PCL行人检测
首先我们知道Hog特征结合SVM分类器已经被广泛应用于图像识别中,尤其在行人检测中获得了极大的成功,HOG+SVM进行行人检测的方法是法国研究人员Dalal在2005的CVPR上提出的,而如今虽然有很多行人检测算法不断提出,但基本都是以HOG+SVM的思路为主,那么PCL中也是利用这一思想来进行行人的检测,
总体思路:
1、提取正负样本hog特征
2、投入svm分类器训练,得到model
3、由model生成检测子
4、利用检测子检测负样本,得到hardexample
5、提取hardexample的hog特征并结合第一步中的特征一起投入训练,得到最终检测子。
首先整合一下理论知识
HOG特征:
方向梯度直方图(Histogram of Oriented Gradient, HOG)特征是一种在计算机视觉和图像处理中用来进行物体检测的特征描述子。它通过计算和统计图像局部区域的梯度方向直方图来构成特征。
具体的是实现方法:首先将图像分成小的连通区域,我们把它叫细胞单元。然后采集细胞单元中各像素点的梯度的或边缘的方向直方图。最后把这些直方图组合起来就可以构成特征描述器。
提高性能: 把这些局部直方图在图像的更大的范围内(我们把它叫区间或block)进行对比度归一化(contrast-normalized),所采用的方法是:先计算各直方图在这个区间(block)中的密度,然后根据这个密度对区间中的各个细胞单元做归一化。通过这个归一化后,能对光照变化和阴影获得更好的效果。
优点:与其他的特征描述方法相比,HOG有很多优点。首先,由于HOG是 在图像的局部方格单元上操作,所以它对图像几何的和光学的形变都能保持很好的不变性,这两种形变只会出现在更大的空间领域上。其次,在粗的空域抽样、精细 的方向抽样以及较强的局部光学归一化等条件下,只要行人大体上能够保持直立的姿势,可以容许行人有一些细微的肢体动作,这些细微的动作可以被忽略而不影响 检测效果。因此HOG特征是特别适合于做图像中的人体检测的。
HOG特征提取算法的实现过程:
1)HOG特征提取方法就是将一个image(你要检测的目标或者扫描窗口)灰度化(x,y,z的三维图像);
2)采用Gamma校正法对输入图像进行颜色空间的标准化(归一化);目的是调节图像的对比度,降低图像局部的阴影和光照变化所造成的影响,同时可以抑制噪音的干扰;
3)计算图像每个像素的梯度(包括大小和方向);主要是为了捕获轮廓信息,同时进一步弱化光照的干扰。
4)将图像划分成小cells(例如6*6像素/cell);
5)统计每个cell的梯度直方图(不同梯度的个数),即可形成每个cell的descriptor;
6)将每几个cell组成一个block(例如3*3个cell/block),一个block内所有cell的特征descriptor串联起来便得到该block的HOG特征descriptor。
7)将图像image内的所有block的HOG特征descriptor串联起来就可以得到该image(你要检测的目标)的HOG特征descriptor了。这个就是最终的可供分类使用的特征向量了。
关于SVM可以参看www.opencv.org.cn/opencvdoc/2.3.2/html/doc/tutorials/ml/introduction_to_svm/introduction_to_svm.html
(2)那么使用PCL 检测行人该如何使用呢?
目标: detecting people walking on the ground plane
输入:RGBXYZ pointcloud ground coeficients
输出:people clusters
流程图:
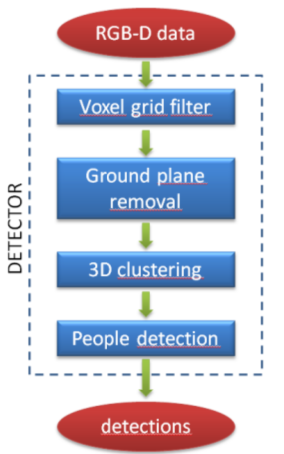

步骤
detected on point cloud
(1)groud plane estimation and removal
(2)Euclidean clustering of remaining points
(3)people vertically splitted int more clusters
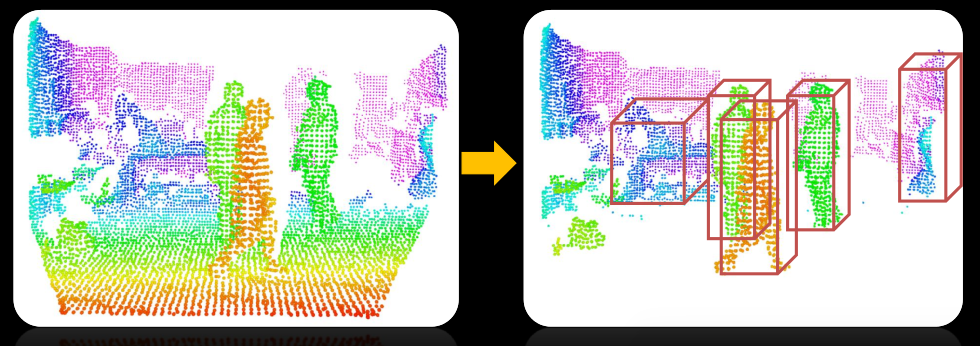
sub-clustering procedure
(4)candidates pruning based on height from the ground plane
(5) merging of clusters close in groud plane coordinates
(6)Subdivision of big clusters by means of head detection
HOG+SVM evaluation
(7)candidate clusters are extened until the ground for achieving robustness to lower limbs occlusion
(8)HOG detector applied to image patches that are projection of 3Dclusters onto the RGB image
pcl::people代码的构架
GroundBasedPeopleDetectionAPP<PointT>
________________|_____________________
| | |
PersonClassifier<pcl::RGB> PersonCluster<PointT> headBasedSubclustering<pointT>
| |
HOG detector HeightMap2D<PointT>
代码解析
#include <pcl/console/parse.h> //命令行解析头文件
#include <pcl/point_types.h> //点云数据类型
#include <pcl/visualization/pcl_visualizer.h> //可视化头文件
#include <pcl/io/openni_grabber.h> //kinect抓取的头文件
#include <pcl/sample_consensus/sac_model_plane.h> //sac_model_plane随机采样一致形平面的模板
#include <pcl/people/ground_based_people_detection_app.h>
#include <pcl/common/time.h> typedef pcl::PointXYZRGBA PointT;
typedef pcl::PointCloud<PointT> PointCloudT; // PCL viewer //
pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer viewer("PCL Viewer"); //可视化 // Mutex: //
boost::mutex cloud_mutex; enum { COLS = , ROWS = }; //窗口大小 int print_help()
{
cout << "*******************************************************" << std::endl;
cout << "Ground based people detection app options:" << std::endl;
cout << " --help <show_this_help>" << std::endl;
cout << " --svm <path_to_svm_file>" << std::endl;
cout << " --conf <minimum_HOG_confidence (default = -1.5)>" << std::endl;
cout << " --min_h <minimum_person_height (default = 1.3)>" << std::endl;
cout << " --max_h <maximum_person_height (default = 2.3)>" << std::endl;
cout << " --sample <sampling_factor (default = 1)>" << std::endl;
cout << "*******************************************************" << std::endl;
return ;
} void cloud_cb_ (const PointCloudT::ConstPtr &callback_cloud, PointCloudT::Ptr& cloud,
bool* new_cloud_available_flag)
{
cloud_mutex.lock (); // for not overwriting the point cloud from another thread锁住进程防止从其他进程写入点云
*cloud = *callback_cloud; //形参点云赋值
*new_cloud_available_flag = true; //标志位赋值为真
cloud_mutex.unlock (); //解锁进程
}
//申明结构体用于传递参数给回调函数
struct callback_args{
// structure used to pass arguments to the callback function
PointCloudT::Ptr clicked_points_3d; //按键三次
pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer::Ptr viewerPtr; //可视化
}; void
pp_callback (const pcl::visualization::PointPickingEvent& event, void* args)
{
struct callback_args* data = (struct callback_args *)args;
if (event.getPointIndex () == -)
return;
PointT current_point;
event.getPoint(current_point.x, current_point.y, current_point.z);
data->clicked_points_3d->points.push_back(current_point);
// Draw clicked points in red:
pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<PointT> red (data->clicked_points_3d, , , );
data->viewerPtr->removePointCloud("clicked_points");
data->viewerPtr->addPointCloud(data->clicked_points_3d, red, "clicked_points");
data->viewerPtr->setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, , "clicked_points");
std::cout << current_point.x << " " << current_point.y << " " << current_point.z << std::endl;
} int main (int argc, char** argv)
{
if(pcl::console::find_switch (argc, argv, "--help") || pcl::console::find_switch (argc, argv, "-h"))
return print_help(); // Algorithm parameters:算法参数
std::string svm_filename = "/home/salm/myopencv/yl_pcl/people/data/trainedLinearSVMForPeopleDetectionWithHOG.yaml";
float min_confidence = -1.5;
float min_width = 0.1;
float max_width = 8.0;
float min_height = 1.3;
float max_height = 2.3;
float voxel_size = 0.06; //体素大小
float sampling_factor = ; //采样因子
Eigen::Matrix3f rgb_intrinsics_matrix;
rgb_intrinsics_matrix << , 0.0, 319.5, 0.0, , 239.5, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0; // Kinect RGB camera intrinsics相机的内参 // Read if some parameters are passed from command line:
pcl::console::parse_argument (argc, argv, "--svm", svm_filename);
pcl::console::parse_argument (argc, argv, "--conf", min_confidence);
pcl::console::parse_argument (argc, argv, "--min_h", min_height);
pcl::console::parse_argument (argc, argv, "--max_h", max_height);
pcl::console::parse_argument (argc, argv, "--sample", sampling_factor); // Read Kinect live stream: 读取kienct的数据流
PointCloudT::Ptr cloud (new PointCloudT);
bool new_cloud_available_flag = false;
pcl::Grabber* interface = new pcl::OpenNIGrabber();
boost::function<void (const pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZRGBA>::ConstPtr&)> f =
boost::bind (&cloud_cb_, _1, cloud, &new_cloud_available_flag);
interface->registerCallback (f);
interface->start (); // Wait for the first frame:等待第一帧数据流
while(!new_cloud_available_flag)
boost::this_thread::sleep(boost::posix_time::milliseconds());
new_cloud_available_flag = false; cloud_mutex.lock (); // for not overwriting the point cloud锁住进程 // Display pointcloud:显示点云
pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerRGBField<PointT> rgb(cloud);
viewer.addPointCloud<PointT> (cloud, rgb, "input_cloud");
viewer.setCameraPosition(,,-,,-,,); //设置相机的位置 // Add point picking callback to viewer:
struct callback_args cb_args;
PointCloudT::Ptr clicked_points_3d (new PointCloudT);
cb_args.clicked_points_3d = clicked_points_3d;
cb_args.viewerPtr = pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer::Ptr(&viewer);
viewer.registerPointPickingCallback (pp_callback, (void*)&cb_args);
std::cout << "Shift+click on three floor points, then press 'Q'..." << std::endl; // Spin until 'Q' is pressed:
viewer.spin();
std::cout << "done." << std::endl; cloud_mutex.unlock (); // Ground plane estimation:
Eigen::VectorXf ground_coeffs;
ground_coeffs.resize();
std::vector<int> clicked_points_indices;
for (unsigned int i = ; i < clicked_points_3d->points.size(); i++)
clicked_points_indices.push_back(i);
pcl::SampleConsensusModelPlane<PointT> model_plane(clicked_points_3d);
model_plane.computeModelCoefficients(clicked_points_indices,ground_coeffs);
std::cout << "Ground plane: " << ground_coeffs() << " " << ground_coeffs() << " " << ground_coeffs() << " " << ground_coeffs() << std::endl; // Initialize new viewer:可视化初始化
pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer viewer("PCL Viewer"); // viewer initialization
viewer.setCameraPosition(,,-,,-,,); // Create classifier for people detection:创建分类器
pcl::people::PersonClassifier<pcl::RGB> person_classifier;
person_classifier.loadSVMFromFile(svm_filename); // load trained SVM // People detection app initialization: 检测初始化
pcl::people::GroundBasedPeopleDetectionApp<PointT> people_detector; // people detection object
people_detector.setVoxelSize(voxel_size); // set the voxel size
people_detector.setIntrinsics(rgb_intrinsics_matrix); // set RGB camera intrinsic parameters
people_detector.setClassifier(person_classifier); // set person classifier
//people_detector.setPersonClusterLimits(min_height, max_height, min_width, max_width);
people_detector.setSamplingFactor(sampling_factor); // set a downsampling factor to the point cloud (for increasing speed)
// people_detector.setSensorPortraitOrientation(true); // set sensor orientation to vertical // For timing:
static unsigned count = ;
static double last = pcl::getTime (); // Main loop:
while (!viewer.wasStopped())
{
if (new_cloud_available_flag && cloud_mutex.try_lock ()) // if a new cloud is available
{
new_cloud_available_flag = false; // Perform people detection on the new cloud:显示检测到的新点云
std::vector<pcl::people::PersonCluster<PointT> > clusters; // vector containing persons clusters
people_detector.setInputCloud(cloud);
people_detector.setGround(ground_coeffs); // set floor coefficients
people_detector.compute(clusters); // perform people detection ground_coeffs = people_detector.getGround(); // get updated floor coefficients // Draw cloud and people bounding boxes in the viewer:
viewer.removeAllPointClouds();
viewer.removeAllShapes();
pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerRGBField<PointT> rgb(cloud);
viewer.addPointCloud<PointT> (cloud, rgb, "input_cloud");
unsigned int k = ;
for(std::vector<pcl::people::PersonCluster<PointT> >::iterator it = clusters.begin(); it != clusters.end(); ++it)
{
if(it->getPersonConfidence() > min_confidence) // draw only people with confidence above a threshold
{
// draw theoretical person bounding box in the PCL viewer:
it->drawTBoundingBox(viewer, k);
k++;
}
}
std::cout << k << " people found" << std::endl;
viewer.spinOnce(); // Display average framerate:
if (++count == )
{
double now = pcl::getTime ();
std::cout << "Average framerate: " << double(count)/double(now - last) << " Hz" << std::endl;
count = ;
last = now;
}
cloud_mutex.unlock ();
}
}
但是我们知道这需要其他的头文件配合。那么其他程序就不再一一贴出来。PCL源码里也有,但是如果你直接编译是编译不过去的,所以需要我们自己写一个CMakeLists.txt文件来编译。
暂时就到这里了。。。。。。
微信公众号号可扫描二维码一起共同学习交流

PCL行人检测的更多相关文章
- 学习OpenCV——行人检测&人脸检测(总算运行出来了)
之前运行haar特征的adaboost算法人脸检测一直出错,加上今天的HOG&SVM行人检测程序,一直报错. 今天总算发现自己犯了多么白痴的错误——是因为外部依赖项lib文件没有添加完整,想一 ...
- Hog SVM 车辆 行人检测
HOG SVM 车辆检测 近期需要对卡口车辆的车脸进行检测,首先选用一个常规的检测方法即是hog特征与SVM,Hog特征是由dalal在2005年提出的用于道路中行人检测的方法,并且取的了不错的识别效 ...
- 从TP、FP、TN、FN到ROC曲线、miss rate、行人检测评估
从TP.FP.TN.FN到ROC曲线.miss rate.行人检测评估 想要在行人检测的evaluation阶段要计算miss rate,就要从True Positive Rate讲起:miss ra ...
- paper 87:行人检测资源(下)代码数据【转载,以后使用】
这是行人检测相关资源的第二部分:源码和数据集.考虑到实际应用的实时性要求,源码主要是C/C++的.源码和数据集的网址,经过测试都可访问,并注明了这些网址最后更新的日期,供学习和研究进行参考.(欢迎补充 ...
- paper 86:行人检测资源(上)综述文献【转载,以后使用】
行人检测具有极其广泛的应用:智能辅助驾驶,智能监控,行人分析以及智能机器人等领域.从2005年以来行人检测进入了一个快速的发展阶段,但是也存在很多问题还有待解决,主要还是在性能和速度方面还不能达到一个 ...
- opencv行人检测里遇到的setSVMDetector()问题
参考了博客http://blog.csdn.net/carson2005/article/details/7841443 后,自己动手后发现了一些问题,博客里提到的一些问题没有解决 ,是关于为什么图像 ...
- opencv+树莓PI的基于HOG特征的行人检测
树莓PI远程控制摄像头请参考前文:http://www.cnblogs.com/yuliyang/p/3561209.html 参考:http://answers.opencv.org/questio ...
- 基于HOG特征的Adaboost行人检测
原地址:http://blog.csdn.net/van_ruin/article/details/9166591 .方向梯度直方图(Histogramof Oriented Gradient, HO ...
- 基于YOLOv3和Qt5的车辆行人检测(C++版本)
概述 YOLOv3: 车辆行人检测算法 GitHub Qt5: 制作简单的GUI OpenCV:主要用于putText.drawRec等 Step YOLOv3检测结果 Fig 1. input im ...
随机推荐
- debian linux 下设置开机自启动
懒得写了,一张图简单明了.其实很简单,一开始没有加上nohup有点问题.现在问题已解决.
- Bug:java.lang.StackOverflowError: stack size 8MB
在开发的时候遇到了这个Bug:java.lang.StackOverflowError: stack size 8MB Log: 11-27 14:16:37.093 21892-21892/com. ...
- python2和Python3异同总结
1. python3 异常不再接收逗号(,)作为参数: ## python3 中这样可以正常运行 try: print("在这里执行的代码,有异常进入except") except ...
- impress.js 一个创建在线幻灯的js库
真的好奇怪,我居然会写前端技术的博客.没有办法的,最近实习,看的大多是前端.所以今天就用这个来练练手了. Impress.js 是一个非常棒的用来创建在线演示的Javascript库.它基于CSS3转 ...
- zabbix 实现对服务器的负载监控
# grep Include /etc/zabbix/zabbix_agentd.conf ### Option: Include # Include= Include=/etc/zabbix/zab ...
- analysis-what-blockchain-technology-means-for-artificial-intelligence-cm888540
http://m.nasdaq.com/article/analysis-what-blockchain-technology-means-for-artificial-intelligence-cm ...
- (原创)C++11改进我们的程序之简化我们的程序(二)
这次要讲的是:C++11如何通过组合函数来简化我们的程序.关于组合函数,大家可能对这个概念有点陌生.组合函数是将N个一元函数组成一种更复杂的函数,每个函数的返回值作为参数传给下一个函数,直到传到最后一 ...
- 将不同级别的logging 日志信息写入不同文件
将不同级别的logging 日志信息写入不同文件 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import os import time from logging.handlers import ...
- Django admin 常用方法 model 增加只读权限
1.Django admin model 设置查看权限 Django model 默认只有增加.删除.修改权限.没有查看权限 #model class Ad_Campaing(models.Model ...
- 图解在VC里使用graphics.h画图(相似TC)
1 www.easyx.cn 下载 EasyX 库 我下的2014;解压后例如以下图: 2 依据自己的VC 版本号进行安装 3 在控制台画一个圆 #include <graphics.h> ...
