JDK(八)JDK1.7&1.8源码对比分析【集合】HashMap
前言
在JDK1.8源码分析【集合】HashMap文章中,我们分析了HashMap在JDK1.8中新增的特性(引进了红黑树数据结构),但是为什么要进行这个优化呢?这篇文章我们通过对比JDK1.7和1.8来分析优化的原因。
众所周知,HashMap底层是基于 数组 + 链表 的方式实现的,不过在JDK1.7和1.8中具体实现稍有不同。
目录
一、对比分析
1. 1.7版本
2. 1.8版本
总结
一、对比分析
1. 1.7版本
1.7 中的数据结构图:
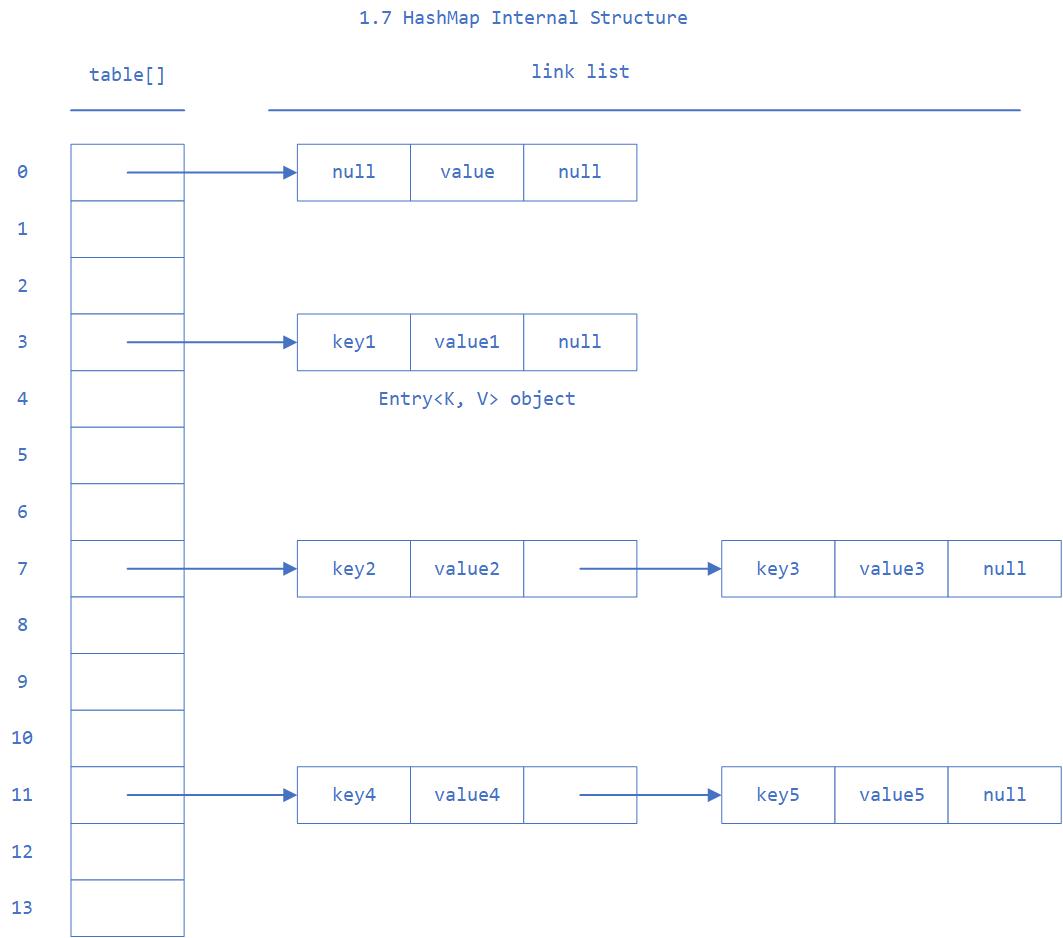
先来看看1.7中几个比较核心的成员变量:
/**
* The default initial capacity - MUST be a power of two.
* 初始桶大小,因为底层是数组,所以这是数组的大小
*/
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; // aka 16 /**
* The maximum capacity, used if a higher value is implicitly specified
* by either of the constructors with arguments.
* MUST be a power of two <= 1<<30.
* 桶最大值
*/
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30; /**
* The load factor used when none specified in constructor.
* 默认的负载因子
*/
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f; /**
* An empty table instance to share when the table is not inflated.
*/
static final Entry<?,?>[] EMPTY_TABLE = {}; /**
* The table, resized as necessary. Length MUST Always be a power of two.
* 真正存放数据的数组
*/
transient Entry<K,V>[] table = (Entry<K,V>[]) EMPTY_TABLE; /**
* The number of key-value mappings contained in this map.
* Map存放数量的大小
*/
transient int size; /**
* The next size value at which to resize (capacity * load factor).
* 桶大小,可在初始化时显式指定
* @serial
*/
// If table == EMPTY_TABLE then this is the initial capacity at which the
// table will be created when inflated.
int threshold; /**
* The load factor for the hash table.
* 负载因子,可在初始化时显式指定
*
* @serial
*/
final float loadFactor;
这几个成员变量中,比较有意思的是负载因子。由于给定的HashMap的容量大小是固定的,比如默认初始化:
/**
* Constructs an empty <tt>HashMap</tt> with the default initial capacity
* (16) and the default load factor (0.75).
*/
public HashMap() {
this(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
} /**
* Constructs an empty <tt>HashMap</tt> with the specified initial
* capacity and load factor.
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity
* @param loadFactor the load factor
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is negative
* or the load factor is nonpositive
*/
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " +
initialCapacity);
if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " +
loadFactor); this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
threshold = initialCapacity;
init();
}
给定的默认容量为 16,负载因子为 0.75。Map 在使用过程中不断的往里面存放数据,当数量达到了 16 * 0.75 = 12 就需要将当前 16 的容量进行扩容,而扩容这个过程涉及到 rehash、复制数据等操作,所以非常消耗性能。因此通常建议能提前预估 HashMap 的大小最好,尽量的减少扩容带来的性能损耗。
根据代码可以看到真正存放数据的是:
transient Entry<K,V>[] table = (Entry<K,V>[]) EMPTY_TABLE;
这个数组,接下来看看它是如何实现的:
static class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final K key;
V value;
Entry<K,V> next;
int hash;
/**
* Creates new entry.
*/
Entry(int h, K k, V v, Entry<K,V> n) {
value = v;
next = n;
key = k;
hash = h;
}
public final K getKey() {
return key;
}
public final V getValue() {
return value;
}
public final V setValue(V newValue) {
V oldValue = value;
value = newValue;
return oldValue;
}
public final boolean equals(Object o) {
if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))
return false;
Map.Entry e = (Map.Entry)o;
Object k1 = getKey();
Object k2 = e.getKey();
if (k1 == k2 || (k1 != null && k1.equals(k2))) {
Object v1 = getValue();
Object v2 = e.getValue();
if (v1 == v2 || (v1 != null && v1.equals(v2)))
return true;
}
return false;
}
public final int hashCode() {
return Objects.hashCode(getKey()) ^ Objects.hashCode(getValue());
}
public final String toString() {
return getKey() + "=" + getValue();
}
/**
* This method is invoked whenever the value in an entry is
* overwritten by an invocation of put(k,v) for a key k that's already
* in the HashMap.
*/
void recordAccess(HashMap<K,V> m) {
}
/**
* This method is invoked whenever the entry is
* removed from the table.
*/
void recordRemoval(HashMap<K,V> m) {
}
}
Entry 是 HashMap 中的一个内部类,从他的成员变量很容易看出:
- key是写入的键;
- value是key对应的值;
- next用于实现链表结构,指向下一个链表节点;
- hash存放的是当前key的hashCode。
知晓了基本结构,再来看看put、get函数:
put函数
/**
* Associates the specified value with the specified key in this map.
* If the map previously contained a mapping for the key, the old
* value is replaced.
*
* @param key key with which the specified value is to be associated
* @param value value to be associated with the specified key
* @return the previous value associated with <tt>key</tt>, or
* <tt>null</tt> if there was no mapping for <tt>key</tt>.
* (A <tt>null</tt> return can also indicate that the map
* previously associated <tt>null</tt> with <tt>key</tt>.)
*/
public V put(K key, V value) {
// 判断当前数组是否需要初始化
if (table == EMPTY_TABLE) {
inflateTable(threshold);
}
// 如果 key 为空,则 put 一个空值进去
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value);
// 根据 key 计算出 hashcode
int hash = hash(key);
// 根据计算出的 hashcode 定位出所在桶
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
// 如果桶是一个链表则需要遍历判断里面的 hashcode、key 是否和传入 key 相等,如果相等则进行覆盖,并返回原来的值
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
} modCount++;
// 如果桶是空的,说明当前位置没有数据存入;新增一个 Entry 对象写入当前位置
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
return null;
}
/**
* Adds a new entry with the specified key, value and hash code to
* the specified bucket. It is the responsibility of this
* method to resize the table if appropriate.
*
* Subclass overrides this to alter the behavior of put method.
*/
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
// 判断是否需要扩容
if ((size >= threshold) && (null != table[bucketIndex])) {
// 如果需要就进行两倍扩充,并将当前的 key 重新 hash 并定位
resize(2 * table.length);
hash = (null != key) ? hash(key) : 0;
bucketIndex = indexFor(hash, table.length);
} // 将当前位置的桶传入到新建的桶中,如果当前桶有值就会在位置形成链表
createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex);
} /**
* Like addEntry except that this version is used when creating entries
* as part of Map construction or "pseudo-construction" (cloning,
* deserialization). This version needn't worry about resizing the table.
*
* Subclass overrides this to alter the behavior of HashMap(Map),
* clone, and readObject.
*/
void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex];
table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);
size++;
}
get函数
再来看看get函数:
/**
* Returns the value to which the specified key is mapped,
* or {@code null} if this map contains no mapping for the key.
*
* <p>More formally, if this map contains a mapping from a key
* {@code k} to a value {@code v} such that {@code (key==null ? k==null :
* key.equals(k))}, then this method returns {@code v}; otherwise
* it returns {@code null}. (There can be at most one such mapping.)
*
* <p>A return value of {@code null} does not <i>necessarily</i>
* indicate that the map contains no mapping for the key; it's also
* possible that the map explicitly maps the key to {@code null}.
* The {@link #containsKey containsKey} operation may be used to
* distinguish these two cases.
*
* @see #put(Object, Object)
*/
public V get(Object key) {
if (key == null)
return getForNullKey();
Entry<K,V> entry = getEntry(key); return null == entry ? null : entry.getValue();
} /**
* Returns the entry associated with the specified key in the
* HashMap. Returns null if the HashMap contains no mapping
* for the key.
*/
final Entry<K,V> getEntry(Object key) {
if (size == 0) {
return null;
} // 根据 key 计算出 hashcode,然后定位到具体的桶中
int hash = (key == null) ? 0 : hash(key);
// 判断该位置是否为链表
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[indexFor(hash, table.length)];
e != null;
e = e.next) {
Object k;
// 根据 key、key 的 hashcode 是否相等来返回值
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
}
// 啥都没取到就直接返回 null
return null;
}
2. 1.8版本
不知道通过1.7的实现大家看出需要优化的点没有?
其中一个很明显的地方就是:当 Hash 冲突严重时,在桶上形成的链表会变的越来越长,这样在查询时的效率就会越来越低;时间复杂度为O(N)。
因此 1.8 中重点优化了这个查询效率。
1.8 中的数据结构图:

还是一样,先来看看几个核心的成员变量:
/**
* The default initial capacity - MUST be a power of two.
*/
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; // aka 16 /**
* The maximum capacity, used if a higher value is implicitly specified
* by either of the constructors with arguments.
* MUST be a power of two <= 1<<30.
*/
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30; /**
* The load factor used when none specified in constructor.
*/
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f; /**
* The bin count threshold for using a tree rather than list for a
* bin. Bins are converted to trees when adding an element to a
* bin with at least this many nodes. The value must be greater
* than 2 and should be at least 8 to mesh with assumptions in
* tree removal about conversion back to plain bins upon
* shrinkage.
* 用于判断是否需要将链表转换为红黑树的阈值
*/
static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8; /**
* The bin count threshold for untreeifying a (split) bin during a
* resize operation. Should be less than TREEIFY_THRESHOLD, and at
* most 6 to mesh with shrinkage detection under removal.
*/
static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6; /**
* The smallest table capacity for which bins may be treeified.
* (Otherwise the table is resized if too many nodes in a bin.)
* Should be at least 4 * TREEIFY_THRESHOLD to avoid conflicts
* between resizing and treeification thresholds.
*/
static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64; /**
* JDK1.7是HashEntry,1.8修改为Node
*/
transient Node<K,V>[] table; /**
* Holds cached entrySet(). Note that AbstractMap fields are used
* for keySet() and values().
*/
transient Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet; /**
* The number of key-value mappings contained in this map.
*/
transient int size; /**
* The number of times this HashMap has been structurally modified
* Structural modifications are those that change the number of mappings in
* the HashMap or otherwise modify its internal structure (e.g.,
* rehash). This field is used to make iterators on Collection-views of
* the HashMap fail-fast. (See ConcurrentModificationException).
*/
transient int modCount; /**
* The next size value at which to resize (capacity * load factor).
*
* @serial
*/
// (The javadoc description is true upon serialization.
// Additionally, if the table array has not been allocated, this
// field holds the initial array capacity, or zero signifying
// DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY.)
int threshold; /**
* The load factor for the hash table.
*
* @serial
*/
final float loadFactor;
Node 的核心组成其实也是和 1.7 中的 HashEntry 一样,存放的都是key、value、hashCode、next 等数据。
再来看看存取数据的put、get函数。
put函数
/**
* Implements Map.put and related methods
*
* @param hash hash for key
* @param key the key
* @param value the value to put
* @param onlyIfAbsent if true, don't change existing value
* @param evict if false, the table is in creation mode.
* @return previous value, or null if none
*/
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
// 判断当前桶是否为空,空的就需要初始化(resize 中会判断是否进行初始化)
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
// 根据当前 key 的 hashcode 定位到具体的桶中并判断是否为空,为空表明没有 Hash 冲突就直接在当前位置创建一个新桶即可
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
Node<K,V> e; K k;
if (p.hash == hash &&
// 如果当前桶有值( Hash 冲突),那么就要比较当前桶中的 key、key 的 hashcode 与写入的 key 是否相等,相等就赋值给 e
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
// 如果当前桶为红黑树,那就要按照红黑树的方式写入数据
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
// 如果是个链表,就需要将当前的 key、value 封装成一个新节点写入到当前桶的后面(形成链表)
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
// 判断当前链表的大小是否大于预设的阈值,大于时就要转换为红黑树
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
// 如果在遍历过程中找到 key 相同时直接退出遍历
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
// 如果 e != null 就相当于存在相同的 key,那就需要将值覆盖
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
// 判断是否需要进行扩容
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
get函数
/**
* Returns the value to which the specified key is mapped,
* or {@code null} if this map contains no mapping for the key.
*
* <p>More formally, if this map contains a mapping from a key
* {@code k} to a value {@code v} such that {@code (key==null ? k==null :
* key.equals(k))}, then this method returns {@code v}; otherwise
* it returns {@code null}. (There can be at most one such mapping.)
*
* <p>A return value of {@code null} does not <i>necessarily</i>
* indicate that the map contains no mapping for the key; it's also
* possible that the map explicitly maps the key to {@code null}.
* The {@link #containsKey containsKey} operation may be used to
* distinguish these two cases.
*
* @see #put(Object, Object)
*/
public V get(Object key) {
Node<K,V> e;
return (e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null ? null : e.value;
} /**
* Implements Map.get and related methods
*
* @param hash hash for key
* @param key the key
* @return the node, or null if none
*/
final Node<K,V> getNode(int hash, Object key) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> first, e; int n; K k;
// 将 key hash 之后取得所定位的桶
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
// 判断桶的第一个位置(有可能是链表、红黑树)的 key 是否为查询的 key,是就直接返回 value
if (first.hash == hash && // always check first node
((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return first;
// 如果第一个不匹配,则判断它的下一个是红黑树还是链表
if ((e = first.next) != null) {
if (first instanceof TreeNode)
// 红黑树就按照树的查找方式返回值
return ((TreeNode<K,V>)first).getTreeNode(hash, key);
// 不然就按照链表的方式遍历匹配返回值
do {
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
return null;
}
从这两个核心方法(get/put)可以看出 1.8 中对大链表做了优化,修改为红黑树之后查询效率直接提高到了O(logn)。
但是 HashMap 原有的问题也都存在,比如在并发场景下使用时容易出现死循环。
final HashMap<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
map.put(UUID.randomUUID().toString(), "");
}
}).start();
}
但是为什么呢?看过上文的还记得在 HashMap 扩容的时候会调用resize() 方法,就是这里的并发操作容易在一个桶上形成环形链表;这样当获取一个不存在的 key 时,计算出的 index 正好是环形链表的下标就会出现死循环。下一篇将详细介绍HashMap死循环的原因。
还有一个值得注意的是 HashMap 的遍历方式,通常有以下几种:
Iterator<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> entryIterator = map.entrySet().iterator();
while (entryIterator.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<String, Integer> next = entryIterator.next();
System.out.println("key=" + next.getKey() + " value=" + next.getValue());
} Iterator<String> iterator = map.keySet().iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
String key = iterator.next();
System.out.println("key=" + key + " value=" + map.get(key)); }
强烈建议使用第一种 EntrySet 进行遍历。第一种可以把 key value 同时取出,第二种还得需要通过 key 取一次 value,效率较低。
总结
HashMap无论是 1.7 还是 1.8 其实都能看出 JDK 没有对它做任何的同步操作,所以并发会出问题,甚至出现死循环导致系统不可用。因此 JDK 推出了专项专用的 ConcurrentHashMap ,该类位于java.util.concurrent 包下,专门用于解决并发问题。
JDK(八)JDK1.7&1.8源码对比分析【集合】HashMap的更多相关文章
- JDK(十)JDK1.7&1.8源码对比分析【集合】ConcurrentHashMap
前言 在JDK1.7&1.8源码对比分析[集合]HashMap中我们对比分析了JDK1.7和1.8版本的HashMap源码,趁热打铁,这篇文章就来看看JDK1.7和1.8版本的Concurre ...
- LinkedHashMap 源码详细分析(JDK1.8)
1. 概述 LinkedHashMap 继承自 HashMap,在 HashMap 基础上,通过维护一条双向链表,解决了 HashMap 不能随时保持遍历顺序和插入顺序一致的问题.除此之外,Linke ...
- JDK1.8源码(七)——java.util.HashMap 类
本篇博客我们来介绍在 JDK1.8 中 HashMap 的源码实现,这也是最常用的一个集合.但是在介绍 HashMap 之前,我们先介绍什么是 Hash表. 1.哈希表 Hash表也称为散列表,也有直 ...
- 阿里P7终于讲完了JDK+Spring+mybatis+Dubbo+SpringMvc+Netty源码
前言 这里普及一下,每个公司都有职别定级系统,阿里也是,技术岗以 P 定级,一般校招 P5, 社招 P6 起.其实阅读源码也是有很多诀窍的,这里分享几点心得: 首先要会用.你要知道这个库是干什么的,掌 ...
- HashMap 源码详细分析(JDK1.8)
一.概述 本篇文章我们来聊聊大家日常开发中常用的一个集合类 - HashMap.HashMap 最早出现在 JDK 1.2中,底层基于散列算法实现.HashMap 允许 null 键和 null 值, ...
- Java -- 基于JDK1.8的ArrayList源码分析
1,前言 很久没有写博客了,很想念大家,18年都快过完了,才开始写第一篇,争取后面每周写点,权当是记录,因为最近在看JDK的Collection,而且ArrayList源码这一块也经常被面试官问道,所 ...
- 【JDK1.8】 Java小白的源码学习系列:HashMap
目录 Java小白的源码学习系列:HashMap 官方文档解读 基本数据结构 基本源码解读 基本成员变量 构造器 巧妙的tableSizeFor put方法 巧妙的hash方法 JDK1.8的putV ...
- Java并发包源码学习系列:JDK1.8的ConcurrentHashMap源码解析
目录 为什么要使用ConcurrentHashMap? ConcurrentHashMap的结构特点 Java8之前 Java8之后 基本常量 重要成员变量 构造方法 tableSizeFor put ...
- HashMap 与 ConcrrentHashMap 使用以及源码原理分析
前奏一:HashMap面试中常见问题汇总 HashMap的工作原理是近年来常见的Java面试题,几乎每个Java程序员都知道HashMap,都知道哪里要用HashMap,知道HashTable和Has ...
随机推荐
- YII关联查询
原文链接:http://keshion.iteye.com/blog/1607994 一.多表关联的配置 在我们使用 AR 执行关联查询之前,我们需要让 AR 知道一个 AR 类是怎样关联到另一个的. ...
- BZOJ2227 [Zjoi2011]看电影(movie)
Description \(k\)个座位,\(n\)个人依次过来,每人随机从\(k\)个座位中选择一个,并从它开始不停向后走直到遇到空座位坐下.求所有人都能坐下的概率(即没有人走到第\(k+1\)个位 ...
- Debian Gun/linux基本用法
添加软件源:vim /etc/apt/sources.list 在文本中添加如下内容:deb http://mirrors.163.com/debian/ stretch main non-free ...
- 【代码笔记】iOS-单击手势的添加
一,效果图. 二,工程图. 三,代码. RootViewController.h #import <UIKit/UIKit.h> @interface RootViewController ...
- git之回退
1:本地已commit,未push到远程仓库 1)git log: 查看commit日志,获取commit的id 2) git reset --hard commit_id: ...
- Web 系统架构一般组成
负载层技术 负载分配层,是单指利用软件实现的计算机系统上的狭义负载均衡.它是根据业务形态设计一种架构方式,将来自外部客户端的业务请求分担到每一个可用的业务节点上 . 1.用户终端不只包括类 ...
- idea 自动导入包设置
- protobuf 源代码分析 (1)准备工作
protobuf简介 protobuf是google开源的跨平台的一种数据序列化的代码自动生成器,支持c++.java和python语言,支持跨网络的传输数据,与平台类型无关.并且其生产的序列化数据具 ...
- 需要警惕的linux命令
Linux shell/terminal命令非常强大,即使一个简单的命令就可能导致文件夹.文件或者路径文件夹等被删除.为了避免这样的事情发生,我们应该时刻注意PHP代码&命令,今天为大家带来9 ...
- systemd 之 systemctl
Systemd 常规操作与彩蛋 一.前言 上了俩个月的RHCE工程师的班,收获颇多.话说回来,在 redhat 7 中有个非常重要的概念,即:systemd systemd 是 Linux 下的一款系 ...
