A/B Testing with Practice in Python (Part One)
I learned A/B testing from a Youtube vedio. The link is https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Bu7OqjYk0jM.
I will divide the note into two parts. The first part is generally an overview of hypothesis testing. Most concepts can be found in the article "Statistics Basics: Main Concepts in Hypothesis Testing" and I will focus on pratical applications here.







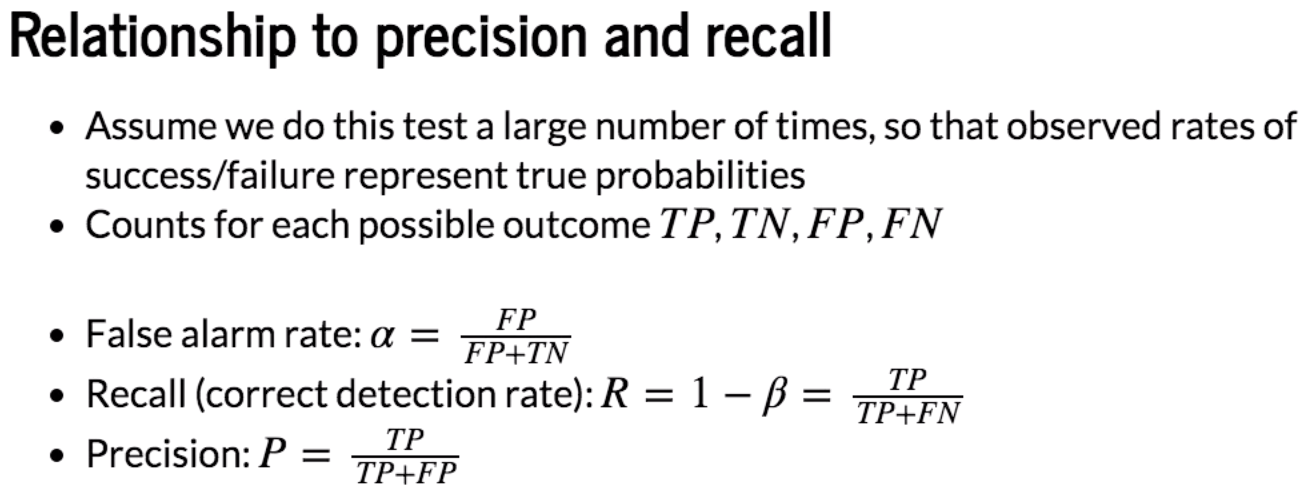
|
Actual Predicted |
T (H1) | F (H0) |
| T (H1) | TP | FP (α) |
| F (H0) | FN (β) | TN |
P = TP/(TP+FN)
R = 1-β =TP/(TP+FN)
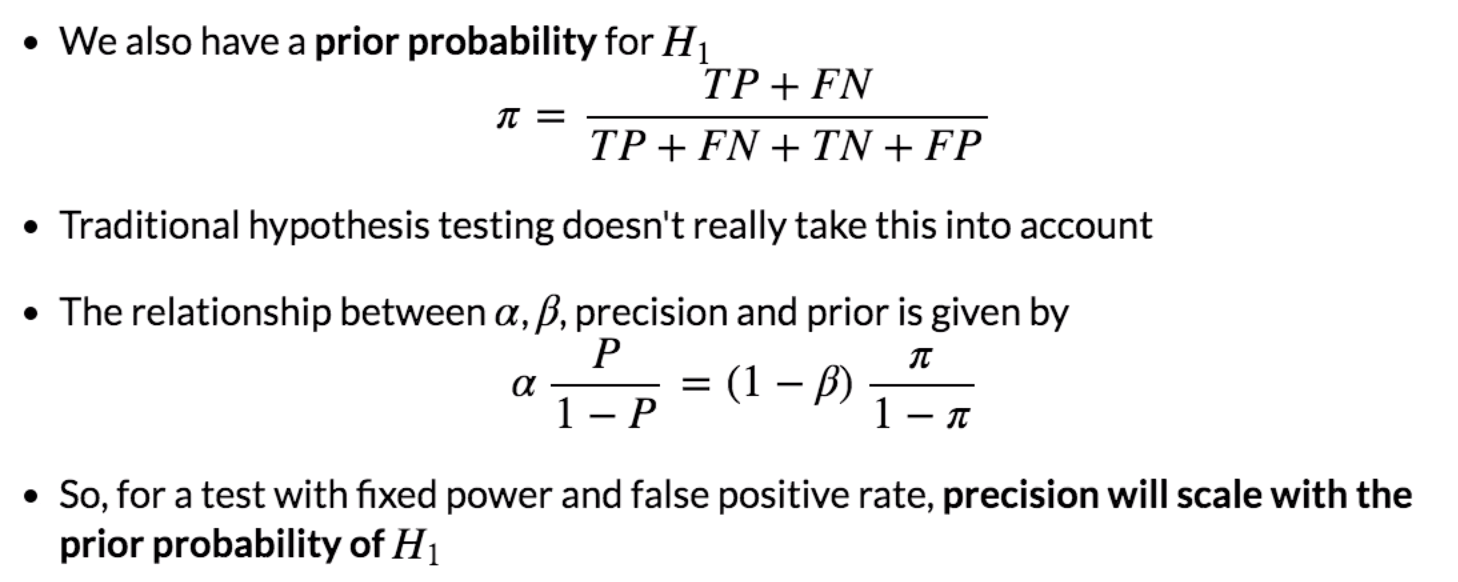

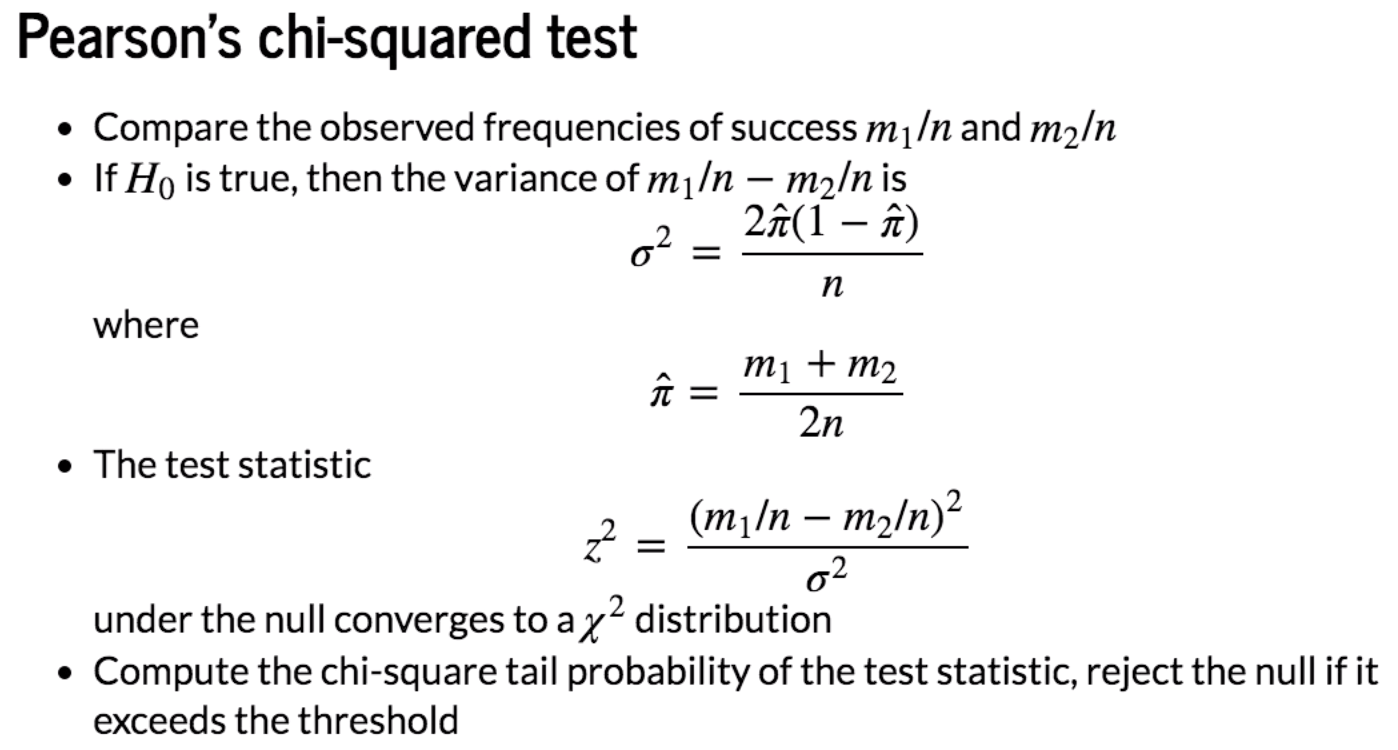
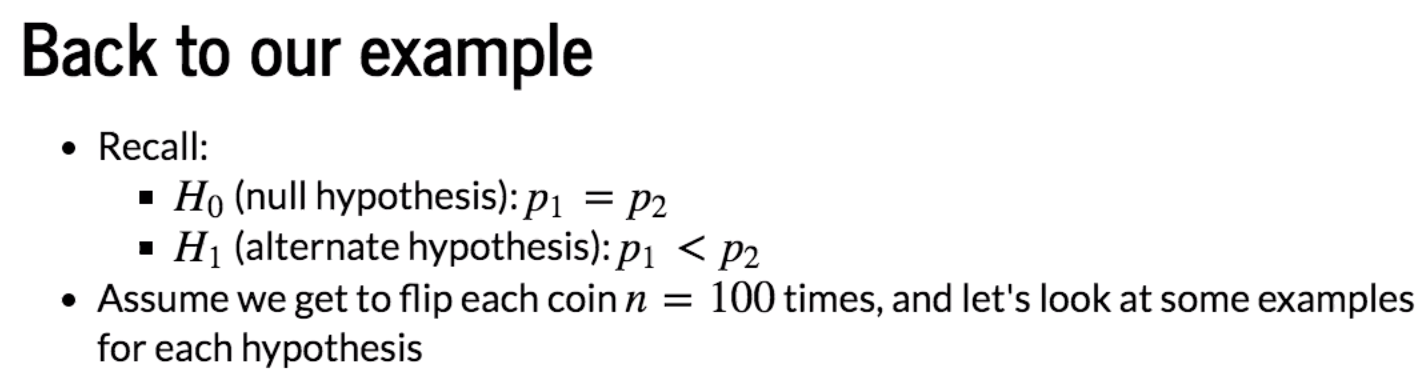
Python Example
Case #1: Alternate hypothesis is true
n = 100
p1 = 0.4
p2 = 0.6 # Compute distributions
x = np.arange(0,n+1)
pmf1 = stats.binom.pmf(x,n,p1)
pmf2 = stats.binom.pmf(x,n,p2)
plot(x,pmf1,pmf2)
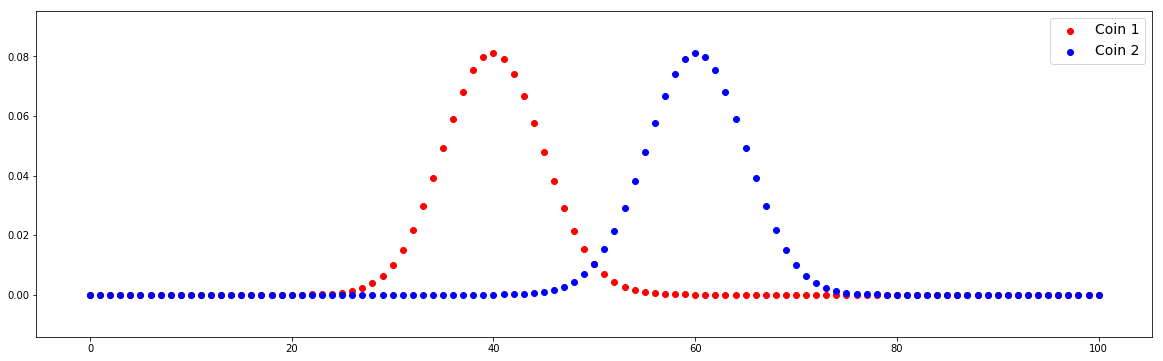
We can find that the distributions between Coin 1 and Coin 2 are different. We check different values of m1 and m2.
# Example outcomes
m1, m2 = 40, 60
table = [[m1, n-m1], [m2, n-m2]]
chi2, pval, dof, expected = stats.chi2_contingency(table)
decision = 'reject H0' if pval<0.05 else 'accept H0'
print('{} ({})'.format(pval,decision))
0.007209570764742524 (reject H0)
# Example outcomes
m1, m2 = 43, 57
table = [[m1, n-m1], [m2, n-m2]]
chi2, pval, dof, expected = stats.chi2_contingency(table)
decision = 'reject H0' if pval<0.05 else 'accept H0'
print('{} ({})'.format(pval,decision))
0.06599205505934735 (accept H0)
In the secod example, m1 and m2 are not different significantly to reject H0.
Case #2: Null hypothesis is true
n = 100
p1 = 0.5
p2 = 0.5 # Compute distributions
x = np.arange(0,n+1)
pmf1 = stats.binom.pmf(x,n,p1)
pmf2 = stats.binom.pmf(x,n,p2)
plot(x,pmf1,pmf2)
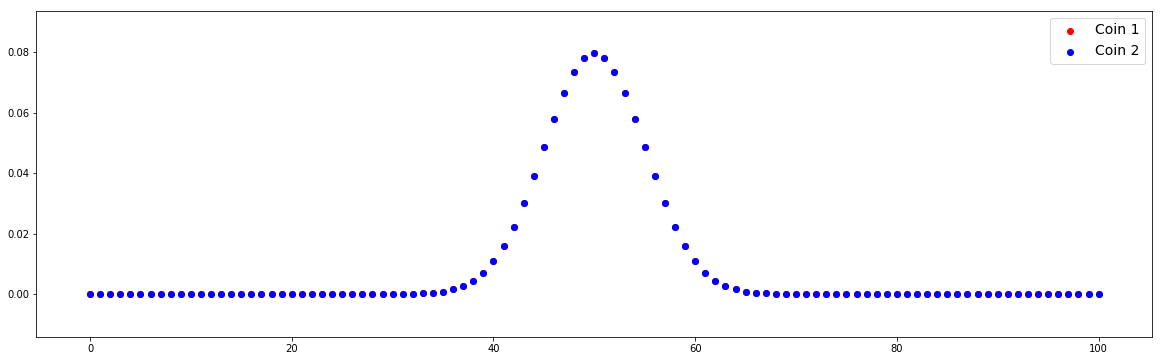
In this case, two distributions overlap because we define the same value of p1 and p2.
# Example outcomes
m1, m2 = 49, 51
table = [[m1, n-m1], [m2, n-m2]]
chi2, pval, dof, expected = stats.chi2_contingency(table)
decision = 'reject H0' if pval<0.05 else 'accept H0'
print('{} ({})'.format(pval,decision))
0.887537083981715 (accept H0)
Actuall, we can only say that m1 and m2 are not different significantly to reject H0. It doesn't mean we should accept H0. The explanation is given in the previous article.
# Example outcomes
m1, m2 = 42, 58
table = [[m1, n-m1], [m2, n-m2]]
chi2, pval, dof, expected = stats.chi2_contingency(table)
decision = 'reject H0' if pval<0.05 else 'accept H0'
print('{} ({})'.format(pval,decision))
0.033894853524689295 (reject H0)


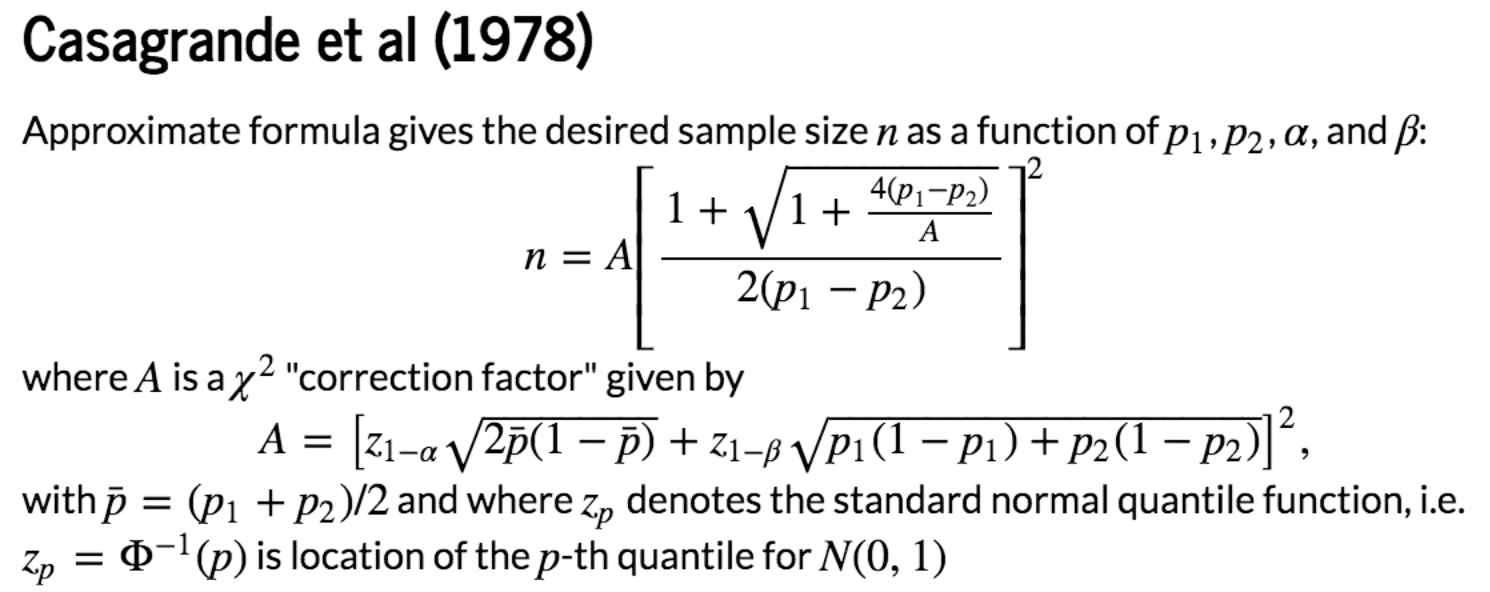

Firstly, calculate the sample size:
p1, p2 = 0.0500, 0.0515
alpha = 0.05
beta = 0.05 # Evaluate quantile function
p_bar = (p1+p2)/2.0
za = stats.norm.ppf(1-alpha/2) # Two-sided test
zb = stats.norm.ppf(1-beta) # Compute correction factor
A = (za*np.sqrt(2*p_bar*(1-p_bar))+ zb*np.sqrt(p1*(1-p1)+p2*(1-p2)))**2 #Estimate samples required
n = A*(((1+np.sqrt(1+4*(p1-p2)/A)))/(2*(p1-p2)))**2 print (n) # we need 2n users
555118.7638311392
So for test and control combined we'll need at least 2n = 1.1 million users. This is where this stuff gets hard and you're trying to measure something that doesn't happen often which is usally the thing to care because if it's rare, it's usually valuable. When you're trying to change it, you usually can't change it much because if you can change it a lot then your business would be easier usually it's harder to change the thing you care the most about. So in that case, it's like the hardest case where a/b testing the most values are unchange.
Next we can perform a/b testing:
n = 555119
n_trials = 10000 # Simulate experimental results when null is true
control0 = stats.binom.rvs (n,p1,size = n_trials)
test0 = stats.binom.rvs(n, p1, size = n_trials) # Test and control are the same
tables0 = [[[a, n-a], [b, n-b]] for a, b in zip(control0, test0)]
results0 = [stats.chi2_contingency(T) for T in tables0]
decisions0 = [x[1] <= alpha for x in results0] # Simulate experimental results when alternate is true
control1 = stats.binom.rvs (n,p1,size = n_trials)
test1 = stats.binom.rvs(n, p2, size = n_trials) # Test and control are the same
tables1 = [[[a, n-a], [b, n-b]] for a, b in zip(control1, test1)]
results1 = [stats.chi2_contingency(T) for T in tables1]
decisions1 = [x[1] <= alpha for x in results1] # Compute false alarm and correct detection rates
alpha_est = sum(decisions0)/float(n_trials)
power_est = sum(decisions1)/float(n_trials) print('Theoretical false alarm rate = {:0.4f}, '.format(alpha)+
'empirical false alarm rate = {:0.4f}'.format(alpha_est))
print('Theoretical power = {:0.4f}, '.format(1-beta)+
'empirical power = {:0.4f}'.format(power_est))
Theoretical false alarm rate = 0.0500, empirical false alarm rate = 0.0509
Theoretical power = 0.9500, empirical power = 0.9536

A/B Testing with Practice in Python (Part One)的更多相关文章
- A/B Testing with Practice in Python (Part Two)
This is the second part of A/B testing notes, which contains the practical issues and alternatives o ...
- [Python + Unit Testing] Write Your First Python Unit Test with pytest
In this lesson you will create a new project with a virtual environment and write your first unit te ...
- Testing shell commands from Python
如何测试shell命令?最近,我遇到了一些情况,我想运行shell命令进行测试,Python称为万能胶水语言,一些自动化测试都可以完成,目前手头的工作都是用python完成的.但是无法从Python中 ...
- [The Basics of Hacking and Penetration Testing] Learn & Practice
Remember to consturct your test environment. Kali Linux & Metasploitable2 & Windows XP
- Automation Testing - Best Practice(书写规范)
Coding Standards Coding Standards are suggestions that will help us to write automation Scripts code ...
- Machine and Deep Learning with Python
Machine and Deep Learning with Python Education Tutorials and courses Supervised learning superstiti ...
- python安装locustio报错error: invalid command 'bdist_wheel'的解决方法
locust--scalable user load testing tool writen in Python(是用python写的.规模化.可扩展的测试性能的工具) 安装locustio需要的环境 ...
- Python框架、库以及软件资源汇总
转自:http://developer.51cto.com/art/201507/483510.htm 很多来自世界各地的程序员不求回报的写代码为别人造轮子.贡献代码.开发框架.开放源代码使得分散在世 ...
- Awesome Python
Awesome Python A curated list of awesome Python frameworks, libraries, software and resources. Insp ...
随机推荐
- 《Cracking the Coding Interview》——第11章:排序和搜索——题目8
2014-03-21 22:23 题目:假设你一开始有一个空数组,你在读入一些整数并将其插入到数组中,保证插入之后数组一直按升序排列.在读入的过程中,你还可以进行一种操作:查询某个值val是否存在于数 ...
- 《算法》C++代码 Dijkstra
单源最短路,复杂度是O(N²),堆优化的是O(NlogN).基本思想是贪心,每次都加入一个当前最近的点,可以证明每次当时最近的点就是当前最短的路径.因此,所有点都加入之后,起点到所有点的最短路径就都求 ...
- jmeter运行脚本后,请求偶发性的传参错误
问题现象:jmeter写好脚本后,请求偶发性的传参错误 排查过程:1.结合报错返回值,看是不是线程并发引起: 2.排除线程并发引起后,看看是不是取值策略:如果是参数化,看看是不是每次迭代,每次都取唯一 ...
- 抓包工具 - Fiddler - (三)
<转载自 miantest> 我们知道Fiddler是位于客户端和服务器之间的代理,它能够记录客户端和服务器之间的所有 HTTP请求,可以针对特定的HTTP请求,分析请求数据.设置断点.调 ...
- 测试基础面试题 + SQL 面试题(选择题有部分答案,难度:低)
测试基础面试题 + SQL 面试题(选择题有部分答案,难度:低) 答案: .A .C .C .A .A .D
- java5初学
1.Eclipse快捷键 alt + / 代码提示,例如自动创建main方法ctrl + d 删除当前行ctrl + alt + up/down 复制当前行alt + up/down 交换行ctrl ...
- java实现最大堆
优先队列 普通的队列是一种先进先出的数据结构,元素在队列尾追加,而从队列头删除.在优先队列中,元素被赋予优先级.当访问元素时,具有最高优先级的元素最先删除.优先队列具有最高级先出 (first in, ...
- Struts2 学习笔记
1)Strust2是以WebWork为核心,采用拦截器的机制对用户请求进行处理. 2)Struts2框架结构: 3)简单来看整个Struts2的处理过程可以简单的理解为 用户的请求发送给对应的Acti ...
- [NC189A]数字权重
题目大意:有一个$n$位的数,设第$i$位为$a_i$(最高位为$a_1$).问满足$(\sum\limits_{i=2}^n(a_i-a_{i-1}))==k$的数的个数(不含前导零) 题解:发现$ ...
- 在Ignite中使用k-最近邻(k-NN)分类算法
在本系列前面的文章中,简单介绍了一下Ignite的线性回归算法,下面会尝试另一个机器学习算法,即k-最近邻(k-NN)分类.该算法基于对象k个最近邻中最常见的类来对对象进行分类,可用于确定类成员的关系 ...
