TCP Congestion Control
TCP Congestion Control
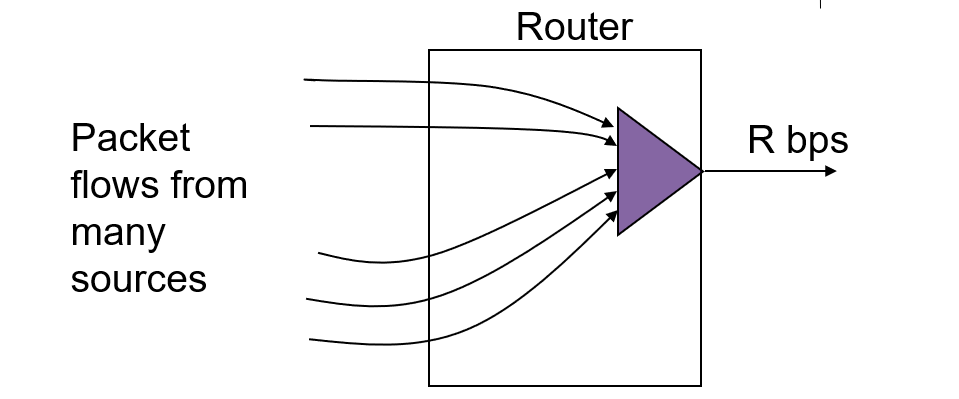
- Congestion occurs when total arrival rate from all packet flows exceeds R over a sustained(维持) period of time
- Buffers(缓冲) at multiplexer will fill and packets will be lost
Phases of Congestion Behavior

- Light traffic
- Arrival Rate << R
- Low delay
- Can accommodate(容纳) more
- Knee (congestion onset)
- Arrival rate approaches R
- Delay increases rapidly
- Throughput(吞吐量) begins to saturate(饱和)
- Congestion collapse
- Arrival rate > R
- Large delays, packet loss
- Useful application throughput drops
Congestion Window
- Desired operating point: just before knee
- TCP sender maintains a congestion window (cwnd) to control congestion at intermediate(中间的) routers
- Effective window is minimum of congestion window and advertised window(广播窗口)
- Problem: senders does not know what its “fair” share of available bandwidth should be
- Solution:
- adapt dynamically to available BW
- Senders probe(探查) the network by increasing cwnd
- When congestion detected, senders reduce rate
- Ideally, sending rate stabilizes(稳定) near optimal(最优) point
Congestion Window (Cont.)
- How does the TCP congestion algorithm change congestion window dynamically according to the most up-to-date state of the network?
- At light traffic: each segment is ACKed quickly
- Increase cwnd aggresively
- At knee: segment ACKs arrive, but more slowly
- Slow down increase in cwnd
- At congestion: segments encounter large delays, timeout, segments are dropped in router buffers
- Reduce transmission rate, then probe again
TCP Congestion Control (1): Slow Start
- Slow start: increase congestion window size by one segment upon receiving an ACK from receiver
- initialized at 2 segments; usually 1 segment
- used at start of data transfer
- congestion window increases exponentially(指数)

TCP Congestion Control (2): Congestion Avoidance
- Algorithm progressively(逐步) sets a congestion threshold(门槛)
- When cwnd > threshold, slow down rate at which cwnd is increased
- Increase congestion window size by one segment per round-trip-time (RTT)
- Each time an** ACK arrives, cwnd is increased by 1/cwnd**
- In one RTT, all ccwnd segments are sent, so total increase in cwnd is cwnd x 1/cwnd = 1
- cwnd grows linearly with time

TCP Congestion Control (3): Congestion
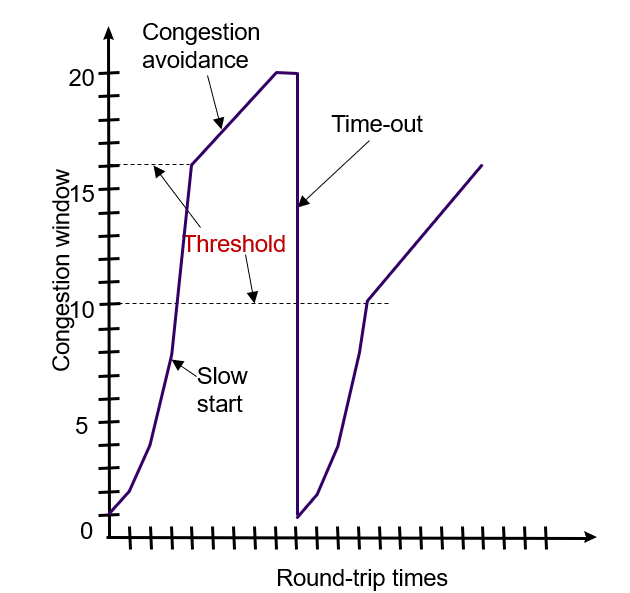
- Congestion is detected upon timeout or receipt of duplicate ACKs
- Assume current cwnd corresponds to available bandwidth
- Adjust congestion threshold = ½ x current cwnd
- Reset cwnd to 1
- Go back to slow-start
- Over several cycles expect to converge(收敛) to congestion threshold equal to about ½ the available bandwidth
Fast Retransmit & Fast Recovery

- Congestion causes many segments to be dropped
- Burt if only a single segment is dropped, then subsequent(随后的) segments trigger duplicate ACKs before timeout
- Can avoid large decrease in cwnd as follows:
- When three duplicate ACKs arrive before timeout expires(期满), retransmit lost segment immediately
- Reset congestion threshold to ½ cwnd
- Reset cwnd to congestion threshold + 3 to account for the three segments that triggered duplicate ACKs
- Remain in congestion avoidance phase
- In absence of timeouts, cwnd will oscillate(振动) around optimal value
TCP Congestion Control: Fast Retransmit & Fast Recovery

TCP Congestion Control的更多相关文章
- Network | TCP congestion control
拥塞控制算法:1. 加性增.乘性减:2. 慢启动:3. 对超时事件作出反应: 整体过程如下: 慢启动->到达阈值->加性增(窗口+1个MSS), 这个阶段叫拥塞避免(CA)->3个冗 ...
- TCP Flow Control and Data Transfer
TCP Flow Control TCP Data Transfer Selective Repeat ARQ with Positive ACK Window slides a byte basis ...
- Google Congestion Control介绍
随着网络带宽的日益增加和便携式设备,如智能手机或平板电脑处理能力的增强,基于互联网的实时通信已经成为热点. 虽然视频会议已商用了多年,特别是SKYPE这样的视频应用在互联网上已有10年时间,但针对实时 ...
- java基础 UDP通信 user datagram protocol 用户数据豆协议 TCP transmission control protocol 传输控制协议 多线程TCP
无连接通信 UDP 客户端 package com.swift.test; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.DatagramPacket; im ...
- Congestion Avoidance in TCP
Congestion Avoidance in TCP Consequence of lack of congestion control When a popular resource is sha ...
- Internet History,Technology,and Security -Transport Control Protocol(TCP)(Week6)
Week6 Technology: Transport Control Protocol(TCP) Welcome to Week 6 of IHTS. We are in our second we ...
- TCP的那些事儿(下)
TCP的那些事儿(下) 这篇文章是下篇,所以如果你对TCP不熟悉的话,还请你先看看上篇<TCP的那些事儿(上)> 上篇中,我们介绍了TCP的协议头.状态机.数据重传中的东西.但是TCP要解 ...
- [转载] tcp那些事2
原文: http://coolshell.cn/articles/11609.html 这篇文章是下篇,所以如果你对TCP不熟悉的话,还请你先看看上篇<TCP的那些事儿(上)> 上篇中,我 ...
- IP, TCP, and HTTP--reference
IP, TCP, and HTTP Issue #10 Syncing Data, March 2014 By Daniel Eggert When an app communicates with ...
随机推荐
- Android xmlns 的作用及其自定义
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/chuchu521/article/details/8052855 xmlns:Android="http://schemas.android ...
- BZOJ3498: PA2009 Cakes(三元环)
题意 题目链接 Sol 按照套路把边转成无向图,我们采取的策略是从权值大的向权值小的连边 然后从按权值从小到大枚举每个点,再枚举他们连出去的点\(v\) 如果\(v\)的度数\(\leqslant M ...
- 360浏览器内核控制标签meta说明
浏览器内核控制标签meta说明 背景介绍 由于众所周知的原因,国内的主流浏览器都是双核浏览器:基于Webkit的内核用于常用网站的高速浏览,基于IE的内核主要用于部分网银.政府.办公系统等网站的正常使 ...
- git之删除过滤
把不想提交的内容删除过滤 git rm --cached **/** -f
- CentOS下调整home和根分区大小
由于我们有时候没法预估或者说错误的盘符分区的时候,常常会导致我们后面的操作出现极大的不方便,这里我就记录下一个错误分区后对home和根分区存储空间大小调整的整个过程! ①查看我们现有机器的分区状况 c ...
- eayui grid 每一页的行号都是从1开始
问题背景: easyui 需要显示行号的时候,我们只需要设置 rownumbers: true, 但是 不管是在哪一页,行号都是从1开始,不能连续 我们在分页的 onSelectPage 函数里去执 ...
- 通过JTS源码分析Rtree(未完待续)
前言 R树在数据库等领域做出的功绩是非常显著的.它很好的解决了在高维空间搜索等问题.它把B树的思想很好的扩展到了多维空间,采用了B树分割空间的思想,并在添加.删除操作时采用合并.分解结点的方法,保证树 ...
- 广告点击率预测(CTR) —— 在线学习算法FTRL的应用
FTRL由google工程师提出,在13的paper中给出了伪代码和实现细节,paper地址:http://www.eecs.tufts.edu/~dsculley/papers/ad-click-p ...
- 微信小程序开发4-JSON
1.JSON是JavaScript语法的子集 2.JSON的语法规则 数据在名称/值对中 数据由逗号分隔 大括号保存对象 中括号保存数组 3.JSON 值可以是: 数字(整数或浮点数) 字符串(在双引 ...
- 封装一个MPermissionsActivity的思路和步骤
http://blog.csdn.net/longkehuawei/article/details/53202804 第一步:检测所有的权限是否都已授权 /** * 检测所有的权限是否都已授权 * * ...
