个数l,r,k以及接下来k个正整数,表示a[l],a[l+1],...,a[r- ...
- HDU——1195Open the Lock(双向BFS)
Open the Lock Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others) To ...
- 使用HttpClient实现对第三方服务器的请求并接受返回数据
/* * 创建日期 2017-4-7 * * TODO 要更改此生成的文件的模板,请转至 * 窗口 - 首选项 - Java - 代码样式 - 代码模板 */ package com.enfo.int ...
