机器学习入门-随机森林温度预测-增加样本数据 1.sns.pairplot(画出两个关系的散点图) 2.MAE(平均绝对误差) 3.MAPE(准确率指标)
在上一个博客中,我们构建了随机森林温度预测的基础模型,并且研究了特征重要性。
在这个博客中,我们将从两方面来研究数据对预测结果的影响
第一方面:特征不变,只增加样本的数据
第二方面:增加特征数,增加样本的数据
1.sns.pairplot 画出两个变量的关系图,用于研究变量之间的线性相关性,sns.pattle([color]) 用于设置调色板, 有点像scatter_matrix
2.MSE round(abs(pred - test_y).mean(), 2) 研究预测值与真实值之差的平均值
3.MAPE round(100 -abs(pred-test_y)/test_y*100, 2) (1 - 误差与真实值的比值)的平均值
代码:
第一步:载入数据
第二步:使用datetime.datetime.strptime() 将年月日进行组合,构造出日期的标签
第三步: 对数据中的温度特征进行画图
第四步:对新增的特征进行画图
第五步:sns.pairplot进行两两变量的关系画图,使用sns.pattle()生成颜色的调色板
第六步:建立随机森林模型,研究新增加的数据对预测精度的影响,不加入新增的特征
第七步:建立随机森林模型,研究新增加的数据对预测精度的影响,加入新增的特征
import datetime
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd # 第一步:导入数据
features = pd.read_csv('data/temps_extended.csv')
print(features.describe())
print(features.columns) # 第二步:使用datetime.datetime.strptime将字符串转换为日期类型
years = features['year']
months = features['month']
days = features['day']
# 先转换为字符串类型
dates = [str(int(year)) + '-' + str(int(month)) + '-' + str(int(day)) for year, month, day in zip(years, months, days)]
# 字符串类型转换为日期类型
dates = [datetime.datetime.strptime(date, '%Y-%m-%d') for date in dates] # 第三步对温度特征进行画图操作 fig, ((ax1, ax2), (ax3, ax4)) = plt.subplots(ncols=2, nrows=2, figsize=(12, 12))
fig.autofmt_xdate(rotation=60) ax1.plot(dates, features['temp_2'], linewidth=4)
ax1.set_xlabel(''); ax1.set_ylabel('temperature'); ax1.set_title('pre two max') ax2.plot(dates, features['temp_1'], linewidth=4)
ax2.set_xlabel(''); ax2.set_ylabel('temperature'); ax2.set_title('pre max') ax3.plot(dates, features['actual'], linewidth=4)
ax3.set_xlabel(''); ax3.set_ylabel('temperature'); ax3.set_title('today max') ax4.plot(dates, features['friend'], linewidth=4)
ax4.set_xlabel(''); ax4.set_ylabel('temperature'); ax4.set_title('friend max') plt.show() # 第四步:对新增的特征和平均温度进行作图 fig, ((ax1, ax2), (ax3, ax4)) = plt.subplots(ncols=2, nrows=2, figsize=(12, 12))
fig.autofmt_xdate(rotation=60) ax1.plot(dates, features['average'])
ax1.set_xlabel(''); ax1.set_ylabel('temperature'); ax1.set_title('average') ax2.plot(dates, features['ws_1'], 'r-')
ax2.set_xlabel(''); ax2.set_ylabel('temperature'); ax2.set_title('WS') ax3.plot(dates, features['prcp_1'], 'r-')
ax3.set_xlabel(''); ax3.set_ylabel('temperature'); ax3.set_title('Prcp') ax4.plot(dates, features['snwd_1'], 'ro')
ax4.set_xlabel(''); ax4.set_ylabel('temperature'); ax4.set_title('Snwd') plt.show()


# 第五步:使用sns.pairplot画两两关系的散点图
# 新增加季节特征,用做画图时的区分
season = []
for month in months:
if month in [12, 1, 2]:
season.append('window')
elif month in [3, 4, 5]:
season.append('spring')
elif month in [6, 7, 8]:
season.append('summer')
else:
season.append('Autumn') feature_matrix = features[['prcp_1', 'temp_1', 'average', 'actual']]
feature_matrix['season'] = season import seaborn as sns sns.set(style='ticks', color_codes=True) palette = sns.xkcd_palette(['dark blue', 'dark green', 'gold', 'orange'])
# hue表示通过什么进行分类
sns.pairplot(feature_matrix, hue='season', palette=palette, plot_kws=dict(alpha=0.7), diag_kind='kde',
diag_kws=dict(shade=True))
plt.show()
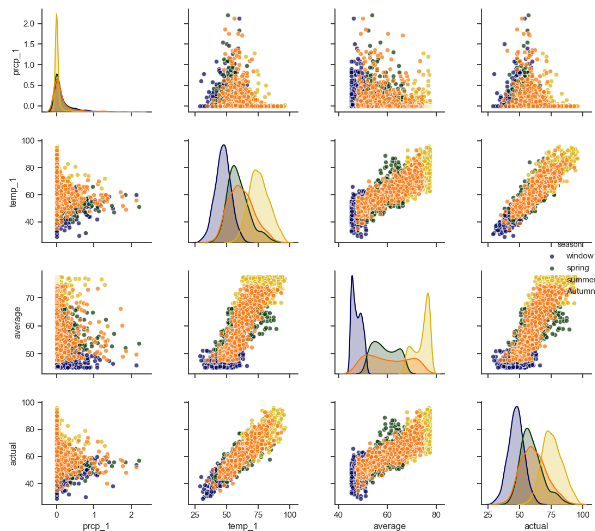
# 第六步使用增加的数据进行随机森林的建模,不添加新增的特征
feature_names = list(features.columns)
feature_indices = [feature_names.index(feature_name) for feature_name in feature_names
if feature_names not in ['ws_1', 'prcp_1', 'snwd_1']]
print(feature_indices)
# 使用pd.get_dummies 将week的文本标签转换为one-hot编码
features = pd.get_dummies(features)
# 提取特征和标签
X = features.iloc[:, feature_indices]
y = np.array(features['actual'])
X = X.drop('actual', axis=1)
X = np.array(X)
# 使用train_test_split 进行训练集和测试集的分开
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
train_x, test_x, train_y, test_y = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.3, random_state=42)
# 构建随机森林模型进行预测
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor rf = RandomForestRegressor(n_estimators=1000, random_state=42)
rf.fit(train_x, train_y)
pred_y = rf.predict(test_x) # 使用MAE指标
MAE = round(abs(pred_y - test_y).mean(), 2) # 使用MAPE指标
MAPE = round(((1-abs(pred_y-test_y)/test_y)*100).mean(), 2) print(MAE, MAPE) # 探讨原来数据的MAE和MAPE
# 使用pd.get_dummies 将week的文本标签转换为one-hot编码
features = pd.read_csv('data/temps.csv')
features = pd.get_dummies(features)
# 提取特征和标签
y = np.array(features['actual'])
X = features.drop('actual', axis=1)
X = np.array(X)
# 使用train_test_split 进行训练集和测试集的分开
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
train_x, test_x, train_y, test_y = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.3, random_state=42)
# 构建随机森林模型进行预测
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor rf = RandomForestRegressor(n_estimators=1000, random_state=42)
rf.fit(train_x, train_y)
pred_y = rf.predict(test_x) # 使用MAE指标
MAE = round(abs(pred_y - test_y).mean(), 2) # 使用MAPE指标
MAPE = round(((1-abs(pred_y-test_y)/test_y)*100).mean(), 2) print(MAE, MAPE) # 第七步: 探讨将新增加的指标也加入对数据结果的影响
features = pd.read_csv('data/temps_extended.csv')
features = pd.get_dummies(features)
# 提取特征和标签
y = np.array(features['actual'])
X = features.drop('actual', axis=1)
X = np.array(X)
# 使用train_test_split 进行训练集和测试集的分开
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
train_x, test_x, train_y, test_y = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.3, random_state=42)
# 构建随机森林模型进行预测
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor rf = RandomForestRegressor(n_estimators=1000, random_state=42)
rf.fit(train_x, train_y)
pred_y = rf.predict(test_x) # 使用MAE指标
MAE = round(abs(pred_y - test_y).mean(), 2) # 使用MAPE指标
MAPE = round(((1-abs(pred_y-test_y)/test_y)*100).mean(), 2) print(MAE, MAPE)
原始数据的MAE,MAPE 3.87 93.96
只增加数据量的MAE, MAPE 3.73 93.72
增加数据量增加特征的MAE,MAPE 3.71 93.76
从上面可以看出增加数据量和样本特征对结果还是能产生正面的影响
机器学习入门-随机森林温度预测-增加样本数据 1.sns.pairplot(画出两个关系的散点图) 2.MAE(平均绝对误差) 3.MAPE(准确率指标)的更多相关文章
- 机器学习入门-随机森林温度预测的案例 1.datetime.datetime.datetime(将字符串转为为日期格式) 2.pd.get_dummies(将文本标签转换为one-hot编码) 3.rf.feature_importances_(研究样本特征的重要性) 4.fig.autofmt_xdate(rotation=60) 对标签进行翻转
在这个案例中: 1. datetime.datetime.strptime(data, '%Y-%m-%d') # 由字符串格式转换为日期格式 2. pd.get_dummies(features) ...
- 机器学习入门-随机森林预测温度-不同参数对结果的影响调参 1.RandomedSearchCV(随机参数组的选择) 2.GridSearchCV(网格参数搜索) 3.pprint(顺序打印) 4.rf.get_params(获得当前的输入参数)
使用了RamdomedSearchCV迭代100次,从参数组里面选择出当前最佳的参数组合 在RamdomedSearchCV的基础上,使用GridSearchCV在上面最佳参数的周围选择一些合适的参数 ...
- 100天搞定机器学习|Day56 随机森林工作原理及调参实战(信用卡欺诈预测)
本文是对100天搞定机器学习|Day33-34 随机森林的补充 前文对随机森林的概念.工作原理.使用方法做了简单介绍,并提供了分类和回归的实例. 本期我们重点讲一下: 1.集成学习.Bagging和随 ...
- Python机器学习笔记——随机森林算法
随机森林算法的理论知识 随机森林是一种有监督学习算法,是以决策树为基学习器的集成学习算法.随机森林非常简单,易于实现,计算开销也很小,但是它在分类和回归上表现出非常惊人的性能,因此,随机森林被誉为“代 ...
- 使用基于Apache Spark的随机森林方法预测贷款风险
使用基于Apache Spark的随机森林方法预测贷款风险 原文:Predicting Loan Credit Risk using Apache Spark Machine Learning R ...
- 100天搞定机器学习|Day33-34 随机森林
前情回顾 机器学习100天|Day1数据预处理 100天搞定机器学习|Day2简单线性回归分析 100天搞定机器学习|Day3多元线性回归 100天搞定机器学习|Day4-6 逻辑回归 100天搞定机 ...
- paper 84:机器学习算法--随机森林
http://www.cnblogs.com/wentingtu/archive/2011/12/13/2286212.html中一些内容 基础内容: 这里只是准备简单谈谈基础的内容,主要参考一下别人 ...
- 【机器学习】随机森林(Random Forest)
随机森林是一个最近比较火的算法 它有很多的优点: 在数据集上表现良好 在当前的很多数据集上,相对其他算法有着很大的优势 它能够处理很高维度(feature很多)的数据,并且不用做特征选择 在训练完后, ...
- 【机器学习】随机森林RF
随机森林(RF, RandomForest)包含多个决策树的分类器,并且其输出的类别是由个别树输出的类别的众数而定.通过自助法(boot-strap)重采样技术,不断生成训练样本和测试样本,由训练样本 ...
随机推荐
- jquery append、prepend、before等等
1.jQuery append() 方法 jQuery append() 方法在被选元素的结尾插入内容. 实例 复制代码代码如下: $("p").append("Some ...
- SELENIUM如何调用FIREFOX时加载插件
当selenium调用firefox时,会发现这个firefox里干净的如同一盆清水,自己定制安装的那些插件都不翼而飞了,这个时候那些插件自然就不能使用了,但是当前又必须使用插件该如何是好呢? 解决办 ...
- centos6 ext4修复
输入root密码后: fsck -y /dev/mapper/vg_logserv-lv_root 修复完后重启 reboot 若忘记了root密码,可用系统ISO盘引导进入Rescue救援模式 在这 ...
- POJ1179 Polygon
题目:http://poj.org/problem?id=1179 石子合并的升级版.有负值.但运算符只有 + 和 * . 考虑负值对原做法正确性的影响:之所以仅记录最大值可能不对,是因为有可能负数 ...
- jmeter ---模拟http请求/发送gzip数据
jmeter中get请求gzip数据的方法: 在jmeter线程组中添加“http信息头管理器”,并添加名称:Accept-Encoding值: gzip,deflate注:HTTP信息头Accept ...
- CentOS启动网络提示connect: Network is unreachable(配置静态路由)
ls /etc/sysconfig/network-script/ifcfg-eth0 一.看是否在上述目录下存在ifcfg-eth0 这个文件,若存在则按下面的步骤操作: 1.手工配置ip看能不能配 ...
- java jni 调用c++ opencv代码成功范例
java上建立接口定义 package com.dtk; public class Rec { public native String RecImage(String src); public st ...
- .Net和SqlServer的事务处理实例
1,SqlServer存储过程的事务处理一种比较通用的出错处理的模式大概如下:Create procdure prInsertProducts( @intProductId int, @chvProd ...
- 知识点查缺补漏贴01-进程间通讯之mmap文件共享
引文: 个人名言:“同一条河里淹死两次的人,是傻子,淹死三次及三次以上的人是超人”.经历过上次悲催的面试,决定沉下心来,好好的补充一下基础知识点.本文是这一系列第一篇:进程间通讯之mmap. 一.概念 ...
- Qt QTableWidget用法总结
转载:李宏兵 QTableWidget是QT程序中常用的显示数据表格的空间,很类似于VC.C#中的DataGrid.说到QTableWidget,就必须讲一下它跟QTabelView的区别了. QTa ...
