单链表(C++实现)
单链表的结构有多种
这里介绍的链表有头结点、有尾节点并且尾节点指向头结点
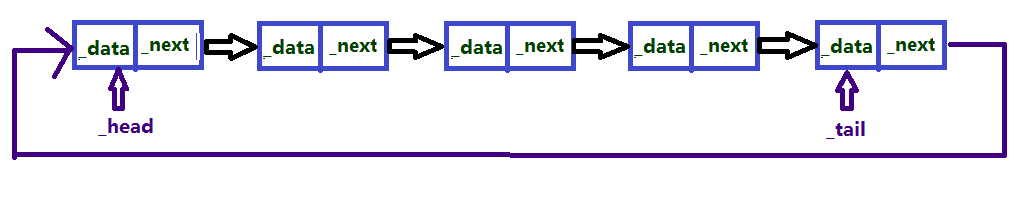
单链表的每个结点的地址存放在其直接前驱结点的指针域中。其中第一个结点没有前驱结点,因此需要一个头指针指向第一个节点,便于我们对整个链表进行操作;这里的单链表的最后一个节点的指针域存放的是头结点的地址。
单链表不能随意存取,必要的时候我们可以通过已知结点的指针域不断遍历从而获取我们要的结点。
SList.h
/****************************************************************************************************/
/*
功能:应用C++语言实现单链表的各项操作
建立链表的节点类LinkNode,封装一个SList类将有效节点链接起来
基本的成员函数:
构造函数、拷贝构造函数、赋值运算符的重载、析构函数
**
**单链表的具体操作:
** 1:在尾部插入节点
** 2:打印单链表
** 3:链表置空
** 4:尾除尾节点
** 5:头插
** 6:删除首节点
** 7:固定位置插入一个节点
** 8:删除某一节点
** 9:查找某节点并返回这个节点的位置
** 10:计算链表节点的数目
** 11:查找某节点并删除
** 12:删除链表中所有的x
** 13:去重
** 14:合并两个链表
** 15:冒泡排序
** 16:翻转单链表
**
** By :Lynn-Zhang
**
*/
/*****************************************************************************************************/
//****************/ typedef int DataType; //节点类(复合形态)
//struct LinkNode
//{
// friend class SList; //将SList设为友元,便于SList类可以访问节点类的私有成员
//public:
// LinkNode(const DataType x);
//private:
// DataType _data; //节点的数据
// LinkNode* _next; //指向该节点的下一个节点
//}; //直接用struct定义LinkNode类,因为struct的成员默认为公有数据成员,所以可直接访问
struct LinkNode //节点类(建议写法)
{
LinkNode(const DataType x);
DataType _data; //节点的数据
LinkNode* _next; //指向该节点的下一个节点
};
class SList
{
public:
SList(); //构造函数
SList(const SList& s); //拷贝构造
SList &operator=(SList& s); //赋值运算符的重载
~SList(); public:
//单链表的具体操作
void Uniqe(); //去重
void Merge(SList &s); //合并
void Sort(); //冒泡
void Reverse(); //翻转
void Swap(SList& s); //交换
void PrintSList(); //打印链表
void PushBack(const DataType& x); //在尾部插入一个节点
void Clear(); //链表置空
void PopBack(); //删除尾节点
void PushFront(DataType x); //头插
void PopFront(); //删除首节点
void Insert(LinkNode* pos, DataType x);//固定位置插入一个节点
void Erase(LinkNode* pos); //删除某一节点
LinkNode* Find(DataType x); //查找节点并返回这个节点的地址
int Amount(); //计算链表节点的数目
void Remove(DataType x); //查找某节点并删除
void RemoveAll(DataType x); //删除链表中所有的x private:
LinkNode* _head; //指向头节点
LinkNode* _tail; //指向尾节点
};
//*********************//
SList.cpp (函数实现)
//**********************/////////
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<assert.h>
#include"SList.h" LinkNode::LinkNode(const DataType x)
:_data(x)
, _next(NULL)
{} SList::SList() //构造函数
:_head(NULL)
, _tail(NULL)
{}
SList::SList(const SList& s) //拷贝构造
:_head(NULL)
, _tail(NULL)
{
if (s._head == NULL)
{
return;
}
LinkNode* tmp = s._head;
do{
PushBack(tmp->_data);
tmp = tmp->_next;
} while (tmp != s._head); }
//赋值运算符的重载(传统方法)
//SList & SList::operator=(const SList& s)
//{
// if (this != &s)
// {
// _head = NULL;
// _tail = NULL;
// LinkNode* tmp = s._head;
// do{
// PushBack(tmp->_data);
// tmp = tmp->_next;
// } while (tmp != s._head);
// }
// return *this;
//} //赋值运算符的重载(高效写法)
/*void SList::Swap(SList& s)
{
swap(_head, s._head);
swap(_tail, s._tail); }
SList& SList::operator=(SList &s)
{
if (this != &s)
{
SList tmp(s);
Swap(tmp);
}
return *this;
}*/ SList& SList::operator=(SList &s) //赋值运算符的重载再优化(推荐写法)
{
if (this != &s)
{
swap(_head, s._head);
swap(_tail, s._tail);
}
return *this;
}
SList::~SList() //析构
{
Clear();
} void SList::Reverse() //链表逆置(利用头插新节点的方法)
{
if (_head == NULL||_head->_next==_tail)
{
return;
}
int ret = Amount();
_tail = new LinkNode(_head->_data);
LinkNode* begin=NULL;
LinkNode* tmp = _tail;
while (--ret)
{
LinkNode* del = _head;
_head = _head->_next;
delete del; //这里不要忘记做清理工作,否则内存泄漏
begin = new LinkNode(_head->_data);
begin->_next = tmp;
_tail->_next = begin;
tmp = begin;
}
_head = begin;
} //打印链表
void SList::PrintSList()
{
//头结点为空时,无需打印链表
if (_head==NULL)
{
cout << "This SList is Empty !" << endl;
return;
}
else
{
LinkNode* tmp = _head;
do{
cout << tmp->_data << "-->";
tmp = tmp->_next;
} while (tmp != _head);
cout << endl;
}
}
void SList::PushBack(const DataType& x) //在尾部插入一个节点
{
//如果链表为空,插入节点后只有一个节点,此时_head=_tail
if (_head == NULL)
{
_head = new LinkNode(x);
_tail = _head;
_tail->_next = _head;
}
else
{
_tail->_next = new LinkNode(x);
_tail = _tail->_next;
_tail->_next = _head;
}
}
void SList::Clear() //链表置空
{
LinkNode* begin = _head;
while (begin != _tail)
{
_head = _head->_next;
delete begin;
begin = _head;
}
_head = NULL;
_tail = NULL;
}
void SList::PopBack() //尾删
{
if (_head == NULL)
{
cout << "This SList is empty !" << endl;
}
else if (_head == _tail)
{
delete _head;
_head = NULL;
_tail = NULL;
}
else
{
LinkNode* cur = _head;
while (cur->_next != _tail)
{
cur = cur->_next;
}
delete _tail;
_tail = cur;
_tail->_next = _head;
}
}
void SList::PushFront(DataType x) //头插
{
if (_head == NULL)
{
PushBack(x);
}
else
{
LinkNode* tmp = _head;
_head = new LinkNode(x);
_head->_next = tmp;
_tail->_next = _head;
}
}
void SList::PopFront() //删除首节点
{
if (_head == NULL)
{
cout << "This SList is empty !" << endl;
return;
}
LinkNode* tmp = _head;
_head = _head->_next;
_tail->_next = _head;
delete tmp;
} //固定位置插入一个节点(这个函数需和Find函数搭配使用)
//先用Find函数找到新节点需要插入的位置
//(将Find函数的返回值传给Insert函数的参数pos),再在pos节点后面插入新节点x
void SList::Insert(LinkNode* pos, DataType x)
{
assert(pos);
if (pos==_tail)
{
PushBack(x);
}
else
{
LinkNode* tmp = new LinkNode(x);
tmp->_next = pos->_next;
pos->_next = tmp;
}
} //删除某一节点,同样,要先找到该节点并传参给Erase函数
void SList::Erase(LinkNode* pos)
{
assert(pos);
if (pos == _tail)
{
PopBack();
}
if (pos == _head)
{
PopFront();
}
else
{
LinkNode* prev = _head;
while (prev->_next != pos)
{
prev = prev->_next;
}
prev->_next = pos->_next;
delete pos;
}
}
LinkNode* SList::Find(DataType x) //查找节点并返回这个节点的地址
{
if (_head == NULL)
{
cout << "This SList is empty !" << endl;
return NULL;
}
else
{
LinkNode* tmp = _head;
do{
if (tmp->_data == x)
{
return tmp;
}
tmp = tmp->_next;
} while (tmp != _head);
return NULL;
}
}
int SList::Amount() //计算链表节点的数目
{
if (_head == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
else
{
int count = 0;
LinkNode* cur = _head;
while (cur != _tail)
{
count++;
cur = cur->_next;
}
return ++count;
}
}
void SList::Remove(DataType x) //查找某节点并删除
{
if (_head == NULL)
{
cout << "This SList is empty !" << endl;
}
else
{
LinkNode* tmp = Find(x);
if (tmp != NULL)
{
Erase(tmp);
}
}
}
void SList::RemoveAll(DataType x) //删除链表中所有的x
{
if (_head == NULL)
{
cout << "This SList is empty !" << endl;
return;
}
//如果链表不为空,设置left和right前后指针,从头至尾遍历一遍,delete节点的data为x的节点 LinkNode* left = _tail;
LinkNode* right = _head;
int count = Amount();
while (count--)
{
//当要删掉的节点是头节点时,需要注意头节点要指向它的下一个节点
//当要删掉的节点是尾节点时,需要注意尾节点要指向它的上一个节点
//当left和right指向同一块要删掉的节点时,将链表置空 if (right->_data == x)
{
if (_head == right)
{
_head = _head->_next;
}
if (_tail == right)
{
_tail =left;
}
if (right == left)
{
_head = NULL;
_tail = NULL;
return;
}
LinkNode* tmp = right;
right = right->_next;
delete tmp;
left->_next = right;
}
else
{
left = right;
right = right->_next;
}
}
}
void SList::Uniqe() //去重(针对有序链表)
{
assert(_head &&_head!= _tail);
LinkNode* left = _head;
LinkNode* right = _head->_next;
while (left != _tail)
{
while(left->_data == right->_data)
{
LinkNode* tmp = right;
right = right->_next;
left->_next = right;
delete tmp;
}
left = left->_next;
right = right->_next;
}
}
void SList::Merge(SList &s) //合并(针对有序链表),合并后依然有序
{
// 1. _head为空
// 2. 链表s为空
if (_head == NULL)
{
_head = s._head;
_tail = s._tail;
}
if (s._head == NULL)
{
return;
}
// 3. 两个链表都不为空
LinkNode* phead = _head;
if (phead->_data <= s._head->_data)
{
phead = phead->_next;
}
else
{
_head = s._head;
s._head = s._head->_next;
}
LinkNode* cur = _head;
while (1)
{
if (phead->_data <= s._head->_data)
{
_head->_next = phead;
_head = _head->_next;
if (phead == _tail)
{
_head->_next = s._head;
_tail=s._tail;
_tail->_next = cur;
break;
}
phead = phead->_next;
}
else
{
_head->_next = s._head;
_head = _head->_next;
if (s._head ==s._tail)
{
_head->_next = phead;
_tail->_next = cur;
break;
}
s._head = s._head->_next;
} }
_head = cur;
}
void SList::Sort() //冒泡排序
{
assert(_head);
if (_head == _tail)
{
return;
}
int size = Amount();
for (int i = 0; i < size-1 ; i++)
{
LinkNode* left = _head;
LinkNode* right = _head->_next;
for (int j = 0; j < size - i-1 ; j++)
{
if (left->_data>right->_data)
{
swap(left->_data, right->_data);
}
right = right->_next;
left = left->_next;
}
}
}
///************************
测试用例(Test.cpp)
#include"SList.h"
#include<stdlib.h> void Test3()
{
//排序 去重 合并
cout << "list 1:" << endl;
SList list1;
/*list1.PushBack(2);
list1.PushBack(3);
list1.PushBack(2);
list1.PushBack(2);
list1.PushBack(1);
list1.PrintSList();
list1.Sort();
list1.PrintSList();
list1.Uniqe();
list1.PrintSList();*/ list1.PushBack(5);
list1.PushBack(3);
list1.PushBack(8);
list1.PushBack(2);
list1.PushBack(9);
list1.PushBack(10);
list1.PushBack(2);
list1.PushBack(2);
list1.PushBack(1);
list1.PrintSList();
list1.Sort();
list1.PrintSList(); cout << "list 2:" << endl;
SList list2;
list2.PushBack(1);
list2.PushBack(6);
list2.PushBack(4);
list2.PushBack(0);
list2.PushBack(7);
list2.PrintSList();
list2.Sort();
list2.PrintSList(); cout << "list 1:" << endl<<endl;
list1.Merge(list2);
list1.PrintSList();
}
void Test2()
{
SList list1;
list1.PushBack(1);
list1.PushBack(3);
list1.PushBack(4);
list1.PushBack(2);
list1.PushBack(6);
list1.PrintSList(); /*list1.RemoveAll(2);
list1.PrintSList();*/ SList list2 = list1;
/*list2.PushBack(2);
list2.PushBack(3);
list2.PushBack(4);
list2.PushBack(2);
list2.PushBack(2);*/
list2.PrintSList();
list2.Reverse();
list2.PrintSList(); }
void Test1()
{
//SList list1;
//list1.PushBack(1);
//list1.PushBack(2);
//list1.PushBack(3);
//list1.PushBack(4);
//list1.PushBack(5);
//list1.PrintSList(); //list1.Remove(2);
//list1.PrintSList(); //int num =list1.Amount();
//cout <<"节点个数:"<< num << endl; /*//检验Erase函数
LinkNode* del = list1.Find(2);
list1.Erase(del);
list1.PrintSList();
*/ /*//找到某节点并在其后插入新节点
LinkNode* In =list1.Find(5);
list1.Insert(In, 0);
list1.PrintSList();*/ /* //删除头结点
list1.PopFront();
list1.PrintSList();
*////// /*//////查找节点
LinkNode* ret=list1.Find(5);
if (ret != NULL)
{
cout << "要查找的节点data是:" << ret->_data << endl;
cout << "要查找的节点adress是:" <<ret<< endl;
}
else
{
cout << "not exit !" << endl;
}*//////// //验证构造函数
//SList list2(list1);
//list2.PrintSList(); //验证赋值运算符的重载
//SList list3 = list2;
//list3.PrintSList(); //验证析构函数
//list3.Clear();
//list3.PrintSList(); //验证尾删和头插
///*list3.PopBack();
//list3.PrintSList();*/
//list3.PushFront(0);
//list3.PrintSList();
} int main()
{
//Test1();
Test2();
system("pause");
}
本文利用C++语言,在Windows平台 Visual Studio 2013开发环境下实现
单链表(C++实现)的更多相关文章
- 时间复杂度分别为 O(n)和 O(1)的删除单链表结点的方法
有一个单链表,提供了头指针和一个结点指针,设计一个函数,在 O(1)时间内删除该结点指针指向的结点. 众所周知,链表无法随机存储,只能从头到尾去遍历整个链表,遇到目标节点之后删除之,这是最常规的思路和 ...
- 单链表的C++实现(采用模板类)
采用模板类实现的好处是,不用拘泥于特定的数据类型.就像活字印刷术,制定好模板,就可以批量印刷,比手抄要强多少倍! 此处不具体介绍泛型编程,还是着重叙述链表的定义和相关操作. 链表结构定义 定义单链表 ...
- Java实现单链表的各种操作
Java实现单链表的各种操作 主要内容:1.单链表的基本操作 2.删除重复数据 3.找到倒数第k个元素 4.实现链表的反转 5.从尾到头输出链表 6.找到中间节点 7.检测链表是否有环 8.在 ...
- [LeetCode] Linked List Cycle II 单链表中的环之二
Given a linked list, return the node where the cycle begins. If there is no cycle, return null. Foll ...
- c++单链表基本功能
head_LinkNode.h /*单链表类的头文件*/#include<assert.h>#include"compare.h"typedef int status; ...
- 单链表、循环链表的JS实现
数据结构系列前言: 数据结构作为程序员的基本知识,需要我们每个人牢牢掌握.近期我也展开了对数据结构的二次学习,来弥补当年挖的坑...... 当时上课的时候也就是跟着听课,没有亲自实现任何一种数据结 ...
- C代码实现非循环单链表
C代码实现非循环单链表, 直接上代码. # include <stdio.h> # include <stdlib.h> # include <malloc.h> ...
- 分离的思想结合单链表实现级联组件:CascadeView
本文介绍自己最近做省市级联的类似的级联功能的实现思路,为了尽可能地做到职责分离跟表现与行为分离,这个功能拆分成了2个组件并用到了单链表来实现关键的级联逻辑,下一段有演示效果的gif图.虽然这是个很常见 ...
- 数据结构:单链表结构字符串(python版)添加了三个新功能
#!/urs/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- #异常类 class stringTypeError(TypeError): pass #节点类 class ...
- 数据结构:单链表结构字符串(python版)改进
此篇文章的replace实现了字符串类的多次匹配,但依然有些不足. 因为python字符串对象为不变对象,所以replace方法并不修改原先的字符串,而是返回修改后的字符串. 而此字符串对象时用单链表 ...
随机推荐
- [译] 回调地狱——JavaScript异步编程指南
原文:Callback Hell 什么是 “回调地狱”? 在 JavaScript 中,我们经常通过回调来实现异步逻辑,一旦嵌套层级多了,代码结构就容易变得很不直观,最后看起来像这样: fs.read ...
- c#创建对象并动态添加属性
//动态类,可以作为基类被继承 dynamic backObj = new ExpandoObject(); //ExpandoObject 为密封类 backObj.image0 = IMGNAME ...
- Iocomp控件教程之LinearGauge--线性刻度尺控件
线性刻度尺-线性刻度尺控件(LinearGauge)是一个具有线性表达式刻度的图像控件.支持多达5种颜色断面和4种指示器样式,相同功能,查看线性对数刻度尺(Linear Log Gauge)控件内容 ...
- unity3d WebPlayer版本号音效无声音问题
unity web player,其是一款浏览器执行unity3d游戏引擎公布的游戏的插件,和Flash Player非常像,安全无毒应该是你玩某款网页游戏安装的.假设以后不玩了就能够卸载 Unity ...
- MySQL四:表操作
阅读目录 表介绍 一 创建表 二 查看表结构 三 数据类型 四 表完整性约束 五 修改表ALTER TABLE 六 复制表 七 删除表 八 完整性约束 九 数据类型 表介绍 表相当于文件,表中的一条记 ...
- OpenGL/GLSL数据传递小记(3.x)(转)
OpenGL/GLSL规范在不断演进着,我们渐渐走进可编程管道的时代的同时,崭新的功能接口也让我们有点缭乱的感觉.本文再次从OpenGL和GLSL之间数据的传递这一点,记录和介绍基于OpenGL3.x ...
- foxmail 客户端 LOGIN Login error password error
显示这个错误是我在更换电脑时,将E:\Foxmail 7.2\Storage\15167136106@163.com 账户 移动到新的电脑上,并在新电脑上创建用户,总是报:账户或密码错误 我输入的密码 ...
- 不同手机根据坐标计算控件、图片的像素,px 与 dp, sp换算公式?
参考该帖子:http://www.cnblogs.com/bluestorm/p/3640786.html PPI = Pixels per inch,每英寸上的像素数,即 "像素密度&qu ...
- saltstack内置state模块file之append
添加文件文本在文件尾部 salt.states.file.append(name, text=None, makedirs=False, source=None, source_hash=None, ...
- ASP.NET动态网站制作(18)-- jq作业讲解及知识补充
前言:这节课主要讲解js及jq作业,并在作业讲解完后补充关于jQuery的一些知识点. 内容: 1.作业讲解:计算器那一块考虑的各种情况还不算完善,只实现了基本的功能,还需多多练习使用jQuery. ...
