Java I/O流 04
I/O流·其他流
序列流
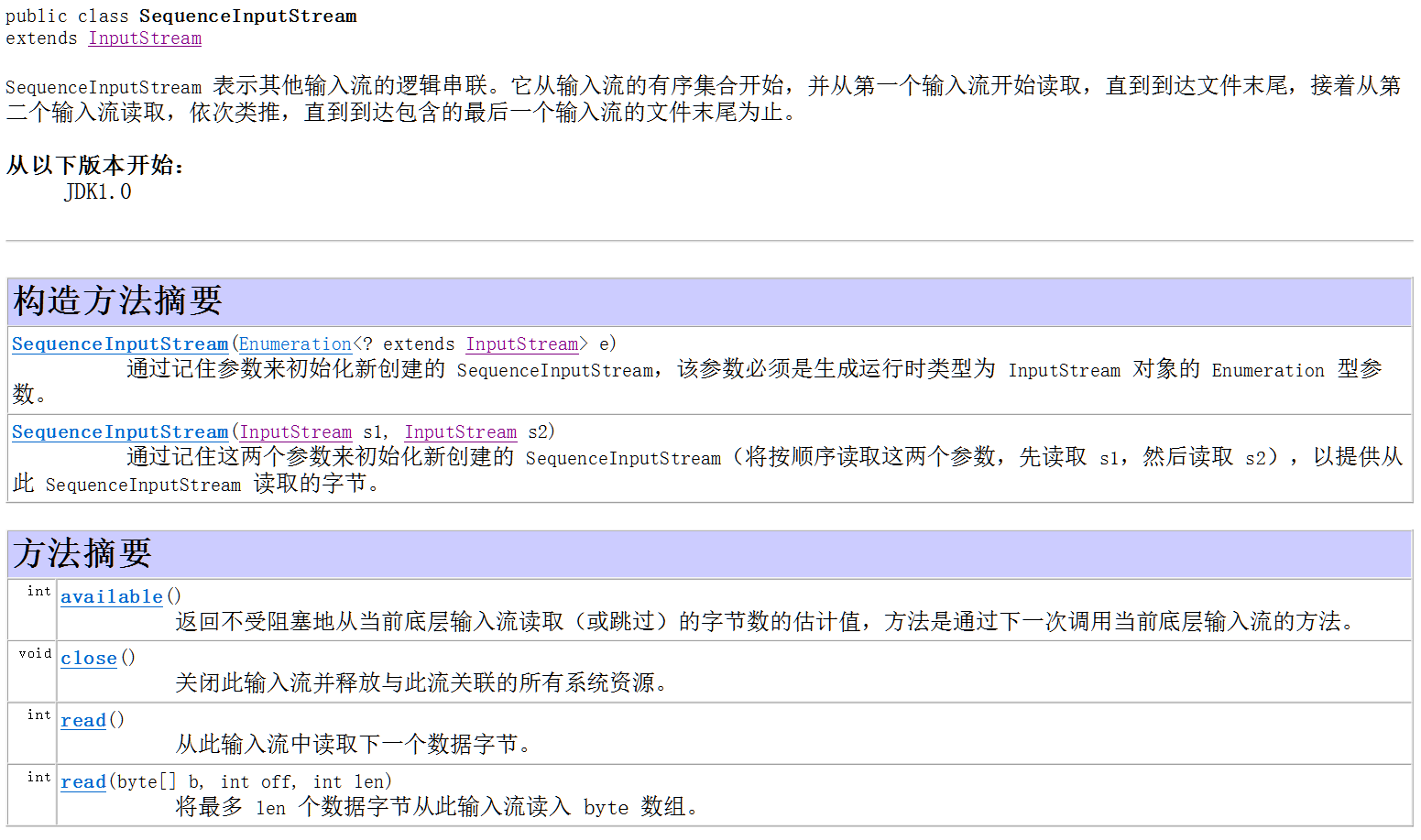
* A:什么是序列流
* 序列流可以把多个字节输入流整合成一个,从序列流中读取数据时,将从被整合的第一个流开始,读完后再读下一个
* B:使用方式
* 整合两个:SequenceInputStream(InputStream, InputStream)
* 整合多个:SequenceInputStream(Enumeration)
package com.heima.otherio; import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.SequenceInputStream;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.Vector; public class Demo1_SequenceInputStream { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// demo1(); // 不用序列流的方法
// demo2(); // 整合两个输入流
// demo3(); // 整合多个输入流
} public static void demo3() throws FileNotFoundException, IOException {
FileInputStream fis1 = new FileInputStream("a.txt"); // 创建字节输入流
FileInputStream fis2 = new FileInputStream("b.txt");
FileInputStream fis3 = new FileInputStream("c.txt"); Vector<FileInputStream> v = new Vector<FileInputStream>(); // 创建泛型为字节输入流的集合对象
v.add(fis1); // 将流对象添加到集合内
v.add(fis2);
v.add(fis3); Enumeration<FileInputStream> e = v.elements(); // 根据Vector集合,创建泛型为字节输入流的枚举对象
SequenceInputStream sis = new SequenceInputStream(e); // 将枚举中的输入流整合成一个
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("d.txt"); // 创建字节输出流 int c;
while ((c = sis.read()) != -1) { // 从序列流中读取数据
fos.write(c);
}
sis.close(); // 关闭序列流
fos.close();
} public static void demo2() throws FileNotFoundException, IOException {
FileInputStream fis1 = new FileInputStream("a.txt"); // 创建字节输入流1
FileInputStream fis2 = new FileInputStream("b.txt"); // 创建字节输入流2
SequenceInputStream sis = new SequenceInputStream(fis1, fis2); // 基于两个字节输入流,创建序列流
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("c.txt"); // 创建字节输出流 int b;
while ((b = sis.read()) != -1) { // 从序列流读取数据
fos.write(b);
}
sis.close(); // sis在关闭的时候会将构造方法中的流对象也都关闭
fos.close();
} public static void demo1() throws FileNotFoundException, IOException {
FileInputStream fis1 = new FileInputStream("a.txt"); // 创建字节输入流,关联a.txt
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("c.txt"); // 创建字节输出流,关联b.txt int c;
while ((c = fis1.read()) != -1) { // 不断地在a.txt上读取字节
fos.write(c); // 将读到的字节写到c.txt上
}
fis1.close(); // 关闭字节输入流1 FileInputStream fis2 = new FileInputStream("b.txt"); // 创建字节输入流,关联c.txt
while ((c = fis2.read()) != -1) { // 不断地在b.txt上读取字节
fos.write(c); // 将读到的字节写到c.txt上
} fis2.close(); // 关闭字节输入流2
fos.close(); // 关闭字节输出流
}
}
SequenceInputStream
内存输出流
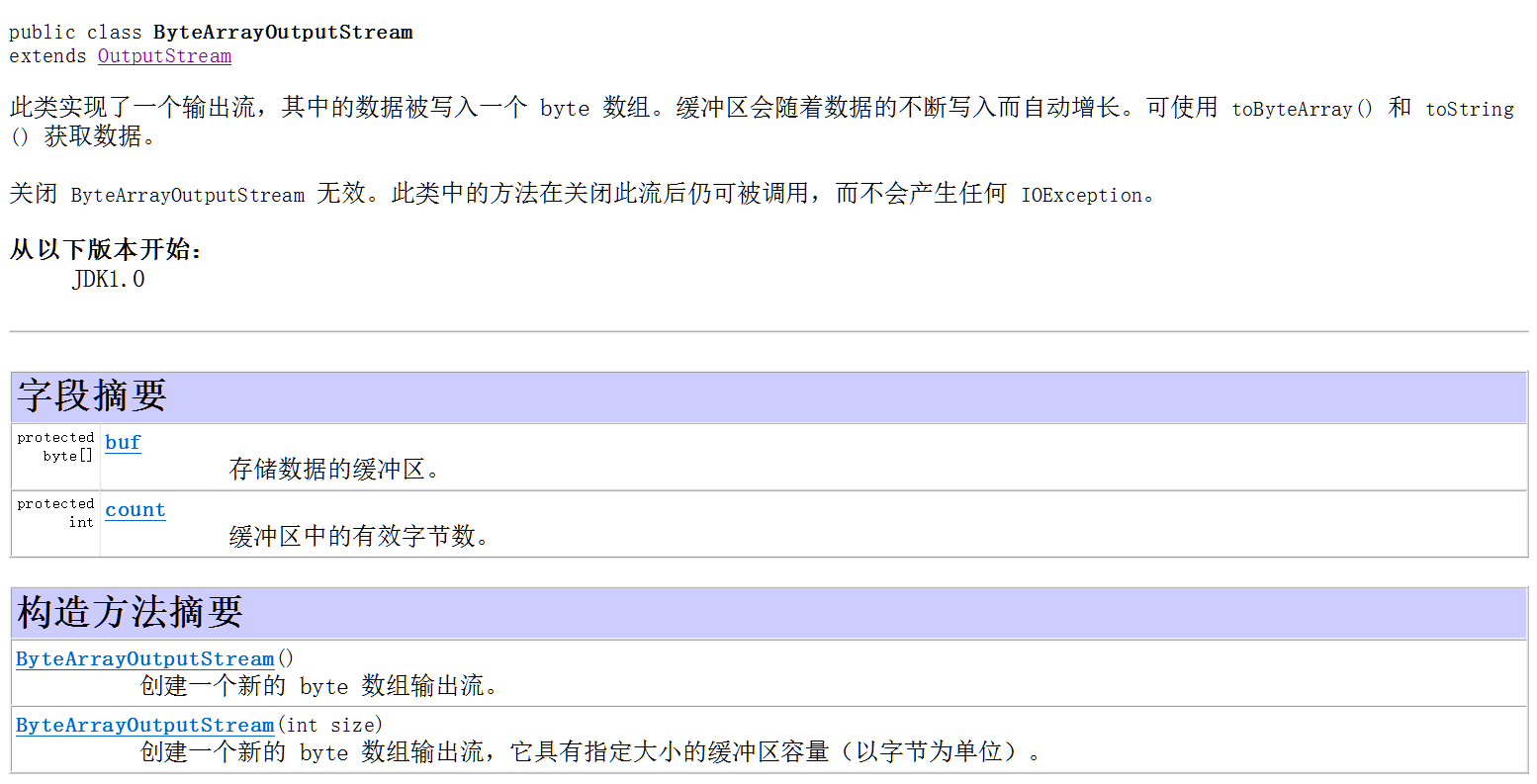
* A:什么是内存输出流
* 该输出流可以向内存中写数据,把内存当作一个缓冲区,写出之后可以一次性获取所有数据
* B:使用方法
* 创建对象:new ByteArrayOutputStream()
* 写出数据:write(int), write(byte[ ] )
* 获取数据:toByteArray()
package com.heima.otherio; import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException; public class Demo2_ByteArrayOutputStream { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// demo1();
// demo2();
} public static void demo2() throws FileNotFoundException, IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("e.txt");
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); // 在内存中创建了可以增长的内存数组 int b;
while ((b = fis.read()) != -1) {
baos.write(b); // 将读取到的数据逐个写到内存中
} byte[] arr = baos.toByteArray(); // 将缓冲区的数据全部或取出来,并赋值给arr数组
System.out.println(new String(arr)); System.out.println(baos.toString()); // 将缓冲区中的内容转换为字符串,使用平台默认的码表转换
fis.close();
// baos.close(); // 内存流不需要关,没有关的意义
} public static void demo1() throws FileNotFoundException, IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("e.txt");
byte[] arr = new byte[4]; int len;
while ((len = fis.read(arr)) != -1) {
System.out.println(new String(arr, 0, len));
}
fis.close();
}
}
ByteArrayOutputStream
面试题
* 定义一个文件输入流,调用read(byte[ ] b)方法,将 a.txt文件中的内容打印出来(byte数组大小限制为5)
package com.heima.test; import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException; public class Test1 {
/*
* 分析:
* 1、read(byte[] b)是字节输入流的方法,因此需要创建FileInputStream,关联a.txt
* 2、创建字节数组,长度为5
* 3、创建内存输出流,将读到的数组写到内存输出流中
* 4、将内存输出流的数据全部转换为字符串打印
* 5、关闭输入流
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("a.txt"); // 创建字节输入流,关联a.txt
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); // 创建内存流 byte[] arr = new byte[5];
int len;
while ((len = fis.read(arr)) != -1) { // 通过长度为5的数组读取数据
baos.write(arr, 0, len); // 将数据写入内存中
} System.out.println(baos); // 将内存中的内容以字符串的形式打印
fis.close(); // 关闭字节流
}
}
Test1
对象操作流ObjectOutputStream
* A:什么是对象操作流
* 该流可以将一个对象写出,或者读取一个对象到程序中,也就是执行了序列化和反序列化的操作
* 对象需要实现序列化接口,可以可选择的重写ID号,类似于软件的版本号
* B:使用方法
* 写出:new ObjectOutputStream(OutputStream), writeObject()
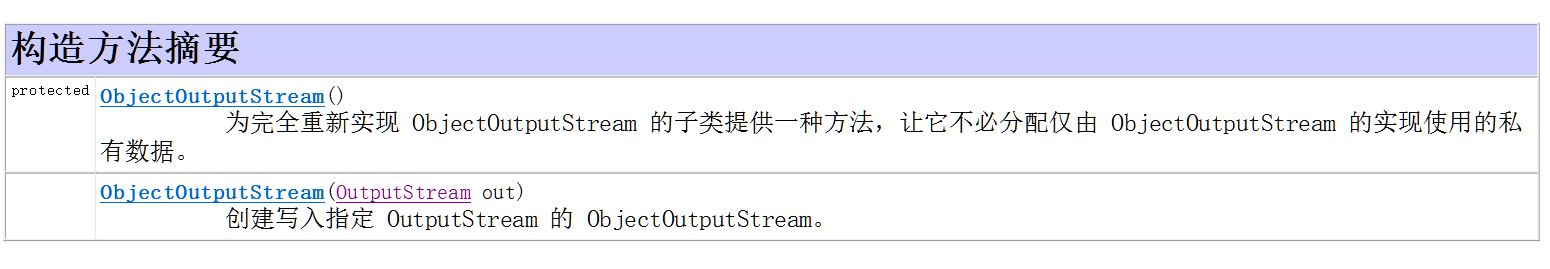
package com.heima.bean;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class Person implements Serializable{
/**
* 对象必须实现 可序列化接口
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = 2L;
private String name;
private int age;
private String gender;
public Person() {
super();
}
public Person(String name, int age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]";
}
}
Person类
package com.heima.otherio; import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.util.ArrayList; import com.heima.bean.Person; public class Demo3_ObjectOutputStream { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, IOException {
// demo1();
// demo2();
} public static void demo2() throws IOException, FileNotFoundException {
Person p1 = new Person("张三", 23);
Person p2 = new Person("李四", 24);
Person p3 = new Person("王五", 25);
Person p4 = new Person("赵六", 26); ArrayList<Person> list = new ArrayList<Person>();
list.add(p1);
list.add(p2);
list.add(p3);
list.add(p4); ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("e.txt"));
oos.writeObject(list); // 把整个集合对象一次写出
oos.close();
} public static void demo1() throws IOException, FileNotFoundException {
Person p1 = new Person("张三",23); // 对象必须可序列化
Person p2 = new Person("李四",24); // FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("f.txt");
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("f.txt")); // 创建对象输出流
oos.writeObject(p1);
oos.writeObject(p2); oos.close();
}
}
ObjectOutputStream
对象操作流ObjectInputStream
* 读取:new ObjectInputStream(InputStream), readObject()
package com.heima.otherio; import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.util.ArrayList; import com.heima.bean.Person; public class Demo4_ObjectInputStream { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
// demo1();
// demo2();
} public static void demo2() throws IOException, FileNotFoundException, ClassNotFoundException {
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("e.txt"));
ArrayList<Person> list = (ArrayList<Person>) ois.readObject(); // 将集合对象一次读取
for (Person person : list) {
System.out.println(person);
}
} public static void demo1() throws IOException, FileNotFoundException, ClassNotFoundException {
// 对象输入流是反序列化
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("e.txt")); // 创建对象输入流 Person p1 = (Person) ois.readObject(); // 从文件中读取对象,需要强转,因为读取时自动类型提升为Object
Person p2 = (Person) ois.readObject(); System.out.println(p1);
System.out.println(p2); ois.close();
}
}
ObjectInputStream
打印流的概述和特点
* A:什么时打印流
* 该流可以很方便的将对象的 toString()结果输出,并自动加上换行,而且可以使用自动刷出的模式
* System.out就是一个PrintStream,其默认向控制台输出信息
* B:使用方式
* 打印:print(), println()
* 自动刷出:PrintWriter(OutputStream out, boolean autoFlush, String encoding)
* 打印流以只操作数据为目的

package com.heima.otherio; import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintStream;
import java.io.PrintWriter; import com.heima.bean.Person; public class Demo5_PrintStream {
/*
* PritnStream和 PrintWriter 分别是打印的字节流和字符流
* 二者是以只操作数据为目的的
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// demo1();
// demo2();
} public static void demo2() throws FileNotFoundException {
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(new FileOutputStream("f.txt"), true); // true表示打开了AutoFlush功能
pw.println(97); // 自动刷出功能只针对println方法
pw.write(97);
pw.print(97);
pw.close();
} public static void demo1() {
System.out.println("aaa");
PrintStream ps = System.out; // 获取标准输出流
ps.println(97); // 打印97,底层通过 Integer.toString()将97 转换成字符串打印
ps.write(97); // 打印a,查找码表,找到对应的值进行打印 Person p1 = new Person("张三", 23);
ps.println(p1); // 默认调用对象的 toString()方法 Person p2 = null; // 打印引用数据类型,如果是null就打印null
ps.println(p2);
ps.close(); // 关闭打印流
}
}
PrintStream
标准输入流输出流概述和输出语句
* A:什么是标准输入输出流
* System.in 是InputStream,标准输入流,默认可以从键盘输入读取字节数据
* System.out 是PrintStream,标准输出流,默认可以向Console中输出字符和字节数据
* B:修改标准输入输出流
* 修改输入流:System.setIn(InputStream)
* 修改输出流:System.setOut(PrintStream)
package com.heima.otherio; import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.PrintStream; public class Demo6_SystermInOut { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
// demo1();
// demo2();
} public static void demo2() throws FileNotFoundException, IOException {
System.setIn(new FileInputStream("a.txt")); // 改变标准输入流
System.setOut(new PrintStream("b.txt")); // 改变标准输出流 InputStream is = System.in; // 获取标准的键盘输入流,默认指向键盘,改变后指向a.txt
PrintStream ps = System.out; // 获取标准输出流,默认指向控制台,改变后指向b.txt int b;
while ((b = is.read())!=-1) {
ps.write(b);
}
is.close();
ps.close();
} public static void demo1() throws IOException {
InputStream is = System.in;
int x = is.read(); // 读取一个字节
System.out.println(x); // is.close(); // 标准输入流只有一个,即使创建多个InputStream也都指向同一个
}
}
System.in
两种方式实现键盘录入
* A:BufferedReader的ReadLine()方法
* BufferedReqader br = new BufferedReqader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
* B:Scanner
package com.heima.otherio; import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.Scanner; public class Demo7_SystemIn { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// demo1();
// demo2();
} public static void demo2() {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); // 也可以读取文件
String line = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println(line);
sc.close();
} public static void demo1() throws IOException {
BufferedReader br =
new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); // 通过转换流将字节流转换为字符流,因为标准输入流是字节流
String line = br.readLine(); // 整行读取
System.out.println(line);
br.close(); // 关流
}
}
Scanner
修改标准输入输出流进行文件拷贝
package com.heima.test; import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.PrintStream; public class Test2 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
System.setIn(new FileInputStream("psb.jpg")); // 改变标准输入流,绑定图片
System.setOut(new PrintStream("copy.jpg")); // 改变标准输出流 InputStream is = System.in;
PrintStream ps = System.out; byte[] arr = new byte[1024]; // 创建字节数组
int len; while ((len = is.read(arr)) != -1) { // 读取数据
ps.write(arr, 0, len); // 写入数据
} is.close(); // 关流
ps.close();
}
}
Test2
随机访问流概述和读写数据
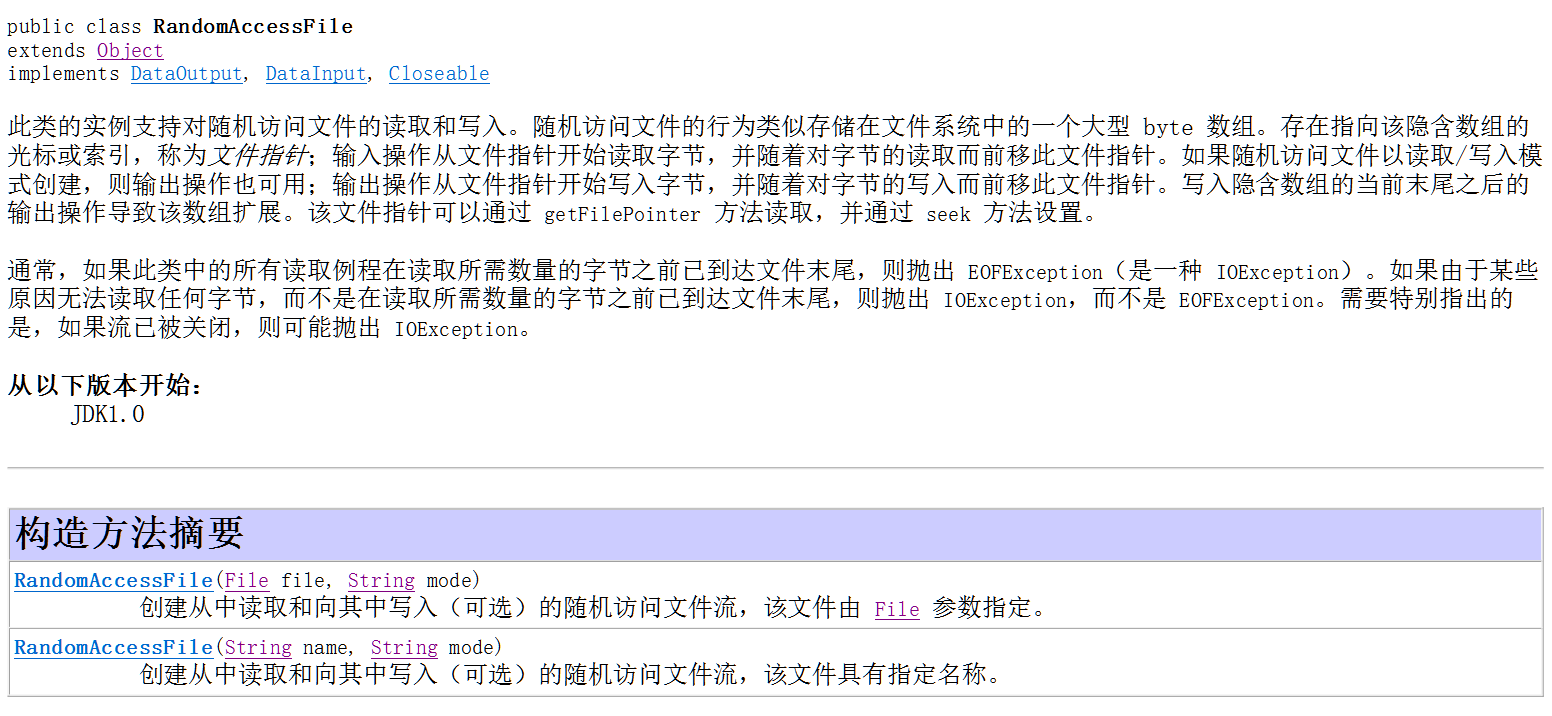
* A:随机访问流概述
* RandomAccessFile概述
* RandomAccessFile类不属于流,是Object类的子类,但是却融合了InputStream和OutputStream的功能
* 支持对随机访问文件的读取和写入
* B:read(), write(), seek()

package com.heima.otherio; import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.RandomAccessFile; public class Demo8_RandomAccessFile { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile("g.txt", "rw"); // 创建随机访问流,指定读写模式
raf.write(97); int x = raf.read();
System.out.println(x); raf.seek(10); // 在指定位置设置指针,可以用来多线程下载
raf.write(98); // 在10的位置写下b
raf.close(); // 关流
}
}
RandomAccessFile
数据输入输出流
* A:什么是数据输入输出流
* DataInputStream,DataOutputStream可以按照基本数据类型大小读写数据
* 例如按照Long大小写出一个数字,写出时,该数据占8个字节,读取的时候也可以按照Long类型读取,一次读取8个字节
* B:使用方式
* DataOutputStream(OutputStream), writeInt(), writeLong()
* DataInputStream(InputStream), readInt(), readLong()

package com.heima.otherio; import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException; public class Demo9_Data { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// demo1();
// demo2();
// demo3();
// demo4();
} public static void demo4() throws FileNotFoundException, IOException {
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream("h.txt")); // 创建数据输入流,并关联文件
int x = dis.readInt(); // 按照int数读取
int y = dis.readInt();
int z = dis.readInt(); System.out.println(x);
System.out.println(y);
System.out.println(z);
dis.close(); // 关流
} public static void demo3() throws FileNotFoundException, IOException {
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("h.txt")); // 创建数据输出流,并关联文件
dos.writeInt(997); // 写入int数
dos.writeInt(998);
dos.writeInt(999);
dos.close(); // 关流
} public static void demo2() throws FileNotFoundException, IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("h.txt");
int x = fis.read(); // 读取时回按照byte形式读取,然后前面加上24个0
int y = fis.read();
int z = fis.read(); System.out.println(x);
System.out.println(y);
System.out.println(z);
} public static void demo1() throws FileNotFoundException, IOException {
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("h.txt");
fos.write(997);
fos.write(998);
fos.write(999); fos.close();
}
}
DataInputStream
Properties的概述和作为Map集合的使用
* A:Properties的概述
* Properties类表示了一个持久的属性集
* Properties可保存在流中或从流中加载
* 属性列表中每个键及其对应值都是一个字符串
* B:Properties的特殊功能
* public Object setProperty(String key, String value)
* public String getProperty(String key)
* public Enumeration<String> stringPropertyNames()
* C:Properties的 load() 和 store() 功能
* C:案例演示
* Properties的特殊功能

package com.heima.otherio; import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.Properties; public class Demo10_Properties {
// Properties 是Hashtable的子类
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// demo1();
// demo2();
// demo3();
} public static void demo3() throws IOException, FileNotFoundException {
Properties prop = new Properties(); prop.load(new FileInputStream("config.properties")); // 将文件上的键值对读取到集合中
prop.setProperty("tel", "18987654321"); // 此时只修改了内存中的值
prop.store(new FileOutputStream("config.properties"), "..."); // 将内存中的数据写入文件中,第二个参数是对列表参数的描述,可以给值,也可以给null
System.out.println(prop);
} public static void demo2() {
Properties prop = new Properties();
prop.setProperty("name", "张三");
prop.setProperty("tel", "18912345678"); // System.out.println(prop);
Enumeration<String> en = (Enumeration<String>) prop.propertyNames(); // 因为properties中没有泛型,所以默认是Object,转化为枚举时需要强转
while (en.hasMoreElements()) {
String key = (String) en.nextElement(); // 获取properties中的每一个键
String valueString = prop.getProperty(key); // 根据键获取值
System.out.println(key + "=" + valueString);
}
} public static void demo1() {
Properties prop = new Properties();
prop.put("abc", 123);
System.out.println(prop);
}
}
Properties
Java I/O流 04的更多相关文章
- Java IO: 字符流的Piped和CharArray
作者: Jakob Jenkov 译者: 李璟(jlee381344197@gmail.com) 本章节将简要介绍管道与字符数组相关的reader和writer,主要涉及PipedReader.Pip ...
- day37-IO流04
JavaIO流04 4.常用的类03 4.4节点流和处理流02 4.4.5对象处理流-ObjectInputStream和ObjectOutputStream 1.序列化和反序列化 例子1: 看一个需 ...
- Java学习笔记(04)
Java学习笔记(04) 如有不对或不足的地方,请给出建议,谢谢! 一.对象 面向对象的核心:找合适的对象做合适的事情 面向对象的编程思想:尽可能的用计算机语言来描述现实生活中的事物 面向对象:侧重于 ...
- 【转】输入/输出流 - 深入理解Java中的流 (Stream)
基于流的数据读写,太抽象了,什么叫基于流,什么是流?Hadoop是Java语言写的,所以想理解好Hadoop的Streaming Data Access,还得从Java流机制入手.流机制也是JAVA及 ...
- Java虚拟机JVM学习04 类的初始化
Java虚拟机JVM学习04 类的初始化 类的初始化 在初始化阶段,Java虚拟机执行类的初始化语句,为类的静态变量赋予初始值. 在程序中,静态变量的初始化有两种途径: 1.在静态变量的声明处进行初始 ...
- 理解Java中字符流与字节流的区别
1. 什么是流 Java中的流是对字节序列的抽象,我们可以想象有一个水管,只不过现在流动在水管中的不再是水,而是字节序列.和水流一样,Java中的流也具有一个“流动的方向”,通常可以从中读入一个字节序 ...
- Java Io 字符流
Java Io 字符流包含: 1. InputStreamReader 它是由byte流解析为char流,并且按照给定的编码解析. 2. OutputStreamWrite 它是char流到byt ...
- mybatis oracle java.sql.SQLException: 流已被关闭问题
/** * 按照页码取值(从current_page页开始,每页page_size条) * @param key * @param params * @param current_page * @pa ...
- Java IO包装流如何关闭?
问题: (1)JAVA的IO流使用了装饰模式,关闭最外面的流的时候会自动调用被包装的流的close()方吗? (2)如果按顺序关闭流,是从内层流到外层流关闭还是从外层到内存关闭? 问题(1)解释: ...
随机推荐
- 远程连接 出现身份验证错误,要求的函数不受支持(这可能是由于CredSSP加密Oracle修正)
修改本地组策略: 计算机配置>管理模板>系统>凭据分配>加密Oracle修正 选择启用并选择"易受攻击". 原文:https://blog.csdn.net ...
- 踏上Revit二次开发之路 2 从“HelloWorld”入手
2 从"HelloWorld"入手 在欧特克的官方网页上有个叫<My First Plug-in Training>的项目,号称可以让一个完全没有编程基础的人照着做出一 ...
- Linux-开机运行流程
目录 CentOS7开机流程 Linux运行级别 systemd进程管理 systemd的优势 systemd相关文件 systemd启动相关命令 systemd开机自启动相关命令 systemd服务 ...
- Pycharm+任务栏悬浮+docked mode
先点下所想改变模式的模块, 然后: Window -> Activate tool window -> docked mode.
- Canvas & encryption image src
Canvas & encode image src 使用 Canvas 加密图片,防盗链 前端黑科技 https://telegram.org/ binary encode ??? https ...
- Redux Middleware All in One
Redux Middleware All in One https://redux.js.org/advanced/middleware https://redux.js.org/api/applym ...
- chown -R & chmod 777 & chmod +x
chown -R & chmod 777 & chmod +x https://linux.die.net/man/1/chown chown - change file owner ...
- SDK & 埋点 & user behavior tracker
SDK & 埋点 & user behavior tracker 同一个 SDK ,根据不同的应用市场, 分别进行统计分析 ? https://www.umeng.com/ user ...
- MacBook Pro 2019 13 inch & screen blink
MacBook Pro 2019 13 inch & screen blink MacBook Pro 闪屏 https://macreports.com/mac-how-to-trouble ...
- Flutter: IntrinsicWidth类,将孩子的宽度调整为孩子的最大内在宽度
文档 原文 class HomePage extends StatefulWidget { @override _HomePageState createState() => _HomePage ...
