UVa 1590 IP网络(简单位运算)
Description

Alex is administrator of IP networks. His clients have a bunch of individual IP addresses and he decided to group all those IP addresses into the smallest possible IP network.
Each IP address is a 4-byte number that is written byte-by-byte in a decimal dot-separated notation ``byte0.byte1.byte2.byte3" (quotes are added for clarity). Each byte is written as a decimal number from 0 to 255 (inclusive) without extra leading zeroes.
IP network is described by two 4-byte numbers - network address and network mask. Both network address and network mask are written in the same notation as IP addresses.
In order to understand the meaning of network address and network mask you have to consider their binary representation. Binary representation of IP address, network address, and network mask consists of 32 bits: 8 bits for byte0 (most significant to least significant), followed by 8 bits for byte1, followed by 8 bits for byte2, and followed by 8 bits for byte3.
IP network contains a range of 2n IP addresses where 0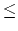 n
n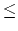 32 . Network mask always has 32 - n first bits set to one, and n last bits set to zero in its binary representation. Network address has arbitrary 32 - n first bits, and n last bits set to zero in its binary representation. IP network contains all IP addresses whose 32 - n first bits are equal to 32 - n first bits of network address with arbitrary n last bits. We say that one IP network is smaller than the other IP network if it contains fewer IP addresses.
32 . Network mask always has 32 - n first bits set to one, and n last bits set to zero in its binary representation. Network address has arbitrary 32 - n first bits, and n last bits set to zero in its binary representation. IP network contains all IP addresses whose 32 - n first bits are equal to 32 - n first bits of network address with arbitrary n last bits. We say that one IP network is smaller than the other IP network if it contains fewer IP addresses.
For example, IP network with network address 194.85.160.176 and network mask 255.255.255.248 contains 8 IP addresses from 194.85.160.176 to 194.85.160.183 (inclusive).
Input
The input file will contain several test cases, each of them as described below.
The first line of the input file contains a single integer number m(1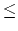 m
m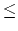 1000) . The following m lines contain IP addresses, one address on a line. Each IP address may appear more than once in the input file.
1000) . The following m lines contain IP addresses, one address on a line. Each IP address may appear more than once in the input file.
Output
For each test case, write to the output file two lines that describe the smallest possible IP network that contains all IP addresses from the input file. Write network address on the first line and network mask on the second line.
Sample Input
3
194.85.160.177
194.85.160.183
194.85.160.178
Sample Output
194.85.160.176
255.255.255.248
思路:这题就是位运算的运用,注意一下相同的情况。我是先确定四个数字中哪个不一样了,然后再去比较这个数字的二进制,确定第几位二进制不同。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std; const int co = << ; int ans[][]; int main()
{
int n,t,k;
//freopen("D:\\txt.txt", "r", stdin);
while (scanf("%d", &n)!=EOF){
for (int i = ; i < n; i++)
{
scanf("%d.%d.%d.%d", &ans[i][], &ans[i][], &ans[i][], &ans[i][]);
} for (int i = ; i < ; i++)
{
t = ans[][i];
int ok = ;
k = i;
for (int j = ; j < n; j++)
{
if (ans[j][i] != t)
{
ok = ;
break;
}
}
if (!ok) break;
} int s = ;
int p = ;
for (int i = ; i >= ; i--)
{
t = (ans[][k] / s) & ;
for (int j = ; j < n; j++)
{
if (((ans[j][k] / s) & ) != t)
{
p = i;
}
}
s = s * ;
} int number = ;
int count = ;
s = ;
for (int i = ; i < p; i++)
{
if ((ans[][k] * s) & co)
{
number += << ( - i);
}
count += << ( - i);
s = s * ;
} if (k == )
{
printf("%d.%d.%d.%d\n", ans[][], ans[][], ans[][], number);
printf("255.255.255.%d\n", count);
}
else if (k == )
{
printf("%d.%d.%d.0\n", ans[][], ans[][], number);
printf("255.255.%d.0\n", count);
}
else if (k == )
{
printf("%d.%d.0.0\n", ans[][], number);
printf("255.%d.0.0\n", count);
}
else
{
printf("%d.0.0.0\n", number);
printf("%d.0.0.0\n", count);
}
}
}
UVa 1590 IP网络(简单位运算)的更多相关文章
- uva 10718 Bit Mask (位运算)
uva 10718 Bit Mask (位运算) Problem A Bit Mask Time Limit 1 Second In bit-wise expression, mask is a ...
- uva 1590 - IP Networks(IP地址)
习题4-5 IP网络(IP Networks, ACM/ICPC NEERC 2005, UVa1590) 可以用一个网络地址和一个子网掩码描述一个子网(即连续的IP地址范围).其中子网 掩码包含32 ...
- Uva 1590 IP Networks
这道题目是一道关于IP地址的题目,要深入理解这道题需要有一定的网络基础. 这道题目我第一次做的时候虽然也AC了,但代码写的比较复杂,不够精炼.近期刚刚参加了网络方面的培训,在有一定知识的基础上,又重写 ...
- UVA 10718 Bit Mask 贪心+位运算
题意:给出一个数N,下限L上限U,在[L,U]里面找一个整数,使得N|M最大,且让M最小. 很明显用贪心,用位运算搞了半天,样例过了后还是WA,没考虑清楚... 然后网上翻到了一个人家位运算一句话解决 ...
- UVA - 13022 Sheldon Numbers(位运算)
UVA - 13022 Sheldon Numbers 二进制形式满足ABA,ABAB数的个数(A为一定长度的1,B为一定长度的0). 其实就是寻找在二进制中满足所有的1串具有相同的长度,所有的0串也 ...
- UVA 1590 IP Networks JAVA
题意:输入m代表接下来的数据个数,计算接下来输入数据的网络掩码,和最小网络地址. 思路:①子网掩码:先将数据转为二进制,判断从哪一位开始有数据不一样,记下下标index,则子网掩码是index的前面是 ...
- 小米oj 反向位整数(简单位运算)
反向位整数 序号:#30难度:一般时间限制:1000ms内存限制:10M 描述 输入32位无符号整数,输出它的反向位. 例,输入4626149(以二进制表示为00000000010001101001 ...
- 位运算基础(Uva 1590,Uva 509题解)
逻辑运算 规则 符号 与 只有1 and 1 = 1,其他均为0 & 或 只有0 or 0 = 0,其他均为1 | 非 也就是取反 ~ 异或 相异为1相同为0 ^ 同或 相同为1相异为0,c中 ...
- 三十天学不会TCP,UDP/IP网络编程-UDP,从简单的开始
如果对和程序员有关的计算机网络知识,和对计算机网络方面的编程有兴趣,欢迎去gitbook(https://www.gitbook.com/@rogerzhu/)star我的这一系列文章,虽然说现在这种 ...
随机推荐
- 类似CFS程式发布注意事项
1.CFS 此AP 程式的验证方式为Forms 验证.需要在IIS 中做如下设置(Forms 身份验证,配套的Web.config 中要有对应节点代码,后台代码中要有获取方式) 2.Forms 身份验 ...
- Hadoop DistributedCache分布式缓存的使用
做项目的时候遇到一个问题,在Mapper和Reducer方法中处理目标数据时,先要去检索和匹配一个已存在的标签库,再对所处理的字段打标签.因为标签库不是很大,没必要用HBase.我的实现方法是把标签库 ...
- Android中Activity的四种开发模式
Activity的四种启动模式:standard.singleTop.singleTask.singleInstance 清单文件中的Activity配置使用:android:launchMode ...
- Pandas之Series+DataFrame
Series是带有标签的一维数组,可以保存任何数据类型(整数,字符串,浮点数,python对象) index查看series索引,values查看series值 series相比于ndarray,是一 ...
- Django实现cookie&session以及认证系统
COOKIE&SESSION 知识储备 由于http协议无法保持状态,但实际情况,我们却又需要“保持状态”,因此cookie就是在这样一个场景下诞生. cookie的工作原理是:由服务器产生内 ...
- ajax课1 源码
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/ ...
- angular前端框架
总所周知,在前端开发中,大家用的比较多的框架就是angular,vue,react等,今天就为大家讲一下angular大家框架的原理及运用 1.本次所举的例子是以依赖require.js的, < ...
- PKU2418_树种统计(map应用||Trie树)
Description Hardwoods are the botanical group of trees that have broad leaves, produce a fruit or nu ...
- CAReplicatorLayer
CAReplicatorLayer CAReplicatorLayer的目的是为了高效生成许多相似的图层.它会绘制一个或多个图层的子图层,并在每个复制体上应用不同的变换.看上去演示能够更加解释这些,我 ...
- python requests 请求的封装
#encoding=utf-8import requestsimport jsonclass HttpClient(object): def __init__(self): pas ...
