Python函数式编程之map/filter/reduce/sorted
Python函数式编程之map/filter/reduce/sorted
关于函数式编程
- 函数式编程Functional Programming,其思想更接近数学计算
- 函数式编程就是一种抽象程度很高的编程范式,纯粹的函数式编程语言编写的函数没有变量,因此,任意一个函数,只要输入是确定的,输出就是确定的。
- Python对函数式编程提供部分支持
- 由于Python允许使用变量,因此,Python不是纯函数式编程语言
- 函数式编程的一个特点就是,允许把函数本身作为参数传入另一个函数,还允许返回一个函数(你会想到,闭包?装饰器?)
map 映射
定义
- 关键是声明和注释,内置方法你可以先忽略
- map(func, *iterables) --> map object # 第一个参数是个函数名,第二个参数是个可迭代的对象
- map的作用是将func作用到迭代器中的每个元素上
class map(object)
| map(func, *iterables) --> map object
|
| Make an iterator that computes the function using arguments from
| each of the iterables. Stops when the shortest iterable is exhausted.
|
| Methods defined here:
|
| __getattribute__(self, name, /)
| Return getattr(self, name).
|
| __iter__(self, /)
| Implement iter(self).
|
| __next__(self, /)
| Implement next(self).
|
| __reduce__(...)
| Return state information for pickling.
|
| ----------------------------------------------------------------------
| Static methods defined here:
|
| __new__(*args, **kwargs) from builtins.type
| Create and return a new object. See help(type) for accurate signature.
实例
从简->难
1. 将列表中每个整数变为平方
list1 = [1,2,3] # --> [1,4,9]
# 循环
list2 = []
for _ in list1:
list2.append(_**2)
# 列表推导式
[i**2 for i in list1]
# map
list(map(lambda x:x**2,list1))
# 等价于
def f(x):
return x * x
list(map(f,list1))
- 从上面你可以看出来,map可以跟列表推导式一定程度上等价,当然也是可以用for来完成的。
- map很多的时候跟lambda结合使用。
- 效果见下图,map映射,有一一对应之意,将这个func(函数)作用到迭代器的每个元素上。
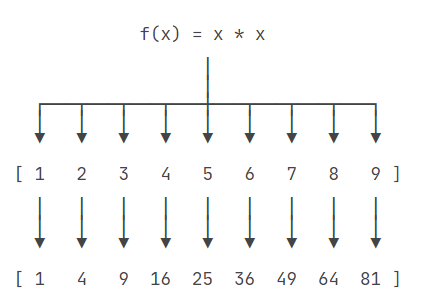
下面都是一些简单的例子而已
2. 将列表中每个整数变为字符串
list1 = [1,2,3]
list(map(str,list1))
- 注意map返回的是map object
3. 得到学生姓名的列表
students = [
{"name": "John Doe",
"father name": "Robert Doe",
"Address": "123 Hall street"
},
{
"name": "Rahul Garg",
"father name": "Kamal Garg",
"Address": "3-Upper-Street corner"
},
{
"name": "Angela Steven",
"father name": "Jabob steven",
"Address": "Unknown"
}
]
像例子1-2是烂大街的map举例的,像3这种就不太明显了,但却非常适合用map
list(map(lambda stu:stu['name'],students))
当然还有一个问题是这样的lambda你是否能想到?(虽然比较简单)
4. 将2个列表中对应的数据相乘
list1 = [1,2,3]
list2 = [4,5,6] # -> [4,10,18] 1*4 2*5 3*6
这个用列表推导式可以吗?反正我不太会做
[i*j for i in list1 for j in list2] # [4, 5, 6, 8, 10, 12, 12, 15, 18] # 可以看到是一个双重for循环用map实现
list(map(lambda x,y:x*y,list1,list2)) # 你可以看到x来自list1,y来自list2
- 是的,map后面第一个参数是函数名,第二个参数是可迭代对象,但可以是多个。
5. 映射多个函数的一个示例
# ×2
def double(x):
return x + x
# 平方
def square(x):
return x * x
# 数据
list1 = [1, 2, 3 ]
# 处理
for i in list1:
temp = tuple(map(lambda x: x(i), (double, square)))
print(temp)
###
# (2, 1)
# (4, 4)
# (6, 9)
6. 其他实例
把用户输入的不规范的英文名字,变为首字母大写,其他小写的规范名字
list1 = ['adam', 'LISA', 'barT']
list(map(lambda x:x.capitalize(),list1))
将一个数字字符串转换为整数的list
list(map(int,'1234'))
提取字典中的key
list(map(int,{1:2,2:3,3:4}))
快速生成26个英文字符
"".join(map(chr, range(ord('a'), ord('z') + 1)))
统计指定字符串每个字符出现的次数,从高到底排列
from collections import Counter
string = "AAABBCCAC"
print("".join(map(lambda x: x[0] + str(x[1]), Counter(string).most_common()))) #A4C3B2
在pandas中大量存在map等应用
filter 过滤
- 筛选满足条件的元素时非常有用
定义
class filter(object)
| filter(function or None, iterable) --> filter object
|
| Return an iterator yielding those items of iterable for which function(item)
| is true. If function is None, return the items that are true.
|
| Methods defined here:
|
| __getattribute__(self, name, /)
| Return getattr(self, name).
|
| __iter__(self, /)
| Implement iter(self).
|
| __next__(self, /)
| Implement next(self).
|
| __reduce__(...)
| Return state information for pickling.
|
| ----------------------------------------------------------------------
| Static methods defined here:
|
| __new__(*args, **kwargs) from builtins.type
| Create and return a new object. See help(type) for accurate signature
实例
1. 找出整数列表中的奇数
nums = [1,2,3,4,5]
list(filter(lambda x:x%2==1,nums))
2. 找出姓名长度不超过5个字符的人员信息
names = ['alice','jordan','richardson','mike','hudson']
list(filter(lambda x:len(x)<=5,names))
3. 求所有的水仙花数
list(filter(lambda num:int(str(num)[0])**3+int(str(num)[1])**3+int(str(num)[2])**3 == num,range(100,1000)))
4. 剔除所有空字符串
def not_empty(s):
return s and s.strip()
list(filter(not_empty, ['A', '', 'B', None, 'C', ' ']))
reduce 递推
reduce是相对来说比较难的一个函数,一方面是不常用,但在某些应用场景中用它就非常巧妙,另外一方面这个递推的过程你得理解。
定义
reduce(...)
reduce(function, sequence[, initial]) -> value
Apply a function of two arguments cumulatively to the items of a sequence,
from left to right, so as to reduce the sequence to a single value.
For example, reduce(lambda x, y: x+y, [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]) calculates
((((1+2)+3)+4)+5). If initial is present, it is placed before the items
of the sequence in the calculation, and serves as a default when the
sequence is empty.
此处的example对理解reduce非常重要
reduce(lambda x, y: x+y, [1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
--->
((((1+2)+3)+4)+5)
有个递归的意思在里面from functools import reduce
实例
1. 把[1,3,5,7,9]变成13579
from functools import reduce
reduce(lambda x,y:10*x+y, [1, 3, 5, 7, 9])
- 注意reduce在functools下面,需要导入
2. 对整数列表中的奇数元素进行求平方
items = [12, 5, 7, 10, 8, 19]
list(map(lambda x: x ** 2, filter(lambda x: x % 2, items)))
# 其实用 列表推导式反而简单了
items = [12, 5, 7, 10, 8, 19]
[x ** 2 for x in items if x % 2]
3. 实现str->int的转换
from functools import reduce
DIGITS = {'0': 0, '1': 1, '2': 2, '3': 3, '4': 4, '5': 5, '6': 6, '7': 7, '8': 8, '9': 9}
def char2num(s):
return DIGITS[s]
def str2int(s):
return reduce(lambda x, y: x * 10 + y, map(char2num, s))
string = '135'
print(str2int(string))
4. 对列表中所有数字相乘
from functools import reduce
def prod(L):
return reduce(lambda x,y:x*y,L)
print('3 * 5 * 7 * 9 =', prod([3, 5, 7, 9]))
if prod([3, 5, 7, 9]) == 945:
print('测试成功!')
else:
print('测试失败!')
sorted 排序
sorted是python的内置函数,可以排序容器,并且自己定义排序的策略
定义
sorted(iterable, /, *, key=None, reverse=False)
Return a new list containing all items from the iterable in ascending order.
A custom key function can be supplied to customize the sort order, and the
reverse flag can be set to request the result in descending order.
- reverse可以用来改变正序->倒序
- key可以用来自定义排序规则
实例
1. 常规正序倒序
list1 = [1,3,5,2,4,6]
sorted(list1) # [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
sorted(list1,reverse=True) # [6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1]
2. 字典的key排序
dict1 = {"zhangsan":18,"lisi":20,"wangwu":23,"hanmeimei":22}
sorted(dict1) # ['hanmeimei', 'lisi', 'wangwu', 'zhangsan']
- dict的sorted得到的结果就是按key来排序
3. 多维数据的排序
list1 = [('A',3,200),('C',1,100),('B',2,300)]
sorted(list1,key=lambda x:x[1])
# [('C', 1, 100), ('B', 2, 300), ('A', 3, 200)]
sorted(list1,key=lambda x:x[0],reverse=False)
# [('A', 3, 200), ('B', 2, 300), ('C', 1, 100)]
sorted(list1,key=lambda x:x[2])
# [('C', 1, 100), ('A', 3, 200), ('B', 2, 300)]
4. 根据字符串的长度排序
urls=['http://c.biancheng.net',
'http://c.biancheng.net/python/',
'http://c.biancheng.net/shell/',
'http://c.biancheng.net/java/',
'http://c.biancheng.net/golang/']
sorted(urls,key=lambda x:len(x))
5. 根据切割后的字典序(忽略大小写)
sorted("This is a test string from Andrew".split(), key=str.lower)
# ['a', 'Andrew', 'from', 'is', 'string', 'test', 'This']
6. 自定义类的排序
class Person:
def __init__(self,name,age):
self.name = name
self.age = age
def __repr__(self):
return self.name
infos = [Person("wuxianfeng",18),Person("zhangsan",23),Person("lisi",21)]
sorted(infos,key=lambda per:per.age) # [wuxianfeng, lisi, zhangsan]
Python函数式编程之map/filter/reduce/sorted的更多相关文章
- Python函数式编程之map()
Python函数式编程之map() Python中map().filter().reduce()这三个都是应用于序列的内置函数. 格式: map(func, seq1[, seq2,…]) 第一个参数 ...
- python 内置函数 map filter reduce lambda
map(函数名,可遍历迭代的对象) # 列组元素全加 10 # map(需要做什么的函数,遍历迭代对象)函数 map()遍历序列得到一个列表,列表的序号和个数和原来一样 l = [2,3,4,5,6, ...
- Python函数式编程中map()、reduce()和filter()函数的用法
Python中map().reduce()和filter()三个函数均是应用于序列的内置函数,分别对序列进行遍历.递归计算以及过滤操作.这三个内置函数在实际使用过程中常常和“行内函数”lambda函数 ...
- python 函数式编程之lambda( ), map( ), reduce( ), filter( )
lambda( ), map( ), reduce( ), filter( ) 1. lambda( )主要用于“行内函数”: f = lambda x : x + 2 #定义函数f(x)=x+2 g ...
- Python函数式编程之lambda表达式
一:匿名函数的定义 lambda parameter_list: expression 二:三元表达式 条件为真时返回的结果 if 条件判断 else 条件为假的时候返回的结果 三:map map(f ...
- Python面试题之Python中的lambda map filter reduce zip
当年龟叔想把上面列出来的这些都干掉.在 “All Things Pythonic: The fate of reduce() in Python 3000”这篇文章中,他给出了自己要移除lambda. ...
- python之内置函数:map ,filter ,reduce总结
map函数: #处理序列中的每个元素,得到的结果是一个'列表',该列表元素个数及位置与原来一样 filter函数: #遍历序列中的每个元素,判断每个元素得到一个布尔值,如果是true,则留下来 peo ...
- python函数式编程之yield表达式形式
先来看一个例子 def foo(): print("starting...") while True: res = yield print("res:",res ...
- Swift函数编程之Map、Filter、Reduce
在Swift语言中使用Map.Filter.Reduce对Array.Dictionary等集合类型(collection type)进行操作可能对一部分人来说还不是那么的习惯.对于没有接触过函数式编 ...
- python常用函数进阶(2)之map,filter,reduce,zip
Basic Python : Map, Filter, Reduce, Zip 1-Map() 1.1 Syntax # fun : a function applying to the iterab ...
随机推荐
- 【题解】CF919D Substring
题面传送门 解决思路: DP 与拓扑结合.\(f_{i,j}\) 表示到 \(i\) 位置 \(j\) 的最大次数. 将 \(a \sim z\) 转成数字 \(0\sim 25\) ,方便存储. 考 ...
- shell文件报错syntax error near unexpected token '$'\r''
本来跑的好好得一个文件,在windows下修改了,然后移植到linux就报错了. 找了一圈以下是解决方案: 这种情况发生的原因是因为你所处理的文件换行符是dos格式的"\r\n" ...
- C++编程笔记(STL学习)
一.顺序容器 1.1.vector 1.2.dequeue 1.3.list 二.关联性容器 2.3.set 2.3.map 三.算法 3.1.遍历算法(for_each ...
- 5:Echarts数据可视化-多条曲线、多个子图、TreeMap类似盒图、树形图、热力图、词云
〇.目标 本次实验主要基于Echarts的Python库实现高维数据.网络和层次化数据.时空数据和文本数据的可视化,掌握可视化的操作流程和相关库的使用. 一.绘制平行坐标系 平行坐标是信息可视化的一种 ...
- 【消息队列面试】6-10:Rebalance机制、副本同步机制、架构设计、zk的作用、kafka的高性能
六.简述kafka的Rebalance[偏向实战,有难度] 1.背景 kafka日志:在消息量大.高并发时,经常会出现rebalance中 rebalance会影响kafka性能,会阻塞partiti ...
- 【Spark】Day04-Spark Streaming:与离线批量比较、架构特点、入门案例、创建(队列、数据源)、转换(有状态、无状态)、输出方式、进阶(累加、转换为DF、缓存持久化)、实战(窗口统计)
一.概述 1.离线和实时计算 离线:数据量大,数据不会变化,MapReduce 实时:数据量小,计算过程要短 2.批量和流式处理 批量:冷数据,数据量大,速度慢 流:在线.实时产生的数据(快速持续到达 ...
- 网络编程 - OSI七层协议详解
目录 网络编程基础 软件开发架构 网络编程简介 OSI七层协议简介 OSI协议之物理连接层 OSI协议之数据链路层 网络相关专业名词 OSI之网络层 OSI协议之传输层 传输层之TCP协议/UDP协议 ...
- Vue 打包报错UnhandledPromiseRejectionWarning: postcss-svgo: Error in parsing SVG
解决方案 检查下自己最新写的css 或者最新引入的样式库,把里面的base64的url替换成双引号形式的 PS:我这报错是因为引入的weui.min.css里面的loading样式的`backgrou ...
- idea里面连接数据库进行sql操作
常用写法 1. private static void test01() throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException{ Class.forName(&quo ...
- [OpenCV实战]38 基于OpenCV的相机标定
文章目录 1 什么是相机标定? 2 图像形成几何学 2.1 设定 2.1.1 世界坐标系 2.1.2 相机坐标系 2.1.3 图像坐标系 2.2 图像形成方法总结 3 基于OpenCV的相机标定原理 ...
