045.集群存储-CSI存储机制
一 CSI存储机制
1.1 CSI简介
1.2 CSI的设计背景
- 存储插件的代码需要与Kubernetes的代码放在同一代码库中,并与Kubernetes的二进制文件共同发布;
- 存储插件代码的开发者必须遵循Kubernetes的代码开发规范;
- 存储插件代码的开发者必须遵循Kubernetes的发布流程,包括添加对Kubernetes存储系统的支持和错误修复;
- Kubernetes社区需要对存储插件的代码进行维护,包括审核、测试等工作;
- 存储插件代码中的问题可能会影响Kubernetes组件的运行,并且很难排查问题;
- 存储插件代码与Kubernetes的核心组件(kubelet和kubecontroller-manager)享有相同的系统特权权限,可能存在可靠性和安全性问题。
- 部署第三方驱动的可执行文件仍然需要宿主机的root权限,存在安全隐患;
- 存储插件在执行mount、attach这些操作时,通常需要在宿主机上安装一些第三方工具包和依赖库,使得部署过程更加复杂,例如部署Ceph时需要安装rbd库,部署GlusterFS时需要安装mount.glusterfs库,等等。
二 CSI架构
2.1 CSI存储组件/部署架构
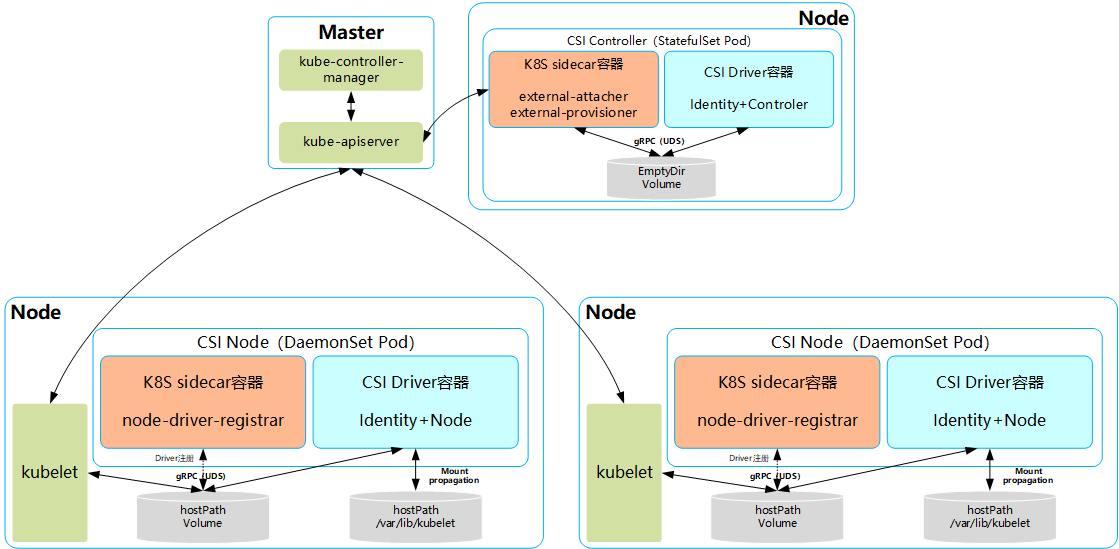
2.2 CSI Controller
- 与Master(kube-controller-manager)通信的辅助sidecar容器。在sidecar容器内又可以包含external-attacher和external-provisioner两个容器,它们的功能分别如下。
- external-attacher:监控VolumeAttachment资源对象的变更,触发针对CSI端点的ControllerPublish和ControllerUnpublish操作。
- external-provisioner:监控PersistentVolumeClaim资源对象的变更,触发针对CSI端点的CreateVolume和DeleteVolume操作。
- CSI Driver存储驱动容器,由第三方存储提供商提供,需要实现上述接口。
2.3 CSI Node
- 与kubelet通信的辅助sidecar容器node-driver-registrar,主要功能是将存储驱动注册到kubelet中;
- CSI Driver存储驱动容器,由第三方存储提供商提供,主要功能是接收kubelet的调用,需要实现一系列与Node相关的CSI接口,例如NodePublishVolume接口(用于将Volume挂载到容器内的目标路径)、NodeUnpublishVolume接口(用于从容器中卸载Volume),等等。
三 CSI插件使用实践
3.1 实验说明
3.2 开启特性
……
- --allow-privileged=true
- --feature-gates=CSIPersistentVolume=true
- --runtime-config=storage.k8s.io/v1alpha1=true
……
……
- --feature-gates=CSIPersistentVolume=true
……
# Note: This dropin only works with kubeadm and kubelet v1.11+
[Service]
Environment="KUBELET_KUBECONFIG_ARGS=--bootstrap-kubeconfig=/etc/kubernetes/bootstrap-kubelet.conf --kubeconfig=/etc/kubernetes/kubelet.conf --feature-gates=CSIPersistentVolume=true"
……
3.3 创建CRD资源对象
apiVersion: apiextensions.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: CustomResourceDefinition
metadata:
name: csidrivers.csi.storage.k8s.io
labels:
addonmanager.kubernetes.io/mode: Reconcile
spec:
group: csi.storage.k8s.io
names:
kind: CSIDriver
plural: csidrivers
scope: Cluster
validation:
openAPIV3Schema:
properties:
spec:
description: Specification of the CSI Driver.
properties:
attachRequired:
description: Indicates this CSI volume driver requires an attach operation,and that Kubernetes should call attach and wait for any attach operationto complete before proceeding to mount.
type: boolean
podInfoOnMountVersion:
description: Indicates this CSI volume driver requires additional pod
information (like podName, podUID, etc.) during mount operations.
type: string
version: v1alpha1
apiVersion: apiextensions.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: CustomResourceDefinition
metadata:
name: csinodeinfos.csi.storage.k8s.io
labels:
addonmanager.kubernetes.io/mode: Reconcile
spec:
group: csi.storage.k8s.io
names:
kind: CSINodeInfo
plural: csinodeinfos
scope: Cluster
validation:
openAPIV3Schema:
properties:
spec:
description: Specification of CSINodeInfo
properties:
drivers:
description: List of CSI drivers running on the node and their specs.
type: array
items:
properties:
name:
description: The CSI driver that this object refers to.
type: string
nodeID:
description: The node from the driver point of view.
type: string
topologyKeys:
description: List of keys supported by the driver.
items:
type: string
type: array
status:
description: Status of CSINodeInfo
properties:
drivers:
description: List of CSI drivers running on the node and their statuses.
type: array
items:
properties:
name:
description: The CSI driver that this object refers to.
type: string
available:
description: Whether the CSI driver is installed.
type: boolean
volumePluginMechanism:
description: Indicates to external components the required mechanism
to use for any in-tree plugins replaced by this driver.
pattern: in-tree|csi
type: string
version: v1alpha1
3.4 创建相应RBAC
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: csi-attacher
# replace with non-default namespace name
namespace: default
---
kind: ClusterRole
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: external-attacher-runner
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["persistentvolumes"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "update"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["nodes"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
- apiGroups: ["csi.storage.k8s.io"]
resources: ["csinodeinfos"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
- apiGroups: ["storage.k8s.io"]
resources: ["volumeattachments"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "update"]
---
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: csi-attacher-role
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: csi-attacher
# replace with non-default namespace name
namespace: default
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: external-attacher-runner
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
---
kind: Role
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
# replace with non-default namespace name
namespace: default
name: external-attacher-cfg
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["configmaps"]
verbs: ["get", "watch", "list", "delete", "update", "create"]
---
kind: RoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: csi-attacher-role-cfg
# replace with non-default namespace name
namespace: default
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: csi-attacher
# replace with non-default namespace name
namespace: default
roleRef:
kind: Role
name: external-attacher-cfg
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: csi-provisioner
# replace with non-default namespace name
namespace: default
---
kind: ClusterRole
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: external-provisioner-runner
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["secrets"]
verbs: ["get", "list"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["persistentvolumes"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "create", "delete"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["persistentvolumeclaims"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "update"]
- apiGroups: ["storage.k8s.io"]
resources: ["storageclasses"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["events"]
verbs: ["list", "watch", "create", "update", "patch"]
- apiGroups: ["snapshot.storage.k8s.io"]
resources: ["volumesnapshots"]
verbs: ["get", "list"]
- apiGroups: ["snapshot.storage.k8s.io"]
resources: ["volumesnapshotcontents"]
verbs: ["get", "list"]
- apiGroups: ["csi.storage.k8s.io"]
resources: ["csinodeinfos"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["nodes"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
---
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: csi-provisioner-role
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: csi-provisioner
# replace with non-default namespace name
namespace: default
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: external-provisioner-runner
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
---
kind: Role
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
# replace with non-default namespace name
namespace: default
name: external-provisioner-cfg
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["endpoints"]
verbs: ["get", "watch", "list", "delete", "update", "create"]
---
kind: RoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: csi-provisioner-role-cfg
# replace with non-default namespace name
namespace: default
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: csi-provisioner
# replace with non-default namespace name
namespace: default
roleRef:
kind: Role
name: external-provisioner-cfg
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: csi-driver-registrar
# replace with non-default namespace name
namespace: default
---
kind: ClusterRole
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: driver-registrar-runner
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["events"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "create", "update", "patch"]
# The following permissions are only needed when running
# driver-registrar without the --kubelet-registration-path
# parameter, i.e. when using driver-registrar instead of
# kubelet to update the csi.volume.kubernetes.io/nodeid
# annotation. That mode of operation is going to be deprecated
# and should not be used anymore, but is needed on older
# Kubernetes versions.
# - apiGroups: [""]
# resources: ["nodes"]
# verbs: ["get", "update", "patch"]
---
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: csi-driver-registrar-role
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: csi-driver-registrar
# replace with non-default namespace name
namespace: default
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: driver-registrar-runner
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
3.5 正式部署
四 测试使用
4.1 确认验证
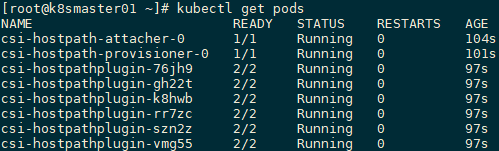
4.2 创建StorageClass
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
kind: StorageClass
metadata:
name: csi-hostpath-sc
provisioner: csi-hostpath
reclaimPolicy: Delete
volumeBindingMode: Immediate
4.3 创建PVC
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: csi-pvc
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi
storageClassName: csi-hostpath-sc

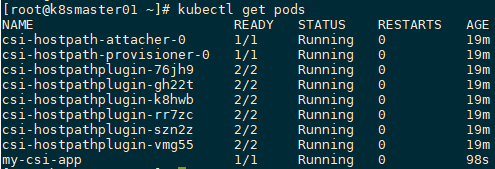
4.4 创建应用
kind: Pod
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: my-csi-app
spec:
containers:
- name: my-frontend
image: busybox
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: "/data"
name: my-csi-volume
command: [ "sleep", "1000000" ]
volumes:
- name: my-csi-volume
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: csi-pvc
045.集群存储-CSI存储机制的更多相关文章
- openstack高可用集群15-后端存储技术—GlusterFS(分布式存储)
- [How to]HBase集群备份方法--Replication机制
1.简介 HBase备份的方法在[How to]HBase集群备份方法文章中已经有些介绍,但是这些方法都不是HBase本身的特性在支持,都是通过MR计算框架结合HBase客户端的方式,或者直接拷贝HB ...
- Jetty集群配置Session存储到MySQL、MongoDB
在Web开发中,Session表示HTTP服务器与客户端(例如浏览器)的“会话”,每个客户端会有其对应的Session保存在服务器端,通常用来保存和客户端关联的一些信息,例如是否登录.购物车等. Se ...
- Jetty容器集群配置Session存储到MySQL、MongoDB
在Web开发中,Session表示HTTP服务器与客户端(例如浏览器)的"会话",每个客户端会有其对应的Session保存在服务器端,通常用来保存和客户端关联的一些信息,例如是否登 ...
- 通过Heketi管理GlusterFS为K8S集群提供持久化存储
参考文档: Github project:https://github.com/heketi/heketi MANAGING VOLUMES USING HEKETI:https://access.r ...
- 二十八. Ceph概述 部署Ceph集群 Ceph块存储
client :192.168.4.10 node1 :192.168.4.11 ndoe2 :192.168.4.12 node3 :192.168.4.13 1.实验环境 准备四台KVM虚 ...
- 设置Hadoop+Hbase集群pid文件存储位置
有时候,我们对运行几天或者几个月的hadoop或者hbase集群做停止操作,会发现,停止命令不管用了,为什么呢? 因为基于java开发的程序,想要停止程序,必须通过进程pid来确定,而hadoop和h ...
- k8s教程:Kubernetes集群使用网络存储NFS
NFS存储 NFS即网络文件系统Network File System,它是一种分布式文件系统协议,最初是由Sun MicroSystems公司开发的类Unix操作系统之上的一款经典网络存储方案,其功 ...
- java架构之路-(分布式zookeeper)zookeeper集群配置和选举机制详解
上次博客我们说了一下zookeeper的配置文件,以及命令的使用https://www.cnblogs.com/cxiaocai/p/11597465.html.我们这次来说一下我们的zookeepe ...
随机推荐
- FormsAuthenticationTicket身份验证通过后无法登陆---可能存在的问题
这是我自己遇到过的,FormsAuthenticationTicket身份验证通过后还是存在无法登录的问题,调试了很长时间还是没有发现问题,最后突然想到是否是因为cookie长度限制,导致不能将信息存 ...
- go微服务框架kratos学习笔记十(熔断器)
目录 go微服务框架kratos学习笔记十(熔断器) 什么是熔断 熔断器逻辑 kratos Breaker kratos 熔断逻辑 kratos熔断器使用说明 bladmaster client br ...
- 使用Navicat或者其他数据库工具连接阿里云EDS(数据库服务器)实例过程详解
使用Navicat或者其他数据库工具连接阿里云EDS(数据库服务器)实例过程详解 背景:这几天从阿里云上面购买了云服务器,最垃圾的那种,还送oss和EDS数据库服务器,只不过EDS数据库服务器只有一个 ...
- window.showModalDialog与window.open()使用
window.showModalDialog 有些浏览器不兼容,尝试用window.open() 封装替代,需要打开子窗口后向父窗口传递数据. <html> <script src= ...
- RabbitMQ 消息模式
消息模式实例 视频教程:https://ke.qq.com/course/304104 编写代码前,最好先添加好用户并设置virtual hosts 一.简单模式 1.导入jar包 <depen ...
- 基于Ubuntu+Python+Tensorflow+Jupyter notebook搭建深度学习环境
基于Ubuntu+Python+Tensorflow+Jupyter notebook搭建深度学习环境 前言一.环境准备环境介绍软件下载VMware下安装UbuntuUbuntu下Anaconda的安 ...
- JS反爬绕过思路之--谷歌学术镜像网链接抓取
首先,从问题出发: http://ac.scmor.com/ 在谷歌学术镜像网收集着多个谷歌镜像的链接.我们目标就是要把这些链接拿到手. F12查看源码可以发现,对应的a标签并不是我们想要的链接,而是 ...
- Java中的IO与NIO
前文开了高并发学习的头,文末说了将会选择NIO.RPC相关资料做进一步学习,所以本文开始学习NIO知识. IO知识回顾 在学习NIO前,有必要先回顾一下IO的一些知识. IO中的流 Java程序通过流 ...
- MySQL 【常识与进阶】
MySQL 事物 InnoDB事务原理 事务(Transaction)是数据库区别于文件系统的重要特性之一,事务会把数据库从一种一致性状态转换为另一种一致性状态. 在数据库提交时,可以确保要么所有修改 ...
- CSS核心概念之盒子模型
盒子模型(Box Model) 关于更多CSS核心概念的文章请关注GitHub--CSS核心概念. 当对一个文档进行布局的时候,浏览器的渲染引擎会根据标准之一的 CSS 基础框盒模型(CSS basi ...
