数据结构( Pyhon 语言描述 ) — — 第3章:搜索、排序和复杂度分析
- 评估算法的性能
- 评价标准
- 正确性
- 可读性和易维护性
- 运行时间性能
- 空间性能(内存)
- 度量算法的运行时间
- 示例
"""
Print the running times for problem sizes that double,
using a aingle loop
"""
import time
print("%12s%16s" % ("Problem Size", "Seconds"))
):
start = time.time()
#The start of algorithm
for x in range(problemSize):
#The end of algorithm
elapsed = time.time() - start
print( "%12d%16.3f" %( problemSize,elapsed ) )
- 运行结果
Problem Size Seconds
1.065
2.078
4.433
7.733
18.676
- 测试时间会受到硬件和软件平台的影响
- 统计指令
- 一个嵌套循环所执行的迭代次数
- 示例
- 嵌套循环
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Author:Lijunjie
"""
File: counting.py
Prints the number of iterations for problem sizes that double,
using a nested loop.
"""
print( "%12s%15s" % ( "Problem Size", "Iteration" ) )
):
#The start of the algorithm
for j in range( problemSize ):
for k in range( problemSize ):
#The end of the algorithm
print( "%12d%15d" % ( problemSize, number ) )
- 结果
Problem Size Iteration
- Fibonacci数列
"""
Print the numbers of calls of a recursive Fibonacci
function with problem size that double
"""
from counter import Counter
def fibonacci( n, counter ):
"""Counter the numbers of calls of the fibonacci function."""
counter.increment()
, counter)
print( "%12s%15s" % ( "Problem Size", "Calls" ) )
):
counter = Counter()
#The start of the algorithm
fibonacci( problemSize, counter )
#The end of the algorithm
print( "%12d%15s" % ( problemSize, counter ) )
- 结果
Problem Size Calls
- 可以显示出算法工作量递增或递减的速率,而且独立于硬件和软件平台
- 度量算法所使用的内存
- 复杂度分析
- 表示方法
- 算法工作量增加的速率,可以用问题规模的函数来表示。
- 复杂度分析要查看算法的代码,以得出这些表示
- 这些表达式使得程序员能够预计,在任何计算机上执行一个算法会表现在有多好或多差
- 复杂度的阶与大O表示法
- 大O表示法
- 使用 O( f(n) ) 表示
- n 是算法问题的大小,f(n) 是要解决该问题所需工作量的一个表达式
- 运行时行为常用的表达式
- 常数阶
-

- 对数阶
-
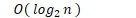
- 线性阶
-
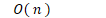
- 平方阶
-
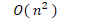
- 指数阶
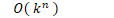
- 搜索算法
- 搜索最小值
- 算法复杂度为 O(n)
- 顺序搜索一个列表
- 最好情况
- 复杂度为 O(1)
- 最坏情况
- 复杂度为 O(n)
- 平均情况
- 平均迭代次数
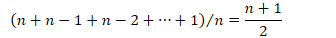
- 复杂度仍为 O(n)
- 有序列表的二叉搜索( 二分搜索 )
- 前提条件是列表有序
- 选用何种算法,取决于列表中数据的组织方式
- 最坏情况下的复杂:
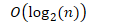
- 比较数据项
- 二叉搜索与搜索最小项,都是假设列表中的项是可以相互比较的
- 在Python中,这意味着这些项具有相同的类型,并且它们都识别比较运算符 ==, < 和 >
- 为了允许算法对一个新对象的类使用比较运算符 ==, > 和 <,应该在类中定义 __eq__,__lt__和__gt__方法,__lt__方法的定义如下:
def __lt__( self, other ):
- 基本排序算法
- 选择排序
- 每一次遍历,先选出最小值,再将其移到指定位置
def selectionSort( lyst ):
""" The selection sort algorithm """
:
minIndex = i
while j < len(lyst):
if lyst[j] < lyst[minIndex]:
minIndex = j
if minIndex != i: #Exchange if needed
swap( lyst, i, minIndex )
- 复杂度分析
- 比较次数
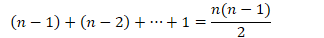
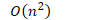
- 交换次数
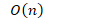
- 冒泡排序
- 每次遍历,把最大项交换到最后
def bubbleSort( lyst ):
n = len( lyst )
:
swapped = False
#start eack bubble
while i < n:
]:
swap( lyst, i, i - 1 ) #exchange if needed
swapped = True
if not swapped: return
- 修正:如果一次遍历的过程中,没有发生交换,说明列表己排好序,可以改进在最好情况下的行为,但是不会影响平均复杂度
- 复杂度
- 平均情况
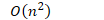
- 最环情况下,冒泡排序的交换工作超过线性方式
- 插入排序
- 相当于排列扑克牌的顺序
def insertionSort( lyst ):
while i < len( lyst ):
itemToInsert = lyst[i]
:
if lyst[j] > itemToInsert:
] = lyst[j]
else:
break
] = itemToInsert
- 复杂度分析
- 最坏情况
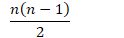
- 平均情况
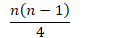
- 每次插入,平均到一半就会退出
- 复杂度
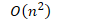
- 列表中排好序的项越多,插入排序的效果越好。如果列表是完全有序的,则其复杂度是线性阶的
- 最好情况,最坏情况和平均情况的性能
- 有些算法,在最好情况和平均情况下的性能是类似的,但是在最坏的情况下,性能可能下降
- 更快的排序
- 排序算法利用递归,分而治之的策略来突破 的限制
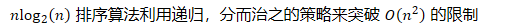
- 快速排序法
- 围绕基准点项来重新排列各项,并且递归的排序基准点两侧的列表
- 代码
def quicksort( lyst ):
""" The quicksort algorithm """
, len( lyst ) - 1 )
def quicksortHelper( lyst, left, right ):
""" The quicksort helper function """
if left < right:
pivotLocation = partition( lyst, left, right )
quicksortHelper( lyst, left, pivotLocation - 1 )
, right )
def partition( lyst, left, right ):
""" partition the list with the middle item """
#find the pivot item and exchange it with the last item
pivot = lyst[middle]
swap(lyst, middle, right)
#set boundary point to the first position
boundary = left
#move item less than pivot to the left
for index in range( left, right ):
if lyst[index] < pivot:
swap( lyst, index, boundary )
#exchange the pivot item and boundary item, then return the boundary
swap( lyst, right, boundary )
return boundary
- 复杂度分析
- 每分一次,大概比较n次,最好情况下,只会分割 次,因此最好情况下的复杂度为:

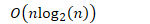
- 如果列表己排序好,而基点位置选的是起始或结束位置,则会分割n 次,此时复杂度为:
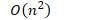
- 空间分析
- 栈的使用
- 最好情况
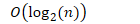
- 最坏情况
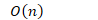
- 为了避免最坏情况,选取基准点应避免开始和结束位置
- 选择一个随机位置
- 选择列表的中间位置
- 选择第一个元素、中间元素、和最后元素之间的中位数的位置
- 合并排序
- 平均分割一个列表,递归的对每一半列表进行排序,然后合并结果
- 代码
from arrays import Array
def mergeSort( lyst ):
"""The mergeSort algorithm."""
#copyBuffer temporary space needed during merge
copyBuffer = Array( len( lyst ) )
, len( lyst ) - 1 )
def mergeSortHelper( lyst, copyBuffer, left, right ):
""" The helper function of mergeSort algorithm """
if left < right:
mergeSortHelper( lyst, copyBuffer, left, middle )
, right )
merge( lyst, copyBuffer, left, middle, right )
def merge( lyst, copyBuffer, left, middle, right ):
""" merge two sorted list into a big one """
#i1: The start of the sublist1
#i2: The start of the sublist2
i1 = left
for i in range( left, right + 1 ):
if i1 > middle:
copyBuffer[i] = lyst[i2]
elif i2 > right:
copyBuffer[i] = lyst[i1]
elif lyst[i1] < lyst[i2]:
copyBuffer[i] = lyst[i1]
else:
copyBuffer[i] = lyst[i2]
for i in range( left, right + 1 ):
lyst[i] = copyBuffer[i]
- arrays 为自定义的文件,如下:
"""
File: arrays.py
An Array is a restricted list whose clients can use
only [], len, iter, and str.
To instantiate, use
<variable> = array(<capacity>, <optional fill value>)
The fill value is None by default.
"""
class Array(object):
"""Represents an array."""
def __init__(self, capacity, fillValue = None):
"""Capacity is the static size of the array.
fillValue is placed at each position."""
self._items = list()
for count in range(capacity):
self._items.append(fillValue)
def __len__(self):
"""-> The capacity of the array."""
return len(self._items)
def __str__(self):
"""-> The string representation of the array."""
return str(self._items)
def __iter__(self):
"""Supports iteration over a view of an array."""
return iter(self._items)
def __getitem__(self, index):
"""Subscript operator for access at index."""
return self._items[index]
def __setitem__(self, index, newItem):
"""Subscript operator for replacement at index."""
self._items[index] = newItem
- 复杂度分析
- 每一层的合并花费为,层级数为
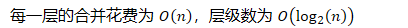
- 在所有情况下的最大运行时间
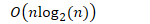
- 空间分析
- 调用栈
- 空间
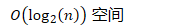
- 复制缓存
- 的空间

- 指数算法:递归式的 Fibonacci 算法
- 调用树
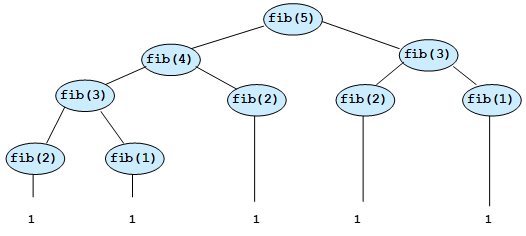
- 完全平衡树的递归调用次数
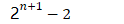
- 递归式Fibonacci 复杂度——指数阶
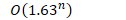
- 将 Fibnocci 转换为一个线性算法
def fibonacci( n ):
""" The liner algorithm of fibonacci """
while count <= n:
sum = first + second
first = second
second = sum
return sum
- 探查器
- 需求
- 编写一个程序,允许程序员探查不同的排序算法
- 分析
- 定义一个排序函数,并且在排序算法的函数头中包含一个 Profiler 对象
- 在排序算法的代码中,涉及统计、统计和交换的地方,用 Profiler 对象运行 comparison() 和 exchange() 方法
- Profiler 类的接口
探查器方法
作用
p.test( function, lyst = None, size = 10, unique = True, comp = Ture, exch = True, trace = False)
用给定的设置运行Function,并输出结果
p.comparison()
自增比较次数
p.exchange()
自增交换次数
p.__str__()
和 str(p) 相同
- 设计
- 两个模块
- Profiler ——定义了 Profiler 类
- Algorithms ——定义了用来进行探查的排序函数
数据结构( Pyhon 语言描述 ) — — 第3章:搜索、排序和复杂度分析的更多相关文章
- 数据结构( Pyhon 语言描述 ) — —第10章:树
树的概览 树是层级式的集合 树中最顶端的节点叫做根 个或多个后继(子节点). 没有子节点的节点叫做叶子节点 拥有子节点的节点叫做内部节点 ,其子节点位于层级1,依次类推.一个空树的层级为 -1 树的术 ...
- 数据结构( Pyhon 语言描述 ) — —第11章:集和字典
使用集 集是没有特定顺序的项的一个集合,集中的项中唯一的 集上可以执行的操作 返回集中项的数目 测试集是否为空 向集中添加一项 从集中删除一项 测试给定的项是否在集中 获取两个集的并集 获取两个集的交 ...
- 数据结构( Pyhon 语言描述 ) — —第9章:列表
概念 列表是一个线性的集合,允许用户在任意位置插入.删除.访问和替换元素 使用列表 基于索引的操作 基本操作 数组与列表的区别 数组是一种具体的数据结构,拥有基于单个的物理内存块的一种特定的,不变的实 ...
- 数据结构( Pyhon 语言描述 ) — — 第7章:栈
栈概览 栈是线性集合,遵从后进先出原则( Last - in first - out , LIFO )原则 栈常用的操作包括压入( push ) 和弹出( pop ) 栈的应用 将中缀表达式转换为后缀 ...
- 数据结构( Pyhon 语言描述 ) — — 第5章:接口、实现和多态
接口 接口是软件资源用户可用的一组操作 接口中的内容是函数头和方法头,以及它们的文档 设计良好的软件系统会将接口与其实现分隔开来 多态 多态是在两个或多个类的实现中使用相同的运算符号.函数名或方法.多 ...
- 数据结构( Pyhon 语言描述 ) — — 第4章:数据和链表结构
数据结构是表示一个集合中包含的数据的一个对象 数组数据结构 数组是一个数据结构 支持按照位置对某一项的随机访问,且这种访问的时间是常数 在创建数组时,给定了用于存储数据的位置的一个数目,并且数组的长度 ...
- 数据结构( Pyhon 语言描述 ) — — 第6章:继承和抽象类
继承 新的类通过继承可以获得已有类的所有特性和行为 继承允许两个类(子类和超类)之间共享数据和方法 可以复用已有的代码,从而消除冗余性 使得软件系统的维护和验证变得简单 子类通过修改自己的方法或者添加 ...
- 数据结构( Pyhon 语言描述 ) — — 第2章:集合概览
集合类型 定义 个或多个其他对象的对象.集合拥有访问对象.插入对象.删除对象.确定集合大小以及遍历或访问集合的对象的操作 分类 根据组织方式进行 线性集合 线性集合按照位置排列其项,除了第一项,每一项 ...
- 数据结构( Pyhon 语言描述 ) — — 第1章:Python编程基础
变量和赋值语句 在同一条赋值语句中可以引入多个变量 交换变量a 和b 的值 a,b = b,a Python换行可以使用转义字符\,下一行的缩进量相同 )\ 帮助文档 help() 控制语句 条件式语 ...
随机推荐
- LSP5513
LSP5513:宽范围高效的DC-DC(输入:4.5~27V;输出0.925~24V,3A),输出电流达3A
- awk一些简单命令
最简单地说, AWK 是一种用于处理文本的编程语言工具.AWK 在很多方面类似于 shell 编程语言,尽管 AWK 具有完全属于其本身的语法. 尽管操作可能会很复杂,但命令的语法始终是: awk ' ...
- TP框架设置验证码
thinkphp框架有专门的的验证码生成的模块 public function shengcheng(){ $n = new \Think\Verify(); $n->entry(); } 下面 ...
- “Debug Assertion” Runtime Error on VS2008 VS2010 winhand.cpp
I'm writing a C++ MFC program on VS2008 and I'm getting this "Debug Assertion Error" when ...
- SQL注入中的整型注入实验
首先搭建一个用于注入的环境 目录结构 conn.php 用来连接数据库的文件PHP文件 index.php 用来执行SQL命令,以及返回查询结构 index.html 一个存 ...
- Xcode 升级后,cocoaPod 问题
当我从Xcode 6.3切换到Xcode6.4的时候,因为我是mac上安装了两个不同的版本,现在把Xcode 6.3卸掉了. 现在再次运行pod install命令的时候,提示如下错误: Upda ...
- Sublime Text 3 使用小记
快捷键: [ // 代码对齐插件 { "keys": ["shift+alt+a"], "command": "alignment ...
- 用python格式化小说txt
下载了<无人生还>的txt版.传到手机,发现阅读器识别得不够好. 原文格式如下: 第一章 一 沃格雷夫法官先生新近离任退休,现在正在头等车厢的吸烟室里,倚角而坐,一 边喷着雪茄烟,一边兴致 ...
- C#语言 数据类型 类型转换
数据类型有 基本数据类型 和 引用数据类型 两大类型. 数据类型 C#语言 .NET(通用语言) 大小(字节) 值区间 基本数据类型 值类型 整型 不能存在小数点,可以有负数 byte Byte ...
- Codeforces Round #275(Div. 2)-C. Diverse Permutation
http://codeforces.com/contest/483/problem/C C. Diverse Permutation time limit per test 1 second memo ...
