分析轮子(九)- Cloneable.java
注:玩的是JDK1.7版本
一:Cloneable.java 接口也是标记接口,所以,它没有任何方法和属性,实现此接口表示的意思是:可以调用 Object.java 类的 clone() 方法,进行简单的属性到属性之间的克隆,如果没有实现此接口的话调用 Object.java 类的 clone() 方法会抛出 java.lang.CloneNotSupportedException 异常。
另外,如果实现了 Cloneabel.java 接口,通常会复写 Object.java 的 clone() 方法,因为,在 Object.java 中 clone() 方法是受保护的,所以,需要提供一个public的 clone() 方法。
package java.lang; /**
* A class implements the <code>Cloneable</code> interface to
* indicate to the {@link java.lang.Object#clone()} method that it
* is legal for that method to make a
* field-for-field copy of instances of that class.
* <p>
* Invoking Object's clone method on an instance that does not implement the
* <code>Cloneable</code> interface results in the exception
* <code>CloneNotSupportedException</code> being thrown.
* <p>
* By convention, classes that implement this interface should override
* <tt>Object.clone</tt> (which is protected) with a public method.
* See {@link java.lang.Object#clone()} for details on overriding this
* method.
* <p>
* Note that this interface does <i>not</i> contain the <tt>clone</tt> method.
* Therefore, it is not possible to clone an object merely by virtue of the
* fact that it implements this interface. Even if the clone method is invoked
* reflectively, there is no guarantee that it will succeed.
*
* @author unascribed
* @see java.lang.CloneNotSupportedException
* @see java.lang.Object#clone()
* @since JDK1.0
*/
public interface Cloneable {
}
二:验证上述结论
1)定义一个简单的类,特意不实现 Cloneabel.java 接口,如下所示:
/**
* @description:人类
* @author:godtrue
* @create:2018-09-09
*/
public class Person{/** 请注意这里,没有实现 Cloneable 接口 **/
/**
* 身份证号
*/
private int id; /**
* 姓名
*/
private String name; /**
* 性别
*/
private boolean sex; /**
* 年龄
*/
private int age; /**
*
*@description: 复写 Object.java 的克隆方法
*@param
*@return: java.lang.Object
*@author: godtrue
*@createTime: 2018-09-18
*@version: v1.0
*/
@Override
public Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return super.clone();
} public int getId() {
return id;
} public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
} public String getName() {
return name;
} public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
} public boolean isSex() {
return sex;
} public void setSex(boolean sex) {
this.sex = sex;
} public int getAge() {
return age;
} public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
} @Override
public String toString() {
final StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("Person{");
sb.append("id=").append(id);
sb.append(", name='").append(name).append('\'');
sb.append(", sex=").append(sex==true?"男":"女");
sb.append(", age=").append(age);
sb.append('}');
return sb.toString();
}
}
2)定义一个测试入口类,如下所示:
/**
* @description:玩一把Cloneable
* @author:godtrue
* @create:2018-09-18
*/
public class PlayCloneable {
/**
*
*@description: 测试入口,主方法
*@param args
*@return: void
*@author: godtrue
*@createTime: 2018-09-18
*@version: v1.0
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException{
Person person = genPerson();
System.out.println("person is "+person); Person personTemp = (Person) person.clone();
personTemp.setId(618);
personTemp.setName("六一八");
System.out.println("personTemp is "+personTemp);
} /**
*
*@description: 生成 Person 对象信息
*@param
*@return: com.godtrue.Person
*@author: godtrue
*@createTime: 2018-09-18
*@version: v1.0
*/
private static Person genPerson(){
Person person = new Person();
person.setId(1111);
person.setSex(true);
person.setName("双十一");
person.setAge(2);
return person;
}
}
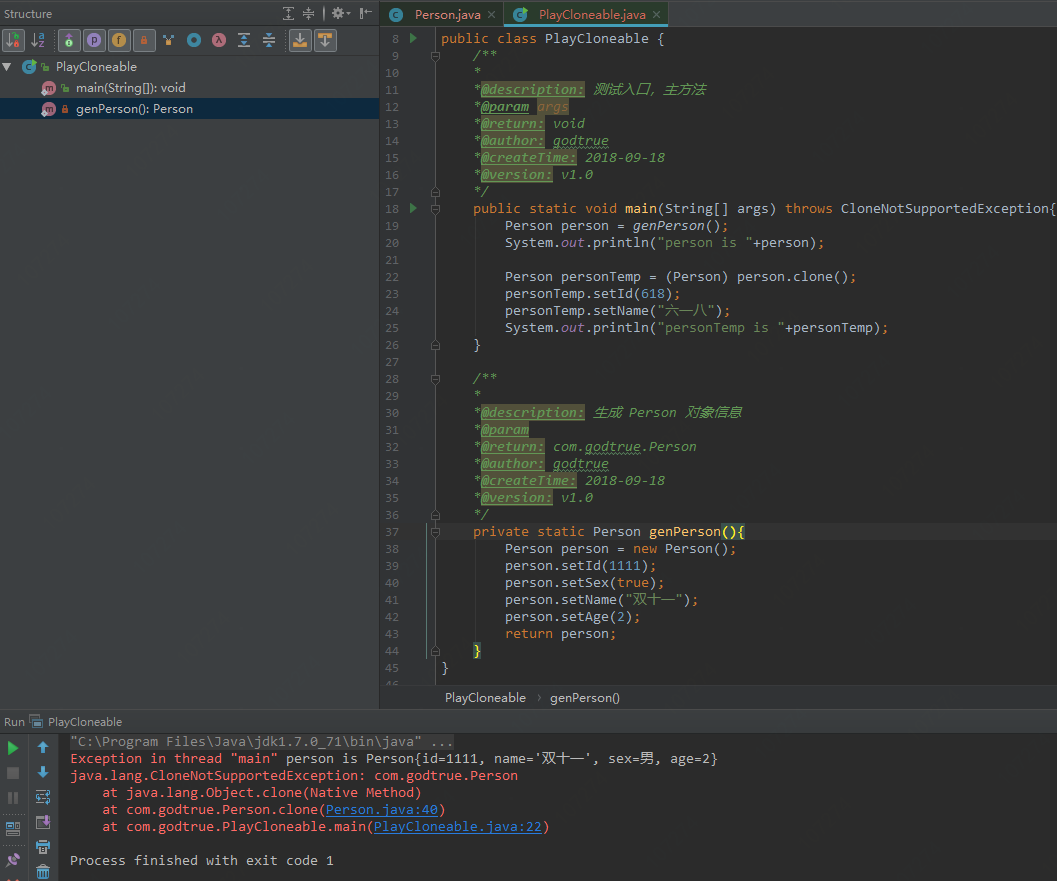
3)测试的结果如下所示(果然,抛出了对应的异常,侧面反映出我们的结论了:没实现Cloneable.java接口时,调用 Object.java 类的 clone() 方法会抛出 java.lang.CloneNotSupportedException 异常):
4)调整 Person.java 类 使其实现 Cloneable.java 接口,然后再实验下,看看什么效果,调整的类如下所示:
/**
* @description:人类
* @author:godtrue
* @create:2018-09-09
*/
public class Person implements Cloneable{/** 请注意这里,实现了 Cloneable 接口 **/
/**
* 身份证号
*/
private int id; /**
* 姓名
*/
private String name; /**
* 性别
*/
private boolean sex; /**
* 年龄
*/
private int age; /**
*
*@description: 复写 Object.java 的克隆方法
*@param
*@return: java.lang.Object
*@author: godtrue
*@createTime: 2018-09-18
*@version: v1.0
*/
@Override
public Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return super.clone();
} public int getId() {
return id;
} public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
} public String getName() {
return name;
} public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
} public boolean isSex() {
return sex;
} public void setSex(boolean sex) {
this.sex = sex;
} public int getAge() {
return age;
} public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
} @Override
public String toString() {
final StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("Person{");
sb.append("id=").append(id);
sb.append(", name='").append(name).append('\'');
sb.append(", sex=").append(sex==true?"男":"女");
sb.append(", age=").append(age);
sb.append('}');
return sb.toString();
}
}
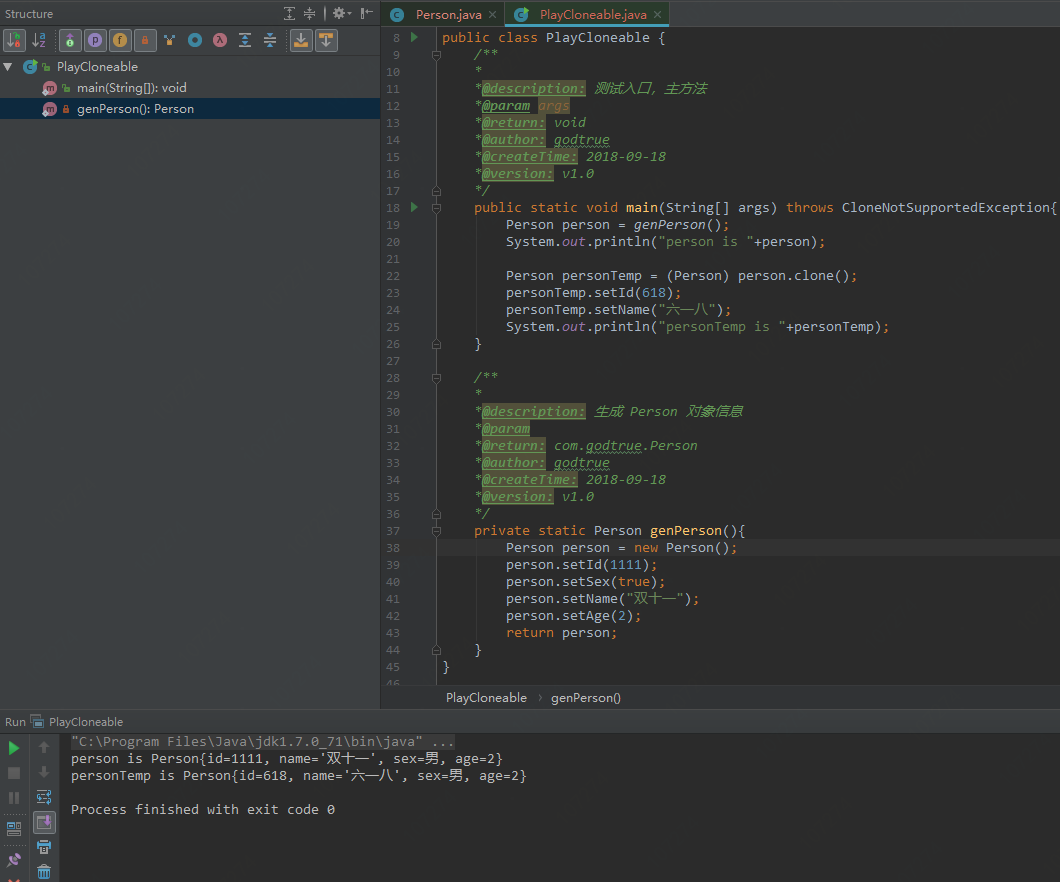
5)运行结果如下所示(正面反映出了我们的结论:当实现Cloneable.java接口时,能够正常调用 Object.java 类的 clone() 方法):
三:为什么会这样呢?
1)先看如下的变种例子,注意 clone() 方法的实现,如下所示
/**
* @description:人类
* @author:godtrue
* @create:2018-09-09
*/
public class Person{/** 请注意这里,没有实现 Cloneable 接口 **/
/**
* 身份证号
*/
private int id; /**
* 姓名
*/
private String name; /**
* 性别
*/
private boolean sex; /**
* 年龄
*/
private int age; /**
*
*@description: 复写 Object.java 的克隆方法
*@param
*@return: java.lang.Object
*@author: godtrue
*@createTime: 2018-09-18
*@version: v1.0
*/
@Override
public Object clone(){
Person copy = new Person();
copy.id = this.id;
copy.name = this.name;
copy.sex = this.sex;
copy.age = this.age; return copy;
} public int getId() {
return id;
} public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
} public String getName() {
return name;
} public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
} public boolean isSex() {
return sex;
} public void setSex(boolean sex) {
this.sex = sex;
} public int getAge() {
return age;
} public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
} @Override
public String toString() {
final StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("Person{");
sb.append("id=").append(id);
sb.append(", name='").append(name).append('\'');
sb.append(", sex=").append(sex==true?"男":"女");
sb.append(", age=").append(age);
sb.append('}');
return sb.toString();
}
}
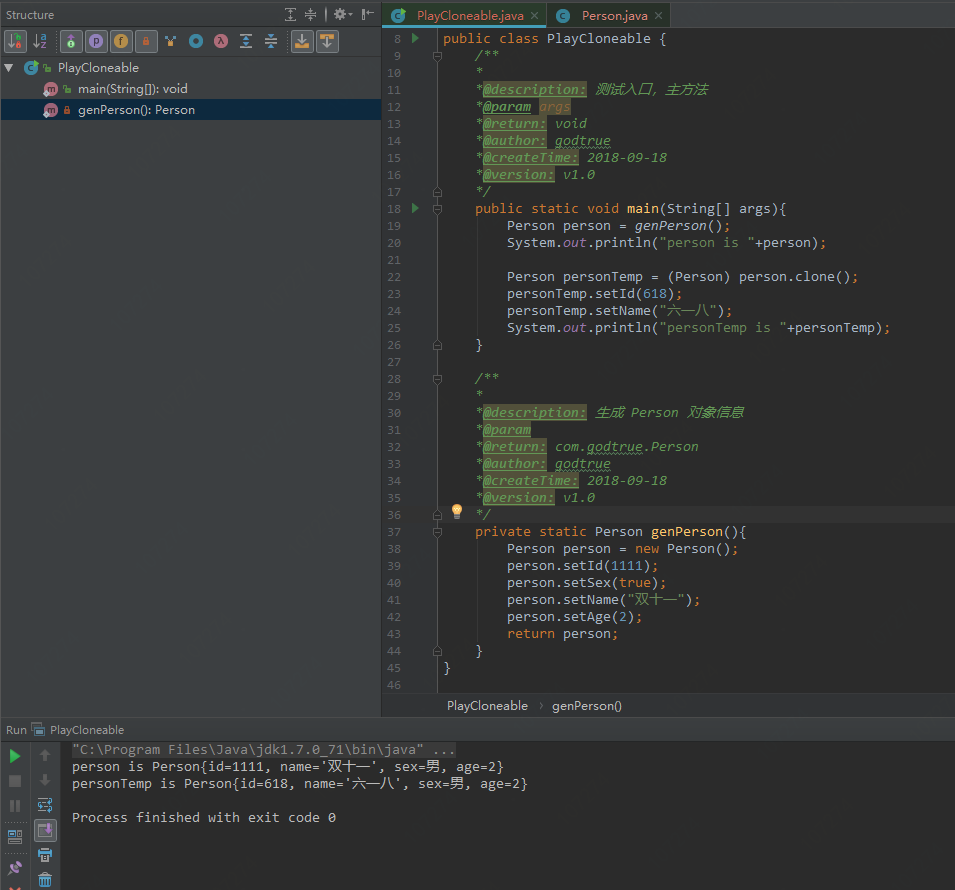
2)运行结果如下所示,注意,不用处理 java.lang.CloneNotSupportedException 因为,我们的 Person.java 的 clone() 方法没用使用 Object.java 的 clone() 方法
3)看一下 Object.java 的 clone() 方法,从注释中我们可以得出如下关键信息
3-1)Object.java 的 clone() 方法是一个 native 方法
3-2)通过 Object.java 的 clone() 方法获取的新对象是一个浅克隆的对象,打个比方:有点类似两个连体双胞胎的关系(这个回头再细说)
3-3)针对没有实现 Cloneable.java 接口的类,如果复写了 Object.java 类的 clone() 方法,且通过 Object.java 类的 clone() 方法实现了对象的浅克隆的话,在调用复写的 clone() 方法的时候,就会抛出 java.lang.CloneNotSupportedException 异常,因为,Object.java 类的 clone() 方法抛出了此异常,所以,对应的应该有捕获或者再抛出的措施才行,(Object.java 类的 clone() 方法的本地实现我还没看,猜测,他会先检查对应的类是否实现了Cloneabe.java接口,如果没有,则会抛出 java.lang.CloneNotSupportedException 异常,如果实现了,则会进行对对象的浅克隆操作)
3-4)复写 Object.java 的 clone() 方法,和是否实现 Cloneable.java 接口没有什么必然关系,复写的 clone() 方法的实现,可以有多种选择,但是一旦选择使用 Object.java 类的 clone() 方法来快速实现一个对象的浅克隆的话,就必须实现 Cloneable.java 接口,否则就会抛出 java.lang.CloneNotSupportedException 异常
3-5)至此,我们也清楚了,Cloneable.java 接口的核心作用在于,可通过 Object.java 类的 clone() 方法进行对象的快速浅克隆,具体实现步骤如下所示:
第一步:实现Cloneable.java接口
第二步:复写Object.java类的clone()方法,使方法到处可用(public的访问权限),调用Object.java类的clone()方法快速的浅克隆对象
第三步:如果想进行深克隆,也可以在浅克隆的基础上再加工处理
/**
* Creates and returns a copy of this object. The precise meaning
* of "copy" may depend on the class of the object. The general
* intent is that, for any object {@code x}, the expression:
* <blockquote>
* <pre>
* x.clone() != x</pre></blockquote>
* will be true, and that the expression:
* <blockquote>
* <pre>
* x.clone().getClass() == x.getClass()</pre></blockquote>
* will be {@code true}, but these are not absolute requirements.
* While it is typically the case that:
* <blockquote>
* <pre>
* x.clone().equals(x)</pre></blockquote>
* will be {@code true}, this is not an absolute requirement.
* <p>
* By convention, the returned object should be obtained by calling
* {@code super.clone}. If a class and all of its superclasses (except
* {@code Object}) obey this convention, it will be the case that
* {@code x.clone().getClass() == x.getClass()}.
* <p>
* By convention, the object returned by this method should be independent
* of this object (which is being cloned). To achieve this independence,
* it may be necessary to modify one or more fields of the object returned
* by {@code super.clone} before returning it. Typically, this means
* copying any mutable objects that comprise the internal "deep structure"
* of the object being cloned and replacing the references to these
* objects with references to the copies. If a class contains only
* primitive fields or references to immutable objects, then it is usually
* the case that no fields in the object returned by {@code super.clone}
* need to be modified.
* <p>
* The method {@code clone} for class {@code Object} performs a
* specific cloning operation. First, if the class of this object does
* not implement the interface {@code Cloneable}, then a
* {@code CloneNotSupportedException} is thrown. Note that all arrays
* are considered to implement the interface {@code Cloneable} and that
* the return type of the {@code clone} method of an array type {@code T[]}
* is {@code T[]} where T is any reference or primitive type.
* Otherwise, this method creates a new instance of the class of this
* object and initializes all its fields with exactly the contents of
* the corresponding fields of this object, as if by assignment; the
* contents of the fields are not themselves cloned. Thus, this method
* performs a "shallow copy" of this object, not a "deep copy" operation.
* <p>
* The class {@code Object} does not itself implement the interface
* {@code Cloneable}, so calling the {@code clone} method on an object
* whose class is {@code Object} will result in throwing an
* exception at run time.
*
* @return a clone of this instance.
* @exception CloneNotSupportedException if the object's class does not
* support the {@code Cloneable} interface. Subclasses
* that override the {@code clone} method can also
* throw this exception to indicate that an instance cannot
* be cloned.
* @see java.lang.Cloneable
*/
protected native Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException;
4)看一下 java.lang.CloneNotSupportedException.java 的存在本意,不实现 Cloneable.java 接口,但是调用了 Object.java 类的 clone() 方法就会抛出此异常了
/**
* Thrown to indicate that the <code>clone</code> method in class
* <code>Object</code> has been called to clone an object, but that
* the object's class does not implement the <code>Cloneable</code>
* interface.
* <p>
* Applications that override the <code>clone</code> method can also
* throw this exception to indicate that an object could not or
* should not be cloned.
*
* @author unascribed
* @see java.lang.Cloneable
* @see java.lang.Object#clone()
* @since JDK1.0
*/ public
class CloneNotSupportedException extends Exception {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 5195511250079656443L; /**
* Constructs a <code>CloneNotSupportedException</code> with no
* detail message.
*/
public CloneNotSupportedException() {
super();
} /**
* Constructs a <code>CloneNotSupportedException</code> with the
* specified detail message.
*
* @param s the detail message.
*/
public CloneNotSupportedException(String s) {
super(s);
}
}
分析轮子(九)- Cloneable.java的更多相关文章
- 分析轮子(五)- Vector.java
注:玩的是JDK1.7版本 一: 先上类图,从类图上看和 ArrayList.java 非常相像,可查看 分析轮子(一)-ArrayList.java 二:然后看源码,发现和 ArrayList.ja ...
- 分析轮子(四)- 我也玩一把 Serializable.java
前言:在写 分析轮子(一)-ArrayList.java 的时候曾经下过一个结论 “实现Serializable接口,表示ArrayList是可序列化的”,这个结论是以往学习的经验所得,并且平时在编程 ...
- Java入门系列之集合LinkedList源码分析(九)
前言 上一节我们手写实现了单链表和双链表,本节我们来看看源码是如何实现的并且对比手动实现有哪些可优化的地方. LinkedList源码分析 通过上一节我们对双链表原理的讲解,同时我们对照如下图也可知道 ...
- Java集合源码分析(九)——HashSet
简介 HashSet就是一个集合,里面不能有重复的元素,元素也是无序的. HashSet其实就是调用了HashMap实现的,所以,它也不是线程安全的. HashSet通过iterator()返回的迭代 ...
- java基础( 九)-----深入分析Java的序列化与反序列化
序列化是一种对象持久化的手段.普遍应用在网络传输.RMI等场景中.本文通过分析ArrayList的序列化来介绍Java序列化的相关内容.主要涉及到以下几个问题: 怎么实现Java的序列化 为什么实现了 ...
- 分析轮子(二)- << ,>>,>> (左移、右移、无符号右移)
前言:写 分析轮子(一)-ArrayList.java 的时候看到源码中有 int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1); 这样的代 ...
- 九大Java性能调试工具,必备至少一款
九款Java性能调试工具,有什么更好.更多的工具,欢迎补充. NetBeans Profiler NetBeans中可以找到NetBeans Profiler. NetBeans分析器是NetBean ...
- Java10-java语法基础(九)——java的封装性
Java10-java语法基础(九)——java的封装性 一.Java的三大特性:封装.多态.继承 封装:通过类封装对象的数据成员和成员方法,保证只有可信的类或者对象能够访问这些方法和数据成员,对不可 ...
- u-boot分析(九)----nand flash初始化|nand flash读写分析
u-boot分析(九) 上篇博文我们按照210的启动流程,分析到了初始化串口,由于接下来的取消存储保护不是很重要,所以我们今天按照u-boot的启动流程对nand flash初始化进行分析. 今天我们 ...
随机推荐
- jOOR
--摘自<android插件化开发指南> 1.jOOR库就一个Reflect.java类很重要 2.Reflect.java包括6个核心方法 1)on:包裹一个类或者对象,表示在这个类或对 ...
- spring mvc简单介绍xml版
spring mvc介绍:其实spring mvc就是基于servlet实现的,只不过他讲请求处理的流程分配的更细致而已. spring mvc核心理念的4个组件: 1.DispatcherServl ...
- lvs负载均衡概述
- SpringBoot使用JdbcTemplate
前言 本文是对SpringBoot使用JdbcTemplate操作数据库的一个介绍,,提供一个小的Demo供大家参考. 操作数据库的方式有很多,本文介绍使用SpringBoot结合JdbcTempla ...
- XamarinAndroid组件教程RecylerView适配器设置动画
XamarinAndroid组件教程RecylerView适配器设置动画 本小节将讲解动画相关设置,如动画的时长.插值器以及复合动画等. 1.设置动画时长 设置动画持续的时间可以使用Animation ...
- BZOJ.4738.[清华集训2016]汽水(点分治 分数规划)
BZOJ UOJ 记\(val_i\)是每条边的边权,\(s\)是边权和,\(t\)是经过边数,\(k\)是给定的\(k\). 在点分治的时候二分答案\(x\),设\(|\frac st-k|=x\) ...
- Kotlin基础(五)Kotlin的类型系统
Kotlin的类型系统 一.可空类型 //s为null的话编译器会报错,没问号不能为空 fun strLen(s : String)=s.length //如果允许s为空可: fun strLen2( ...
- PowerShell一次执行多条命令
PowerShell一次执行多条命令语句 使用CMD之后换到PS之后想一次执行多条命令会很不习惯,因为原来的&&语句连接符已经不能用了. 在各种搜索后没有发现网上有说明这个的.无奈只能 ...
- vector.erase用法注意事项
转自->这里 vector::erase():从指定容器删除指定位置的元素或某段范围内的元素 vector::erase()方法有两种重载形式 如下: iterator erase(iterat ...
- BZOJ4267 : 小强的颜色
首先剔除$1$号心情不能到达的无用心情,然后采用分割法进行DFA的最小化. 每次遍历所有集合,将集合中和集合中第一个心情行为或者转移所在集合不同的心情放入新集合中. 最后按字典序依次给每个集合编号即可 ...
