使Volley完美支持自定义证书的Https
其实在最早的版本里,Volley甚至是不支持https协议的,只能跑http,当然你也可以自己修改他的源码让他支持,如今volley的代码经过一些改进以后,
已经可以完美支持https协议了,无论是在2.3版本以上还是在2.3版本以下,大家可以尝试用volley去访问github 是成功的,但是你如果用volley去访问
12306这种类似的 用自定义证书的网站 就很容易失败。那我下面就把volley 代码稍作修改,让volley也可以完美支持自定义证书的https请求。
当然代码只是展示功能使用,你们可以用更优雅的方式 ----实现一个HttpStack,然后直接传你自定义好的stack即可。我这里图简便就写了个最简单
的演示代码。其实难倒是也不难,主要还是要考虑2.3版本以上和以下的两种情况。
第一步,把你的自定义证书 拷贝到res/raw/下。
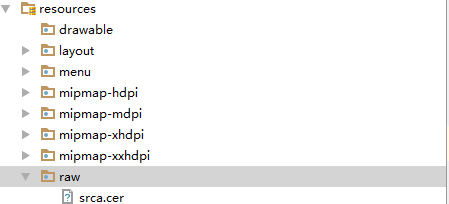
第二步,稍微修改下volley的源码
/*
* Copyright (C) 2012 The Android Open Source Project
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/ package com.android.volley.toolbox; import android.content.Context;
import android.content.pm.PackageInfo;
import android.content.pm.PackageManager.NameNotFoundException;
import android.net.http.AndroidHttpClient;
import android.os.Build;
import android.util.Log; import com.android.volley.Network;
import com.android.volley.RequestQueue; import org.apache.http.client.HttpClient;
import org.apache.http.conn.scheme.PlainSocketFactory;
import org.apache.http.conn.scheme.Scheme;
import org.apache.http.conn.scheme.SchemeRegistry;
import org.apache.http.impl.client.DefaultHttpClient;
import org.apache.http.impl.conn.tsccm.ThreadSafeClientConnManager;
import org.apache.http.params.BasicHttpParams;
import org.apache.http.params.HttpParams; import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.security.KeyManagementException;
import java.security.KeyStore;
import java.security.KeyStoreException;
import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException;
import java.security.UnrecoverableKeyException;
import java.security.cert.Certificate;
import java.security.cert.CertificateException;
import java.security.cert.CertificateFactory; import javax.net.ssl.SSLContext;
import javax.net.ssl.SSLSocketFactory;
import javax.net.ssl.TrustManagerFactory; public class Volley { /**
* Default on-disk cache directory.
*/
private static final String DEFAULT_CACHE_DIR = "volley"; private Context mContext; /**
* Creates a default instance of the worker pool and calls {@link RequestQueue#start()} on it.
*
* @param context A {@link Context} to use for creating the cache dir.
* @param stack An {@link HttpStack} to use for the network, or null for default.
* @return A started {@link RequestQueue} instance.
*/
public static RequestQueue newRequestQueue(Context context, HttpStack stack, boolean selfSignedCertificate, int rawId) {
File cacheDir = new File(context.getCacheDir(), DEFAULT_CACHE_DIR); String userAgent = "volley/0";
try {
String packageName = context.getPackageName();
PackageInfo info = context.getPackageManager().getPackageInfo(packageName, );
userAgent = packageName + "/" + info.versionCode;
} catch (NameNotFoundException e) {
} if (stack == null) {
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= ) {
if (selfSignedCertificate) {
stack = new HurlStack(null, buildSSLSocketFactory(context, rawId));
} else {
stack = new HurlStack();
}
} else {
// Prior to Gingerbread, HttpUrlConnection was unreliable.
// See: http://android-developers.blogspot.com/2011/09/androids-http-clients.html
if (selfSignedCertificate)
stack = new HttpClientStack(getHttpClient(context, rawId));
else {
stack = new HttpClientStack(AndroidHttpClient.newInstance(userAgent));
}
}
} Network network = new BasicNetwork(stack); RequestQueue queue = new RequestQueue(new DiskBasedCache(cacheDir), network);
queue.start(); return queue;
} /**
* Creates a default instance of the worker pool and calls {@link RequestQueue#start()} on it.
*
* @param context A {@link Context} to use for creating the cache dir.
* @return A started {@link RequestQueue} instance.
*/
public static RequestQueue newRequestQueue(Context context) {
return newRequestQueue(context, null, false, );
} private static SSLSocketFactory buildSSLSocketFactory(Context context, int certRawResId) {
KeyStore keyStore = null;
try {
keyStore = buildKeyStore(context, certRawResId);
} catch (KeyStoreException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (CertificateException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} String tmfAlgorithm = TrustManagerFactory.getDefaultAlgorithm();
TrustManagerFactory tmf = null;
try {
tmf = TrustManagerFactory.getInstance(tmfAlgorithm);
tmf.init(keyStore); } catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (KeyStoreException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} SSLContext sslContext = null;
try {
sslContext = SSLContext.getInstance("TLS");
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
sslContext.init(null, tmf.getTrustManagers(), null);
} catch (KeyManagementException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} return sslContext.getSocketFactory(); } private static HttpClient getHttpClient(Context context, int certRawResId) {
KeyStore keyStore = null;
try {
keyStore = buildKeyStore(context, certRawResId);
} catch (KeyStoreException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (CertificateException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if (keyStore != null) {
}
org.apache.http.conn.ssl.SSLSocketFactory sslSocketFactory = null;
try {
sslSocketFactory = new org.apache.http.conn.ssl.SSLSocketFactory(keyStore);
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (KeyManagementException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (KeyStoreException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (UnrecoverableKeyException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} HttpParams params = new BasicHttpParams(); SchemeRegistry schemeRegistry = new SchemeRegistry();
schemeRegistry.register(new Scheme("http", PlainSocketFactory.getSocketFactory(), ));
schemeRegistry.register(new Scheme("https", sslSocketFactory, )); ThreadSafeClientConnManager cm = new ThreadSafeClientConnManager(params, schemeRegistry); return new DefaultHttpClient(cm, params);
} private static KeyStore buildKeyStore(Context context, int certRawResId) throws KeyStoreException, CertificateException, NoSuchAlgorithmException, IOException {
String keyStoreType = KeyStore.getDefaultType();
KeyStore keyStore = KeyStore.getInstance(keyStoreType);
keyStore.load(null, null); Certificate cert = readCert(context, certRawResId);
keyStore.setCertificateEntry("ca", cert); return keyStore;
} private static Certificate readCert(Context context, int certResourceID) {
InputStream inputStream = context.getResources().openRawResource(certResourceID);
Certificate ca = null; CertificateFactory cf = null;
try {
cf = CertificateFactory.getInstance("X.509");
ca = cf.generateCertificate(inputStream); } catch (CertificateException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return ca;
}
}
第三步就是调用方式稍微做下修改:
其实主要就是你如果想使用自定义的证书https的时候 第三个参数记得传true,并且把证书也传进去,
当然写的优雅的话还是最好自己写个httpstack,然后volley的源码可以不用改,只需要在使用的时候
传自己的stack即可

http://liuwangshu.cn/application/network/4-volley-sourcecode.html
使Volley完美支持自定义证书的Https的更多相关文章
- Android 使Volley完美支持自定义证书的Https
其实在最早的版本里,Volley甚至是不支持https协议的,只能跑http,当然你也可以自己修改他的源码让他支持,如今volley的代码经过一些改进以后, 已经可以完美支持https协议了,无论是在 ...
- 让个人域名下GithubPage完美支持https
让个人域名下GithubPage完美支持https 欢迎访问完美HTTPS支持的GithubPage个人博客 : https://zggdczfr.cn/ 前言 最近笔记本挂了送去维修,耽误了我的学习 ...
- Retrofit 2.0 超能实践(一),okHttp完美支持Https传输
http: //blog.csdn.net/sk719887916/article/details/51597816 Tamic首发 前阵子看到圈子里Retrofit 2.0,RxJava(Andro ...
- Retrofit 2.0 超能实践,完美支持Https传输
http://blog.csdn.NET/sk719887916/article/details/51597816 前阵子看到圈子里Retrofit 2.0,RxJava(Android), OkHt ...
- Volley框架支持HTTPS请求。
第一次写帖子,嘿嘿. 最近了解到google2013IO大会出了个网络框架,正好项目也需要用到,就看了下. 最后发现接口都是HTTPS的,但是Volley默认是不支持HTTPS,网上找了好久,都没有对 ...
- 并发编程概述 委托(delegate) 事件(event) .net core 2.0 event bus 一个简单的基于内存事件总线实现 .net core 基于NPOI 的excel导出类,支持自定义导出哪些字段 基于Ace Admin 的菜单栏实现 第五节:SignalR大杂烩(与MVC融合、全局的几个配置、跨域的应用、C/S程序充当Client和Server)
并发编程概述 前言 说实话,在我软件开发的头两年几乎不考虑并发编程,请求与响应把业务逻辑尽快完成一个星期的任务能两天完成绝不拖三天(剩下时间各种浪),根本不会考虑性能问题(能接受范围内).但随着工 ...
- iOS 的三种自建证书方法https请求相关配置
如果你的app服务端安装的是SLL颁发的CA,可以使用系统方法直接实现信任SSL证书,关于Apple对SSL证书的要求请参考:苹果官方文档CertKeyTrustProgGuide 这种方式不需要在B ...
- 使用Go和Let's Encrypt证书部署HTTPS
为什么要使用HTTPS?使用HTTPS的途径有哪些?如何用Go来部署HTTPS?拿出你的小本本,你要的干货都在这儿! HTTPS的好处我们已在之前的文章中提高好多.它加密浏览器和服务器之间的流量,保障 ...
- iOS使用自签名证书实现HTTPS请求
概述 在16年的WWDC中,Apple已表示将从2017年1月1日起,所有新提交的App必须强制性应用HTTPS协议来进行网络请求. 默认情况下非HTTPS的网络访问是禁止的并且不能再通过简单粗暴的向 ...
随机推荐
- 多个git使用的 ssh key共存
ssh-keygen -t rsa -C "ljkj028@qq.com" 不要一直回车,指定密钥为 id_rsa_ljkj 默认为(id_rsa) 同理 创建其他密钥 打开ssh ...
- 聊聊我面试过的一个最奇葩的 Java 程序猿!
上周我聊了聊最让我反感的 10 种程序猿,无奈一个小时就进行了删除,详细原因就不说了,容易招黑. 今天聊的我面试过的最奇葩的一个程序猿,绝对是奇葩中的奇葩,简直是程序猿中的另类,最让我反感的程序猿又添 ...
- apache和tomcat的区别和联系
两者既有联系又有区别,是两个软件,可独立使用,也可整合使用.Apache是web服务器(静态解析,如HTML),本身只支持html,Web服务器专门处理HTTP请求(request),可以通过插件支持 ...
- MySql安装与使用(linux)
安装 MySQL 注意:此处安装是yum安装为例: MySQL安装 #yum install mysql-server 完后显示如下: MySQL初始化 #service mysqld start 查 ...
- [提权]MS16-016提权EXP
MS16-016提权EXP[K8]Tested On Win7 x86Usage: ms16-016_win7.exe "whoami"by K8拉登哥哥 20160216 下载: ...
- C# DataGridView 在最左侧显示行号方法
代码: private void dataGridView1_RowPostPaint(object sender, DataGridViewRowPostPaintEventArgs e) { Da ...
- Java高并发之线程池详解
线程池优势 在业务场景中, 如果一个对象创建销毁开销比较大, 那么此时建议池化对象进行管理. 例如线程, jdbc连接等等, 在高并发场景中, 如果可以复用之前销毁的对象, 那么系统效率将大大提升. ...
- Linux排序不准确的问题,用以下两行代码解决
export LC_ALL=C ...
- javaWeb代码工程统计
直接放在src/test/java包内运行 /** * 代码行数统计 * @author ThinkGem * @version 2014-7-22 */ public class CodeCount ...
- got & plt
got plt类似与Windows PE文件中IAT(Import Address Table). 要使的代码地址无关,基本思想就是把与地址相关的部分放到数据段里面. ELF的做法是在数据段里面建立一 ...
