SpringMVC DispatcherServlet-------视图渲染过程
整个spring mvc的架构如下图所示:
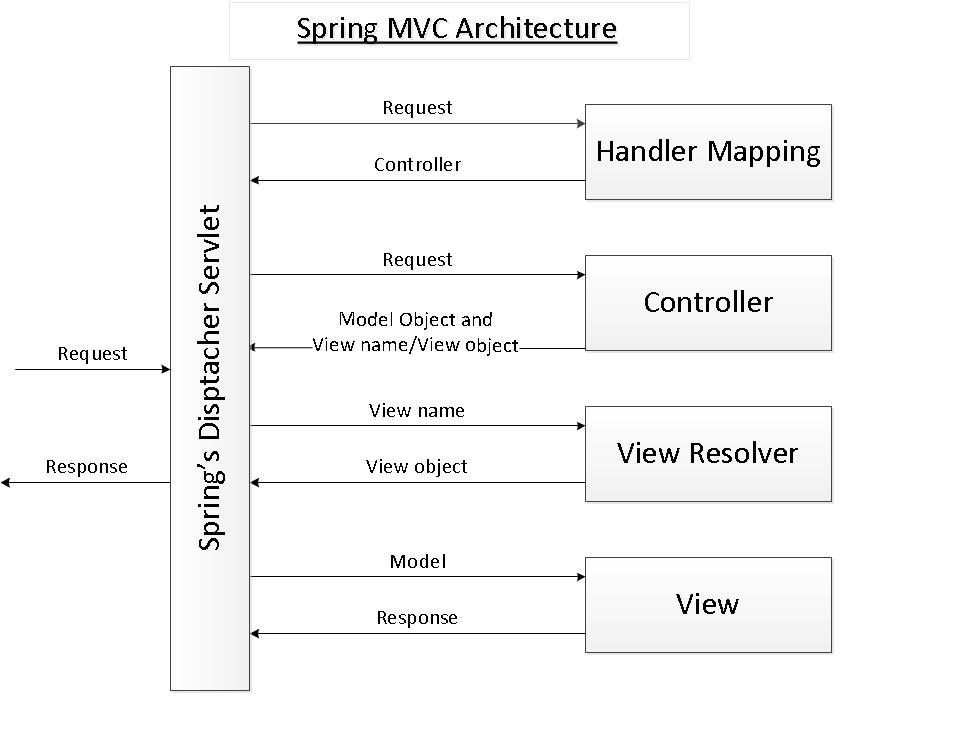
现在来讲解DispatcherServletDispatcherServlet的最后一步:视图渲染。视图渲染的过程是在获取到ModelAndView后的过程。
视图渲染的过程:
DispatcherServlet.java
doService()--->doDispatch()--->processDispatchResult()--->render()
processDispatchResult():主要处理异常、请求状态及触发请求完成事件,图的渲染工作交给了render().
render()渲染过程如下:
1. 判断ModelAndView中view是否为view name,没有获取其实例对象:如果是根据name,如果是则需要调用resolveViewName从视图解析器获取对应的视图(View)对象;否则ModelAndView中使用getview方法获取view对象。
2. 然后调用view的render()方法。
代码如下:
/**
* Render the given ModelAndView.
* <p>This is the last stage in handling a request. It may involve resolving the view by name.
* @param mv the ModelAndView to render
* @param request current HTTP servlet request
* @param response current HTTP servlet response
* @throws ServletException if view is missing or cannot be resolved
* @throws Exception if there's a problem rendering the view
*/
protected void render(ModelAndView mv, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
// Determine locale for request and apply it to the response.
Locale locale = this.localeResolver.resolveLocale(request);
response.setLocale(locale); View view;
if (mv.isReference()) {
// We need to resolve the view name.
view = resolveViewName(mv.getViewName(), mv.getModelInternal(), locale, request);
if (view == null) {
throw new ServletException("Could not resolve view with name '" + mv.getViewName() +
"' in servlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
}
else {
// No need to lookup: the ModelAndView object contains the actual View object.
view = mv.getView();
if (view == null) {
throw new ServletException("ModelAndView [" + mv + "] neither contains a view name nor a " +
"View object in servlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
} // Delegate to the View object for rendering.
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Rendering view [" + view + "] in DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
try {
view.render(mv.getModelInternal(), request, response);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Error rendering view [" + view + "] in DispatcherServlet with name '" +
getServletName() + "'", ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
那么view 是如何渲染的?我们来看看view的定义:
org.springframework.web.servlet
Interface View All Known Subinterfaces:
SmartView
All Known Implementing Classes:
AbstractAtomFeedView, AbstractExcelView, AbstractFeedView, AbstractJasperReportsSingleFormatView, AbstractJasperReportsView, AbstractJExcelView, AbstractPdfStamperView, AbstractPdfView, AbstractRssFeedView, AbstractTemplateView, AbstractUrlBasedView, AbstractView, ConfigurableJasperReportsView, FreeMarkerView, InternalResourceView, JasperReportsCsvView, JasperReportsHtmlView, JasperReportsMultiFormatView, JasperReportsPdfView, JasperReportsXlsView, JstlView, MappingJackson2JsonView, MappingJacksonJsonView, MarshallingView, RedirectView, TilesView, TilesView, VelocityLayoutView, VelocityToolboxView, VelocityView, XsltView -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- public interface ViewMVC View for a web interaction. Implementations are responsible for rendering content, and exposing the model. A single view exposes multiple model attributes.
This class and the MVC approach associated with it is discussed in Chapter 12 of Expert One-On-One J2EE Design and Development by Rod Johnson (Wrox, 2002). View implementations may differ widely. An obvious implementation would be JSP-based. Other implementations might be XSLT-based, or use an HTML generation library. This interface is designed to avoid restricting the range of possible implementations. Views should be beans. They are likely to be instantiated as beans by a ViewResolver. As this interface is stateless, view implementations should be thread-safe.
spring提供了如此多的视图,那么肯定的是也会有很多视图解析器:
org.springframework.web.servlet
Interface ViewResolver All Known Implementing Classes:
AbstractCachingViewResolver, AbstractTemplateViewResolver, BeanNameViewResolver, ContentNegotiatingViewResolver, FreeMarkerViewResolver, InternalResourceViewResolver, JasperReportsViewResolver, ResourceBundleViewResolver, TilesViewResolver, TilesViewResolver, UrlBasedViewResolver, VelocityLayoutViewResolver, VelocityViewResolver, XmlViewResolver, XsltViewResolver
Functional Interface:
This is a functional interface and can therefore be used as the assignment target for a lambda expression or method reference. -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- public interface ViewResolverInterface to be implemented by objects that can resolve views by name.
View state doesn't change during the running of the application, so implementations are free to cache views. Implementations are encouraged to support internationalization, i.e. localized view resolution.
其中,针对JSP提供的InternalResourceViewResolver与InternalResourceView。
我们先看一下view的render方法是什么样子的?
根据InternalResourceView的继承关系:
- org.springframework.web.servlet.view.AbstractView
- org.springframework.web.servlet.view.AbstractUrlBasedView
- org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceView
- org.springframework.web.servlet.view.AbstractUrlBasedView
最终找到render方法在AbstractView中,如下代码所示:
/**
* Prepares the view given the specified model, merging it with static
* attributes and a RequestContext attribute, if necessary.
* Delegates to renderMergedOutputModel for the actual rendering.
* @see #renderMergedOutputModel
*/
@Override
public void render(Map<String, ?> model, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Rendering view with name '" + this.beanName + "' with model " + model +
" and static attributes " + this.staticAttributes);
} Map<String, Object> mergedModel = createMergedOutputModel(model, request, response);
prepareResponse(request, response);
renderMergedOutputModel(mergedModel, request, response);
}
流程如下:
创建一个动态值和静态属性的map;
设置response 报文头;
把渲染view的工作放到renderMergedOutputModel()实现中,这个留给InternalResourceView来实现。
我们看看这个实现:
/**
* Render the internal resource given the specified model.
* This includes setting the model as request attributes.
*/
@Override
protected void renderMergedOutputModel(
Map<String, Object> model, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { // Determine which request handle to expose to the RequestDispatcher.
HttpServletRequest requestToExpose = getRequestToExpose(request); // Expose the model object as request attributes.
exposeModelAsRequestAttributes(model, requestToExpose); // Expose helpers as request attributes, if any.
exposeHelpers(requestToExpose); // Determine the path for the request dispatcher.
String dispatcherPath = prepareForRendering(requestToExpose, response); // Obtain a RequestDispatcher for the target resource (typically a JSP).
RequestDispatcher rd = getRequestDispatcher(requestToExpose, dispatcherPath);
if (rd == null) {
throw new ServletException("Could not get RequestDispatcher for [" + getUrl() +
"]: Check that the corresponding file exists within your web application archive!");
} // If already included or response already committed, perform include, else forward.
if (useInclude(requestToExpose, response)) {
response.setContentType(getContentType());
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Including resource [" + getUrl() + "] in InternalResourceView '" + getBeanName() + "'");
}
rd.include(requestToExpose, response);
} else {
// Note: The forwarded resource is supposed to determine the content type itself.
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Forwarding to resource [" + getUrl() + "] in InternalResourceView '" + getBeanName() + "'");
}
rd.forward(requestToExpose, response);
}
}
流程可以归纳为以下几步:
1. 包装request,供RequestDispatcher来使用;
2. 将map中的属性和值作为属性放入包装的request;
3. 将不同实现类的helper放入包装的request中;
4. 渲染前的准备,确定request dispatcher要跳向(或者inclue)的路径
5. 获取request dispatcher。
6. 根据request中是否包含include uri属性来确实是forward或者include方法。
forward是跳向服务器的servlet, JSP文件, 或者 HTML文件。
Includes the content of a resource (servlet, JSP page,HTML file) in the response.
注意,在上述流程中出现了RequestDispatcher,那么这类的作用是什么呢?
getRequestDispatcher RequestDispatcher getRequestDispatcher(java.lang.String path)
Returns a RequestDispatcher object that acts as a wrapper for the resource located at the given path. A RequestDispatcher object can be used to forward a request to the resource or to include the resource in a response. The resource can be dynamic or static.
The pathname specified may be relative, although it cannot extend outside the current servlet context. If the path begins with a "/" it is interpreted as relative to the current context root. This method returns null if the servlet container cannot return a RequestDispatcher. The difference between this method and ServletContext#getRequestDispatcher is that this method can take a relative path.
简洁的来说,
1. RequestDispatcher 是一个包装器,它将制定路径的(静态或者动态)资源包装起来。RequestDispatcher 可以用于将一个请求分发给指定的资源或者包裹响应报文中的资源。
2. RequestDispatcher 的获取,有这种形式,一种使用ServletRequest.getRequestDispatcher(java.lang.String path). 另一种是servletContext.getRequestDispatcher(java.lang.String path);不同之处在于:前面的方法支持相对路径,以'/'作为当前上下文的跟路径;后一种不支持后一种不支持相对路径。
可以看到视图的渲染过程是把model包装成map形式通过request的属性带到服务器端。
SpringMVC DispatcherServlet-------视图渲染过程的更多相关文章
- spring mvc DispatcherServlet详解之四---视图渲染过程
整个spring mvc的架构如下图所示: 现在来讲解DispatcherServletDispatcherServlet的最后一步:视图渲染.视图渲染的过程是在获取到ModelAndView后的过程 ...
- SpringMVC核心——视图渲染(包含视图解析)问题
一.本来想说的是返回值处理问题,但在 SpringMVC 中,返回值处理问题的核心就是视图渲染.所以这里标题叫视图渲染问题. 本来想在上一篇文章中对视图解析进行说明的,但是通过源码发现,它应该算到视图 ...
- 微信小程序教学第四章第二节(含视频):小程序中级实战教程:详情-视图渲染
§ 详情 - 数据渲染 本文配套视频地址: https://v.qq.com/x/page/x055550lrvd.html 开始前请把 ch4-2 分支中的 code/ 目录导入微信开发工具 这一节 ...
- SpringMVC之四:渲染Web视图
理解视图解析 在前面的例子中,我们看到控制器返回的都是一个逻辑视图的名称,然后把这个逻辑视图名称交给view resolver,然后返回渲染后的 html 页面给 client. 将控制器中请求处理的 ...
- Spring框架系列(13) - SpringMVC实现原理之DispatcherServlet的初始化过程
前文我们有了IOC的源码基础以及SpringMVC的基础,我们便可以进一步深入理解SpringMVC主要实现原理,包含DispatcherServlet的初始化过程和DispatcherServlet ...
- Yii2.0源码阅读-视图(View)渲染过程
之前的文章我们根据源码的分析,弄清了Yii如何处理一次请求,以及根据解析的路由如何调用控制器中的action,那接下来好奇的可能就是,我在控制器action中执行了return $this->r ...
- (二)SpringMVC之执行的过程
(DispatcherServlet在Spring当中充当一个前端控制器的角色,它的核心功能是分发请求.请求会被分发给对应处理的Java类,Spring MVC中称为Handle.) ① 用户把请 ...
- 学习SpringMVC——说说视图解析器
各位前排的,后排的,都不要走,咱趁热打铁,就这一股劲我们今天来说说spring mvc的视图解析器(不要抢,都有位子~~~) 相信大家在昨天那篇如何获取请求参数篇中都已经领略到了spring mvc注 ...
- SpringMVC重定向视图RedirectView小分析
目录 前言 RedirectView介绍 实例讲解 总结 前言 SpringMVC是目前主流的Web MVC框架之一. 如果有同学对它不熟悉,那么请参考它的入门blog:http://www.cnbl ...
随机推荐
- 《Redis设计与实现》阅读笔记(二)--简单动态字符串
简单动态字符串 Redis只在一些无需对字符串进行修改的地方使用C字符串,大部分时候使用简单动态字符串(simple dynamic string, SDS),字符串的抽象类型.二进制安全,可以存放任 ...
- mysql安装(rpm)
mysql安装(rpm) 1.卸载系统自带的 mariadb-lib [root@centos-linux ~]# rpm -qa|grep mariadb mariadb-libs-5.5.44-2 ...
- 基于Ubuntu+kodexplorer可道云的私有云网盘
1.可用的服务器:组装PC机一台,操作系统为Ubuntu 14.04 LTS,无桌面环境,放在机房,使用远程终端进行访问.有安装了Apache2,运行着svn服务.内网IP地址为192.168.0.1 ...
- docker中创建MySQL及在外部使用Navicat连接
1:获取MySQL镜像 运行 docker pull mysql [root@MyCentos7- ~]# docker pull mysql Using default tag: latest la ...
- 图解 Go 并发
你很可能从某种途径听说过 Go 语言.它越来越受欢迎,并且有充分的理由可以证明. Go 快速.简单,有强大的社区支持.学习这门语言最令人兴奋的一点是它的并发模型. Go 的并发原语使创建多线程并发程序 ...
- BOM 头是什么,怎么除去
WINDOWS自带的记事本,在保存一个以 UTF-8 编码的文件时,会在文件开始的地方插入三个不可见的字符(0xEF 0xBB 0xBF,即BOM).它是一串隐藏的字符,用于让记事本等编辑器识别这个文 ...
- 微软职位内部推荐-SW Engineer II for Enterprise Platform
微软近期Open的职位: Job posting title: SDE II Location: China, Beijing Group Overview Discovery & Colla ...
- b5
吴晓晖(组长) 过去两天完成了哪些任务 完善推荐算法 展示GitHub当日代码/文档签入记录 接下来的计划 推荐算法 还剩下哪些任务 组员:刘帅珍 过去两天完成了哪些任务: 修改原型,整理背景 明日计 ...
- slf4j+log4j的初次使用
关于这两者的组合应用带来的好处,google都有 就不说了. 首先说下配置, 工作笔记:在myeclipse 中创建一个java project 创建一个 TestSlf4J 类 package co ...
- 我是一名IT小小鸟
我是一只it小小鸟 书中介绍了it界大牛们大学期间的学习方法和对未来的职业规划,相比他们,自我感觉相距甚远,对这学科的热情程度也远远比不上他们. 就拿目前数据结构这门高深的课程,应通过更多的课外扩展来 ...
