Java-NIO 之 Selector 与 Pipe
关于阻塞与非阻塞:https://www.cnblogs.com/jhxxb/p/11272727.html
一、传统的 IO 流都是阻塞式的
当一个线程调用 read() 或 write() 时,该线程被阻塞,直到有一些数据被读取或写入,该线程在此期间不能执行其他任务。
因此,在网络通信进行 IO 操作时,由于线程会阻塞,所以服务器端必须为每个客户端都提供一个独立的线程进行处理,当服务器端需要处理大量客户端时,性能急剧下降。
package nio; import org.junit.Test; import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Scanner; public class TestBlockingNIO { // 客户端
@Test
public void client() throws IOException {
// 获取通道
SocketChannel sChannel = SocketChannel.open(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 9898)); // 分配指定大小的缓冲区
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); // 发送到服务端
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
while (scan.hasNext()) {
String str = scan.next();
buf.put(str.getBytes());
buf.flip();
sChannel.write(buf);
buf.clear(); if ("exit".equals(str)) {
break;
}
} // 接收服务端的反馈
sChannel.shutdownOutput();
int len = 0;
while ((len = sChannel.read(buf)) != -1) {
buf.flip();
System.out.println(new String(buf.array(), 0, len));
buf.clear();
} // 关闭通道
sChannel.close();
} // 服务端
@Test
public void server() throws IOException {
// 获取通道
ServerSocketChannel ssChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open(); // 绑定连接
ssChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(9898)); retry:
while (true) {
// 获取客户端连接的通道
SocketChannel sChannel = ssChannel.accept(); // 分配指定大小的缓冲区
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); // 接收客户端的数据
while (sChannel.read(buf) != -1) {
String str = new String(buf.array()).trim();
if ("exit".equals(str)) {
break retry;
}
buf.flip();
System.out.println(str);
buf.clear();
} // 发送反馈给客户端
buf.put("服务端接收数据成功!".getBytes());
buf.flip();
sChannel.write(buf); // 关闭通道
sChannel.close();
} // 关闭通道
ssChannel.close();
}
}
二、Java NIO 是非阻塞式的
当线程从某通道进行读写数据时,若没有数据可用时,该线程可以进行其他任务。
线程通常将非阻塞 IO 的空闲时间用于在其他通道上执行 IO 操作,所以单独的线程可以管理多个输入和输出通道。
因此,NIO 可以让服务器端使用一个或有限几个线程来同时处理连接到服务器端的所有客户端。
注:NIO 的 IO 行为还是同步的。
/*
* 使用 NIO 完成网络通信的三个核心:
*
* 1. 通道(Channel):负责连接
* java.nio.channels.Channel 接口:
* |--SelectableChannel
* |--SocketChannel
* |--ServerSocketChannel
* |--DatagramChannel
*
* |--Pipe.SinkChannel
* |--Pipe.SourceChannel
*
* 2. 缓冲区(Buffer):负责数据的存取
*
* 3. 选择器(Selector):是 SelectableChannel 的多路复用器。用于监控 SelectableChannel 的 IO 状况
* 可以监听的事件类型(可使用 SelectionKey 的四个常量表示)
* 读: SelectionKey.OP_READ (1)
* 写: SelectionKey.OP_WRITE (4)
* 连接: SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT(8)
* 接收: SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT (16)
*
* Selector 常用方法
* Set<SelectionKey> keys():所有的 SelectionKey 集合。代表注册在该 Selector上的 Channel
* selectedKeys():被选择的 SelectionKey 集合。返回此Selector的已选择键集
* intselect():监控所有注册的 Channel,当它们中间有需要处理的 IO 操作时,该方法返回,并将对应得的 SelectionKey 加入被选择的 SelectionKey 集合中,该方法返回这些 Channel 的数量。
* int select(long timeout):可以设置超时时长的 select() 操作
* int selectNow():执行一个立即返回的 select() 操作,该方法不会阻塞线程
* Selector wakeup():使一个还未返回的 select() 方法立即返回
* void close():关闭该选择器
*/
1.TCP-SocketChannel
package nio; import org.junit.Test; import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Scanner; public class TestNonBlockingNIO { //客户端
@Test
public void client() throws IOException {
// 获取通道
SocketChannel sChannel = SocketChannel.open(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 9898)); // 切换非阻塞模式
sChannel.configureBlocking(false); // 分配指定大小的缓冲区
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); // 发送数据给服务端
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); while (scan.hasNext()) {
String str = scan.next();
buf.put((new Date().toString() + "\n" + str).getBytes());
buf.flip();
sChannel.write(buf);
buf.clear();
} // 关闭通道
sChannel.close();
} //服务端
@Test
public void server() throws IOException {
// 获取通道
ServerSocketChannel ssChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open(); // 切换非阻塞模式
ssChannel.configureBlocking(false); // 绑定连接
ssChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(9898)); // 获取选择器
Selector selector = Selector.open(); // 将通道注册到选择器上, 并且指定“监听接收事件”
ssChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT | SelectionKey.OP_READ); // 轮询式的获取选择器上已经“准备就绪”的事件
while (selector.select() > 0) { // 获取当前选择器中所有注册的“选择键(已就绪的监听事件)”
Iterator<SelectionKey> it = selector.selectedKeys().iterator(); while (it.hasNext()) {
// 获取准备“就绪”的是事件
SelectionKey sk = it.next(); // 判断具体是什么事件准备就绪
if (sk.isAcceptable()) {
// 若“接收就绪”,获取客户端连接
SocketChannel sChannel = ssChannel.accept(); // 切换非阻塞模式
sChannel.configureBlocking(false); // 将该通道注册到选择器上
sChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
} else if (sk.isReadable()) {
// 获取当前选择器上“读就绪”状态的通道
SocketChannel sChannel = (SocketChannel) sk.channel(); // 读取数据
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); int len = 0;
while ((len = sChannel.read(buf)) > 0) {
buf.flip();
System.out.println(new String(buf.array(), 0, len));
buf.clear();
}
} // 移除当前 SelectionKey
it.remove();
}
}
}
}
2.UDP-DatagramChannel
package nio; import org.junit.Test; import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.DatagramChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Scanner; public class TestNonBlockingNIO2 { @Test
public void send() throws IOException{
DatagramChannel dc = DatagramChannel.open(); dc.configureBlocking(false); ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); while(scan.hasNext()){
String str = scan.next();
buf.put((new Date().toString() + ":\n" + str).getBytes());
buf.flip();
dc.send(buf, new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 9898));
buf.clear();
} dc.close();
} @Test
public void receive() throws IOException{
DatagramChannel dc = DatagramChannel.open(); dc.configureBlocking(false); dc.bind(new InetSocketAddress(9898)); Selector selector = Selector.open(); dc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ); while(selector.select() > 0){
Iterator<SelectionKey> it = selector.selectedKeys().iterator(); while(it.hasNext()){
SelectionKey sk = it.next(); if(sk.isReadable()){
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); dc.receive(buf);
buf.flip();
System.out.println(new String(buf.array(), 0, buf.limit()));
buf.clear();
}
} it.remove();
}
}
}
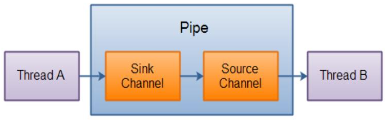
三、Pipe(管道)
Java NIO 管道是 2 个线程之间的单向数据连接。Pipe 有一个 source 通道和一个 sink 通道。数据会被写到 sink 通道,从 source 通道读取。
package nio; import org.junit.Test; import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.Pipe; public class TestPipe { @Test
public void test() throws IOException {
// 获取管道
Pipe pipe = Pipe.open(); ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
buf.put("通过单向管道发送数据".getBytes());
buf.flip(); // 将缓冲区中的数据写入管道
Pipe.SinkChannel sinkChannel = pipe.sink();
sinkChannel.write(buf); ByteBuffer buf2 = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
// 读取缓冲区中的数据
Pipe.SourceChannel sourceChannel = pipe.source();
int len = sourceChannel.read(buf2);
System.out.println(new String(buf2.array(), 0, len)); sourceChannel.close();
sinkChannel.close();
}
}
Java-NIO 之 Selector 与 Pipe的更多相关文章
- Java NIO类库Selector机制解析(下)
五. 迷惑不解 : 为什么要自己消耗资源? 令人不解的是为什么我们的Java的New I/O要设计成这个样子?如果说老的I/O不能多路复用,如下图所示,要开N多的线程去挨个侦听每一个Channel ...
- Java NIO类库Selector机制解析(上)
一. 前言 自从J2SE 1.4版本以来,JDK发布了全新的I/O类库,简称NIO,其不但引入了全新的高效的I/O机制,同时,也引入了多路复用的异步模式.NIO的包中主要包含了这样几种抽象数据类型: ...
- Java NIO类库Selector机制解析--转
一. 前言 自从J2SE 1.4版本以来,JDK发布了全新的I/O类库,简称NIO,其不但引入了全新的高效的I/O机制,同时,也引入了多路复用的异步模式.NIO的包中主要包含了这样几种抽象数据类型: ...
- Java NIO 选择器(Selector)的内部实现(poll epoll)
http://blog.csdn.net/hsuxu/article/details/9876983 之前强调这么多关于linux内核的poll及epoll,无非是想让大家先有个认识: Java NI ...
- Java NIO之Selector(选择器)
历史回顾: Java NIO 概览 Java NIO 之 Buffer(缓冲区) Java NIO 之 Channel(通道) 其他高赞文章: 面试中关于Redis的问题看这篇就够了 一文轻松搞懂re ...
- Java NIO 选择器(Selector)的内部实现(poll epoll)(转)
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/hsuxu/article/details/9876983 之前强调这么多关于linux内核的poll及epoll,无非是想让大家先有个认识: Java ...
- 转:Java NIO系列教程(九) Pipe
Java NIO 管道是2个线程之间的单向数据连接.Pipe有一个source通道和一个sink通道.数据会被写到sink通道,从source通道读取. 这里是Pipe原理的图示: 创建管道 通过Pi ...
- Java NIO之Selector
选择器是JavaNIO重磅推出的一个概念:在旧有的系统中为了跟踪多端口消息,需要为每一个端口配备一个线程做监听:但是有了selector就不需要了,一个Selector可以管理一众渠道(channel ...
- Java NIO学习笔记八 Pipe
Java NIO Pipe Java NIO管道是两个线程之间的单向数据连接.Pipe 具有源信道和接受通道.您将数据写入sink通道.然后可以从源通道读取该数据. 这是一个原理的Pipe流程图: J ...
- Netty快速入门(05)Java NIO 介绍-Selector
Java NIO Selector Selector是Java NIO中的一个组件,用于检查一个或多个NIO Channel的状态是否处于可读.可写.如此可以实现单线程管理多个channels,也就是 ...
随机推荐
- React的性能优化
1. 在constructor中绑定事件函数的this指向 把一个函数赋值给一个变量,然后用那个变量去执行函数会造成this的丢失,所以需要绑定this,把绑定放在构造函数中可以保证只绑定一次函数,如 ...
- HTTP中GET,POST和PUT的区别
一.HTTP中定义了以下几种请求方法: 1.GET:2.POST:3.PUT:4.DELETE;5.HEAD:6.TRACE:7.OPTIONS: 二.各个方法介绍: 1.GET方法:对这个资源的查操 ...
- 使用ABAP批量下载Markdown源文件里的图片到本地
执行我github里的这个report: 选中一段markdown文档,ctrl C: 然后直接执行report: 执行完毕: 所有文件都下载到本地文件夹: 这个report使用到的工具类:zcl_c ...
- Hadoop Shell 操作
此随笔仅记录一下常用的Hadoop shell 操作的命令 参考官方文档 http://hadoop.apache.org/docs/r1.0.4/cn/hdfs_shell.html FS S ...
- 如何自动运行loadrunner脚本
问题背景 在凌晨之后,自然流量比较低,无需人值守的情况自动运行loadruner脚本. 实现思路 windows定时任务+BAT脚本 BAT脚本: SET M_ROOT=C:\Program File ...
- 学java编程软件开发,非计算机专业是否能学
近几年互联网的发展越来越好,在国外,java程序员已经成为高薪以及稳定职业的代表,虽然国内的有些程序员很苦逼,但是那只是少数,按照国外的大方向来看,程序员还是一个很吃香的职业.根据编程语言的流行程度, ...
- 7.Bconsole操作
1. Bconsole操作 启动控制台 cd /usr/local/bacula/bin ./bconsole *help Command Description ======= ...
- React 入门与实战-课时7 虚拟DOM的本质和目的
DOM树的概念: 一个网页呈现的过程: 1.浏览器请求服务器获取页面HTML代码 2.浏览器先在内存中,解析DOM结构,并在浏览器内存中,渲染出一颗DOM树: 3.浏览器把DOM树,呈现到页面上: R ...
- metal cmd执行时间
https://developer.apple.com/library/archive/documentation/3DDrawing/Conceptual/MTLBestPracticesGuide ...
- 小tip: 使用SVG寥寥数行实现圆环loading进度效果(转载)
设计师设计了一个图片上传圆环loading进度效果.如下截图: 首先,CSS3是可以实现的,以前写过一篇转大饼的文章:“CSS3实现鸡蛋饼饼状图loading等待转转转”.原理跟这个一模一样,两个半区 ...
