Service discovery
In k8s, we usually will more than make an application instance, and also the corresponding multiple pod, if through the pod IP access to the pod service will be hard to manage. Kubernetes provides the concept of service can be accessed through the VIP pod services, but in the use of the time there is a problem: how do you know an application of the VIP?We have two application, for example, an APP, one is the DB, manage each application using the rc, and provide services through service exposed the port.APP needs to connect to the DB application, we only know the name of a DB application, but do not know the VIP address.
The simplest way from kubernetes provides query API.But this is a bad practice, every application must first write queries at start-up time rely on the service logic, this itself is repeat and increases the complexity of the application;Second leading to applications rely on kubernetes, will not be able to deploy and run separately (of course, if by adding configuration option is also can be done, but it is increase in degrees).
At first, the method of kubernetes adopted docker used - environment variables.Start each pod, will be put through the environment variable is set all service of IP and port information, so that the application of the pod can be read by the environment variable to rely on the service address information.Matching relation between service and environment variables this way has a certain specification, use rise also relatively simple, but there is a big problem: rely on the service must be started in the pod existed before, otherwise will not appear in the environment variable.
A more ideal solution is: application can directly use the name of the service, don't need to care about it the IP address of the actual, in the middle of the conversion can be done automatically.DNS is name and IP conversion between the function of the system, so kubernetes is also provides the DNS method to solve this problem.
DNS Service
The DNS service is not independent of the system, but an addon, as a plug-in to install, not kubernetes cluster must (but very recommended installation).Can take it as a run on the application of the cluster, it's just the application is special.
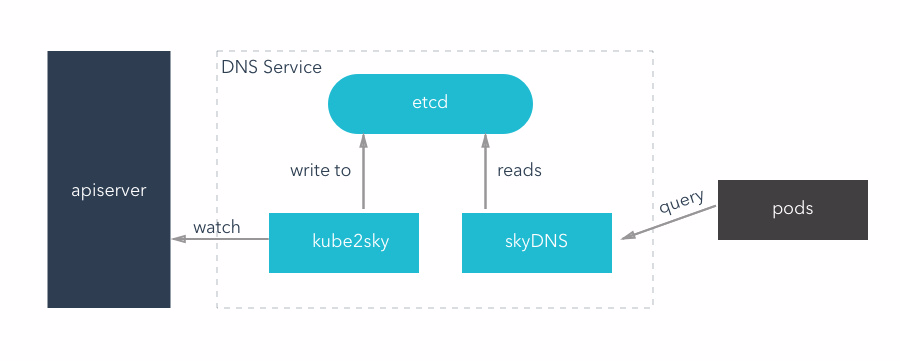
There are two kinds of DNS configuration mode, using etcd + kube2sky + skydns way before version 1.3, can be used after 1.3 kubedns + dnsmasq way.
kube2sky mode
This model mainly has three containers in operation:
- Kube2sky is responsible for the continuous monitoring k8s apiserver, once has the service creation, will obtain the service IP, and stored in the etcd
- Etcd in the form of the key - value is used to store the service name and the corresponding "ClusterIP"
- SkyDNS: according to the data of the etcd, external DNS query service
Service discovery
In k8s, we usually will more than make an application instance, and also the corresponding multiple pod, if through the pod IP access to the pod service will be hard to manage. Kubernetes provides the concept of service can be accessed through the VIP pod services, but in the use of the time there is a problem: how do you know an application of the VIP?We have two application, for example, an APP, one is the DB, manage each application using the rc, and provide services through service exposed the port.APP needs to connect to the DB application, we only know the name of a DB application, but do not know the VIP address.
The simplest way from kubernetes provides query API.But this is a bad practice, every application must first write queries at start-up time rely on the service logic, this itself is repeat and increases the complexity of the application;Second leading to applications rely on kubernetes, will not be able to deploy and run separately (of course, if by adding configuration option is also can be done, but it is increase in degrees).
At first, the method of kubernetes adopted docker used - environment variables.Start each pod, will be put through the environment variable is set all service of IP and port information, so that the application of the pod can be read by the environment variable to rely on the service address information.Matching relation between service and environment variables this way has a certain specification, use rise also relatively simple, but there is a big problem: rely on the service must be started in the pod existed before, otherwise will not appear in the environment variable.
A more ideal solution is: application can directly use the name of the service, don't need to care about it the IP address of the actual, in the middle of the conversion can be done automatically.DNS is name and IP conversion between the function of the system, so kubernetes is also provides the DNS method to solve this problem.
DNS Service
The DNS service is not independent of the system, but an addon, as a plug-in to install, not kubernetes cluster must (but very recommended installation).Can take it as a run on the application of the cluster, it's just the application is special.
There are two kinds of DNS configuration mode, using etcd + kube2sky + skydns way before version 1.3, can be used after 1.3 kubedns + dnsmasq way.
kube2sky mode
This model mainly has three containers in operation:
- Kube2sky is responsible for the continuous monitoring k8s apiserver, once has the service creation, will obtain the service IP, and stored in the etcd
- Etcd in the form of the key - value is used to store the service name and the corresponding "ClusterIP"
- SkyDNS: according to the data of the etcd, external DNS query service
example:
There is a DB, a APP server, APP server needs to connect DB for data reading and writing
1.DB server, through the RC created a pod, and at the same time to create a service for integration of the pod,DB service named DB_server.This is accomplished by k8s - apiserver,Will be a cluster IP for DB service distribution,for example: 192.168.20.3,ClusterIP can only be used for use within the cluster.
2.kube2sky listening to APIserver operations, access to the service name: DB_server and clusterIP: 192.168.20.3, and will write etcd.
3.APP server configured in the DB address for 'DB_server', this is the name of DB service,Use the service name instead of IP
4.Pod will send service name: DB_server to skyDNS, loading from etcd skyDNS service name corresponding IP, returned to the Pod
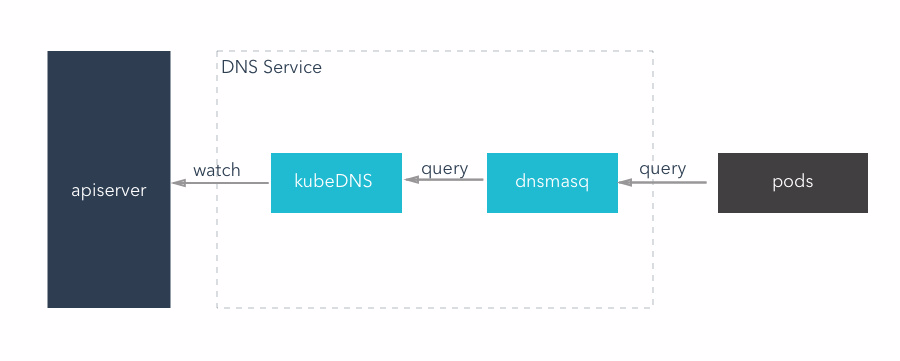
kubeDNS mode
This mode, kubeDNS container replace the function of the original three container, it will be to monitor apiserver and put all the service and the result of the endpoints using appropriate data structure stored in memory, and external DNS query service.
- KubeDNS: to provide the original kube2sky + etcd + skyDNS function, can provide DNS query service
- A lightweight DNS service software, can provide DNS cache function.KubeDNS mode, dnsmasq in memory set aside a block size (the default is 1g), save the current most commonly used DNS query record, if there is no to find records in the cache, it will into kubeDNS query, and the results are cached
example:
1.DB server, through the RC created a pod, and at the same time to create a service for integration of the pod,DB service named DB_server.This is accomplished by k8s - apiserver,Will be a cluster IP for DB service distribution,for example: 192.168.20.3,ClusterIP can only be used for use within the cluster.
2. kubeDNS listening to APIserver operations,access to the service name: DB_server and clusterIP: 192.168.20.3, and use tree structure write cache.
3. dnsmasq:DNS rules obtained through kubedns container, in a cluster to provide DNS query service, equivalent to the DNS server.
4. APP server configured in the DB address for 'DB_server', this is the name of DB service,Use the service name instead of IP
5. Pod will send service name: DB_server to dnsmasq,dnsmasq query to the service of the corresponding IP is returned to the pod, if not checked, will contact the kubeDNS,If kubeDNS no record, it will return an error report to the APP server pod.
example:
There is a DB, a APP server, APP server needs to connect DB for data reading and writing
1.DB server, through the RC created a pod, and at the same time to create a service for integration of the pod,DB service named DB_server.This is accomplished by k8s - apiserver,Will be a cluster IP for DB service distribution,for example: 192.168.20.3,ClusterIP can only be used for use within the cluster.
2.kube2sky listening to APIserver operations, access to the service name: DB_server and clusterIP: 192.168.20.3, and will write etcd.
3.APP server configured in the DB address for 'DB_server', this is the name of DB service,Use the service name instead of IP
4.Pod will send service name: DB_server to skyDNS, loading from etcd skyDNS service name corresponding IP, returned to the Pod
kubeDNS mode
This mode, kubeDNS container replace the function of the original three container, it will be to monitor apiserver and put all the service and the result of the endpoints using appropriate data structure stored in memory, and external DNS query service.
- KubeDNS: to provide the original kube2sky + etcd + skyDNS function, can provide DNS query service
- A lightweight DNS service software, can provide DNS cache function.KubeDNS mode, dnsmasq in memory set aside a block size (the default is 1g), save the current most commonly used DNS query record, if there is no to find records in the cache, it will into kubeDNS query, and the results are cached
example:
1.DB server, through the RC created a pod, and at the same time to create a service for integration of the pod,DB service named DB_server.This is accomplished by k8s - apiserver,Will be a cluster IP for DB service distribution,for example: 192.168.20.3,ClusterIP can only be used for use within the cluster.
2. kubeDNS listening to APIserver operations,access to the service name: DB_server and clusterIP: 192.168.20.3, and use tree structure write cache.
3. dnsmasq:DNS rules obtained through kubedns container, in a cluster to provide DNS query service, equivalent to the DNS server.
4. APP server configured in the DB address for 'DB_server', this is the name of DB service,Use the service name instead of IP
5. Pod will send service name: DB_server to dnsmasq,dnsmasq query to the service of the corresponding IP is returned to the pod, if not checked, will contact the kubeDNS,If kubeDNS no record, it will return an error report to the APP server pod.
- Open-Source Service Discovery
Service discovery is a key component of most distributed systems and service oriented architectures. ...
- Spring Boot Dubbo Dubbok spring cloud
比较spring cloud和dubbo,各自的优缺点是什么 - 趁年轻再疯狂一次吧 - CSDN博客 https://blog.csdn.net/u010664947/article/details ...
- springcloud情操陶冶-初识springcloud
许久之前便听到了springcloud如雷贯耳的大名,但是不曾谋面,其主要应用于微服务的相关架构.笔者对微服务并不是很了解,但其既然比较出众,遂也稍微接触研究下 springcloud特性 sprin ...
- 微服务领域是不是要变天了?Spring Cloud Alibaba正式入驻Spring Cloud官方孵化器!
引言 微服务这个词的热度自它出现以后,就一直是高烧不退,而微服务之所以这么火,其实和近几年互联网的创业氛围是分不开的. 与传统行业不同,互联网企业有一个特点,那就是市场扩张速度非常之快,可能也就是几天 ...
- springcloud
基本术语 1.服务器 服务器:是提供计算服务的设备.由于服务器需要响应服务请求,并进行处理,因此一般来说服务器应具备承担服务并且保障服务的能力.服务器的构成:包括处理器.硬盘.内存.系统总线等,和通用 ...
- 微服务之Spring cloud
微服务 Spring cloud Spring Cloud provides tools for developers to quickly build some of the common patt ...
- Spring Cloud简介
一.本文介绍 Web应用由最早的单体应用发展成为集群式的部署,再到现在的分布式系统.尤其是这两年分布式相关的技术发展的很快,一方面是以Dubbo为代表的,另一方面则是以Spring Cloud系列为代 ...
- Spring Cloud Summary
Spring Cloud Summary https://cloud.spring.io/spring-cloud-static/Finchley.RC1/single/spring-cloud.ht ...
- 搭建Spring Initializr服务器
前言 按照网上很多教程,出错特别多.首先是GitHub和maven仓库的网络环境比较差,踩了很多坑:其次是SpringInitializr更新迭代几个版本,0.7.0我也没能弄成功.索性就用了旧版本0 ...
随机推荐
- javascript之DOM(Document Object Model) 文档对象模型
<html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; char ...
- AndroidManifest.xml中的<uses-feature>以及和<uses-permission>之间的联系
概述:<uses-feature>用来声明应用中需要用的硬件和软件的功能. 硬件特性:表明您的应用需要用的硬件功能. 功能类型 特征描述 描述 音频 android.hardware.au ...
- iOS 应用"无法安装应用程序 因为证书无效"的解决方案
原因是由于iOS7.1要安装企业应用,url必须是https的,不能是http,这就要求我们的服务器要支持https.因此,只要将原链接: itms-services://?action=downlo ...
- 手动集成 Ironic 裸金属管理服务(Rocky)
目录 文章目录 目录 前文列表 横向扩展裸金属管理服务节点 配置基础设施 安装 Ironic(BareMetal) 安装 Nova Compute(BareMetal) 配置 Neutron 提供 P ...
- SQLSERVER大批量数据快速导入Redis
目的 把单表近5千万的某单个字段导入到Redis,作为一个list存储. 方案一: 使用sqlcmd工具(sqlserver自带),直接生成命令在Redis-cli中执行. 方案一. 使用sqlcmd ...
- SQL学习(八)日期处理
不同数据库中,针对日期处理的函数不同 Oracle中常用日期函数 (1.sysdate: 获取当前系统时间 如: select sysdate() ----返回当前时间,包括年月日 时分秒 (2.to ...
- 数据库高级数据库学习--上机练习5(Transact-SQL)
上机练习5 启动SQL Server 2008中的 SQL Server Management Studio,恢复数据库ClassDB: 采用Transact-SQL程序设计完成以下练习: . 求1到 ...
- SPSS学习笔记之——Kaplan-Meier生存分析
SPSS学习笔记之--Kaplan-Meier生存分析 一.概述 关于生存分析的相关概念,Kaplan-Meier用于估计生存函数,允许有一个分组变量进行生存率的组间比较,还容许一个分层变量.若不考虑 ...
- 分布式架构-Redis 从入门到精通 完整案例 附源码
导读 篇幅较长,干货十足,阅读需要花点时间,全部手打出来的字,难免出现错别字,敬请谅解.珍惜原创,转载请注明出处,谢谢~! NoSql介绍与Redis介绍 什么是Redis? Redis是用C语言开发 ...
- Vi或者Vim下按了ctrl+s后终端卡住了咋办?
在Vi或者Vim下按了ctrl+s后终端卡住了咋办? 习惯了在windows下写程序,也习惯了按ctrl+s 保存代码. 在用vim的时候,也习惯性的按ctrl+s结果就是如同终端死掉了一样. 原因: ...