Gnome排序
Gnome排序(地精排序),起初由Hamid Sarbazi-Azad 于2000年提出,并被称为stupid排序,后来被Dick Grune描述并命名为“地精排序”,作为一个排序算法,和插入排序类似,除了移动一个元素到最终的位置,是通过交换一系列的元素实现,就像冒泡排序一样。概念上十分简单,不需要嵌套循环。时间复杂度为O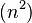 ,但是如果初始数列基本有序,时间复杂度将降为O(n)。实际上Gnome算法可以和插入排序算法一样快。平均运行时间为O
,但是如果初始数列基本有序,时间复杂度将降为O(n)。实际上Gnome算法可以和插入排序算法一样快。平均运行时间为O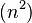 .
.
Gnome排序算法总是查找最开始逆序的一对相邻数,并交换位置,基于交换两元素后将引入一个新的相邻逆序对,并没有假定当前位置之后的元素已经有序
Description
下面gnome排序算法的伪代码,使用0起始索引数组:
procedure gnomeSort(a[])
pos :=
while pos < length(a)
if (a[pos] >= a[pos-])
pos := pos +
else
swap a[pos] and a[pos-]
if (pos > )
pos := pos -
end if
end if
end while
end procedure
实例
给定一个无序数组, a = [5, 3, 2, 4], gnome排序将在while循环中执行如下的步骤. "current position"采用加粗黑体:
| Current array | Action to take |
|---|---|
| [5, 3, 2, 4] | a[pos] < a[pos-1], swap: |
| [3, 5, 2, 4] | a[pos] >= a[pos-1], increment pos: |
| [3, 5, 2, 4] | a[pos] < a[pos-1], swap and pos > 1, decrement pos: |
| [3, 2, 5, 4] | a[pos] < a[pos-1], swap and pos <= 1, increment pos: |
| [2, 3, 5, 4] | a[pos] >= a[pos-1], increment pos: |
| [2, 3, 5, 4] | a[pos] < a[pos-1], swap and pos > 1, decrement pos: |
| [2, 3, 4, 5] | a[pos] >= a[pos-1], increment pos: |
| [2, 3, 4, 5] | a[pos] >= a[pos-1], increment pos: |
| [2, 3, 4, 5] | pos == length(a), finished. |
C代码如下:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<ctype.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<time.h> void swap(int *a, int *b) //交换两元素的值
{
int t;
t=*a;
*a=*b;
*b=t;
} void printArray(int a[], int count) //打印数组元素
{
int i;
for(i=; i<count; i++)
printf("%d ",a[i]);
printf("\n");
} void gnome_sort(int *a, int len) //gnome排序算法
{
int pos=;
while(pos<len)
{
if(a[pos]>=a[pos-])
{
pos++;
}
else
{
swap(&a[pos],&a[pos-]);
if(pos>) pos--;
}
}
} int main(void)
{
int a[]={, , , , , , , , };
int n=sizeof(a)/sizeof(*a);
printArray(a,n);
gnome_sort(a,n);
printArray(a,n);
return ;
}
优化算法
gnome算法还可以通过引入一个变量,用于存储每次返回到数组前面的位置来进行优化。采用这样的优化,gnome排序将成为一个变种插入排序,下面优化后gnome排序算法的伪代码,使用0起始索引数组:
procedure optimizedGnomeSort(a[])
pos :=
last :=
while pos < length(a)
if (a[pos] >= a[pos-])
if (last != )
pos := last
last :=
end if
pos := pos +
else
swap a[pos] and a[pos-]
if (pos > )
if (last == )
last := pos
end if
pos := pos -
else
pos := pos +
end if
end if
end while
end procedure
C代码如下:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<ctype.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<time.h> void swap(int *a, int *b) //交换两元素的值
{
int t;
t=*a;
*a=*b;
*b=t;
} void printArray(int a[], int count) //打印数组元素
{
int i;
for(i=; i<count; i++)
printf("%d ",a[i]);
printf("\n");
} void optimizedGnome_Sort(int *a, int len) //优化后的gnome排序
{
int last,pos;
last=; pos=;
while(pos<len)
{
if(a[pos]>=a[pos-])
{
if(last!=)
{
pos=last;
last=;
}
pos++;
}
else
{
swap(&a[pos],&a[pos-]);
if(pos>)
{
if(last==)
last=pos;
pos--;
}
else
{
pos++;
}
}
}
} int main(void)
{
int a[]={, , , , , , , , };
int n=sizeof(a)/sizeof(*a);
printArray(a,n);
optimizedGnome_Sort(a,n);
printArray(a,n);
return ;
}
Gnome排序的更多相关文章
- Gnome排序算法
Gnome排序(地精排序),起初由Hamid Sarbazi-Azad 于2000年提出,并被称为stupid排序,后来被Dick Grune描述并命名为“地精排序”,作为一个排序算法,和插入排序类似 ...
- 部分博文目录索引(C语言+算法)
今天将本博客的部分文章建立一个索引,方便大家进行阅读,当然每一类别中的文章都会持续的添加和更新(PS:博文主要使用C语言) 博客地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/archimedes ...
- 数据结构杂谈(二)简单有趣的地精排序Gnome sort
很早之前便听说过地精排序的名字,今天自己看来一下,发现这是一种非常简单而且有趣的排序算法. 为什么叫地精排序? 地精排序在2000年由Dr. Hamid Sarbazi-Azad 提出的时候被称作 s ...
- 地精排序(Gnome Sort) 算法
gnome应该是最简单排序的排序算法吧!Gnome Sort,这是该算法的作者命名的,O(n*n)时间复杂度,O(1)空间复杂度,属于稳定的排序算法.算法的思想是每趟循环找到第一个逆序的元素,把它和在 ...
- 地精排序Gnome Sort
号称最简单的排序算法,只有一层循环,默认情况下前进冒泡,一旦遇到冒泡的情况发生就往回冒,直到把这个数字放好为止 直接看它排序的过程,待排数组[6 2 4 1 5 9] 先设计一个标识i=0然后从头开始 ...
- 只有一重循环的排序——侏儒排序(Gnome Sort)
侏儒排序:从头(i=0)开始遍历元素,如果当前元素比前一个元素大(array[i]>array[i-1]),就把它跟前一个元素互换(Swap(a[i],a[i-1]))并继续检查它(i--),否 ...
- 13个Cat命令管理(显示,排序,建立)文件实例
在Linux系统中,大多数配置文件.日志文件,甚至shell脚本都使用文本文件格式,因此,Linux系统存在着多种文本编辑器,但当你仅仅想要查看一下这些文件的内容时,可使用一个简单的命令-cat. c ...
- 【Unity3D自学记录】可视化对照十多种排序算法(C#版)
在这篇文章中.我会向大家展示一些排序算法的可视化过程.我还写了一个工具.大家可对照查看某两种排序算法. 下载源代码 – 75.7 KB 下载演示样例 – 27.1 KB 引言 首先,我觉得是最重要的是 ...
- CodeForces - 138C: Mushroom Gnomes - 2 (线段树&概率&排序)
One day Natalia was walking in the woods when she met a little mushroom gnome. The gnome told her th ...
随机推荐
- Mybatis最入门---数据库的下载与安装
[一步是咫尺,一步即天涯] 近期.因为工作进度调整,之前的Spring教程就先临时告一段落了,兴许找个时间继续更新,假设有那位看官想了解某个内容的,敬请留言,大家一起学习. 作为数据库工具的使用开篇. ...
- js scrollIntoViewIfNeeded
根据 MDN的描述,Element.scrollIntoView()方法让当前的元素滚动到浏览器窗口的可视区域内. 而Element.scrollIntoViewIfNeeded()方法也是用来将不在 ...
- 如何通过SSH及其Client 批量分发文件和执行管理命令
一.前提:已经配置好root和hadoop用户的无密码的SSH访问 二.直接上代码 ##复制单个文件[hadoop@nn1 hadoop]$ for ip in 102 103 104 111 112 ...
- glibc中fork系统调用传参
因为想跟踪下在新建进程时,如何处理新建进程的vruntime,所以跟踪了下fork. 以glic-2.17中ARM为例(unicore架构的没找到),实际上通过寄存器向系统调用传递的参数为: r7: ...
- ITIL之“变更管理”
首先要说明的是ITIL的变更是指“上线系统的变更”,而不是指系统建设的变更. ITIL的变更的流程如下: 整个变更管理在实际操作中有几个注意点: 1. 现存的企业中,变更咨询委员会(CAB)可能只有信 ...
- 多个Tomcat之间实现Session共享
对于高访问量.高并发量的网站或web应用来说,目前最常见的解决方案应该就是利用负载均衡进行server集群,例如比较流行的nginx+memcache+tomcat.集群之后比如我们有N个Tomcat ...
- [RN] 04 - React Navigation
react-navigation和react-router的对比: 支持的平台: react-navigation: react-native react-router: react-native.r ...
- [Arch] 02. Design principle and Software Pattern
Ref: 软件设计的七大原则 有时间的话,还需进一步深入理解. Figure, 重要的前五个原则 单一职责原则 (Simple responsibility pinciple SRP) 类的设计趋向于 ...
- SpringBoot------添加保存时自动编译插件
.右键Java项目 .选择“Spring Tools” 3.选择“Add Boot DevTools” 4.每次使用Ctrl + S键时就会自动编译了 实际上是在Pom.xml文件中添加了如下Java ...
- iOS 解决UIScrollView布局问题(布局受statusBar和NavigationBar影响)
iOS APP中有一个非常好用的功能,那就是当我们在滚动一个UIScrollView滚动了很远很远的时候,假如我们想让UIScrollView回到顶部,我们绝大多数人的做法就是慢慢慢慢的滚动UIScr ...
