ISLR系列:(1)线性回归 Linear Regression
Linear Regression
此博文是 An Introduction to Statistical Learning with Applications in R 的系列读书笔记,作为本人的一份学习总结,也希望和朋友们进行交流学习。
该书是The Elements of Statistical Learning 的R语言简明版,包含了对算法的简明介绍以及其R实现,最让我感兴趣的是算法的R语言实现。
【转载时请注明来源】:http://www.cnblogs.com/runner-ljt/
Ljt 勿忘初心 无畏未来
作为一个初学者,水平有限,欢迎交流指正。
主要内容
线性回归一章主要围绕以下7个问题进行了简明的阐述,这7个问题也是我们在建立线性模型时的基本步骤:
(1) Is there a relationship between advertising sales and budget?
(2) How strong is the relationship?
(3) Which media contribute to sales?
(4) How large is the effect of each medium on sales?
(5) How accurately can we predict future sales?
(6) Is the relationship linear?
(7) Is the synergy among the advertising media?
这七个问题又是以线性模型的建立和检验两方面为主:
这一部分的详细内容可以参考之前关于线性回归诊断的两篇博文
(一)模型的建立
(1) 自变量和因变量之间是否存在线性关系,若存在那么这种线性关系有多强?
1.整体上是否存在线性关系----回归方程显著性F检验
2.线性关系的强弱----拟合优度检验(样本决定系数R2 --R2 measures the proportion of variability in Y that can be explained using X)
(2) 哪些自变量和因变量之间存在显著的线性关系?
回归系数的显著性t检验
(二)模型检验
(1) 线性模型建立的假设是否成立?
假设1:随机干扰项 ε 服从零均值,同方差,零协方差(相互独立)的正态分布
同方差--->异方差检验 ; 零协方差--->自相关性检验 ; 正太分布--->正太性检验
假设2:模型为线性关系
线性关系--->残差图检验 ; 自变量之间是否存在高度相关--->共线性检验
(2) 样本数据检验
异常值检验:离群点检验、强影响点检验
(3) 模型预测
置信区间:因变量新值的平均值的区间预测
预测区间:因变量新值(单个值)的区间预测
建立线性模型
lm(y~x,data=Boston):线性回归拟合函数
coef(lm.fit):提取线性回归的系数
confint(lm.fit):回归系数置信区间
predict(lm.fit,data.frame(c(....)),interval='confidence') :置信区间
predict(lm.fit,data.frame(c(....)),interval='prediction') :预测区间
>
> library(MASS)
> library(ISLR)
> head(Boston)
crim zn indus chas nox rm age dis rad tax ptratio black lstat medv
1 0.00632 18 2.31 0 0.538 6.575 65.2 4.0900 1 296 15.3 396.90 4.98 24.0
2 0.02731 0 7.07 0 0.469 6.421 78.9 4.9671 2 242 17.8 396.90 9.14 21.6
3 0.02729 0 7.07 0 0.469 7.185 61.1 4.9671 2 242 17.8 392.83 4.03 34.7
4 0.03237 0 2.18 0 0.458 6.998 45.8 6.0622 3 222 18.7 394.63 2.94 33.4
5 0.06905 0 2.18 0 0.458 7.147 54.2 6.0622 3 222 18.7 396.90 5.33 36.2
6 0.02985 0 2.18 0 0.458 6.430 58.7 6.0622 3 222 18.7 394.12 5.21 28.7
>
> attach(Boston)
> lm.fit<-lm(medv~lstat)
> summary(lm.fit) Call:
lm(formula = medv ~ lstat) Residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-15.168 -3.990 -1.318 2.034 24.500 Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) 34.55384 0.56263 61.41 <2e-16 ***
lstat -0.95005 0.03873 -24.53 <2e-16 ***
---
Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1 Residual standard error: 6.216 on 504 degrees of freedom
Multiple R-squared: 0.5441, Adjusted R-squared: 0.5432
F-statistic: 601.6 on 1 and 504 DF, p-value: < 2.2e-16 > names(lm.fit)
[1] "coefficients" "residuals" "effects" "rank" "fitted.values" "assign"
[7] "qr" "df.residual" "xlevels" "call" "terms" "model"
>
> #回归系数
> coef(lm.fit)
(Intercept) lstat
34.5538409 -0.9500494
> #回归系数的置信区间
> confint(lm.fit)
2.5 % 97.5 %
(Intercept) 33.448457 35.6592247
lstat -1.026148 -0.8739505
> #预测:置信区间和预测区间
> predict(lm.fit,data.frame(lstat=c(5,10,15,20)),interval='confidence')
fit lwr upr
1 29.80359 29.00741 30.59978
2 25.05335 24.47413 25.63256
3 20.30310 19.73159 20.87461
4 15.55285 14.77355 16.33216
> predict(lm.fit,data.frame(lstat=c(5,10,15,20)),interval='prediction')
fit lwr upr
1 29.80359 17.565675 42.04151
2 25.05335 12.827626 37.27907
3 20.30310 8.077742 32.52846
4 15.55285 3.316021 27.78969
>
>
线性模型检验
abline(lm.fit):画回归拟合直线
plot(lm.fit):画回归诊断图(残差图、Q-Q图、标准化残差图、杠杆图)
par(mfrow=c(2,3)):图板分区
>
> #测试数据散点图
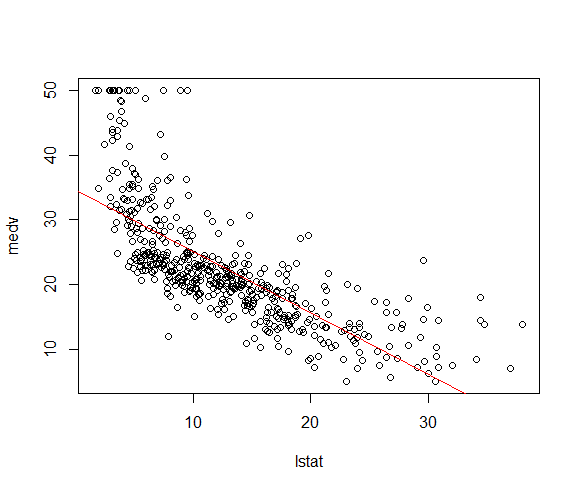
> plot(lstat,medv)
> #画回归拟合直线
> abline(lm.fit,col='red')
>
> #诊断图
> #图板分区
> par(mfrow=c(2,2))
>
> plot(lm.fit)
>
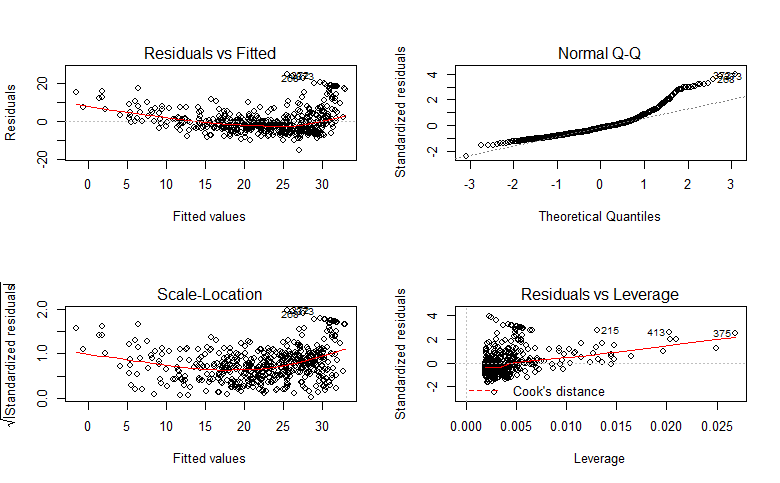
残差图和标准化残差图显示有明显的非线性关系,杠杆图表明第375个样本点是高杠杆点。
多元线性回归
summary(lm.fit)$r.sq:提取回归方程的决定系数R2 ;通过?summary.lm 查看可提取的信息
vif(lm.fit):查看方差扩大因子(一般回归方程的方差扩大因子大于10的几个变量间存在着多重共线性),需要加载car包。
>
> #多元线性回归
> lm.fit<-lm(medv~lstat+age,data=Boston)
> summary(lm.fit) Call:
lm(formula = medv ~ lstat + age, data = Boston) Residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-15.981 -3.978 -1.283 1.968 23.158 Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) 33.22276 0.73085 45.458 < 2e-16 ***
lstat -1.03207 0.04819 -21.416 < 2e-16 ***
age 0.03454 0.01223 2.826 0.00491 **
---
Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1 Residual standard error: 6.173 on 503 degrees of freedom
Multiple R-squared: 0.5513, Adjusted R-squared: 0.5495
F-statistic: 309 on 2 and 503 DF, p-value: < 2.2e-16 >
> lm.summary<-summary(lm.fit)
> #提取R^2
> lm.summary$r.sq
[1] 0.5512689
>
> ##方差扩大因子
> library(car)
> vif(lm.fit)
lstat age
1.569395 1.569395
>
非线性
lm(y~x1+x2+x1:x2) : x1:x2 只表示x1.x2 ; x1*x2 表示x1+x2+x1.x2 ;
lm(y~x+I(x^2)) : 在lm(...)内表示变量的高次项 I(x^2),直接用x^2是错误的。
>
>
> ##变量间的交互项
>
> lm.fit<-lm(medv~lstat+age+lstat:age,data=Boston)
> summary(lm.fit) Call:
lm(formula = medv ~ lstat + age + lstat:age, data = Boston) Residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-15.806 -4.045 -1.333 2.085 27.552 Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) 36.0885359 1.4698355 24.553 < 2e-16 ***
lstat -1.3921168 0.1674555 -8.313 8.78e-16 ***
age -0.0007209 0.0198792 -0.036 0.9711
lstat:age 0.0041560 0.0018518 2.244 0.0252 *
---
Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1 Residual standard error: 6.149 on 502 degrees of freedom
Multiple R-squared: 0.5557, Adjusted R-squared: 0.5531
F-statistic: 209.3 on 3 and 502 DF, p-value: < 2.2e-16 >
> ##变量的高次项
> lm.fit2<-lm(medv~lstat+I(lstat^2))
> summary(lm.fit2) Call:
lm(formula = medv ~ lstat + I(lstat^2)) Residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-15.2834 -3.8313 -0.5295 2.3095 25.4148 Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) 42.862007 0.872084 49.15 <2e-16 ***
lstat -2.332821 0.123803 -18.84 <2e-16 ***
I(lstat^2) 0.043547 0.003745 11.63 <2e-16 ***
---
Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1 Residual standard error: 5.524 on 503 degrees of freedom
Multiple R-squared: 0.6407, Adjusted R-squared: 0.6393
F-statistic: 448.5 on 2 and 503 DF, p-value: < 2.2e-16 >
> ##方差分析
> lm.fit1<-lm(medv~lstat)
>
> anova(lm.fit1,lm.fit2)
Analysis of Variance Table Model 1: medv ~ lstat
Model 2: medv ~ lstat + I(lstat^2)
Res.Df RSS Df Sum of Sq F Pr(>F)
1 504 19472
2 503 15347 1 4125.1 135.2 < 2.2e-16 ***
---
Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1
>
>
定性变量
contrasts(...) : 查看及设置虚拟变量
>
> head(Carseats)
Sales CompPrice Income Advertising Population Price ShelveLoc Age Education Urban US
1 9.50 138 73 11 276 120 Bad 42 17 Yes Yes
2 11.22 111 48 16 260 83 Good 65 10 Yes Yes
3 10.06 113 35 10 269 80 Medium 59 12 Yes Yes
4 7.40 117 100 4 466 97 Medium 55 14 Yes Yes
5 4.15 141 64 3 340 128 Bad 38 13 Yes No
6 10.81 124 113 13 501 72 Bad 78 16 No Yes
>
> lm.fit<-lm(Sales~CompPrice+Income+ShelveLoc,data=Carseats)
> summary(lm.fit) Call:
lm(formula = Sales ~ CompPrice + Income + ShelveLoc, data = Carseats) Residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-7.5611 -1.6096 -0.1409 1.6263 6.1845 Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) 2.875874 1.023857 2.809 0.00522 **
CompPrice 0.010634 0.007489 1.420 0.15638
Income 0.018388 0.004111 4.473 1.01e-05 ***
ShelveLocGood 4.750942 0.340955 13.934 < 2e-16 ***
ShelveLocMedium 1.861994 0.280481 6.639 1.05e-10 ***
---
Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1 Residual standard error: 2.285 on 395 degrees of freedom
Multiple R-squared: 0.3519, Adjusted R-squared: 0.3454
F-statistic: 53.63 on 4 and 395 DF, p-value: < 2.2e-16 >
> ##查看虚拟变量
> contrasts(Carseats$ShelveLoc)
Good Medium
Bad 0 0
Good 1 0
Medium 0 1
>
ISLR系列:(1)线性回归 Linear Regression的更多相关文章
- 机器学习方法:回归(一):线性回归Linear regression
欢迎转载,转载请注明:本文出自Bin的专栏blog.csdn.net/xbinworld. 开一个机器学习方法科普系列:做基础回顾之用,学而时习之:也拿出来与大家分享.数学水平有限,只求易懂,学习与工 ...
- TensorFlow 学习笔记(1)----线性回归(linear regression)的TensorFlow实现
此系列将会每日持续更新,欢迎关注 线性回归(linear regression)的TensorFlow实现 #这里是基于python 3.7版本的TensorFlow TensorFlow是一个机器学 ...
- Stanford机器学习---第二讲. 多变量线性回归 Linear Regression with multiple variable
原文:http://blog.csdn.net/abcjennifer/article/details/7700772 本栏目(Machine learning)包括单参数的线性回归.多参数的线性回归 ...
- 机器学习(三)--------多变量线性回归(Linear Regression with Multiple Variables)
机器学习(三)--------多变量线性回归(Linear Regression with Multiple Variables) 同样是预测房价问题 如果有多个特征值 那么这种情况下 假设h表示 ...
- Ng第二课:单变量线性回归(Linear Regression with One Variable)
二.单变量线性回归(Linear Regression with One Variable) 2.1 模型表示 2.2 代价函数 2.3 代价函数的直观理解 2.4 梯度下降 2.5 梯度下 ...
- 斯坦福第二课:单变量线性回归(Linear Regression with One Variable)
二.单变量线性回归(Linear Regression with One Variable) 2.1 模型表示 2.2 代价函数 2.3 代价函数的直观理解 I 2.4 代价函数的直观理解 I ...
- 斯坦福CS229机器学习课程笔记 Part1:线性回归 Linear Regression
机器学习三要素 机器学习的三要素为:模型.策略.算法. 模型:就是所要学习的条件概率分布或决策函数.线性回归模型 策略:按照什么样的准则学习或选择最优的模型.最小化均方误差,即所谓的 least-sq ...
- 机器学习 (一) 单变量线性回归 Linear Regression with One Variable
文章内容均来自斯坦福大学的Andrew Ng教授讲解的Machine Learning课程,本文是针对该课程的个人学习笔记,如有疏漏,请以原课程所讲述内容为准.感谢博主Rachel Zhang的个人笔 ...
- 机器学习 (二) 多变量线性回归 Linear Regression with Multiple Variables
文章内容均来自斯坦福大学的Andrew Ng教授讲解的Machine Learning课程,本文是针对该课程的个人学习笔记,如有疏漏,请以原课程所讲述内容为准.感谢博主Rachel Zhang 的个人 ...
- ML 线性回归Linear Regression
线性回归 Linear Regression MOOC机器学习课程学习笔记 1 单变量线性回归Linear Regression with One Variable 1.1 模型表达Model Rep ...
随机推荐
- JS判断PC还是移动端打开网页
最近在做移动端网站,也需兼容PC端.还没找到更好的方法,只能用javascr判断用户是在PC端打开还是移动端打开. JS判断 var isPC = function (){ var userAg ...
- 衣带渐宽终不悔,为伊消得人憔悴--DbHelper增强版
核心理念 如何使用 测试实例 数据库内详细数据信息 测试代码 数据库连接池测试 测试集 延伸 相关下载链接 前几日,写了一篇关于一个 轻量级数据持久化的框架的博客(点击浏览: http://blog. ...
- 【mybatis深度历险系列】深入浅出mybatis中原始dao的开发和mapper代理开发
使用Mybatis开发Dao,通常有两个方法,即原始Dao开发方法和Mapper接口开发方法.mybatis在进行dao开发的时候,涉及到三姐妹,分别是SqlSessionFactoryBuilder ...
- how to output quotes in bash prompt
introduction In certain situations, quotes are required to be output in the command prompt. To do th ...
- 理解性能的奥秘——应用程序中慢,SSMS中快(4)——收集解决参数嗅探问题的信息
本文属于<理解性能的奥秘--应用程序中慢,SSMS中快>系列 接上文:理解性能的奥秘--应用程序中慢,SSMS中快(3)--不总是参数嗅探的错 前面已经提到过关于存储过程在SSMS中运行很 ...
- 关于bootstrap在IE8下不能支持自适应的问题
说到这个问题,我就想吐槽下IE了,开发这么多版本,每个版本都有一些这样那样的问题不支持,别的正常的浏览器咋都能支持呢?真是垃圾浏览器!!!! 说归说,但是IE现在用的人多啊,怎么办?这个问题还是得解决 ...
- 值集&快速编码(Lookup_code)
--值集 SELECT ffv.flex_value, ffv.description FROM fnd_flex_values_vl ffv, fnd_flex_value_sets ffs ...
- hive元数据库表分析及操作
在安装Hive时,需要在hive-site.xml文件中配置元数据相关信息.与传统关系型数据库不同的是,hive表中的数据都是保存的HDFS上,也就是说hive中的数据库.表.分区等都可以在HDFS找 ...
- sh里的变量 $0 $1 $$ $#
$0就是该bash文件名 $?显示最后命令的退出状态.0表示没有错误,其他任何值表明有错误. $*所有位置参数的内容:就是调用调用本bash shell的参数. $@基本上与上面相同.只不过是 &qu ...
- hbase操作(shell 命令,如建表,清空表,增删改查)以及 hbase表存储结构和原理
两篇讲的不错文章 http://www.cnblogs.com/nexiyi/p/hbase_shell.html http://blog.csdn.net/u010967382/article/de ...
