NIO源码阅读
自己对着源码敲一遍练习,写上注释。发现NIO编程难度好高啊。。虽然很复杂,但是NIO编程的有点还是很多:
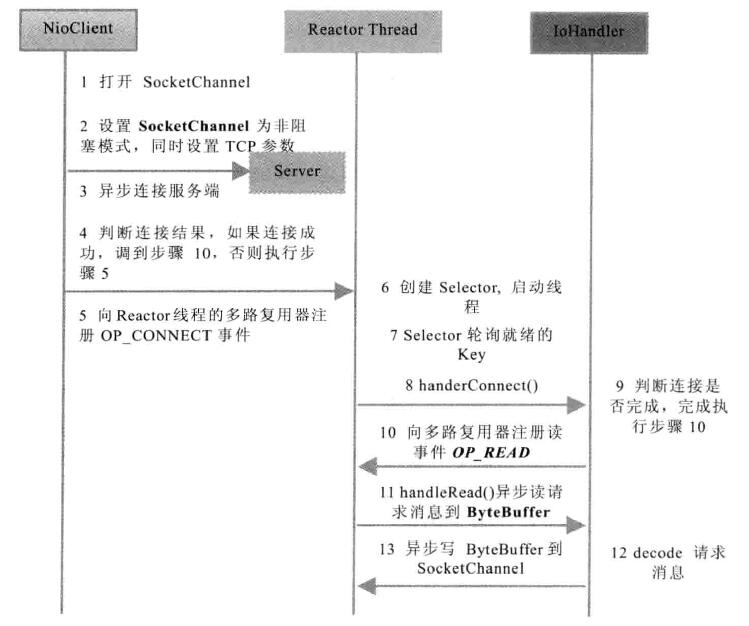
1、客户端发起的连接操作是异步的,可以通过在多路复用器注册OP_CONNECTION等待后续结果,不需要像BIO的客户端一样被同步阻塞。
2、SocketChannel的读写操作都是异步的,如果没有可读写的数据它不会同步等待,直接返回,这样I/O通信模型就可以处理其他的链路,不需要同步等待这个链路可用。
3、线程模型的优化:由于JDK的Selector在Linux等主流操作系统上通过epoll实现,没有连接句柄的限制,那么Selector线程可以同时处理成千上万个客户端连接,而且性能不会随着客户端的增加而线性下降。所以它非常适合做高性能、高负载的网络服务器。
TimeClient:
package nio;
public class TimeClient {
public static void main(String args[]){
int port = 8080;
if(args != null && args.length > 0){
try{
port = Integer.valueOf(args[0]);
}catch(NumberFormatException e){
//采用默认值
}
}
new Thread(new TimeClientHandle("120.0.0.1",port),"TimeClient-001").start();
}
}
TimeClientHandler:
package nio; import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set; public class TimeClientHandle implements Runnable{
private String host;
private int port;
private Selector selector;
private SocketChannel socketChannel;
private volatile boolean stop; public TimeClientHandle(String host,int port){
this.host = host == null ? "127.0.0.1" : host;
this.port = port;
try{
selector = Selector.open();
socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
System.exit(1);
}
} public void run() {
//发送请求连接
try{
doConnect();
}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
System.exit(1);
}
while(!stop){
try{
selector.select(1000);
Set<SelectionKey> selectedKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> it = selectedKeys.iterator();
SelectionKey key = null;
//当有就绪的Channel时,执行handleInput(key)方法
while(it.hasNext()){
key = it.next();
it.remove();
try{
handleInput(key);
}catch(Exception e){
if(key != null){
key.cancel();
if(key.channel() != null){
key.channel().close();
}
}
}
}
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
System.exit(1);
}
} //多路复用器关闭后,所有注册在上面的Channel和Pipe等资源都会被自动去注册并关闭,所以不需要重复释放资源
if(selector != null){
try{
selector.close();
}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
} } private void handleInput(SelectionKey key) throws IOException{
if(key.isValid()){
SocketChannel sc = (SocketChannel)key.channel();
//判断是否连接成功
if(key.isConnectable()){
if(sc.finishConnect()){
sc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}else{
System.exit(1);
}
} if(key.isReadable()){
ByteBuffer readBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int readBytes = sc.read(readBuffer);
if(readBytes > 0){
readBuffer.flip();
byte[] bytes = new byte[readBuffer.remaining()];
readBuffer.get(bytes);
String body = new String(bytes,"UTF-8");
System.out.println("Now is :" + body);
this.stop = true;
}else if(readBytes < 0){
//对端链路关闭
key.cancel();
sc.close();
}else{
; //读到0字节,忽略
}
}
}
} private void doConnect() throws IOException{
//如果直接连接成功,则注册到多路复用器上,发送请求信息,读应答
if(socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress(host,port))){
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
doWrite(socketChannel);
}else{
//说明服务器没有返回TCP祸首应答消息,但这并不代表连接失败,当服务器返回TCP syn-ack消息后,Selector就能够轮训这个SocketChannel处于连接就绪状态
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT);
}
} private void doWrite(SocketChannel sc) throws IOException{
byte[] req = "QUERY TIME ORDER".getBytes();
ByteBuffer writeBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(req.length);
writeBuffer.put(req);
writeBuffer.flip();
sc.write(writeBuffer);
if(!writeBuffer.hasRemaining()){
System.out.println("Send order 2 server succeed.");
}
} }
TimeServer:
package nio;
import java.io.IOException;
public class TimeServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
int port = 8080;
if(args != null && args.length >0){
try{
port = Integer.valueOf(args[0]);
}catch(NumberFormatException e){
//采用默认值
}
}
//多路复用类,是一个独立的线程,负责轮训多路复用器Selctor,处理多个客户端的并发接入。
MultiplexerTimeServer timeServer = new MultiplexerTimeServer(port);
new Thread(timeServer,"NIO-MultiplexerTimeServer-001").start();
}
}
MultiplexerTimeServer:
package nio; import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Iterator;
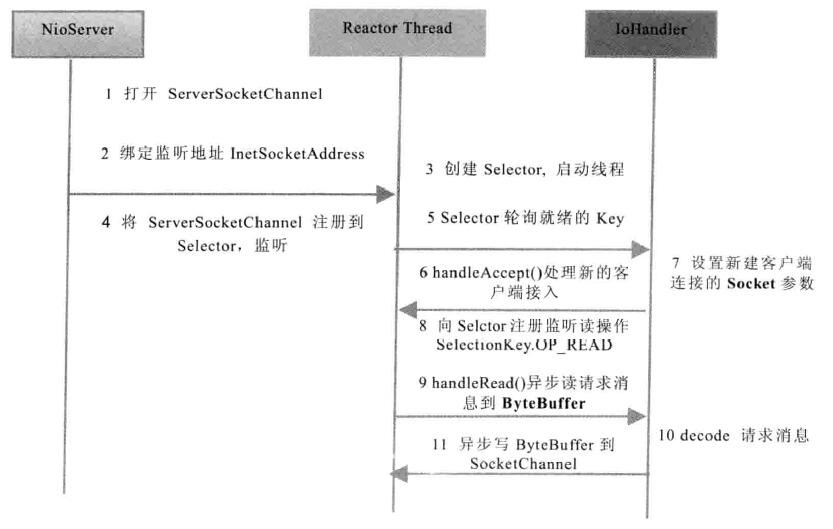
import java.util.Set; public class MultiplexerTimeServer implements Runnable { private Selector selector; private ServerSocketChannel servChannel; private volatile boolean stop; public MultiplexerTimeServer(int port){
try{ selector = Selector.open();
servChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//将ServerSocketChannel 设置为异步非阻塞,backlog设置为1024
servChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(port),1024);
//将ServerSocket Channel注册到Selector,监听SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT操作位,如果初始化失败,则退出
servChannel.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
System.out.println("The time server is start in port:" + port);
}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
System.exit(1);
}
} public void stop(){
this.stop = true;
} public void run() {
while(!stop){
try{
//遍历时间设置1秒,每隔一秒唤醒一次,当有处于就绪状态的Channel时,selector将返回就绪状态的Channel的SelectionKey集合
selector.select(1000);
Set<SelectionKey> selectedKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> it = selectedKeys.iterator();
SelectionKey key = null;
//通过对就绪状态的Channel集合进行迭代,可以进行网络的异步读写操作
while(it.hasNext()){
key = it.next();
it.remove();
try{
handleInput(key);
}catch(Exception e){
if(key != null){
key.cancel();
if(key.channel() != null){
key.channel().close();
}
}
}
}
}catch(Throwable t){
t.printStackTrace();
}
} //多路复用器关闭后,所有注册在上面的Channel和Pipe等资源都会被自动去注册并关闭,所以不需要重复释放资源
if(selector != null){
try{
selector.close();
}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
} //处理新接入的请求消息
private void handleInput(SelectionKey key) throws IOException{
if(key.isValid()){ //根据SelectionKey的操作位进行判断即可获知网络事件的类型,通过accept接收客户端的连接请求并创建SocketChannel实例,完成上述操作相当于
//完成了TCP的三次握手,TCP物理链路正式建立
if(key.isAcceptable()){
ServerSocketChannel ssc = (ServerSocketChannel)key.channel();
SocketChannel sc = ssc.accept();
sc.configureBlocking(false);
//Add the new connection tothe selector
sc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
} if(key.isReadable()){
//Read the data SocketChannel sc = (SocketChannel)key.channel();
ByteBuffer readBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int readBytes = sc.read(readBuffer);
if(readBytes > 0){
//将缓冲区当前的limit设置为position,position设置为0,用于后续对缓冲区的读取操作
readBuffer.flip();
byte[] bytes = new byte[readBuffer.remaining()];
readBuffer.get(bytes);
String body = new String(bytes,"UTF-8");
System.out.println("The time server receive order: + body");
String currentTime = "QUERY TIME ORDER".equalsIgnoreCase(body) ? new java.util.Date(System.currentTimeMillis()).toString() : "BAD ORDER";
doWrite(sc,currentTime);
}else if(readBytes < 0){
//对端链路关闭
key.cancel();
sc.close();
}else{
; //读到0字节,忽略
}
}
}
} private void doWrite(SocketChannel channel,String response) throws IOException{
if(response != null && response.trim().length() >0){
byte[] bytes = response.getBytes();
ByteBuffer writeBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(bytes.length);
writeBuffer.put(bytes);
writeBuffer.flip();
channel.write(writeBuffer);
}
}
}
NIO源码阅读的更多相关文章
- Spark源码阅读之存储体系--存储体系概述与shuffle服务
一.概述 根据<深入理解Spark:核心思想与源码分析>一书,结合最新的spark源代码master分支进行源码阅读,对新版本的代码加上自己的一些理解,如有错误,希望指出. 1.块管理器B ...
- JDK源码阅读(1)_简介+ java.io
1.简介 针对这一个版块,主要做一个java8的源码阅读笔记.会对一些在javaWeb中应用比较广泛的java包进行精读,附上注释.对于容易混淆的知识点给出相应的对比分析. 精读的源码顺序主要如下: ...
- JDK 1.8 源码阅读和理解
根据 一篇文章教会你,如何做到招聘要求中的“要有扎实的Java基础” 的指引,决定开始阅读下JDK源码. 本文将作为源码阅读总纲 一.精读部分 java.io java.lang java.util ...
- Mina源码阅读笔记(四)—Mina的连接IoConnector2
接着Mina源码阅读笔记(四)-Mina的连接IoConnector1,,我们继续: AbstractIoAcceptor: 001 package org.apache.mina.core.rewr ...
- netty(一)---服务端源码阅读
NIO Select 知识 select 示例代码 : //创建 channel 并设置为非阻塞 ServerSocketChannel serverChannel = ServerSocketCha ...
- 利用IDEA搭建JDK源码阅读环境
利用IDEA搭建JDK源码阅读环境 首先新建一个java基础项目 基础目录 source 源码 test 测试源码和入口 准备JDK源码 下图框起来的路径就是jdk的储存位置 打开jdk目录,找到sr ...
- JDK源码阅读-ByteBuffer
本文转载自JDK源码阅读-ByteBuffer 导语 Buffer是Java NIO中对于缓冲区的封装.在Java BIO中,所有的读写API,都是直接使用byte数组作为缓冲区的,简单直接.但是在J ...
- JDK源码阅读-FileDescriptor
本文转载自JDK源码阅读-FileDescriptor 导语 操作系统使用文件描述符来指代一个打开的文件,对文件的读写操作,都需要文件描述符作为参数.Java虽然在设计上使用了抽象程度更高的流来作为文 ...
- JDK源码阅读-DirectByteBuffer
本文转载自JDK源码阅读-DirectByteBuffer 导语 在文章JDK源码阅读-ByteBuffer中,我们学习了ByteBuffer的设计.但是他是一个抽象类,真正的实现分为两类:HeapB ...
随机推荐
- MySQL的左连接、右连接和全连接的实现
表student:+----+-----------+------+| id | name | age |+----+-----------+------+| 1 | Jim | 18 || 2 | ...
- java 集合:实现
集合本来就是为了方便开发的,实现了一些基本数据结构,一般来说数据结构有两种物理的实现:数组和链表.数组是连续的空间,链表是不连续的.基于这两种又扩展了很多的数据结构.队列,栈,hash表,树. 在ja ...
- jsp编程
jsp编程 jsp的实质和工作原理 注释 九大内置对象 jsp文件的结构解析 脚本语法 jsp指令 jsp动作元素 EL表达式 jsp的实质和工作原理: jsp (全称:Java Server Pa ...
- discuz不能发表投票、附件上传等
如何开启和发表投票主题 本教程主要讲述如何开启和发表投票的帖子.具体的操作如下: 1.论坛后台 => 用户 => 用户组 => 详情 => 特殊主题 => 允许发起投票设 ...
- RTSP协议媒体数据发包相关的细节
最近完成了一RTSP代理网关,这是第二次开发做RTSP协议相关的开发工作了,相比11年的简单粗糙的版本,这次在底层TCP/IP通讯和RTSP协议上都有了一些新的积累,这里记录一下.基本的RTSP协议交 ...
- js 获取当前焦点所在的元素、给元素和input控件添加键盘监听事件、添加页面级的键盘监听事件
页面级的键盘监听事件 document.onkeydown = function (event) { var e = event || window.event || arguments.callee ...
- ImageLoader框架的使用、调用系统相册显示图片并裁剪显示、保存图片的两种方式
ImageLoader虽然说是一个相对于比较老的一个框架了 ,但是总的来说,还是比较好用的,今天我就总结了一下它的用法.还有调用系统相册并裁剪,以及,通过sharedpreference和文件存储来保 ...
- oracle执行cmd的实现方法
网络上找到的在sqlplus中执行cmd的一些命令,主要有四种方法,这边都做了一下测试,这里做一下记录: 测试环境:window2003+Oracle 11.2.0.1.0 第一种方法: 最简单的执行 ...
- hdu 1010 深搜+剪枝
深度搜索 剪枝 还不是很理解 贴上众神代码 //http://blog.csdn.net/vsooda/article/details/7884772#include<iostream> ...
- sql中的跨库查询
在sql查询时,需要关联2个服务器上的不同数据库,只需要在所需查询的表名前加上服务器地址即可. 例如:在 192.168.0.15,8020的db110库 和 192.168.0.150,8082的d ...
