Codeforces Round #628 (Div. 2) 题解
人闲桂花落,夜静春山空。
月出惊山鸟,时鸣春涧中。——王维
A. EhAb AnD gCd
You are given a positive integer x. Find any such 2 positive integers a and b such that GCD(a,b)+LCM(a,b)=x.
As a reminder, GCD(a,b) is the greatest integer that divides both a and b. Similarly, LCM(a,b) is the smallest integer such that both a and b divide it.
It's guaranteed that the solution always exists. If there are several such pairs (a,b), you can output any of them.
Input
The first line contains a single integer t (1≤t≤100) — the number of testcases.
Each testcase consists of one line containing a single integer, x
(2≤x≤10^9).
Output
For each testcase, output a pair of positive integers a and b (1≤a,b≤109) such that GCD(a,b)+LCM(a,b)=x. It's guaranteed that the solution always exists.
If there are several such pairs (a,b), you can output any of them.
Example
input
2
2
14
output
1 1
6 4
Note
In the first testcase of the sample, GCD(1,1)+LCM(1,1)=1+1=2.
In the second testcase of the sample, GCD(6,4)+LCM(6,4)=2+12=14.
题目大意:给定正整数x,找到两个正整数a、b,使得GCD(a,b) + LCM(a,b) = x。
显然,这道题只需要求一可行解即可,并非需要数论进行思考。
考虑:1,x - 1,满足题意。
代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int T;
scanf("%d", &T);
while(T --)
{
int x;
scanf("%d", &x);
printf("1 %d\n", x - 1);
}
return 0;
}
B. CopyCopyCopyCopyCopy
Ehab has an array a of length n. He has just enough free time to make a new array consisting of n copies of the old array, written back-to-back. What will be the length of the new array's longest increasing subsequence?
A sequence a is a subsequence of an array b if a can be obtained from b by deletion of several (possibly, zero or all) elements.The longest increasing subsequence of an array is the longest subsequence such that its elements are ordered in strictly increasing order.
Input
The first line contains an integer t — the number of test cases you need to solve. The description of the test cases follows.
The first line of each test case contains an integer n (1≤n≤105) — the number of elements in the array a.
The second line contains n space-separated integers a1, a2, …, an
(1≤ai≤109)
— the elements of the array a.
The sum of n across the test cases doesn't exceed 105.
Output
For each testcase, output the length of the longest increasing subsequence of a if you concatenate it to itself n times.
Example
input
2
3
3 2 1
6
3 1 4 1 5 9
output
3
5
Note
In the first sample, the new array is [3,2,1,3,2,1,3,2,1]. The longest increasing subsequence is marked in bold.
In the second sample, the longest increasing subsequence will be [1,3,4,5,9].
保证严格单调递增的选取方法:排序、去重。
代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 300000 + 5;
int n, a[maxn];
int main()
{
int T, cnt = 0;
scanf("%d", &T);
while(T --)
{
scanf("%d", &n);
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++ i)
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
sort(a, a + n);
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++ i)
if(!i || a[i] != a[i - 1]) ++ cnt;
printf("%d\n", cnt);
memset(a, 0, sizeof(a));
cnt = 0;
}
return 0;
}
C. Ehab and Path-etic MEXs
You are given a tree consisting of n nodes. You want to write some labels on the tree's edges such that the following conditions hold:
Every label is an integer between 0 and n−2 inclusive.
All the written labels are distinct.
The largest value among MEX(u,v) over all pairs of nodes (u,v) is as small as possible.
Here, MEX(u,v) denotes the smallest non-negative integer that isn't written on any edge on the unique simple path from node u to node v.
Input
The first line contains the integer n
(2≤n≤10^5)
— the number of nodes in the tree.
Each of the next n−1 lines contains two space-separated integers u and v (1≤u,v≤n) that mean there's an edge between nodes u and v. It's guaranteed that the given graph is a tree.
Output
Output n−1 integers. The ith of them will be the number written on the ith edge (in the input order).
Examples
input
3
1 2
1 3
output
0
1
input
6
1 2
1 3
2 4
2 5
5 6
output
0
3
2
4
1
Note
The tree from the second sample:
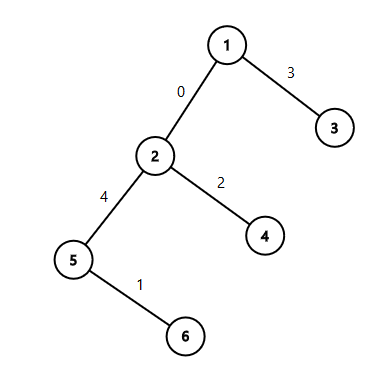
我当时思路是这样子:如果一条边出现在所有路径中的次数多于另一条边,那么它的边权成为为价值的最大值就更不容易。
因为它出现次数最多,意味着多数情况下路径的价值不用考虑它。
因此,我们就对这棵树每条边计算它的出现次数,排序;次数多的分支越应该优先填大的数。
代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
#define pil pair <int, long long>
#define maxn 3000000 + 5
using namespace std;
vector <int> G[maxn];
pil table[maxn];
int n, size[maxn] = {}, ans[maxn] = {}, fa[maxn] = {};
int input[maxn][2];
bool cmp(pil x, pil y)
{
return x.second < y.second;
}
void dfs(int Fa, int x)
{
fa[x] = Fa;
for(int i = 0; i < G[x].size(); ++ i)
{
int v = G[x][i];
if(v != Fa)
{
dfs(x, v);
size[x] += size[v];
}
}
++ size[x];
return;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d", &n);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i) G[i].clear();
for(int i = 1; i < n; ++ i)
{
scanf("%d %d", &input[i][0], &input[i][1]);
G[input[i][1]].push_back(input[i][0]);
G[input[i][0]].push_back(input[i][1]);
}
dfs(0, 1);
for(int i = 1; i < n; ++ i)
{
int x = input[i][0], y = input[i][1];
table[i].first = i;
if(fa[x] == y) table[i].second = (long long) size[x] * (n - size[x]);
else
{
table[i].second = (long long) size[y] * (n - size[y]);
}
}
sort(table + 1, table + n, cmp);
for(int i = 1; i < n; ++ i) ans[table[i].first] = i;
for(int i = 1; i < n; ++ i)
printf("%d\n", ans[i] - 1);
return 0;
}
D. Ehab the Xorcist
Given 2 integers u and v, find the shortest array such that bitwise-xor of its elements is u, and the sum of its elements is v.
Input
The only line contains 2 integers u and v (0≤u,v≤1018).
Output
If there's no array that satisfies the condition, print "-1". Otherwise:
The first line should contain one integer, n, representing the length of the desired array. The next line should contain n positive integers, the array itself. If there are multiple possible answers, print any.
Examples
input
2 4
output
2
3 1
input
1 3
output
3
1 1 1
input
8 5
output
-1
input
0 0
output
0
Note
In the first sample, 3⊕1=2 and 3+1=4. There is no valid array of smaller length.
Notice that in the fourth sample the array is empty.
这道题我第一反应使用搜索。
...
迭代加深搜索啊!!
...
怎么剪枝??
...
其实,如果加上剪枝,效率依旧不如以下做法:
考虑d = v - u,若d < 0 或者 d是奇数,输出-1。
为什么?因为数的累和>=异或和,而第一位数相加与异或的结果应该是一样的,因此u和v奇偶性相同。
再考虑:让第一个数是u,再让后两个数与第一个数凑出v,后两个数异或和为0;
不难想到:a = u,b = d / 2,c = d / 2;
由于d一定为偶数,刚刚讲过了,满足题意。
那么是否存在两个解呢?
a = u + d / 2,b = d / 2,如果a和b异或值等于v,即满足题意。
如果d = 0,那么仅需要a即可。
如果u = v = 0,则不需要啦。
代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
long long u, v, d;
int main()
{
scanf("%lld %lld", &u, &v);
d = v - u;
if(d < 0 || d & 1) puts("-1");
else
{
if(d == 0)
{
if(u == 0)
{
puts("0");
}
else
{
puts("1");
printf("%lld\n", v);
}
return 0;
}
if(((u + (d >> 1)) ^ (d >> 1)) == u)
{
puts("2");
printf("%lld %lld\n", u + (d >> 1), d >> 1);
return 0;
}
puts("3");
printf("%lld %lld %lld\n", u, d >> 1, d >> 1);
}
return 0;
}
Codeforces Round #628 (Div. 2) 题解的更多相关文章
- Codeforces Round #182 (Div. 1)题解【ABCD】
Codeforces Round #182 (Div. 1)题解 A题:Yaroslav and Sequence1 题意: 给你\(2*n+1\)个元素,你每次可以进行无数种操作,每次操作必须选择其 ...
- Codeforces Round #608 (Div. 2) 题解
目录 Codeforces Round #608 (Div. 2) 题解 前言 A. Suits 题意 做法 程序 B. Blocks 题意 做法 程序 C. Shawarma Tent 题意 做法 ...
- Codeforces Round #525 (Div. 2)题解
Codeforces Round #525 (Div. 2)题解 题解 CF1088A [Ehab and another construction problem] 依据题意枚举即可 # inclu ...
- Codeforces Round #528 (Div. 2)题解
Codeforces Round #528 (Div. 2)题解 A. Right-Left Cipher 很明显这道题按题意逆序解码即可 Code: # include <bits/stdc+ ...
- Codeforces Round #466 (Div. 2) 题解940A 940B 940C 940D 940E 940F
Codeforces Round #466 (Div. 2) 题解 A.Points on the line 题目大意: 给你一个数列,定义数列的权值为最大值减去最小值,问最少删除几个数,使得数列的权 ...
- Codeforces Round #677 (Div. 3) 题解
Codeforces Round #677 (Div. 3) 题解 A. Boring Apartments 题目 题解 简单签到题,直接数,小于这个数的\(+10\). 代码 #include &l ...
- Codeforces Round #665 (Div. 2) 题解
Codeforces Round #665 (Div. 2) 题解 写得有点晚了,估计都官方题解看完切掉了,没人看我的了qaq. 目录 Codeforces Round #665 (Div. 2) 题 ...
- Codeforces Round #160 (Div. 1) 题解【ABCD】
Codeforces Round #160 (Div. 1) A - Maxim and Discounts 题意 给你n个折扣,m个物品,每个折扣都可以使用无限次,每次你使用第i个折扣的时候,你必须 ...
- Codeforces Round #383 (Div. 2) 题解【ABCDE】
Codeforces Round #383 (Div. 2) A. Arpa's hard exam and Mehrdad's naive cheat 题意 求1378^n mod 10 题解 直接 ...
随机推荐
- JAVA实现图片验证
一.什么是图片验证码? 可以参考下面这张图: 我们在一些网站登陆的时候,经常需要填写以上图片的信息. 这种图片验证方式是我们最常见的形式,它可以有效的防范恶意攻击者采用恶意工具,来进行窃取用户的密码 ...
- B 【ZJOI2007】时态同步
时间限制 : - MS 空间限制 : 265536 KB 评测说明 : 1s 256m 问题描述 小Q在电子工艺实习课上学习焊接电路板.一块电路板由若干个元件组成,我们不妨称之为节点,并将其用数 ...
- C/C++知识总结 一 C/C++常识概述
C/C++常识概述 程序与计算机语言 C/C++简介与发展 C/C++异同 C/C++编译特点 学习编程建议 程序与计算机语言 程序:是一组计算机能识别和执行.预先编好的一些指令操作合集. 计算机语言 ...
- Python等同于PHP的 strip_tags?
我感觉目前最好的方式 from django.utils.html import strip_tags
- scratch 如何改变变量的作用域
在新建变量的时候,有个选项是“适用于所有角色”还是“仅适用于当前角色”.通常称前者为全局变量,所有角色都可以访问到这个变量:后者,称为局部变量,只能在当前角色里访问到这个变量.例如,在使用克隆功能时, ...
- BadMethodCallException : Call to undefined method App\Models\Article::setContainer()
如果你执行 php artisan db:seed 发生如下错误 说是模型中不存在 静态方法 setContainer()方法,那么你应该检查下你的DatabaseSeeder.php 文件 中的 r ...
- 11. SpringCloud实战项目-初始化数据库和表
SpringCloud实战项目全套学习教程连载中 PassJava 学习教程 简介 PassJava-Learning项目是PassJava(佳必过)项目的学习教程.对架构.业务.技术要点进行讲解. ...
- C语言数据结构栈
#include<stdio.h>#include<stdlib.h>typedef struct Node{ int data; struct Node* pnext;}no ...
- 修改Sysvol复制方式
最近博主在做公司的AD系统升级,首先在做AD系统升级前,一定要认真的调研!!!!在调研是否可升级的过程中 博主发现我司SYSVOL的复制方式还是FRS(没升级前公司是Windows server 20 ...
- nmon 的下一代工具 njmon
njmon njmon = nmon + JSON format + real-time push to a stats database + instant graphing of "al ...
