day38 14-Spring的Bean的属性的注入:集合属性的注入
集合:List、Set、Map。



package cn.itcast.spring3.demo6; import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.Set;
//集合属性的注入
public class CollectionBean {
private List<String> list;
private Set<String> set;
private Map<String,Integer> map;
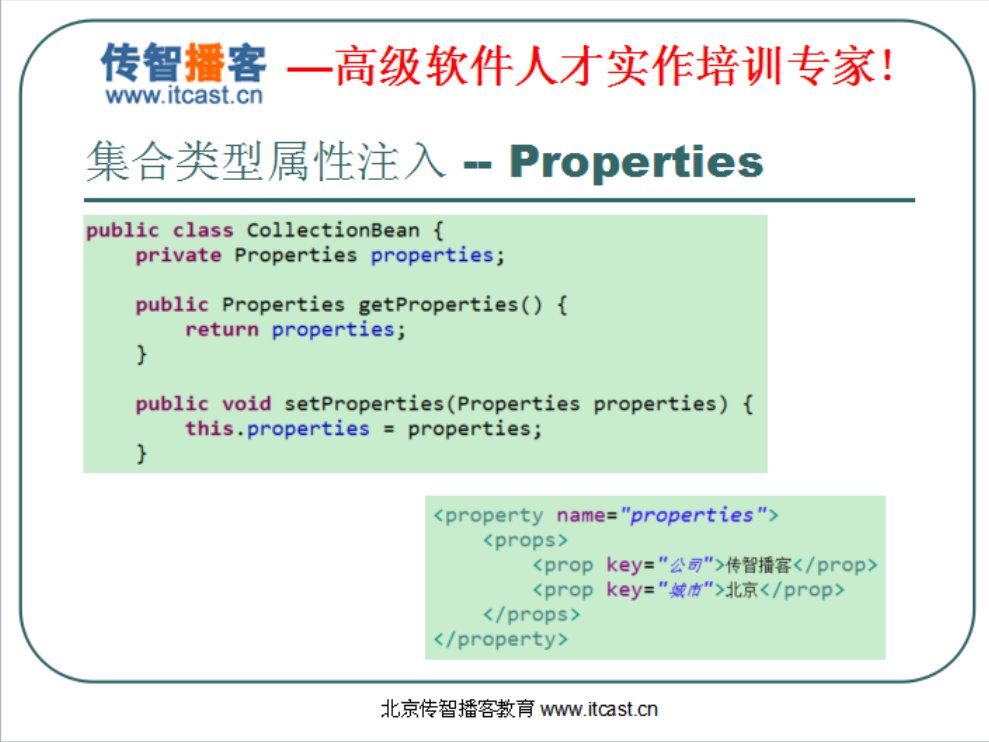
private Properties properties;//还可以注入属性对象
//这个属性对象Properties它底层继承HashTable,就是线程安全的那个对象
//还可以注入数组,数组的注入和List是一样的.
// public List<String> getList() {
// return list;
// } /* public Set<String> getSet() {
return set;
}*/ public void setSet(Set<String> set) {
this.set = set;
} public void setList(List<String> list) {
this.list = list;
} /* @Override
public String toString() {
return "CollectionBean [list=" + list + ", set=" + set + "]";
}*/ /* public Map<String, Integer> getMap() {
return map;
}*/ public void setMap(Map<String, Integer> map) {
this.map = map;
} /* @Override
public String toString() {
return "CollectionBean [list=" + list + ", set=" + set + ", map=" + map
+ "]";
}*/ /* public Properties getProperties() {
return properties;
}*/ public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
this.properties = properties;
} @Override
public String toString() {
return "CollectionBean [list=" + list + ", set=" + set + ", map=" + map
+ ", properties=" + properties + "]";
} /* @Override
public String toString() {
return "CollectionBean [list=" + list + "]";
}*/ /* public List<String> getList() {
return list;
}*/ }
package cn.itcast.spring3.demo6; import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class SpringTest6 {
@Test
public void demo1(){//注入list
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
CollectionBean collectionBean = (CollectionBean) applicationContext.getBean("collectionBean"); System.out.println(collectionBean); }
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!-- 别去schema,schema是文件,本地的文件,你得引那个头 --> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- demo1快速入门================================================= -->
<!-- 把接口和实现类在这个配置文件中配置,有了实现类的全路径之后到时候才能用工厂反射 --> <!-- 通过一个<bean>标签来设置类的信息,通过id属性为类起个标识. -->
<!-- 接口,实现类,配置文件也都有了 -->
<!-- 现在有一个工厂Spring为我们提供好了,其实就是解析这个XML文件 -->
<!-- 这个工厂你自己写会不会写?你用dom4j找里面的bean标签,找到class的属性值,然后就可以Class.forName()反射生成类的实例.其实Spring
也是这么做的,只不过工厂由Spring提供好了
-->
<bean id="helloService" class="cn.itcast.spring3.demo1.HelloServiceImpl">
<!-- 使用<property>标签注入属性
value指的是普通值
ref指的是对象
-->
<property name="info" value="传智播客"></property>
</bean>
<!-- demo1快速入门 -->
<!-- demo2Bean的实例化 -->
<!-- 默认情况下使用的就是无参数的构造方法. -->
<!--
<bean id="bean1" class="cn.itcast.spring3.demo2.Bean1"></bean>
-->
<!--
<bean name="bean1" class="cn.itcast.spring3.demo2.Bean1"></bean>
-->
<!-- 第二种使用静态工厂实例化 不能写class了,因为现在不是由Spring直接帮你创建对象了-->
<!--
<bean id="bean2" class="cn.itcast.spring3.demo2.Bean2Factory" factory-method="getBean2"></bean>
-->
<!-- 第三种使用实例工厂实例化 -->
<!--
<bean id="bean3" factory-bean="bean3Factory" factory-method="getBean3"></bean>
-->
<!-- 要先把Bean3Factory实例化 -->
<!--
<bean id="bean3Factory" class="cn.itcast.spring3.demo2.Bean3Factory"></bean>
-->
<!-- demo2Bean的实例化====================== end--> <!-- demo3Bean的作用范围======================= -->
<!--
<bean id="customer" class="cn.itcast.spring3.demo3.Customer" scope="prototype"></bean>
-->
<!--
<bean id="product" class="cn.itcast.spring3.demo3.Product" init-method="setup" destroy-method="teardown" scope="singleton">
<property name="name" value="空调">-->
<!-- 把Product类的属性name注入进来 -->
<!--
</property>
</bean>
--> <!-- demo4Bean的生命周期======================= -->
<!--
<bean id="customerService" class="cn.itcast.spring3.demo4.CustomerServiceImpl" init-method="setup" destroy-method="teardown"> <property name="name" value="itcast"></property>
</bean>
-->
<!-- 后处理Bean是由Spring容器自动调用不用你管,我们起个id是为了我们在程序中去获得它。但是这个类不用由我们获得, 由Spring自动调用。cn.itcast.spring3.demo4.MyBeanPostProcessor是后处理Bean-->
<!-- <bean class="cn.itcast.spring3.demo4.MyBeanPostProcessor"></bean>-->
<!-- demo5Bean的属性注入=====================================================================================================================================-->
<!-- 构造方法的注入 -->
<bean id="car" class="cn.itcast.spring3.demo5.Car">
<constructor-arg name="name" value="宝马"><!-- 通过这个标签为类注入属性 -->
</constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="price" value="1000000"><!-- 通过这个标签为类注入属性 -->
</constructor-arg>
<!--
<constructor-arg index="0" type="java.lang.String" value="奔驰">--><!-- 通过这个标签为类注入属性 -->
<!-- </constructor-arg>-->
<!--
<constructor-arg index="1" type="java.lang.Double" value="2000000">--><!-- 通过这个标签为类注入属性 --> <!-- </constructor-arg>-->
</bean>
<!--
<bean id="car2" class="cn.itcast.spring3.demo5.Car2">
-->
<!-- <property>标签中name就是属性名称,value是普通属性的值,
ref:引用其他的对象
-->
<!--
<property name="name" value="保时捷奇瑞QQ"></property>
<property name="price" value="500000020000"></property>
</bean>
-->
<!-- p名称空间的写法
<bean id="car2" class="cn.itcast.spring3.demo5.Car2" p:name="宝马" p:price="400000">
</bean>
-->
<!-- SpEL写法 -->
<bean id="car2" class="cn.itcast.spring3.demo5.Car2" >
<property name="name" value="#{'大众'}"></property>
<property name="price" value="#{'120000'}"></property>
</bean> <!--
<bean id="person" class="cn.itcast.spring3.demo5.Person">
<property name="name" value="任童"></property>
<property name="car2" ref="car2"></property>
</bean>
--> <!-- p名称空间的写法 -->
<!--
<bean id="person" class="cn.itcast.spring3.demo5.Person" p:name="童童" p:car2-ref="car2">
</bean>
-->
<!-- SpEL写法 -->
<bean id="person" class="cn.itcast.spring3.demo5.Person">
<!--
<property name="name" value="#{'小边'}"></property>
-->
<!--
<property name="name" value="#{personInfo.name}"></property>
-->
<property name="name" value="#{personInfo.showName()}"></property>
<property name="car2" value="#{car2}"></property> </bean> <!--
<property name="name" value="任童"></property>
<property name="car2" ref="car2"></property>
-->
<bean id="personInfo" class="cn.itcast.spring3.demo5.PersonInfo">
<property name="name" value="张三"></property> </bean>
<!-- demo5Bean的属性的注入============================================================== -->
<!-- demo6Bean的集合属性的注入 ==============================================================-->
<bean id="collectionBean" class="cn.itcast.spring3.demo6.CollectionBean">
<!-- 注入List集合 -->
<property name="list">
<list>
<value>童童</value>
<value>小凤</value>
</list>
</property> <!-- 注入set集合 -->
<property name="set">
<set>
<value>杜宏</value>
<value>如花</value>
</set>
</property>
<!-- 注入map集合 -->
<property name="map"> <map>
<entry key="刚刚" value="111"></entry>
<entry key="娇娇" value="333"></entry> </map> </property>
<property name="properties">
<props>
<prop key="username">root</prop><!-- prop有key和value的形式,属性文件就是key和value的形式 -->
<prop key="password">123</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
day38 14-Spring的Bean的属性的注入:集合属性的注入的更多相关文章
- [原创]java WEB学习笔记98:Spring学习---Spring Bean配置及相关细节:如何在配置bean,Spring容器(BeanFactory,ApplicationContext),如何获取bean,属性赋值(属性注入,构造器注入),配置bean细节(字面值,包含特殊字符,引用bean,null值,集合属性list map propert),util 和p 命名空间
本博客的目的:①总结自己的学习过程,相当于学习笔记 ②将自己的经验分享给大家,相互学习,互相交流,不可商用 内容难免出现问题,欢迎指正,交流,探讨,可以留言,也可以通过以下方式联系. 本人互联网技术爱 ...
- Spring学习(三)几种集合属性的注入方式
1.前言 众所周知.java中不只有八大简单类型.还有一些集合类型.本文围绕集合类型的注入做一个总结. 2.项目骨架 3.过程 1.创建实体类AllCollectionType package com ...
- 使用Jquery动态加入对象的集合属性,提交集合属性到表单
1.设置模型,引入构造函数,初始化集合 public class Person { public Person() //引入构造函数,初始化集合.如果未设置构造函数,集合会出现错误. { Skills ...
- Spring学习--集合属性
Spring 中可以通过一组内置的 xml 标签(例如: <list> , <set> 或 <map>) 来配置集合属性. 配置java.util.Set 需要使用 ...
- IoC容器-Bean管理XML方式(注入集合类型属性)
Ico操作Bean管理(xml注入集合属性) 1,注入数组类型属性 2,注入List集合类型属性 3,注入Map集合类型属性 (1)创建类,定义数组.list.map.set类型属性,生成对应set方 ...
- 编写高质量代码改善C#程序的157个建议——建议25:谨慎集合属性的可写操作
建议25:谨慎集合属性的可写操作 如果类型的属性中有集合属性,那么应该保证属性对象是由类型本身产生的.如果将属性设置为可写,则会增加抛出异常的几率.一般情况下,如果集合属性没有值,则它返回的Count ...
- (转)Hibernate框架基础——映射集合属性
http://blog.csdn.net/yerenyuan_pku/article/details/52745486 集合映射 集合属性大致有两种: 单纯的集合属性,如像List.Set或数组等集合 ...
- Spring - 配置Bean - 自动装配 关系 作用域 引用外部属性文件
1 Autowire自动装配1.1 使用:只需在<bean>中使用autowire元素<bean id="student" class="com.kej ...
- Spring框架bean的配置(2):SpEL:引用 Bean、属性和方法。。。
将这些架包放入在工程目录下建立的lib文件夹里,并解压 commons-logging-1.1.1 spring-aop-4.0.0.RELEASE spring-beans-4.0.0.RELEAS ...
- spring中bean的scope属性理解
bean的scope属性有prototype,singleton,request, session几个属性 spring和struts2整合的时候,struts2的action要配置成scope=&q ...
随机推荐
- hbase master一直报启动不起来问题(region空洞和region卡在spilt)
数据不重要或者一直卡着的情况下,可以切换hdfs用户到hbase的wal目录下对spilting的数据进行重命名.具体步骤如下 1.关闭hbase集群 2.切换hdfs用户 3.到hbasewal目录 ...
- springboot4.1.1的log4j2配置
一.默认情况下,Spring Boot会用Logback来记录日志,并用INFO级别输出到控制台: 日志输出内容元素具体如下: 时间日期:精确到毫秒 日志级别:ERROR, WARN, INFO, D ...
- 路飞学城-Python爬虫集训-第二章
本次爬虫集训的第二次作业是web微信. 先贴一下任务: 作业中使用到了Flask. Flask是一个使用 Python 编写的轻量级 Web 应用框架.其 WSGI 工具箱采用 Werkzeug ,模 ...
- c语言学习笔记 - 顺序查找和哨兵查找比较
今天学习C时用到了顺序查找和哨兵查找,做了一个比较,主要是学习下哨兵查找法 例如在一个数组里查找一个元素,没找到返回-1,找到了则返回这个数组的下标也就是键值. 用循序查找法: void arr_se ...
- vue 编写插件
1. 将插件逻辑封装成一个对象 最后在install编写业务代码暴露给Vue对象 好处: 可以添加任意参数在这个对象上 方便将install函数封装的更加精简 可拓展性也比较高 2. 将所有 ...
- Spring注解驱动开发(七)-----servlet3.0、springmvc
ServletContainerInitializer Shared libraries(共享库) / runtimes pluggability(运行时插件能力) 1.Servlet容器启动会扫描, ...
- Django项目: 5.新闻主页
一.功能需求分析 1.功能 轮播图 推荐文章列表 文章标签导航 文章列表 分页 二.模型设计 根据功能分析,我们需要如下表 1.表和字段分析 文章分类表 文章表 文章评论表 推荐文章表 轮播图表 2. ...
- Python的Django REST框架中的序列化及请求和返回
Python的Django REST框架中的序列化及请求和返回 序列化Serialization 1. 设置一个新的环境 在我们开始之前, 我们首先使用virtualenv要创建一个新的虚拟环境,以使 ...
- python禁止函数修改列表的实现方法
python禁止函数修改列表的实现方法 有时候,需要禁止函数修改列表.例如要对裂变进行修改操作,也要保留原来的未打印的设计列表,以供备案.为解决这个问题,可向函数传递列表的副本而不是原件:这样函数所做 ...
- nginx日志修改时间格式为年月日时分秒
先解除这段注释,使用自定义日志格式 $time_iso8601 生成格式:--20T09::+: $time_local 生成格式: /Apr/::: + 还是选择年月日时分秒看起来舒服一点
