YARN :Architecture
Apache Hadoop NextGen MapReduce (YARN)
MapReduce has undergone a complete overhaul in hadoop-0.23 and we now have, what we call, MapReduce 2.0 (MRv2) or YARN.
The fundamental idea of MRv2 is to split up the two major functionalities of the JobTracker, resource management and job scheduling/monitoring, into separate daemons. The idea is to have a global ResourceManager (RM) and per-application ApplicationMaster (AM). An application is either a single job in the classical sense of Map-Reduce jobs or a DAG of jobs.
The ResourceManager and per-node slave, the NodeManager (NM), form the data-computation framework. The ResourceManager is the ultimate authority that arbitrates resources among all the applications in the system.
The per-application ApplicationMaster is, in effect, a framework specific library and is tasked with negotiating resources from the ResourceManager and working with the NodeManager(s) to execute and monitor the tasks.
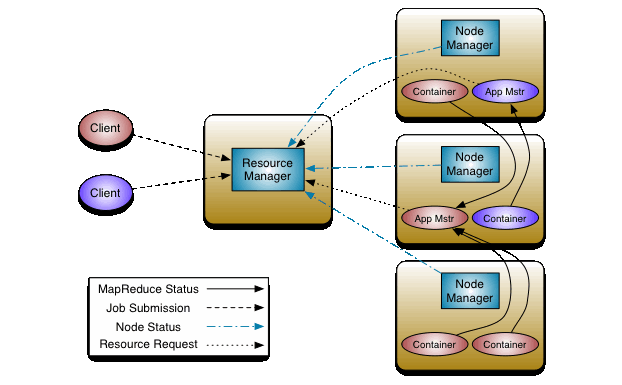
The ResourceManager has two main components: Scheduler and ApplicationsManager.
The Scheduler is responsible for allocating resources to the various running applications subject to familiar constraints of capacities, queues etc. The Scheduler is pure scheduler in the sense that it performs no monitoring or tracking of status for the application. Also, it offers no guarantees about restarting failed tasks either due to application failure or hardware failures. The Scheduler performs its scheduling function based the resource requirements of the applications; it does so based on the abstract notion of a resource Container which incorporates elements such as memory, cpu, disk, network etc. In the first version, only memory is supported.
The Scheduler has a pluggable policy plug-in, which is responsible for partitioning the cluster resources among the various queues, applications etc. The current Map-Reduce schedulers such as the CapacityScheduler and the FairScheduler would be some examples of the plug-in.
The CapacityScheduler supports hierarchical queues to allow for more predictable sharing of cluster resources
The ApplicationsManager is responsible for accepting job-submissions, negotiating the first container for executing the application specific ApplicationMaster and provides the service for restarting the ApplicationMaster container on failure.
The NodeManager is the per-machine framework agent who is responsible for containers, monitoring their resource usage (cpu, memory, disk, network) and reporting the same to the ResourceManager/Scheduler.
The per-application ApplicationMaster has the responsibility of negotiating appropriate resource containers from the Scheduler, tracking their status and monitoring for progress.
MRV2 maintains API compatibility with previous stable release (hadoop-1.x). This means that all Map-Reduce jobs should still run unchanged on top of MRv2 with just a recompile.
from:http://hadoop.apache.org/docs/current/hadoop-yarn/hadoop-yarn-site/YARN.html
YARN :Architecture的更多相关文章
- Storm on Yarn :原理分析+平台搭建
Storm on YARN: Storm on YARN被视为大规模Web应用与传统企业应用之间的桥梁.它将Storm事件处理平台与YARN(Yet Another Resource Negotiat ...
- [BigData - Hadoop - YARN] YARN:下一代 Hadoop 计算平台
Apache Hadoop 是最流行的大数据处理工具之一.它多年来被许多公司成功部署在生产中.尽管 Hadoop 被视为可靠的.可扩展的.富有成本效益的解决方案,但大型开发人员社区仍在不断改进它.最终 ...
- Apache Hadoop YARN: 背景及概述
从2012年8月开始Apache Hadoop YARN(YARN = Yet Another Resource Negotiator)成了Apache Hadoop的一项子工程.自此Apache H ...
- Spark on Yarn:任务提交参数配置
当在YARN上运行Spark作业,每个Spark executor作为一个YARN容器运行.Spark可以使得多个Tasks在同一个容器里面运行. 以下参数配置为例子: spark-submit -- ...
- Spark On Yarn:提交Spark应用程序到Yarn
转载自:http://lxw1234.com/archives/2015/07/416.htm 关键字:Spark On Yarn.Spark Yarn Cluster.Spark Yarn Clie ...
- 【原创】大数据基础之Spark(2)Spark on Yarn:container memory allocation容器内存分配
spark 2.1.1 最近spark任务(spark on yarn)有一个报错 Diagnostics: Container [pid=5901,containerID=container_154 ...
- AeroSpike踩坑手记1:Architecture of a Real Time Operational DBMS论文导读
又开了一个新的坑,笔者工作之后维护着一个 NoSQL 数据库.而笔者维护的数据库正是基于社区版本的 Aerospike打造而来.所以这个踩坑系列的文章属于工作总结型的内容,会将使用开发 Aerospi ...
- 第1节 yarn:15、关于yarn中常用的参数设置
第一个参数:container分配最小内存 yarn.scheduler.minimum-allocation-mb 1024 给应用程序container分配的最小内存 第二个参数:co ...
- 第1节 yarn:14、yarn集群当中的三种调度器
yarn当中的调度器介绍: 第一种调度器:FIFO Scheduler (队列调度器) 把应用按提交的顺序排成一个队列,这是一个先进先出队列,在进行资源分配的时候,先给队列中最头上的应用进行分配资源 ...
随机推荐
- Anyconnect的VPN环境部署(2)-在Linux客户机上连接Anyconnect
由于之前已经在机房IDC安装了Anyconnect的VPN服务环境(参考:Anyconnect的VPN环境部署(1)-OpenConnect server(ocserv)服务安装)今天介绍下在linu ...
- 【MVC版本】MVC3、MVC4之MODEL验证大比拼
1.密码验证 MVC3 [System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Compare("Password", ErrorMessage = &quo ...
- 数据库 SQL语法二
聚合函数 -SUM([DISTINCT] FIELDNAME) 求指定列之和,[DISTINCT]选项表示剔除重复记录 例如:SELECT SUM(age) FROM TABLE1; SELECT S ...
- C#命名空间的嵌套
namespace abc.e.f//等价于下面分层嵌套的写法.且这种写法不管命名空间abc有没有定义过,也不管命名空间e有没有定义过 { class ctest { public void func ...
- 数据库mark
LOAD DATA INFILE 'I:\QQpwd\\1.txt' IGNORE INTO TABLE sgk.top1 FIELDS TERMINATED BY '----' OPTIONALLY ...
- 细数Javascript技术栈中的四种依赖注入
作为面向对象编程中实现控制反转(Inversion of Control,下文称IoC)最常见的技术手段之一,依赖注入(Dependency Injection,下文称DI)可谓在OOP编程中大行其道 ...
- TextBoxFor控件的扩展---Bootstrap在mvc上的应用
TextBoxFor控件的问题: 1:自带了样式,再用bootstrap样式会有冲突. 2:要加水印,js事件,限制输入长度比较麻烦. 因此需要对textboxfor控件进行扩展. 目标: 1:能使用 ...
- C#访问Azure的资源
官方参考资料在这里:https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/azure/dn722415.aspx,本文放一些重点及遇到的坑的解决办法. 身份验证 不是说,我 ...
- Collection中Set集合在应用中常见的方法和注意点
Set集合 : 元素无序的,元素不允许重复. ---->HashSet : 存值方式使用哈希表来存值的. 原理 : 如果HashSet中存放对象 ...
- java知识点、重点知识点
重点章节: 面对对象章节 重点知识点: Lambda表达式 数据:内存-->数据库 知识点一拦: 类.面向对象.对象.封装.继承.多态.消息.UML建模.数据类型(基本类型.引用类型).数据类型 ...
