「SOL」E-Lite (Ural Championship 2013)
为什么这数据能水到可以枚举角度 ac 啊
# 题面
给你 \(n\) 个平面向量 \((x_i,y_i)\),对于每个 \(k=1\sim n\),求「从给出的 \(n\) 个向量中不重复地选择 \(k\) 个,\(k\) 个向量的和的模长最大是多少」。
数据规模:\(n\le1000\)。
# 解析
这种「选择 \(k\) 个」的题目,我们之前往往会从 DP 考虑,或者贪心求解。但是我们发现向量并不满足局部最优就是全局最优。
于是这道题我们换一个思路,不从选的过程考虑,而从选的结果 —— 也就是答案的角度考虑。
如果我们知道了答案为 \(\mathbf{v}\),那么一定是由在 \(\mathbf{v}\) 方向上投影最大的 \(k\) 个向量组成的。于是我们可以尝试「旋转」答案向量的方向,然后贪心地选取向量。
虽然数据水,离散地枚举答案向量角度可以 ac,但是角度毕竟是连续的,这种做法不是很靠谱(但是很难卡掉)。
连续的枚举一般考虑枚举临界点。不妨设我们逆时针旋转答案向量 \(\mathbf{v}\),记 id[i] 表示当前在 \(\mathbf{v}\) 方向上投影从大到小第 \(i\) 个向量是哪一个,同理定义 rnk[i] 表示 \(i\) 向量的排名(rnk[id[i]] = i)。
我们发现只有 id 发生变化 —— 也即两个向量的相对投影大小改变时,答案才会改变。设 \(\mathbf{u,v}\) 为两个方向不同的向量:
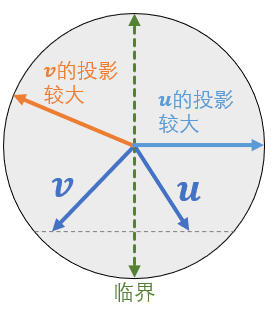
于是一对向量会产生两个临界点,总共会有 \(\mathcal{O}(n^2)\) 个临界。将它们极角排序过后逆时针扫一遍。
每经过一个临界点,就会有 rank 相邻的两个向量的 rank 发生交换(记为 rnk, rnk + 1)。扫描时,维护当前 rank,当 rnk, rnk + 1 交换时,只会改变前 rnk 个和前 rnk + 1 个向量的和,\(\mathcal{O}(1)\) 更新答案即可。
唯一的麻烦点是给出的 \(n\) 个向量可能重叠……我的处理是把重叠的向量看成一个,记录一下个数。只能自己意会一下或者看一看代码了。
# 源代码
/*Lucky_Glass*/
#include <cmath>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <cassert>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long double ldouble;
const int N = 1005;
const ldouble EPS = 1e-12;
#define con(typ) const typ &
#define sec second
#define fir first
template<class typ> typ iAbs(con(typ) key) {return key < 0 ? -key : key;}
template<class typ> int sgn(con(typ) key) {
if ( iAbs(key) <= EPS ) return 0;
return key < 0 ? -1 : 1;
}
struct Vector {
ldouble x, y;
Vector() {}
Vector(con(ldouble) _x, con(ldouble) _y) : x(_x), y(_y) {}
ldouble len() const {return x * x + y * y;}
Vector operator - (con(Vector) p) const {
return Vector(x - p.x, y - p.y);
}
Vector operator + (con(Vector) p) const {
return Vector(x + p.x, y + p.y);
}
friend ldouble dot(con(Vector) p, con(Vector) q) {
return p.x * q.x + p.y * q.y;
}
Vector operator -() const {return Vector(-x, -y);}
bool operator != (con(Vector) p) const {
return sgn(x - p.x) || sgn(y - p.y);
}
bool operator < (con(Vector) p) const {
if ( sgn(x - p.x) ) return sgn(x - p.x) < 0;
return sgn(y - p.y) < 0;
}
Vector cwise90() const {return Vector(y, -x);}
} sum[N];
struct Data {
Vector v; int cnt;
Data() {}
Data(con(Vector) _v, con(int) _c) : v(_v), cnt(_c) {}
} dat[N];
int nn, n, ndv;
pair<int, int> inp[N];
int cnt[N], rnk[N];
ldouble ans[N];
struct Divi {
int a, b;
ldouble ang;
Divi() {}
Divi(con(int) _a, con(int) _b, con(ldouble) _ang)
: a(_a), b(_b), ang(_ang) {}
bool operator == (con(Divi) p) const {return !sgn(ang - p.ang);}
static bool cmpAng(con(Divi) p, con(Divi) q) {return sgn(p.ang - q.ang) < 0;}
static bool cmpID(con(Divi) p, con(Divi) q) {
if ( rnk[p.a] != rnk[q.a] ) return rnk[p.a] < rnk[q.a];
return rnk[p.b] < rnk[q.b];
}
} dv[N * N];
void init() {
sum[0] = Vector(0, 0);
for (int i = 1, tmp = 0; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= dat[i].cnt; j++) {
tmp++;
sum[tmp] = sum[tmp - 1] + dat[i].v;
ans[tmp] = sum[tmp].len();
}
rnk[i] = i, cnt[i] = tmp;
}
}
// q is better than p then
void done(con(int) p, con(int) q) {
// assert( rnk[p] == rnk[q] - 1 );
int tmp = cnt[rnk[p] - 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= dat[q].cnt; i++) {
tmp++;
sum[tmp] = sum[tmp - 1] + dat[q].v;
ans[tmp] = max(ans[tmp], sum[tmp].len());
}
cnt[rnk[p]] = tmp;
for (int i = 1; i <= dat[p].cnt; i++) {
tmp++;
sum[tmp] = sum[tmp - 1] + dat[p].v;
ans[tmp] = max(ans[tmp], sum[tmp].len());
}
swap(rnk[p], rnk[q]);
}
int main() {
scanf("%d", &nn);
for (int i = 1; i <= nn; i++)
scanf("%d%d", &inp[i].fir, &inp[i].sec);
sort(inp + 1, inp + 1 + nn);
for (int i = 1; i <= nn;) {
int j = i;
while ( j <= nn && inp[i] == inp[j] ) j++;
dat[++n] = Data(Vector(inp[i].fir, inp[i].sec), j - i);
inp[n] = inp[i];
i = j;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = i + 1; j <= n; j++) {
double k1 = atan2(inp[j].fir - inp[i].fir, inp[i].sec - inp[j].sec),
k2 = atan2(inp[i].fir - inp[j].fir, inp[j].sec - inp[i].sec);
dv[++ndv] = Divi(j, i, k1);
dv[++ndv] = Divi(i, j, k2);
}
sort(dv + 1, dv + 1 + ndv, Divi::cmpAng);
init();
for (int i = 1; i <= ndv; ) {
int j = i;
while ( j <= ndv && dv[i] == dv[j] ) j++;
sort(dv + i, dv + j, Divi::cmpID);
while ( i < j ) {
done(dv[i].a, dv[i].b);
i++;
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= nn; i++)
printf("%.8f\n", (double)sqrt(ans[i]));
return 0;
}
THE END
Thanks for reading!
「SOL」E-Lite (Ural Championship 2013)的更多相关文章
- loj#2013. 「SCOI2016」幸运数字 点分治/线性基
题目链接 loj#2013. 「SCOI2016」幸运数字 题解 和树上路径有管...点分治吧 把询问挂到点上 求出重心后,求出重心到每个点路径上的数的线性基 对于重心为lca的合并寻味,否则标记下传 ...
- loj #2013. 「SCOI2016」幸运数字
#2013. 「SCOI2016」幸运数字 题目描述 A 国共有 n nn 座城市,这些城市由 n−1 n - 1n−1 条道路相连,使得任意两座城市可以互达,且路径唯一.每座城市都有一个幸运数字,以 ...
- AC日记——「SCOI2016」幸运数字 LiBreOJ 2013
「SCOI2016」幸运数字 思路: 线性基: 代码: #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; #define maxn 20005 # ...
- FileUpload控件「批次上传 / 多档案同时上传」的范例--以「流水号」产生「变量名称」
原文出處 http://www.dotblogs.com.tw/mis2000lab/archive/2013/08/19/multiple_fileupload_asp_net_20130819. ...
- 一本通1648【例 1】「NOIP2011」计算系数
1648: [例 1]「NOIP2011」计算系数 时间限制: 1000 ms 内存限制: 524288 KB [题目描述] 给定一个多项式 (ax+by)k ,请求出多项式展开后 x ...
- 「SCOI2016」背单词
「SCOI2016」背单词 Lweb 面对如山的英语单词,陷入了深深的沉思,「我怎么样才能快点学完,然后去玩三国杀呢?」.这时候睿智的凤老师从远处飘来,他送给了 Lweb 一本计划册和一大缸泡椒,然后 ...
- loj2009. 「SCOI2015」小凸玩密室
「SCOI2015」小凸玩密室 小凸和小方相约玩密室逃脱,这个密室是一棵有 $ n $ 个节点的完全二叉树,每个节点有一个灯泡.点亮所有灯泡即可逃出密室.每个灯泡有个权值 $ A_i $,每条边也有个 ...
- 「译」JUnit 5 系列:条件测试
原文地址:http://blog.codefx.org/libraries/junit-5-conditions/ 原文日期:08, May, 2016 译文首发:Linesh 的博客:「译」JUni ...
- 「译」JUnit 5 系列:扩展模型(Extension Model)
原文地址:http://blog.codefx.org/design/architecture/junit-5-extension-model/ 原文日期:11, Apr, 2016 译文首发:Lin ...
- JavaScript OOP 之「创建对象」
工厂模式 工厂模式是软件工程领域一种广为人知的设计模式,这种模式抽象了创建具体对象的过程.工厂模式虽然解决了创建多个相似对象的问题,但却没有解决对象识别的问题. function createPers ...
随机推荐
- Python_七十二变_二进制和字符编码
第二章 七十二变 二进制和字符编码 8bit为1byte 字节 1024byte为1KB 千 1024KB为1MB 兆 1024MB为1GB 吉 1024GB为1TB 太 ASCLL字符 ...
- (已解决)nginx+tp,怎么设置 省略index.php的url访问。
打开vhosts.conf,在localhost / {}里面加入下面的代码: if (!-e $request_filename) { rewrite ^(.*)$ /index.php?s=$1 ...
- 性能测试-top-实时显示系统中各个进程的资源占用状况, 也可以查看线程
1.top命令介绍 top命令是Linux系统中常用的性能分析工具,可以实时地查看系统的运行情况,比如内存.CPU.负载以及各个进程的资源占用情况 top界面主要分为两个部分,前5行展示的是系统的整体 ...
- 牛客算法进阶——树形dp
1. 小G有一个大树(求树的重心) 删除该点后最大连通块的节点数最小 设f[x]表示以x为根的子树大小,那么删除x之后的各子树大小为f[to]和n-f[x] 求max(max(f[to]),n-f[x ...
- (0501)phase机制
(1)启动seq: (2) 0312:
- 用FineBI实现hive图表的可视化
图表的可视化,本来我以为很麻烦,因为看着图就感觉很难的样子,其实用FineBI来做很简单. 1.安装FineBI 2将下列jar包导入FineBI,webapps\webroot\WEB-INF\li ...
- VM安装linux2022、设置root密码、设置国内更新源
一.创建虚拟机 1.打开VM软件选择"创建新的虚拟机" 2.选择"典型"即可 3.选择"稍后安装操作系统" 4.选择客户机操作系统为&quo ...
- 常用的Shell实用脚本
1.检测两台服务器指定目录下的文件的一致性 #!/bin/bash######################################检测两台服务器指定目录下的文件一致性########### ...
- 解决pycharm中cv2报错问题,anaconda安装opencv
写在前面的话:cv2 报错是因为没安装opencv安装包所导致,并且在pycharm终端不可使用pip install cv2 进行安装! 如何解决cv2报错: 首先,值得注意的是在pycharm中, ...
- csec的key更新
在对csec的使用中(其他遵循hsm key update协议的芯片也适用),kdf的运算过程中遇到的数据都是128bit.不需要考虑padding的问题.目前并没有找到对padding的一致性的处理 ...
