[Redux] Important things in Redux
Root Smart component can be overloaded, divide 'smart' component wisely & using Provider.
Problem: Something the root component can be overloaded, means it handle too many application logics. For a larger application, it will be hard to maintain.
Solution: We can use Provider from 'react-redux' to inject props into child component.
Install:
npm i -s react-redux
Wrap your <App /> into provider and provide store.
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
import {Provider} from 'react-redux';
import {Router, Route, browserHistory} from 'react-router';
import {App} from './App'; import {configStore} from './store';
const store = configStore(); ReactDOM.render(
<Provider store={store}>
<Router history={browserHistory}>
<Route path="/(:filter)" component={App}></Route>
</Router>
</Provider>,
document.getElementById('root')
);
So from now on, we can divide logic into different smart component, so the root component doesn't need to handle many logic.
root component:
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { VisibleTodoList, AddTodo } from './containers';
import {Footer} from './components';
export class TodoApp extends Component {
render() {
return (
<section>
<AddTodo />
<VisibleTodoList />
<Footer />
</section>
);
}
}
As you can see, root component becomes a dump component actually, can change to functional componet syntax if needed. So next let's see how to inject props and dispatch to those smart component.
Inject props and dispatch to smart component by using connect & withRouter.
This is somehow similar to Angular dependecy injection.
If we don't need component lifecycle, we can do:
import React from 'react';
import { connect } from 'react-redux';
import {withRouter} from 'react-router';
import { TodoList } from '../components';const mapStateToProps = (state, {params}) => ({
todos: TodosSelector.getVisibleTodos(params.filter, state.todos)
}); const mapDispatchToProps = (dispatch) => ({
onTodoClick: (id) => dispatch(toggleTodoAction(id))
}); /*
* VisibleTodoList: Will be the container component to render TodoList presentational component.
*
* TodoList: The presentational component to render the todos
*
* mapStateToProps: using connect to pass redux state ('todos'), make it available to TodoList component
*
* mapDispatchToProps: using connect to pass callback to make it available to TodoList component
* */
export const VisibleTodoList = withRouter(connect(
mapStateToProps,
mapDispatchToProps
)(TodoList));
withRouter allows to inject router params into props.
Now, TodoList dump component will get props and dispatch action in props, so we can use.
import React from 'react';
import {Todo} from './todo.component'; export const TodoList = ({todos, onTodoClick}) => {
const list = todos.map(
todo => (
<Todo
{...todo}
key={todo.id}
onClick={() => onTodoClick(todo.id)}>
</Todo>
)
);
return (
<ul>
{list}
</ul>
);
};
If you do need component lifecycle, you can inject props into itself.
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { connect } from 'react-redux';
import { withRouter } from 'react-router';
import { TodoList } from '../components';
import { fetchingTodosAction } from '../../actions'
import { getVisibleTodos } from '../../reducers';
export class VisibleTodoList extends Component {
componentDidMount() {
this.fetchTodos();
}
componentDidUpdate(prevProps) {
if (this.props.params.filter !== prevProps.params.filter) {
this.fetchTodos();
}
}
fetchTodos = () => {
const { params: { filter = 'all' }, fetchingTodos } = this.props;
fetchingTodos(filter);
};
render() {
return (
<section>
<TodoList
{...this.props}
/>
</section>
);
}
}
const mapStateToProps = (state, { params }) => ({
todos: getVisibleTodos(params.filter, state.todos)
});
VisibleTodoList = withRouter(connect(
mapStateToProps,
{
onTodoClick: toggleTodoAction
}
)(VisibleTodoList));
So in the VisibleTodoList component, we reassign injected version to itself. In the component, we add two lifecycle methods 'componentDidMount' & 'componentDidUpdate'. componentDidMount is used for fetching data when component loaded, and componentDidUpdate will be triggered when props updated.
Shorthand syntax for mapDispatchToProps.
Notice here we didn't write mapDispatchToProps function instead we just pass an object:
VisibleTodoList = withRouter(connect(
mapStateToProps,
{
onTodoClick: toggleTodoAction
}
)(VisibleTodoList));
This is a shorthand syntax.
Another example for shorthand syntax.
/*
* We can reassign AddTodo = connect()(AddTodo);
* It will pass the dispatch function to AddTodo's props.
*
* In AddTodo Component, we don't need state, just need dispatch function.
* SO we can write:
* AddTodo = connect(
* null,
* dispatch => ({dispatch})
* )(AddTodo)
*
* And by default, connect function will link dispatch function to props,
* so it means we even don't need to pass the dispatch function
* SO we can write:
* AddTodo = connect(null, null)(AddTodo);
*
* In short, we can write:
* AddTodo = connect()(AddTodo);
* */
Introduce to "Selector" to the Reducers to encapsulate state shape.
We still has something to be improved in mapStateToProps function. Because the current mapStateToProps function requires component to know the state shape.
const mapStateToProps = (state, { params }) => ({
todos: getVisibleTodos(params.filter, state.todos)
});
This is not good enough because if state shape change later, we have to come back to all the component that related to it and modify those component.
What we want is keep component unchanged no matter how state shape change in the future.
So what we can do is using "selector" to encapsulate state shape inside reudcer. Notice that "selector" is nothing related to new libaray or functions from redux libarary. It is just a concept which we can (should) adopt from best partice.
For exmaple:
import { combineReducers } from 'redux';
/*
* Redux does not enforce that you encapsulate the knowledge about the state
* shape in particular reducer files.
* However, it's a nice pattern,
* because it lets you change the state that is stored by reducers
* without having to change your components or your tests
* if you use selectors together with reducers in your tests.
* */
const createList = (filter) => {
const ids = (state = [], action) => {
switch( action.type ) {
case 'FETCHING_TODOS_SUCCESS':
if(action.payload.filter !== filter){
return state;
}
return action.payload.response.result;
case 'ADD_TODO_SUCCESS':
return filter !== 'completed' ?
[...state, action.response.result]:
state;
default:
return state;
}
};
const isFetching = (state = false, action) => {
if (action.payload && action.payload.filter !== filter) {
return state;
}
switch( action.type ) {
case 'FETCHING_TODOS_SUCCESS':
return false;
case 'FETCHING_TODOS_FAILD':
return false;
case 'FETCHING_TODOS':
return true;
default:
return state;
}
};
const errorMessage = (state = null, action) => {
switch(action.type) {
case 'FETCHING_TODOS_FAILD':
return action.payload.message;
case 'FETCHING_TODOS':
case 'FETCHING_TODOS_SUCCESS':
return null;
default:
return state;
}
};
return combineReducers({
ids,
isFetching,
errorMessage
})
};
/*
Using default export for Reducer
*/
export default createList;
/*
Using name export for selectors.
Selectors are recommended to keep in the same location as redux
*/
export const getIds = (state) => state.ids;
export const isFetchingTodos = (state) => state.isFetching;
export const getErrorMessage = (state) => state.errorMessage;
Here we have three reducers combine as one single reducer export to outside (mainly for create store).
/*
Using default export for Reducer
*/
export default createList;
And we also have three selectors corresponding to three single reducers. The selector's job is to take the whole state from outside and return the piece of state which necessary.
export const getIds = (state) => state.ids;
export const isFetchingTodos = (state) => state.isFetching;
export const getErrorMessage = (state) => state.errorMessage;
And if you divide you reducer into multi levels (whic is also good), the high order reducer will NOT interactive which your low level reducer directly. It should go thought selector.
For example:
high order reducer, it call low level reducers' selector function we just see and export its selectors to outside:
import { combineReducers } from 'redux';
import byId, * as fromById from './byId.reducer';
import createList, * as fromList from './createList.reducer';
const listByFilter = combineReducers({
open: createList('open'),
completed: createList('completed'),
all: createList('all')
});
const todosReducer = combineReducers({
byId,
listByFilter
});
export default todosReducer;
/*
* Selectors
* */
export const getVisibleTodos = (filter, state) => {
const ids = fromList.getIds(state.todos.listByFilter[filter]);
return ids.map(id => fromById.getTodo(state.todos.byId, id));
};
export const getErrorMessage = (filter, state) => {
return fromList.getErrorMessage(state.todos.listByFilter[filter]);
};
export const isFetchingTodos = (state, filter) => {
return fromList.isFetchingTodos(state.todos.listByFilter[filter]);
};
So inside component, we can call selector function:
import { getVisibleTodos, isFetchingTodos, getErrorMessage } from '../../reducers';
const mapStateToProps = (state, { params }) => ({
todos: getVisibleTodos(params.filter, state), // we just pass in the whole state, selector will take care
errorMessage: getErrorMessage(params.filter, state),
isFetching: isFetchingTodos(state, params.filter)
});
To summary:
Rule1: Default export is for reducer, named export for selectors.
Rule2: Each reducer is recommended to have a selector (not must, but a good approach)
Rule3: Component will interactive each selector only NOT reudce, and we just need to pass in the whole state, let selector to figure out the right piece of state for the reducer.
Normalize your API response and return data shape.
It is quite normal that we get Array of object from backend. Then in the front end we deal with array.
But there is another way to doing this, which is similar to "Id lookup", so we will get an array of ids. This array is just a lookup table.
Then we will have an big object using the structure {[id]: objItem}. So we can use the id in the lookup table to query the item in the big object.
So the way we conver an array of object to lookup tables and big object pair is using normalizrlibaray.
Define a schema.js:
import {schema} from 'normalizr';
export const todoSchema = new schema.Entity('todos');
export const arrayOfTodosSchema = new schema.Array(todoSchema);
We create a entity call 'todos'. Since we know the response data from API is array, so we can define array of todos by using:
export const arrayOfTodosSchema = new schema.Array(todoSchema);
// OR
export const arrayOfTodosSchema = [todoSchema];
So in action creator, we can do this normalizion:
import { normalize } from 'normalizr';
import * as schema from './schema';
export const fetchingTodoSuccessAction = (response, filter) => ({
type: 'FETCHING_TODOS_SUCCESS',
payload: {
response: normalize(response, schema.arrayOfTodosSchema),
filter
}
});
For example:
The data we get from server is:
[
{
"id": ,
"name": "redux",
"completed": false
},
{
"id": ,
"name": "react",
"completed": true
}
]
After normalized, it should be:
{
result: [, ],
entities: {
"": { "id": "", "name": "redux", "completed": false },
"": { "id": "", "name": "react", "completed": true }
}
}
Remove side effect from action creator.
Normally you can use 'redux-thunk' or 'redux-promise' to handle async opreations in action creator. But it becomes hard to test for action creator. What is good is that keep action creator as a pure funciton. Handle effect side in a spreated thread.
There are many libaraies to do so, for exmaple 'redux-saga' & 'redux-observable'. Since I am quite used to RxJS. I choose 'redux-observble' as an example.
First, let's what the articuture can be when using side effect.
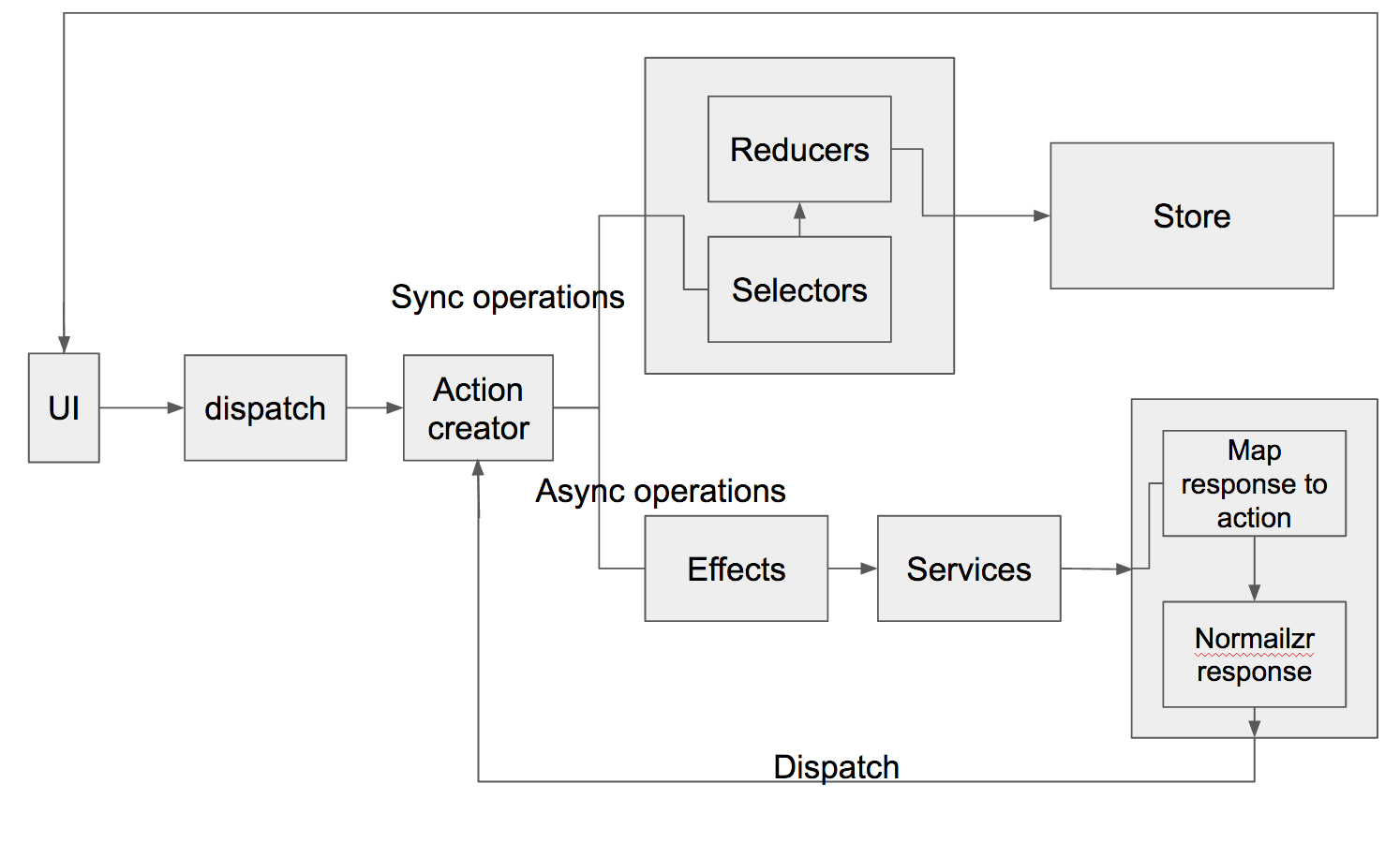
So as you can see, after dispatch an action, there are tow branches to handle the rest opreations. And those opreations are divided into tow parts.
1. All the sync oprations are handled by the Reducer.
2. All the async opreations are handled by Effect.
"Effect" is serving as a listener. Once match an async action, Effect will deal with "Service" which talk to server. After get the response from backend, we will normalizr it first and dispatch a new action. This action can be sync or async, if it is sync action, then after it is dispatched, the reducer will handle it.
For example,
You dispatch an action called 'FECHTING_TODOS'.
It will be only handled by Effect. After get response from server, will either dispatch 'FETCHING_TODOS_SUCCESS' or 'FETCHING_TODOS_ERROR'. And those actions will be handled by Reducer.
Effect:
import * as API from '../api';
import {
fetchingTodoSuccessAction,
fetchingTodoFaildAction
} from '../actions';
import { Observable } from 'rxjs'; export const fetchingTodoEpic = action$ =>
action$.ofType('FETCHING_TODOS')
.switchMap((action) => {
return API.getTodosAPI(action.payload.filter)
.map((response) =>
fetchingTodoSuccessAction(response, action.payload.filter))
.takeUntil(action$.ofType('CANCEL_REQUEST'))
.catch((err) => Observable.of(fetchingTodoFaildAction(err, action.payload.filter)));
});
Service:
export const getTodosAPI = (filter) => {
return Observable.ajax(`${baseURL}/${filter}`)
.retryWhen((err) => err.delay()
.take()
.concat(Observable.throw({
xhr: {
response: {
message: 'CANNOT FETCH TODOS'
}
}
})))
.map(data => data.response);
};
The benifits we can get form RxJS is really powerful API we can use, for example, 'switchMap', 'retryWhen'.
Downsides of redux-observable:
1. It is quite hard to test, even in the document, there is no suggested way to do test.
2. Quite a long learning curve to get used to it.
Source code: Github
[Redux] Important things in Redux的更多相关文章
- redux源码解析-redux的架构
redux很小的一个框架,是从flux演变过来的,尽管只有775行,但是它的功能很重要.react要应用于生成环境必须要用flux或者redux,redux是flux的进化产物,优于flux. 而且r ...
- react第十六单元(redux的认识,redux相关api的掌握)
第十六单元(redux的认识,redux相关api的掌握) #课程目标 掌握组件化框架实现组件之间传参的几种方式,并了解两个没有任何关系组件之间通信的通点 了解为了解决上述通点诞生的flux架构 了解 ...
- [Redux + Webpack] Hot reloading Redux Reducers with Webpack
Webpack will hot reload the component, but the reducer we need hard refresh. To sovle the problem, g ...
- Redux学习笔记:Redux简易开发步骤
该文章不介绍Redux基础,也不解释各种乱乱的概念,网上一搜一大堆.只讲使用Redux开发一个功能的步骤,希望可以类我的小白们,拜托它众多概念的毒害,大牛请绕道! 本文实例源代码参考:React-Re ...
- redux sample with slim redux source code
code sample没有package.json文件,也就没有任何外部依赖,直接使用slim redux source code. slim resux只有90多行. nodejs对es6的impo ...
- 1.Redux学习1,Redux
Redux流程图如上: Action就是一条命令 Store顾名思义就是存储数据的, Reducers是一个回调函数用于处理数据,它处理完数据会返回给Store存储起来 基本流程就是:组件中用Stor ...
- 4 react 简书 引入 redux 的 combineReducers 对 redux 数据进行管理
1. src 下的 common 下的 header 创建 store 文件夹 下创建 reducer.js # src/common/header/store/reducer.js const st ...
- React之redux学习日志(redux/react-redux/redux-saga)
redux官方中文文档:https://www.redux.org.cn/docs/introduction/CoreConcepts.html react-redux Dome:https://co ...
- redux学习总结
redux学习总结 *:first-child { margin-top: 0 !important; } body > *:last-child { margin-bottom: 0 !imp ...
随机推荐
- action中json的应用
这篇文章重点介绍action中json数据的返回处理:假设须要看前端代码的一些特效或ajax的json接收,请看上一篇博客:http://blog.csdn.net/yangkai_hudong/ar ...
- OC文件操作、获取文件属性
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h> //获取文件的属性 int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) { @autorel ...
- 11.Cocos2dx2.2下使用JNI技术调用jar包里面的一些方法遇到的一些问题及解决方式。
<span style="font-family: Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif;">步骤一:导入JniHelper.h头文件.</s ...
- Something-Summary
1.Combinatorial Mathematics 1.1 Bell Number: \(B_n\)表示元素个数为n的集合划分成若干个不相交集合的方案数. \(B_{n + 1} = \sum_{ ...
- 手动删除RMAN备份的方法
查询 RMAN> list backup; using target database control file instead of recovery catalog List of Back ...
- 【2017 ACM-ICPC 亚洲区(西安赛区)网络赛 B】
[链接]h在这里写链接 [题意] 一个硬币正面朝上的概率为q/p; 抛k次,问你偶数次朝上的概率为多少. [题解] [错的次数] 0 [反思] 在这了写反思 [代码] #include <bit ...
- Mosquito的优化——订阅树优化(八)
本文由逍遥子撰写.转发请标注原址: http://blog.csdn.net/houjixin/article/details/46413783 或 http://houjixin.blog.163. ...
- js进阶 13-1 jquery动画中的显示隐藏函数有哪些
js进阶 13-1 jquery动画中的显示隐藏函数有哪些 一.总结 一句话总结:show(),hide(),toggle(),这三个. 1.jquery动画中显示隐藏效果函数有哪些? show()h ...
- 三国武将查询系统 //Java 訪问 数据库
import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.*; import java.awt.event.ActionListener; import java.awt.event ...
- ldd 查看程序/动态库 的依赖
今天在帮同事查看一个问题时, 需要用到ldd, 于是就顺便看了一下ldd的实现. 好在ldd本身只是一个脚本, 而不是executable, 可以直接查看实现的代码. 根据注释: 21 # This ...
