3. 源码分析---SOFARPC客户端服务调用
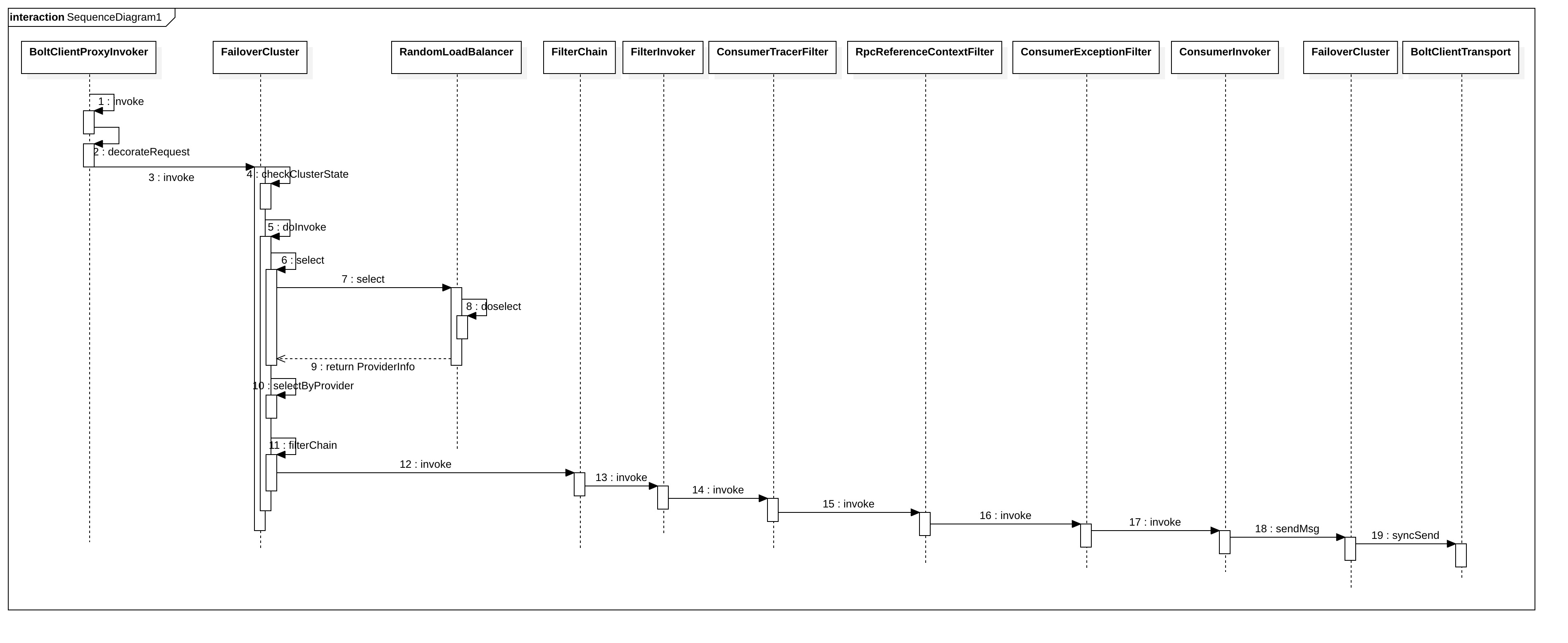
我们首先看看BoltClientProxyInvoker的关系图
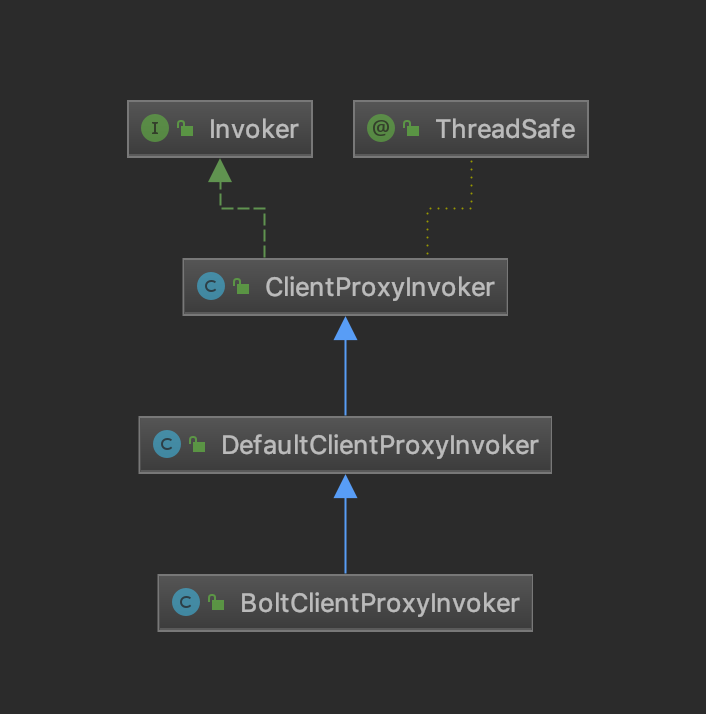
所以当我们用BoltClientProxyInvoker#invoke的时候实际上是调用了父类的invoke方法
ClientProxyInvoker#invoke
@Override
public SofaResponse invoke(SofaRequest request) throws SofaRpcException {
SofaResponse response = null;
Throwable throwable = null;
try {
RpcInternalContext.pushContext();
RpcInternalContext context = RpcInternalContext.getContext();
context.setProviderSide(false);
// 包装request请求
decorateRequest(request);
try {
// 产生开始调用事件
if (EventBus.isEnable(ClientStartInvokeEvent.class)) {
EventBus.post(new ClientStartInvokeEvent(request));
}
// 得到结果
response = cluster.invoke(request);
} catch (SofaRpcException e) {
throwable = e;
throw e;
} finally {
// 产生调用结束事件
if (!request.isAsync()) {
if (EventBus.isEnable(ClientEndInvokeEvent.class)) {
EventBus.post(new ClientEndInvokeEvent(request, response, throwable));
}
}
}
// 包装响应
decorateResponse(response);
return response;
} finally {
RpcInternalContext.removeContext();
RpcInternalContext.popContext();
}
}
这个方法主要做了几件事:
- 包装request请求,设置必要的参数
- 调用FailOverCluster的invoke方法,将reques请求发送出去,并得到response相应
- 包装response响应
我们在调用FailOverCluster的时候实际上是调用的父类AbstractCluster的invoker方法,FailOverCluster关系图如下:
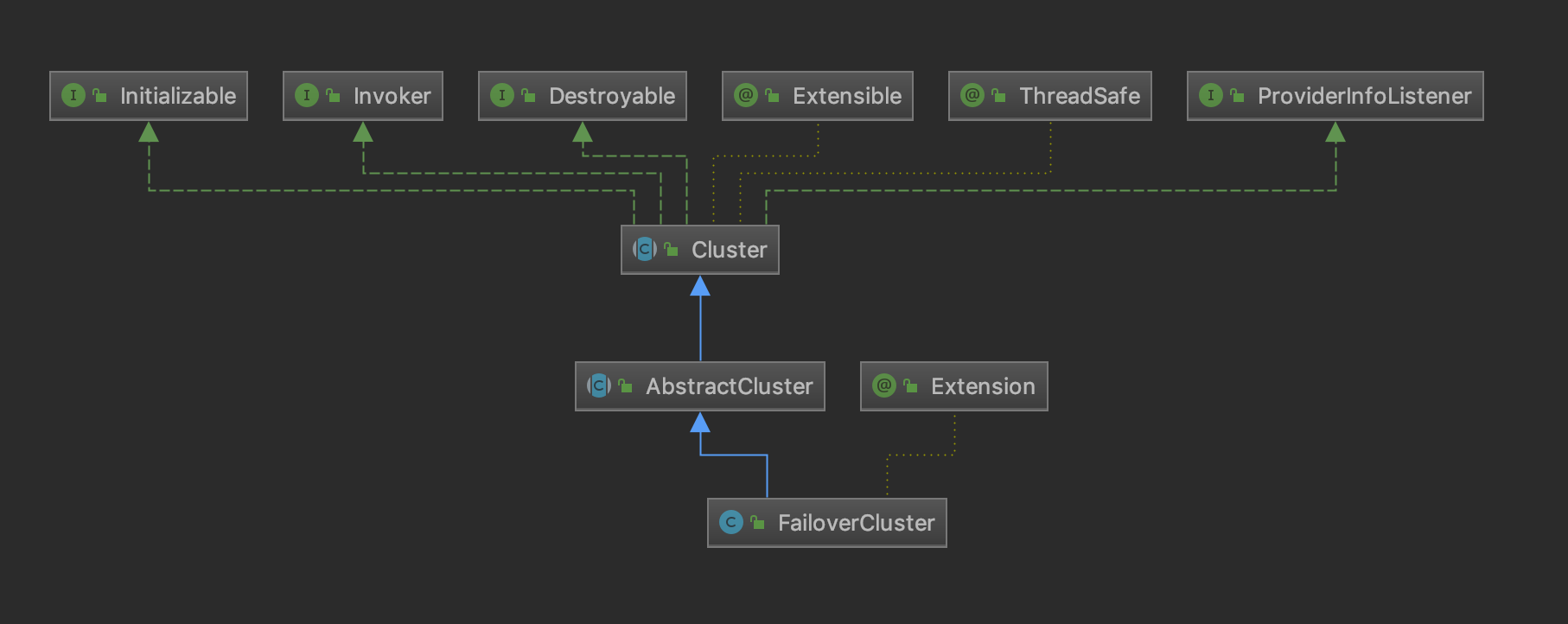
所以我们进入到AbstractCluster的invoker方法中:
@Override
public SofaResponse invoke(SofaRequest request) throws SofaRpcException {
SofaResponse response = null;
try {
// 做一些初始化检查,例如未连接可以连接
checkClusterState();
// 开始调用
countOfInvoke.incrementAndGet(); // 计数+1
response = doInvoke(request);
return response;
} catch (SofaRpcException e) {
// 客户端收到异常(客户端自己的异常)
throw e;
} finally {
countOfInvoke.decrementAndGet(); // 计数-1
}
}
checkClusterState方法主要是用来校验是否已销毁了,或是调用了init方法进行初始化了。
然后会在调用之前记一下数。
然后我们进入到doInvoke方法中:
public SofaResponse doInvoke(SofaRequest request) throws SofaRpcException {
String methodName = request.getMethodName();
int retries = consumerConfig.getMethodRetries(methodName);
int time = 0;
SofaRpcException throwable = null;// 异常日志
List<ProviderInfo> invokedProviderInfos = new ArrayList<ProviderInfo>(retries + 1);
do {
//负载均衡
ProviderInfo providerInfo = select(request, invokedProviderInfos);
try {
//调用过滤器链
SofaResponse response = filterChain(providerInfo, request);
if (response != null) {
if (throwable != null) {
if (LOGGER.isWarnEnabled(consumerConfig.getAppName())) {
LOGGER.warnWithApp(consumerConfig.getAppName(),
LogCodes.getLog(LogCodes.WARN_SUCCESS_BY_RETRY,
throwable.getClass() + ":" + throwable.getMessage(),
invokedProviderInfos));
}
}
return response;
} else {
throwable = new SofaRpcException(RpcErrorType.CLIENT_UNDECLARED_ERROR,
"Failed to call " + request.getInterfaceName() + "." + methodName
+ " on remote server " + providerInfo + ", return null");
time++;
}
} catch (SofaRpcException e) { // 服务端异常+ 超时异常 才发起rpc异常重试
if (e.getErrorType() == RpcErrorType.SERVER_BUSY
|| e.getErrorType() == RpcErrorType.CLIENT_TIMEOUT) {
throwable = e;
time++;
} else {
throw e;
}
} catch (Exception e) { // 其它异常不重试
throw new SofaRpcException(RpcErrorType.CLIENT_UNDECLARED_ERROR,
"Failed to call " + request.getInterfaceName() + "." + request.getMethodName()
+ " on remote server: " + providerInfo + ", cause by unknown exception: "
+ e.getClass().getName() + ", message is: " + e.getMessage(), e);
} finally {
if (RpcInternalContext.isAttachmentEnable()) {
RpcInternalContext.getContext().setAttachment(RpcConstants.INTERNAL_KEY_INVOKE_TIMES,
time + 1); // 重试次数
}
}
invokedProviderInfos.add(providerInfo);
} while (time <= retries);
throw throwable;
}
这个方法里面主要做了这这件事:
- 如果失败的话就循环调用
- 负载均衡,选取provider
- 通过过滤器链调用服务端,并返回结果
- 异常处理
接着我们进入到filterChain方法中,根据过滤器链最后会跳到ConsumerInvoker中的invoke方法
@Override
public SofaResponse invoke(SofaRequest sofaRequest) throws SofaRpcException {
// 设置下服务器应用
ProviderInfo providerInfo = RpcInternalContext.getContext().getProviderInfo();
String appName = providerInfo.getStaticAttr(ProviderInfoAttrs.ATTR_APP_NAME);
if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(appName)) {
sofaRequest.setTargetAppName(appName);
}
// 目前只是通过client发送给服务端
return consumerBootstrap.getCluster().sendMsg(providerInfo, sofaRequest);
}
consumerBootstrap.getCluster()会返回FailOverCluster实例,然后调用父类AbstractCluster的sendMsg方法
public SofaResponse sendMsg(ProviderInfo providerInfo, SofaRequest request) throws SofaRpcException {
ClientTransport clientTransport = connectionHolder.getAvailableClientTransport(providerInfo);
if (clientTransport != null && clientTransport.isAvailable()) {
return doSendMsg(providerInfo, clientTransport, request);
} else {
throw unavailableProviderException(request.getTargetServiceUniqueName(), providerInfo.getOriginUrl());
}
}
protected SofaResponse doSendMsg(ProviderInfo providerInfo, ClientTransport transport,
SofaRequest request) throws SofaRpcException {
RpcInternalContext context = RpcInternalContext.getContext();
// 添加调用的服务端远程地址
RpcInternalContext.getContext().setRemoteAddress(providerInfo.getHost(), providerInfo.getPort());
try {
checkProviderVersion(providerInfo, request); // 根据服务端版本特殊处理
String invokeType = request.getInvokeType();
int timeout = resolveTimeout(request, consumerConfig, providerInfo);
SofaResponse response = null;
// 同步调用
if (RpcConstants.INVOKER_TYPE_SYNC.equals(invokeType)) {
long start = RpcRuntimeContext.now();
try {
response = transport.syncSend(request, timeout);
} finally {
if (RpcInternalContext.isAttachmentEnable()) {
long elapsed = RpcRuntimeContext.now() - start;
context.setAttachment(RpcConstants.INTERNAL_KEY_CLIENT_ELAPSE, elapsed);
}
}
}
// 单向调用
else if (RpcConstants.INVOKER_TYPE_ONEWAY.equals(invokeType)) {
long start = RpcRuntimeContext.now();
try {
transport.oneWaySend(request, timeout);
response = buildEmptyResponse(request);
} finally {
if (RpcInternalContext.isAttachmentEnable()) {
long elapsed = RpcRuntimeContext.now() - start;
context.setAttachment(RpcConstants.INTERNAL_KEY_CLIENT_ELAPSE, elapsed);
}
}
}
// Callback调用
else if (RpcConstants.INVOKER_TYPE_CALLBACK.equals(invokeType)) {
// 调用级别回调监听器
SofaResponseCallback sofaResponseCallback = request.getSofaResponseCallback();
if (sofaResponseCallback == null) {
SofaResponseCallback methodResponseCallback = consumerConfig
.getMethodOnreturn(request.getMethodName());
if (methodResponseCallback != null) { // 方法的Callback
request.setSofaResponseCallback(methodResponseCallback);
}
}
// 记录发送开始时间
context.setAttachment(RpcConstants.INTERNAL_KEY_CLIENT_SEND_TIME, RpcRuntimeContext.now());
// 开始调用
transport.asyncSend(request, timeout);
response = buildEmptyResponse(request);
}
// Future调用
else if (RpcConstants.INVOKER_TYPE_FUTURE.equals(invokeType)) {
// 记录发送开始时间
context.setAttachment(RpcConstants.INTERNAL_KEY_CLIENT_SEND_TIME, RpcRuntimeContext.now());
// 开始调用
ResponseFuture future = transport.asyncSend(request, timeout);
// 放入线程上下文
RpcInternalContext.getContext().setFuture(future);
response = buildEmptyResponse(request);
} else {
throw new SofaRpcException(RpcErrorType.CLIENT_UNDECLARED_ERROR, "Unknown invoke type:" + invokeType);
}
return response;
} catch (SofaRpcException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Throwable e) { // 客户端其它异常
throw new SofaRpcException(RpcErrorType.CLIENT_UNDECLARED_ERROR, e);
}
}
sendMsg方法最后会调用到doSendMsg。
soSendMsg里面主要做了如下几件事:
- 如果是同步调用,则直接返回封装好的参数
- 如果是单向调用,则调用buildEmptyResponse方法,返回一个空的response
- 如果是callback调用asyncSend,RPC在获取到服务端的结果后会自动执行该回调实现。
- 服务端返回响应结果被 RPC 缓存,当客户端需要响应结果的时候需要主动获取结果,获取结果的过程阻塞线程。
3. 源码分析---SOFARPC客户端服务调用的更多相关文章
- 2. 源码分析---SOFARPC客户端服务引用
我们先上一张客户端服务引用的时序图. 我们首先来看看ComsumerConfig的refer方法吧 public T refer() { if (consumerBootstrap == null) ...
- 7.源码分析---SOFARPC是如何实现故障剔除的?
我在服务端引用那篇文章里面分析到,服务端在引用的时候会去获取服务端可用的服务,并进行心跳,维护一个可用的集合. 所以我们从客户端初始化这部分说起. 服务连接的维护 客户端初始化的时候会调用cluste ...
- 9.源码分析---SOFARPC是如何实现故障剔除的?
SOFARPC源码解析系列: 1. 源码分析---SOFARPC可扩展的机制SPI 2. 源码分析---SOFARPC客户端服务引用 3. 源码分析---SOFARPC客户端服务调用 4. 源码分析- ...
- 11.源码分析---SOFARPC数据透传是实现的?
先把栗子放上,让大家方便测试用: Service端 public static void main(String[] args) { ServerConfig serverConfig = new S ...
- 10.源码分析---SOFARPC内置链路追踪SOFATRACER是怎么做的?
SOFARPC源码解析系列: 1. 源码分析---SOFARPC可扩展的机制SPI 2. 源码分析---SOFARPC客户端服务引用 3. 源码分析---SOFARPC客户端服务调用 4. 源码分析- ...
- 4. 源码分析---SOFARPC服务端暴露
服务端的示例 我们首先贴上我们的服务端的示例: public static void main(String[] args) { ServerConfig serverConfig = new Ser ...
- 5.源码分析---SOFARPC调用服务
我们这一次来接着上一篇文章<4. 源码分析---SOFARPC服务端暴露>讲一下服务暴露之后被客户端调用之后服务端是怎么返回数据的. 示例我们还是和上篇文章一样使用一样的bolt协议来讲: ...
- Spring源码分析之`BeanFactoryPostProcessor`调用过程
前文传送门: Spring源码分析之预启动流程 Spring源码分析之BeanFactory体系结构 本文内容: AbstractApplicationContext#refresh前部分的一点小内容 ...
- mybatis源码分析(方法调用过程)
十一月月底,宿舍楼失火啦,搞得20多天没有网,目测直到放假也不会来了... 正题 嗯~,其实阅读源码不是为了应付面试,更重要的让你知道,大师是怎样去写代码的,同样是用Java,为啥Clinton Be ...
随机推荐
- C++用EGE简单实现别踩白块游戏
本项目已开源:https://github.com/wmpscc/AvoidBlank 关于EGE 介绍:EGE(Easy Graphics Engine),是windows下的简易绘图库,是一个类似 ...
- Selenium驱动如何选择?
最近有朋友也想学Selenium然后问我应该用什么Python版本.装什么驱动.用什么浏览器,然后今天在这里总结一下 Python版本的话个人用的是3.7 ,比较推荐,目前比较流行的是Python 3 ...
- Kibana 7.1.1 安装及简单使用
1. 下载 & 解压 # 下载 wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/kibana/kibana-7.1.1-linux-x86_64.tar ...
- Unity3D热更新之LuaFramework篇[06]--Lua中是怎么实现脚本生命周期的
前言 用c#开发的时候,新建的脚本都默认继承自Monobehaviour, 因此脚本才有了自己的生命周期函数,如Awake,Start, Update, OnDestroy等. 在相应的方法中实现游戏 ...
- SQL Server 2016 + AlwaysOn 无域集群
目录 AlwaysOn 搭建 WSFC 配置计算机的 DNS 后缀 安装故障转移集群 验证集群 创建集群 创建文件共享见证 配置 AlwaysOn 新建可用性组 创建侦听器 可读副本的负载均衡 主角色 ...
- APM系统SkyWalking介绍
公司最近在构建服务化平台,需要上线APM系统,本篇文章简单的介绍SkyWalking APM APM全称Application Performance Management应用性能管理,目的是通过各种 ...
- JavaScript循环及输出方式
好一段时间没写了,今天写一下JavaScript的循环和输出吧! 其实JavaScrip的循环跟C#.Java的循环用法是相同的. <!DOCTYPE html> <html> ...
- 分布式事务(3)---RocketMQ实现分布式事务原理
分布式事务(3)-RocketMQ实现分布式事务原理 之前讲过有关分布式事务2PC.3PC.TCC的理论知识,博客地址: 1.分布式事务(1)---2PC和3PC原理 2.分布式事务(2)---TCC ...
- 基于SpringBoot-Dubbo的微服务快速开发框架
简介: 基于Dubbo的分布式/微服务基础框架,为前端提供脚手架开发服务,结合前一篇--Web AP快速开发基础框架,可快速上手基于Dubbo的分布式服务开发,项目代码: https://github ...
- break使用不当引发的一个“血案”
最近在网上冲浪,读到一则新闻,摘抄下这则新闻: ======================= 以下文字摘抄自互联网==================== 1990年1月15日,AT&T电话 ...
