JavaScript Event Delegation, and event.target vs. event.currentTarget
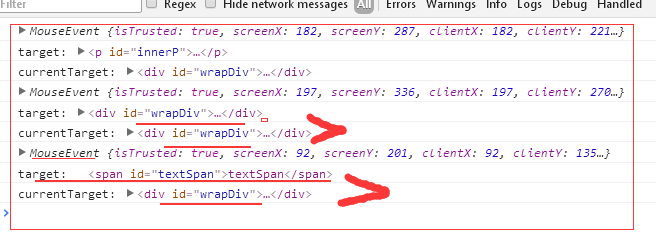
In this case, at the time you call console.log(e), there's a DOM element in the currentTarget property. But sometime later, that property is reset to null for some reason. When you expand the event object, that's what you see.
你的情况是,当调用console.log(e)时,currentTarget属性是有值的,但是过后这个值就被重置为null了。所以当你展开事件对象,看到的就是null。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en"> <head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style type="text/css">
#wrapDiv,
#innerP,
#textSpan {
margin: 5px;
padding: 5px;
box-sizing: border-box;
cursor: default;
} #wrapDiv {
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
border: indianred 3px solid;
} #innerP {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
border: hotpink 3px solid;
} #textSpan {
display: block;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
border: orange 3px solid;
}
</style>
</head> <body>
<div id="wrapDiv">wrapDiv
<p id="innerP">innerP
<span id="textSpan">textSpan</span>
</p>
</div>
<script>
var div = document.getElementById('wrapDiv');
var p = document.getElementById('innerP');
var span = document.getElementById('textSpan'); div.onclick = function(ev){
console.log(ev); //
console.log("target:", ev.target);
console.log("currentTarget:", ev.currentTarget);
}
</script>
</body> </html>
-----------------------------------------------
Event delegation is a popular methodology in JavaScript. It allows us to add an event listener to one parent, and avoid to add many event listeners to specific nodes. We can demonstrate this technique with simple example.
Let’s say we have a list with thousands of items:
<body>
<div id="container">
<ul id="list">
<li><a href="#">Item 1</a></li>
<li><a href="#">Item 2</a></li>
<li><a href="#">Item 3</a></li>
<li><a href="#">Item 4</a></li>
..................................
<li><a href="#">Item 1000</a></li>
</ul>
</div>
</body>With such number of items, it would be a nightmare to loop through every <a> element on the page, adding an event listener one after one. Moreover, it may “freeze” the page when JavaScript is trying to create them all.
So here comes the event delegation: When the event bubbles up to the body element, we can check the element that triggered the event, using the event object’s target property.
document.addEventListener("click", function(e) {
if(e.target && e.target.nodeName == "A") {
console.log("List item ", e.target.textContent, " was clicked!");
}
});
// When we click the 2nd item, the page prints out:
"List item Item 2 was clicked!"
target vs. currentTarget
Since we already talked about the event.target property, there is another property called event.currentTarget in JavaScript event. It can be very confused by just reading about them on JavaScript documentation.
As we’ve seen from the last example, when we clicked the a element, clickevent bubbles up to <body> node of the document like below:
<a> → <li> → <ul> → <div> → <body>
Let’s add one more line of code and prints out what the e.currentTarget is from the example we used above:
document.addEventListener(“click”, function(e) {
if(e.target && e.target.nodeName == “A”) {
console.log(“List item “, e.target.textContent, “ was clicked!”); // "List item Item 2 was clicked!"
}
console.log(e.currentTarget); // #document
});
It prints out “document” since we attached current event listener to the document while e.target refers to <a> which we clicked.
We can also look at one more example to see the differences between target and currentTarget. This time, we add the event listener to the <ul>:
document.getElementById(“list”).addEventListener(“click”, function(e) {
console.log(e.currentTarget); //<ul><li>...</li><ul>
console.log(e.target); //<a href="#">Item 2</a>
);
Again, the currentTarget refers to the element that the event listener directly attached to while the target still refers to the specific <a> we clicked.
With these two properties target and currentTarget, we can easily manipulate the node when the event gets triggered, as well as the node the event is attached to.
JavaScript Event Delegation, and event.target vs. event.currentTarget的更多相关文章
- Event对象中的target属性和currentTarget属性的区别
先上结论: Event.target:触发事件的元素: Event.currentTarget:事件绑定的元素: 通过下面的例子来理解这两个属性的区别: 使用Event.target属性的例子:(我在 ...
- JavaScript Interview Questions: Event Delegation and This
David Posin helps you land that next programming position by understanding important JavaScript fund ...
- javascript 事件委托 event delegation
事件委托 event delegation 一.概念: 假设我们有很多个子元素,每个元素被点击时都会触发相应事件,普通的做法是给每个子元素添加一个事件监听. 而,事件委托则是给它们的父元素添加一个事件 ...
- javascript事件代理(Event Delegation)
看了几篇文章,放上来供参考 司徒正美的文章,Event Delegation Made Easy --------------------------------------------------- ...
- JavaScript------事件委托(event delegation)
简单的说,事件委托(event delegation)是在DOM上层(也就是在触发事件的元素的父元素上)定义事件的处理程序,而不是定义在触发事件的元素本身上. 首先我们来举这样一个例子:我有N个li元 ...
- window.event.srcElement与window.event.target 触发事件的元素 触发事件对象的获取,window.event与时间函数参数的event是同一个 事件对象
判断事件触发的元素: var tag = window.event.target || window.event.srcElement; if (tag.tagName.toLowerC ...
- JS:event对象下的target属性和取消冒泡事件
1.target 通过获取DOM元素 var box = document.getElementById("box"); document.box.onclick = functi ...
- 【前端】event.target 和 event.currentTarget 的区别
event.target 和 event.currentTarget 的区别 举例说明: <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <tit ...
- javascript运行模式:并发模型 与Event Loop
看了阮一峰老师的JavaScript 运行机制详解:再谈Event Loop和[朴灵评注]的文章,查阅网上相关资料,把自己对javascript运行模式和EVENT loop的理解整理下,不一定对,日 ...
随机推荐
- python实现括号匹配
1.用一个栈[python中可以用List]就可以解决,时间和空间复杂度都是O(n) # -*- coding: utf8 -*- # 符号表 SYMBOLS = {'}': '{', ']': '[ ...
- python 列表的浅拷贝和深拷贝
转自:https://www.cnblogs.com/laolibk/p/7821369.html 浅拷贝 shallow copy 和深拷贝 deep copy list.copy() 浅拷贝:复制 ...
- 机器学习之路: python 支持向量机 LinearSVC 手写字体识别
使用python3 学习sklearn中支持向量机api的使用 可以来到我的git下载源代码:https://github.com/linyi0604/MachineLearning # 导入手写字体 ...
- [POI2015]Pieczęć
[POI2015]Pieczęć 题目大意: 一张\(n\times m(n,m\le1000)\)的方格纸,有些格子需要印成黑色,剩下的格子需要保留白色. 你有一个\(a\times b(a,b\l ...
- hdu 1973 bfs+素数判断
题意:给出两个四位数,现要改变第一个数中的个,十,百,千位当中的一个数使它最终变成第二个数,要求这过程中形成的数是素数,问最少的步骤题解:素数筛选+bfsSample Input31033 81791 ...
- Codeforces Round #356 (Div. 2) C. Bear and Prime 100 水题
C. Bear and Prime 100 题目连接: http://www.codeforces.com/contest/680/problem/C Description This is an i ...
- ZOJ 3626 Treasure Hunt I 树上DP
E - Treasure Hunt I Time Limit:2000MS Memory Limit:65536KB Description Akiba is a dangerous country ...
- Vue 组件 data为什么是函数?
在创建或注册模板的时候,传入一个data属性作为用来绑定的数据.但是在组件中,data必须是一个函数,而不能直接把一个对象赋值给它. Vue.component('my-component', { t ...
- DIOCP
DIOCP GITHUB: https://github.com/ymofen/diocp-v5.git diocp5====== ## 快速开始 从那里得到: git更新(推荐同步更新) 1.htt ...
- 【xshell】xshell设置快捷键 设置Ctrl+C Ctrl+V快捷键为复制粘贴
在使用xshell的时候,总是不能顺手的进行复制粘贴的操作. 那能不能设置xhsell的快捷键呢? 点击工具--->选项---> 选择 键盘和鼠标 选项卡--->点击编辑----&g ...
