Distributed traceability with Spring Cloud: Sleuth and Zipkin
I. Sleuth
0. Concept
- Trace
- A set of spans that form a call tree structure, forms the trace of the request.
- Span
- It is the basic unit of work, for example a call to a service. They are identified with a span ID and a trace ID to which span is owned. They have start and end, and with it you get track the response time between requests.
- Tag
- Key/value pair that identifies certain information in the span. It doesn't contain timestamps, it just identifies.
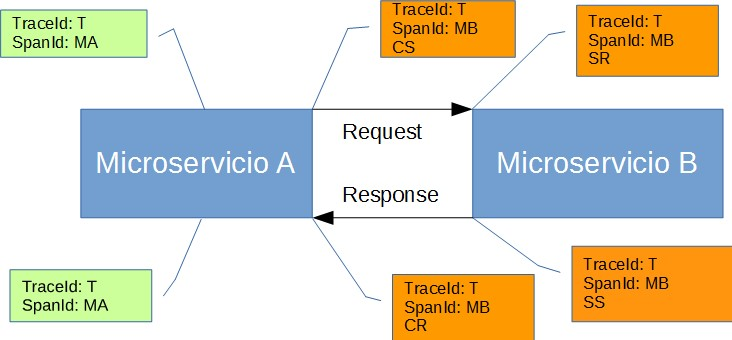
Annotation: Used to record the existence of an event in time. With Brave instrumentation, we no longer need to set special events for Zipkin to understand who the client and server are, where the request started, and where it ended. For learning purposes, however, we mark these events to highlight what kind of an action took place.
- cs: Client Sent. The client has made a request. This annotation indicates the start of the span.
- sr: Server Received: The server side got the request and started processing it. Subtracting the
cstimestamp from this timestamp reveals the network latency. - ss: Server Sent. Annotated upon completion of request processing (when the response got sent back to the client). Subtracting the
srtimestamp from this timestamp reveals the time needed by the server side to process the request. - cr: Client Received. Signifies the end of the span. The client has successfully received the response from the server side. Subtracting the
cstimestamp from this timestamp reveals the whole time needed by the client to receive the response from the server.
1. pom
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-sleuth</artifactId>
</dependency>
2. config
1) sampler
---
spring:
sleuth:
sampler:
probability: 1.0
II. zipkin
0. way
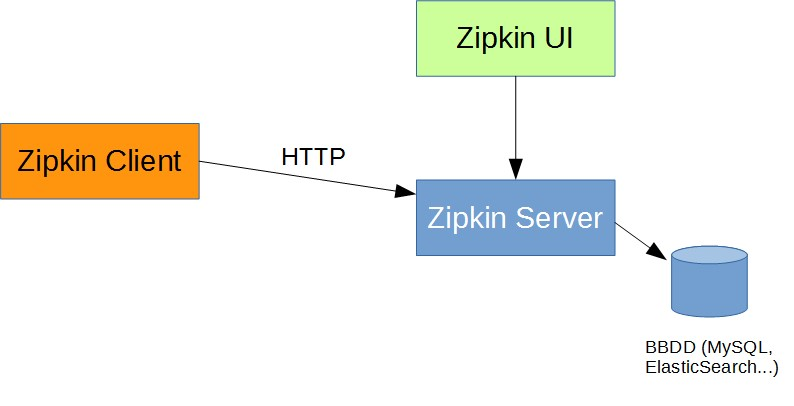
1) http
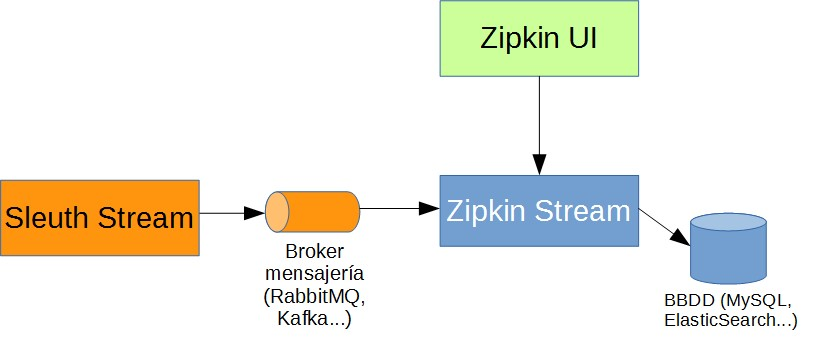
2) Messaging Brokers
0. zipkin client
1) pom
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-zipkin</artifactId>
</dependency>
2) config
(1) base url
---
spring:
zipkin:
base-url: http://localhost:9411
(2) sender
A. RabbitMQ
---
spring:
zipkin:
sender:
type: RABBIT
B. Kafka
---
spring:
zipkin:
sender:
type: KAFKA
C. Web
default
1. zipkin server
upgrade to Spring Boot 2.0 NoClassDefFoundError UndertowEmbeddedServletContainerFactory
1) down
https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/io.zipkin.java/zipkin-server
2) run
es2.4.x安装在WSL中。详细 see 《Elasticsearch 2.4 安装》
(1) for Rabbit
version: RabbitMQ3.7.13(erlang 21.3)
java -jar zipkin-server--exec.jar --RABBIT_URI=amqp://admin:admin@192.168.42.124:5672/sleuth --STORAGE_TYPE=elasticsearch --ES_HOSTS=http://localhost:9200 --ES_HTTP_LOGGING=BASIC
(2) for kafka
version: Kafka1.0.2(Scale 2.11)
java -jar zipkin-server--exec.jar --KAFKA_BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS=,, --STORAGE_TYPE=elasticsearch --ES_HOSTS=http://localhost:9200 --ES_HTTP_LOGGING=BASIC
III. MQ
1. RabbitMQ
0) pom
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-stream</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-stream-binder-rabbit</artifactId>
</dependency>
1) config
---
spring:
rabbitmq:
addresses: 192.168.42.124
port: 5672
username: admin
password: admin
virtual-host: sleuth
2) virtual hosts
切换到Admin选项卡,点击右侧的virtual hosts

2. Kafka
0) pom
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-stream</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-stream-binder-kafka</artifactId>
</dependency>
1) config
spring:
kafka:
bootstrap-servers:
- 192.168.42.186:9092
- 192.168.42.187:9092
- 192.168.42.188:9092
IV. Effect Diagram
0. gateway
http://localhost:8311/user/listPage

1. zipkin server
http://localhost:9411

2. RabbitMQ
连接了4个服务:zipkin server
gateway->user-service->userDetails
http://192.168.42.124:15672/#/connections

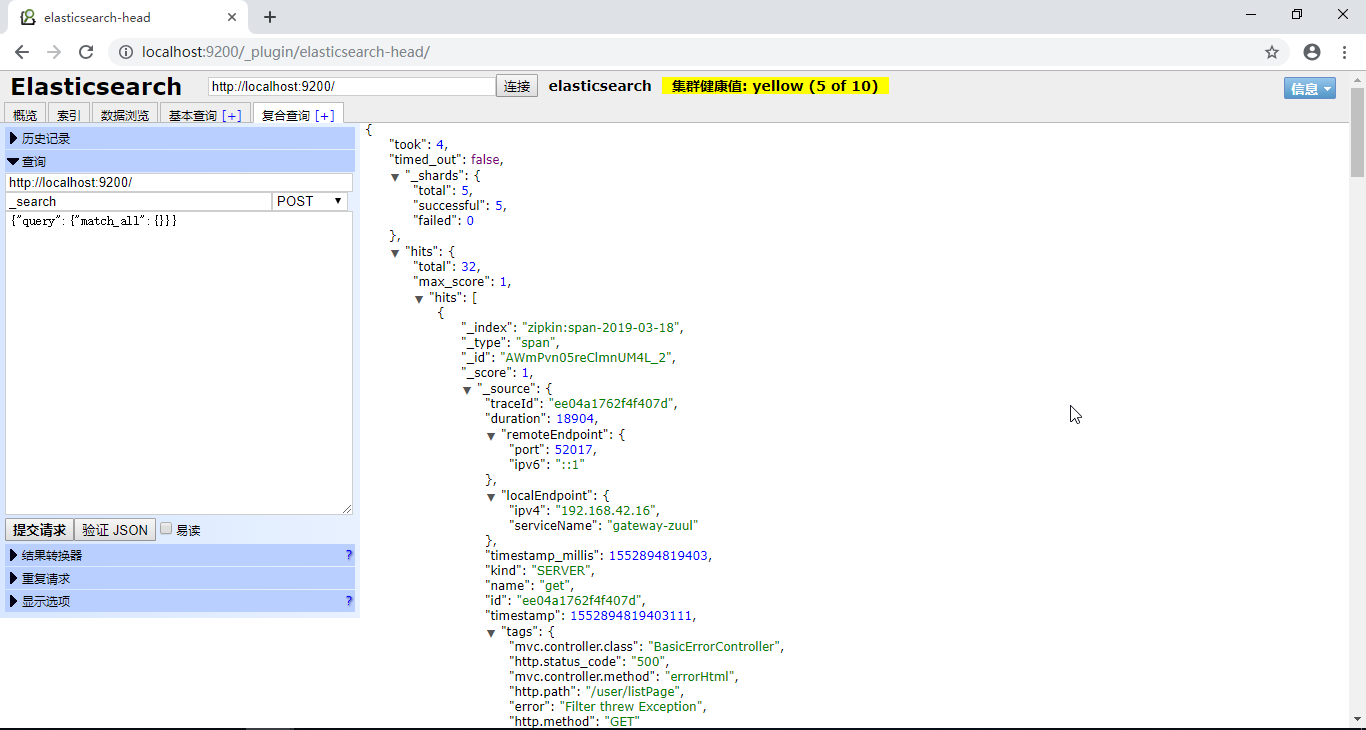
3. ES2.4.x
http://localhost:9200/_plugin/elasticsearch-head
Reference:
1. Trazabilidad Distribuida con Spring Cloud: Sleuth y Zipkin
Distributed traceability with Spring Cloud: Sleuth and Zipkin的更多相关文章
- 跟我学SpringCloud | 第十一篇:使用Spring Cloud Sleuth和Zipkin进行分布式链路跟踪
SpringCloud系列教程 | 第十一篇:使用Spring Cloud Sleuth和Zipkin进行分布式链路跟踪 Springboot: 2.1.6.RELEASE SpringCloud: ...
- Spring Cloud sleuth with zipkin over RabbitMQ教程
文章目录 Spring Cloud sleuth with zipkin over RabbitMQ demo zipkin server的搭建(基于mysql和rabbitMQ) 客户端环境的依赖 ...
- spring cloud 入门系列八:使用spring cloud sleuth整合zipkin进行服务链路追踪
好久没有写博客了,主要是最近有些忙,今天忙里偷闲来一篇. =======我是华丽的分割线========== 微服务架构是一种分布式架构,微服务系统按照业务划分服务单元,一个微服务往往会有很多个服务单 ...
- Spring Cloud Sleuth 和 Zipkin 进行分布式跟踪使用指南
分布式跟踪允许您跟踪分布式系统中的请求.本文通过了解如何使用 Spring Cloud Sleuth 和 Zipkin 来做到这一点. 对于一个做所有事情的大型应用程序(我们通常将其称为单体应用程序) ...
- springcloud(十二):使用Spring Cloud Sleuth和Zipkin进行分布式链路跟踪
随着业务发展,系统拆分导致系统调用链路愈发复杂一个前端请求可能最终需要调用很多次后端服务才能完成,当整个请求变慢或不可用时,我们是无法得知该请求是由某个或某些后端服务引起的,这时就需要解决如何快读定位 ...
- 使用Spring Cloud Sleuth和Zipkin进行分布式链路跟踪
原文:http://www.cnblogs.com/ityouknow/p/8403388.html 随着业务发展,系统拆分导致系统调用链路愈发复杂一个前端请求可能最终需要调用很多次后端服务才能完成, ...
- spring cloud深入学习(十三)-----使用Spring Cloud Sleuth和Zipkin进行分布式链路跟踪
随着业务发展,系统拆分导致系统调用链路愈发复杂一个前端请求可能最终需要调用很多次后端服务才能完成,当整个请求变慢或不可用时,我们是无法得知该请求是由某个或某些后端服务引起的,这时就需要解决如何快读定位 ...
- 【spring cloud】spring cloud Sleuth 和Zipkin 进行分布式链路跟踪
spring cloud 分布式微服务架构下,所有请求都去找网关,对外返回也是统一的结果,或者成功,或者失败. 但是如果失败,那分布式系统之间的服务调用可能非常复杂,那么要定位到发生错误的具体位置,就 ...
- springcloud --- spring cloud sleuth和zipkin日志管理(spring boot 2.18)
前言 在spring cloud分布式架构中,系统被拆分成了许多个服务单元,业务复杂性提高.如果出现了异常情况,很难定位到错误位置,所以需要实现分布式链路追踪,跟进一个请求有哪些服务参与,参与的顺序如 ...
随机推荐
- HTTP请求属性说明
1)URL:页面地址. 2)Method :页面的提交方式,POST或GET. 3)EncType:编码类型.此参数给出一个内容类型(Content-Type),指定其做为回放脚本时“Content- ...
- python 高阶函数学习, map、reduce
一个函数可以接收另一个函数作为参数,这样的函数叫做高阶函数. 函数map(): map()函数接收两个参数,一个是函数,一个是Iterable, map把函数作用于序列的每一个元素,并把结果作为Ite ...
- Redis Cluster 4.0高可用集群安装、在线迁移操作记录
之前介绍了redis cluster的结构及高可用集群部署过程,今天这里简单说下redis集群的迁移.由于之前的redis cluster集群环境部署的服务器性能有限,需要迁移到高配置的服务器上.考虑 ...
- jmeter --响应断言详解
jmeter --响应断言详解 响应断言 :对服务器的响应进行断言校验 (1)应用范围: main sample and sub sample, main sample only , sub-samp ...
- golang channel几点总结
golang提倡使用通讯来共享数据,而不是通过共享数据来通讯.channel就是golang这种方式的体现. Channel 在golang中有两种channel:带缓存的和不带缓存. 带缓存的cha ...
- PHP 解压 ZIP 文件到指定文件夹
本类实现参考 php manual 评论 [php] view plain copy /** * function: 解压zip 格式的文件 * author:friker * date:2015-1 ...
- 自动加载以及Composer的实现
类的自动加载 两个函数 __autoload()魔术方法.spl_autoload_register 当php文件中使用了new关键字实例化一个对象时,如果该类没有在本php文件中被定义,将会触发__ ...
- SynergyS7G2RTC时钟模块的使用
RTC功能描述 RTC时钟模块是Synergy芯片的一个时间外设,主要用于日期时间的存储和控制,有别于一般MCU中的Timer,RTC时钟有两种计时模式,日期模式和二进制计时模式,其中日期模式的时间可 ...
- 【Shell】使用sed命令替换文件中的某一行
原始文件内容 -bash-3.2# cat configTest.xml <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> ...
- PyQt5学习笔记14----初识pyqt多线程操作
转载:翻滚吧挨踢男 首先来看一个例子: # coding=utf-8 __author__ = 'a359680405' from PyQt5.QtCore import * from PyQt5.Q ...
