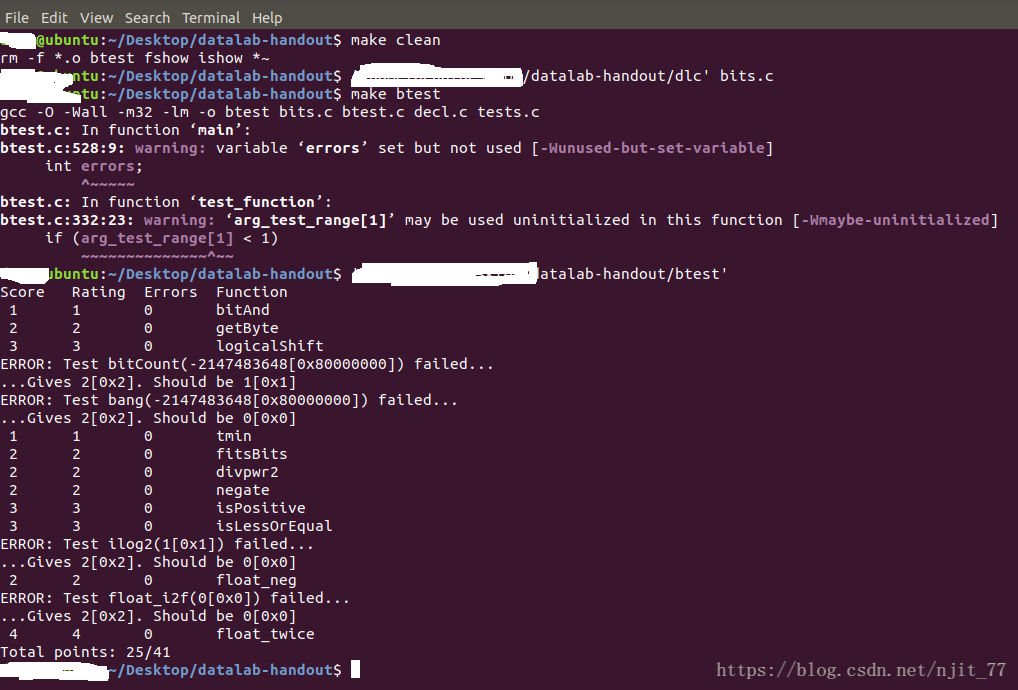
datalab (原发布 csdn 2018年09月21日 20:42:54)
首先声明datalab本人未完成,有4道题目没有做出来。本文博客记录下自己的解析,以便以后回忆。如果能帮助到你就更好了,如果觉得本文没啥技术含量,也望多多包涵。
/*
* bitAnd - x&y using only ~ and |
* Example: bitAnd(6, 5) = 4
* Legal ops: ~ |
* Max ops: 8
* Rating: 1
*/
int bitAnd(int x, int y) {
return ~(~x | ~y);
}
/*
* getByte - Extract byte n from word x
* Bytes numbered from 0 (LSB) to 3 (MSB)
* Examples: getByte(0x12345678,1) = 0x56
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 6
* Rating: 2
*/
int getByte(int x, int n) {
int offsetValue = 0xff;
int offsetIndex = n << 3;
int value = (x & (offsetValue << offsetIndex)) >> offsetIndex;
return value & offsetValue;
}
/*
* logicalShift - shift x to the right by n, using a logical shift
* Can assume that 0 <= n <= 31
* Examples: logicalShift(0x87654321,4) = 0x08765432
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 20
* Rating: 3
*/
int logicalShift(int x, int n) {
int offset = 0x1 << 31;
int offsetValue = ~(offset >> n << 1);
return (x >> n) & offsetValue;
}
/*
* bitCount - returns count of number of 1's in word
* Examples: bitCount(5) = 2, bitCount(7) = 3
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 40
* Rating: 4
*/
int bitCount(int x) {
return 2;
}
/*
* bang - Compute !x without using !
* Examples: bang(3) = 0, bang(0) = 1
* Legal ops: ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 12
* Rating: 4
*/
int bang(int x) {
return 2;
}
/*
* tmin - return minimum two's complement integer
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 4
* Rating: 1
*/
int tmin(void) {
return (0x1 << 31);
}
/*
* fitsBits - return 1 if x can be represented as an
* n-bit, two's complement integer.
* 1 <= n <= 32
* Examples: fitsBits(5,3) = 0, fitsBits(-4,3) = 1
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 15
* Rating: 2
*/
int fitsBits(int x, int n) {
int offsetValue = 0x1 << n;
int addValue = (offsetValue >> 1) & (~offsetValue);//2^(n-1)
int value1 = x + addValue;//x - {-[2^(n-1)]}
int value2 = addValue + (~x);//[2^(n-1)-1] - x
int maxValue = 0x1 << 31;
return (n >> 5) | ((!(value1 & maxValue)) & (!(value2 & maxValue)));
}
/*
* divpwr2 - Compute x/(2^n), for 0 <= n <= 30
* Round toward zero
* Examples: divpwr2(15,1) = 7, divpwr2(-33,4) = -2
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 15
* Rating: 2
*/
int divpwr2(int x, int n) {
int maxValue = 0x1 << 31;
int offsetValue = ~(0x1 << 31 >> (32 + ~n));
int andValue = offsetValue & x;
return (x >> n) + ((!!(x & maxValue)) & (!!(andValue)));
}
/*
* negate - return -x
* Example: negate(1) = -1.
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 5
* Rating: 2
*/
int negate(int x) {
return ~x + 1;
}
/*
* isPositive - return 1 if x > 0, return 0 otherwise
* Example: isPositive(-1) = 0.
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 8
* Rating: 3
*/
int isPositive(int x) {
return (!(x >> 31)) ^ (!x);
}
/*
* isLessOrEqual - if x <= y then return 1, else return 0
* Example: isLessOrEqual(4,5) = 1.
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 24
* Rating: 3
*/
int isLessOrEqual(int x, int y) {
int offsetValue = 0x1;
int offsetIndex = 31;
int offsetSign = offsetValue << offsetIndex;
int signX = !(x & offsetSign);
int signY = !(y & offsetSign);
int value1 = ((!signX) & signY )^ 0x0;
int value2 = (signX & (!signY)) ^ 0x1;
int value3 = (!((y + ~x + 1) & offsetSign)) ^ 0x0;
return value1 | (value2 & value3);
}
/*
* ilog2 - return floor(log base 2 of x), where x > 0
* Example: ilog2(16) = 4
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 90
* Rating: 4
*/
int ilog2(int x) {
return 2;
}
/*
* float_neg - Return bit-level equivalent of expression -f for
* floating point argument f.
* Both the argument and result are passed as unsigned int's, but
* they are to be interpreted as the bit-level representations of
* single-precision floating point values.
* When argument is NaN, return argument.
* Legal ops: Any integer/unsigned operations incl. ||, &&. also if, while
* Max ops: 10
* Rating: 2
*/
unsigned float_neg(unsigned uf) {
int offsetValue = 0x1;
int offsetIndex = 0;
int andValue = 0;
int signValue;
while (offsetIndex < 31)
{
signValue = (uf & offsetValue) >> offsetIndex;
if (offsetIndex < 23)
{
andValue = andValue | signValue;
}
else
{
andValue = andValue & signValue;
}
offsetIndex += 1;
offsetValue <<= 1;
}
if (andValue)
{
return uf;//NaN
}
return uf ^ offsetValue;
}
/*
* float_i2f - Return bit-level equivalent of expression (float) x
* Result is returned as unsigned int, but
* it is to be interpreted as the bit-level representation of a
* single-precision floating point values.
* Legal ops: Any integer/unsigned operations incl. ||, &&. also if, while
* Max ops: 30
* Rating: 4
*/
unsigned float_i2f(int x) {
return 2;
}
/*
* float_twice - Return bit-level equivalent of expression 2*f for
* floating point argument f.
* Both the argument and result are passed as unsigned int's, but
* they are to be interpreted as the bit-level representation of
* single-precision floating point values.
* When argument is NaN, return argument
* Legal ops: Any integer/unsigned operations incl. ||, &&. also if, while
* Max ops: 30
* Rating: 4
*/
unsigned float_twice(unsigned uf) {
int signIndex = 31;
int expIndex = 23;
int offsetValue = 0x1;
int offsetSign = offsetValue << signIndex;
int andValue = 1;
int orValue = 0;
int signValue;
int offsetIndex = expIndex;
while (offsetIndex < signIndex)
{
signValue = (uf & (offsetValue << offsetIndex)) >> offsetIndex;
andValue = andValue & signValue;
orValue = orValue | signValue;
offsetIndex += 1;
}
if (andValue == 1)//exp==255
{
return uf;
}
else if (orValue == 0)//非规格化
{
signValue = !!(uf & offsetSign);
uf <<= 1;
if (signValue == 0)
{
return uf & (~offsetSign);
}
return uf | offsetSign;
}
else
{
signValue = ((uf >> expIndex) + 1) << expIndex;
offsetIndex = expIndex;
while (offsetIndex < signIndex)
{
uf &= ~(offsetValue << offsetIndex);
offsetIndex += 1;
}
return uf | signValue;
}
}
datalab (原发布 csdn 2018年09月21日 20:42:54)的更多相关文章
- c# Equal函数 and 运算符'==' (原发布 csdn 2017年10月15日 20:39:26)
1.==.!=.<.>.<= 和>= 运算符为比较运算符(comparison operator).C#语言规范5.0中文版中比较运算符的描述如下: 2.通用类型系统 3.值类 ...
- 关于“关于C#装箱的疑问”帖子的个人看法 (原发布csdn 2017年10月07日 10:21:10)
前言 昨天晚上闲着无事,就上csdn逛了一下,突然发现一个帖子很有意思,就点进去看了一下. 问题很精辟 int a = 1; object b=a; object c = b; c = 2; 为什么b ...
- getDate() 获取时间 如2018年09月21日 11:32:11
function p(s) { return s < 10 ? '0' + s: s;} function getDate() { var myDate = new Date(); //获取当前 ...
- 2018年1月21日--2月4日 NAS
二十号去比赛时,与同事闲聊时说起家庭服务器,后来搜到nas(网络附着存储器),找到freenas,突然觉得很有用,手机拍了大量的照片视频,存储在电脑,已经换过几次硬盘了,对于这些珍贵的资料,万一硬盘坏 ...
- java自动化测试开发环境搭建(更新至2018年10月8日 11:42:15)
1.安装JDK的1.8版本 官网下载地址:https://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/javase/downloads/jdk8-downloads-2133151 ...
- 2014年12月23日00:42:54——PS4
http://tieba.baidu.com/p/3415598015?see_lz=1&pn=1 http://tieba.baidu.com/p/3188981817 http://tie ...
- 【12月21日】A股滚动市盈率PE历史新低排名
2010年01月01日 到 2018年12月21日 之间,滚动市盈率历史新低排名.上市三年以上的公司,2018年12月21日市盈率在300以下的公司. 1 - 厦门象屿(SH600057) - 历史新 ...
- RxJava2.0学习笔记2 2018年7月3日 周二
摘记: 1.map -- 转换 有些服务端的接口设计,会在返回的数据外层包裹一些额外信息,这些信息对于调试很有用,但本地显示是用不到的.使用 map() 可以把外层的格式剥掉,只留下本地会用到的核心 ...
- 导航狗IT周报-2018年05月27日
原文链接:https://www.daohanggou.cn/2018/05/27/it-weekly-9/ 摘要: “灰袍技能圈子”将闭圈:物理安全:为什么我们现在的生活节奏越来越快? 技术干货 1 ...
随机推荐
- .net 通过反射实现两个相同结构实体类的转换
public static T2 CopyToModel<T1, T2>(T1 source) { T2 model = default(T2); PropertyInfo[] pi = ...
- Java基础--常用API--IO流相关API
一.IO流 1.定义: IO流指的是Input/Output流,即输入流/输出流. 输入流:将外界信息写入程序,即从外界获取信息,属于读操作. 输出流:将程序数据发送给外界,即向外界传输数据,属于写操 ...
- JavaScript之找LHS查询和RHS查询
LHS和RHS,当变量出现在赋值操作的左侧时进行LHS 查询,出现在右侧时进行RHS 查询. LHS 查询是试图找到变量的容器本身,从而可以对其赋值. RHS 理解成retrieve his sour ...
- 2019年上半年收集到的人工智能GAN干货文章
2019年上半年收集到的人工智能GAN干货文章 GAN简介及其常见应用 训练GAN,你应该知道的二三事 了解生成对抗网络(GAN) CosmoGAN:训练GAN,让AI寻找宇宙中的暗物质 关于GAN的 ...
- 用redis和cookie做单用户登录
因为公司的项目需要用到单用户登录,于是今天用redis和cookie给系统添加了单用户登录功能,再次简单记录一下. 单用户登录是为了防止同一账户在不同电脑和不同浏览器里面同时登录.所以我这边的思路是: ...
- QT QNetworkAccessManager 如何支持RESTFul的HTTP Patch方法
HTTP Patch方法是除了post,get,put,delete之外的一个新方式, 网上查不到的,也算是独家吧: 主要用下面这个方法: QNetworkReply *sendCustomReque ...
- MBProgressHUD源码(上)
本篇博文记录MBProgressHUD源码学习过程,从官方提供的Demo项目入手,一步步了解其代码结构,学习它使用的技术,体会作者的编程思想. 一.结构 我们先来看下MBProgressHUD的结构, ...
- 使用 gitlab 进行代码管理
这里使用 gitlab 做服务器, 客户端主要使用 git extensions. ============================= gitlab 项目成员类型: ============= ...
- Tensorflow的不足之处
Tensorflow还是有不足的地方.第一体现在Tensorflow的数据机制,由于tensor只是占位符,在没有用tf.Session().run接口填充值之前是没有实际值的.
- luoguP2463 [SDOI2008]Sandy的卡片
题意 显然加上一个数相等就是差分数组相等,于是问题变为求几个串的最长公共子串. 这里我学习了如何用SA求LCS. 首先问题要转化成求一些后缀的最长公共前缀,要求这些后缀分属不同的串. 于是二分答案,于 ...