[原创]Zynq AXI-CDMA的使用
Xilinx 提供了3种DMA
- AXI-DMA
- AXI-CDMA
- AXI-VDMA
使用CDMA能够满足项目需求(MM-MM),DS文档介绍如下:
The Xilinx LogiCORE™ IP AXI Central Direct Memory Access (CDMA) core is a soft Xilinx Intellectual Property (IP) core for use with the Vivado® Design Suite. The AXI CDMA provides high-bandwidth Direct Memory Access (DMA) between a memory-mapped source address and a memory-mapped destination address using the AXI4 protocol. An optional Scatter Gather (SG) feature can be used to offload control and sequencing tasks from the system CPU. Initialization, status, and control registers are accessed through an AXI4-Lite slave interface, suitable for the Xilinx MicroBlaze™ processor.

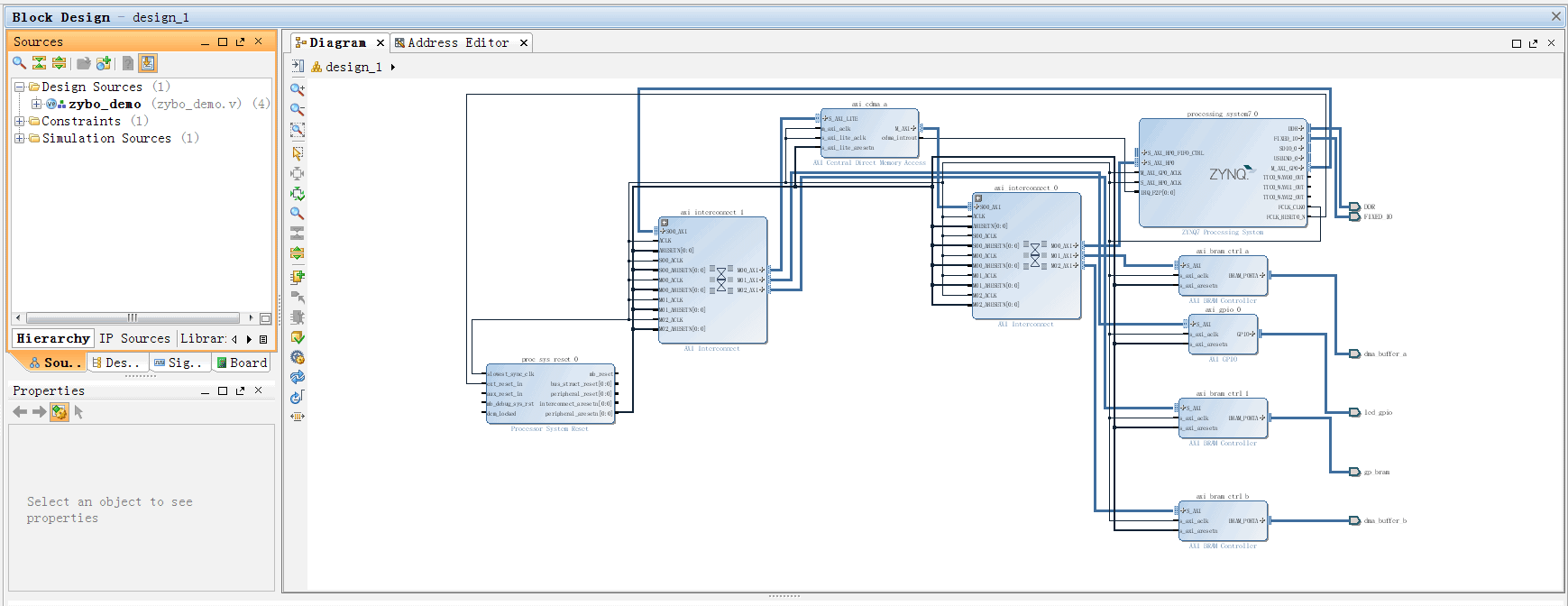
BD连接如下:
Standalone APP代码
#include "xparameters.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include "xaxicdma.h"
#include "xil_cache.h"
#include "xscutimer.h"
#define TIMER_LOAD_VALUE 0xFFFFFFFF
#define BRAM_GP0_ADDR 0x40000000
XAxiCdma_Config *axi_cdma_cfg;
XAxiCdma axi_cdma;
#define PS_OCM_Addr 0x10000000 // some address in OCM
#define PL_BRAM_Addr 0xC0000000 // Not 'seen' by the PS //#define BUFF_LEN 16*4
//16384*32bit/8=65536Byte
//32768*32bit/8=131072Byte
#define BUFF_LEN 131072 XScuTimer Timer;
void hs_timer(void)
{
int Status;
XScuTimer_Config *ConfigPtr;
XScuTimer *TimerInstancePtr=&Timer;
/*
* Initialize the Scu Private Timer so that it is ready to use.
*/
ConfigPtr = XScuTimer_LookupConfig(XPAR_PS7_SCUTIMER_0_DEVICE_ID); /*
* This is where the virtual address would be used, this example
* uses physical address.
*/
Status = XScuTimer_CfgInitialize(TimerInstancePtr, ConfigPtr, ConfigPtr->BaseAddr);
if (Status != XST_SUCCESS) {
return XST_FAILURE;
}
else
xil_printf("XScuTimer_CfgInitialize OK\n\r");
} int main()
{
xil_printf("%c[2J",27); int i,k;
int Status;
volatile int CntValue1,CntValue2;
u32 *Saddr2 = (u32 *)0x02000000; u32 *rx_buffer = (u32 *) PS_OCM_Addr;
u32 *tx_buffer = (u32 *) PL_BRAM_Addr;
u32 *rd_ram = (u32 *) BRAM_GP0_ADDR;
hs_timer() ;
xil_printf("-----------------------*-----------------------\n\r");
xil_printf("-Simple DMA demo based on Zybo board -\n\r");
xil_printf("-write some data to DDR -\n\r");
xil_printf("-move those data to bram and read it from GP0 -\n\r");
xil_printf("-----------------------*-----------------------\n\r"); // Set up the AXI CDMA
printf("--Set up the AXI CDMA\n\r");
axi_cdma_cfg = XAxiCdma_LookupConfig(XPAR_AXICDMA_0_DEVICE_ID);
if (!axi_cdma_cfg) {
printf("AXAxiCdma_LookupConfig failed\n\r");
} Status = XAxiCdma_CfgInitialize(&axi_cdma, axi_cdma_cfg, axi_cdma_cfg->BaseAddress);
if (Status == XST_SUCCESS ){
printf("XAxiCdma_CfgInitialize succeed\n\r");
}
printf("--Disable Interrupt of AXI CDMA\n\r");
XAxiCdma_IntrDisable(&axi_cdma, XAXICDMA_XR_IRQ_ALL_MASK); if (XAxiCdma_IsBusy(&axi_cdma)) {
printf("AXI CDMA is busy...\n\r");
while (XAxiCdma_IsBusy(&axi_cdma));
} Xil_DCacheFlush(); XScuTimer_LoadTimer(&Timer, TIMER_LOAD_VALUE);
CntValue1 = XScuTimer_GetCounterValue(&Timer);
XScuTimer_Start(&Timer);
Status = XAxiCdma_SimpleTransfer(
&axi_cdma,
(u32) tx_buffer,
(u32) rx_buffer,
BUFF_LEN,
NULL,
NULL); Xil_DCacheFlush(); CntValue2 = XScuTimer_GetCounterValue(&Timer);
XScuTimer_Stop(&Timer); printf("DMA Move 32768*32bit Total Time: %d us\n\r", (CntValue1-CntValue2)*3/1000); // Wait until core isn't busy
if (XAxiCdma_IsBusy(&axi_cdma)) {
printf("AXI CDMA is busy...\n\r");
while (XAxiCdma_IsBusy(&axi_cdma));
} Xil_DCacheInvalidateRange((u32)PS_OCM_Addr, BUFF_LEN); for(i=0; i<4; i++)
//for(i=0; i<BUFF_LEN/4; i++)
{
k = *(rx_buffer + i);
xil_printf("The DMA read from address = %2d, the read value = %8x-----------------------\n\r",i,k);
xil_printf("The DMA read from address = %2d, the MSB read value = %8d-----------------------\n\r",i,k >> 16);
xil_printf("The DMA read from address = %2d, the LSB read value = %8d-----------------------\n\n\n\r",i,k & 0x0000FFFF);
}
for(i=32764; i<=32767; i++)
//for(i=0; i<BUFF_LEN/4; i++)
{
k = *(rx_buffer + i);
xil_printf("The DMA read from address = %2d, the read value = %8x-----------------------\n\r",i,k);
xil_printf("The DMA read from address = %2d, the MSB read value = %8d-----------------------\n\r",i,k >> 16);
xil_printf("The DMA read from address = %2d, the LSB read value = %8d-----------------------\n\n\n\r",i,k & 0x0000FFFF);
} return 0;
}
Linux APP代码
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <sys/time.h> #define CDMA_BASE_ADDRESS 0x7E200000
#define GPIO_DATA_OFFSET 0
#define GPIO_DIRECTION_OFFSET 4
#define PL_BRAM_SRC_ADDRESS 0xC0000000
#define DDR_BASE_ADDRESS 0x10000000 #define DDR_BASE_WRITE_ADDRESS 0x10000000 #define XGPIO_CHAN_OFFSET 8 #define XAXICDMA_CR_OFFSET 0x00000000 /**< Control register */
#define XAXICDMA_SR_OFFSET 0x00000004 /**< Status register */
#define XAXICDMA_CDESC_OFFSET 0x00000008 /**< Current descriptor pointer */
#define XAXICDMA_TDESC_OFFSET 0x00000010 /**< Tail descriptor pointer */
#define XAXICDMA_SRCADDR_OFFSET 0x00000018 /**< Source address register */
#define XAXICDMA_DSTADDR_OFFSET 0x00000020 /**< Destination address register */
#define XAXICDMA_BTT_OFFSET 0x00000028 /**< Bytes to transfer */ /** @name Bitmasks of XAXICDMA_CR_OFFSET register
* @{
*/
#define XAXICDMA_CR_RESET_MASK 0x00000004 /**< Reset DMA engine */
#define XAXICDMA_CR_SGMODE_MASK 0x00000008 /**< Scatter gather mode */ /** @name Bitmask for interrupts
* These masks are shared by XAXICDMA_CR_OFFSET register and
* XAXICDMA_SR_OFFSET register
* @{
*/
#define XAXICDMA_XR_IRQ_IOC_MASK 0x00001000 /**< Completion interrupt */
#define XAXICDMA_XR_IRQ_DELAY_MASK 0x00002000 /**< Delay interrupt */
#define XAXICDMA_XR_IRQ_ERROR_MASK 0x00004000 /**< Error interrupt */
#define XAXICDMA_XR_IRQ_ALL_MASK 0x00007000 /**< All interrupts */
#define XAXICDMA_XR_IRQ_SIMPLE_ALL_MASK 0x00005000 /**< All interrupts for
simple only mode */
/*@}*/ /** @name Bitmasks of XAXICDMA_SR_OFFSET register
* This register reports status of a DMA channel, including
* idle state, errors, and interrupts
* @{
*/
#define XAXICDMA_SR_IDLE_MASK 0x00000002 /**< DMA channel idle */
#define XAXICDMA_SR_SGINCLD_MASK 0x00000008 /**< Hybrid build */
#define XAXICDMA_SR_ERR_INTERNAL_MASK 0x00000010 /**< Datamover internal err */
#define XAXICDMA_SR_ERR_SLAVE_MASK 0x00000020 /**< Datamover slave err */
#define XAXICDMA_SR_ERR_DECODE_MASK 0x00000040 /**< Datamover decode err */
#define XAXICDMA_SR_ERR_SG_INT_MASK 0x00000100 /**< SG internal err */
#define XAXICDMA_SR_ERR_SG_SLV_MASK 0x00000200 /**< SG slave err */
#define XAXICDMA_SR_ERR_SG_DEC_MASK 0x00000400 /**< SG decode err */
#define XAXICDMA_SR_ERR_ALL_MASK 0x00000770 /**< All errors */
/*@}*/ #define MAP_SIZE 4096UL
#define MAP_MASK (MAP_SIZE - 1) #define DDR_MAP_SIZE 0x00100000
#define DDR_MAP_MASK (DDR_MAP_SIZE - 1) #define DDR_WRITE_OFFSET 0x10000000 #define BUFFER_BYTESIZE 32768 // Length of the buffers for DMA transfer
long times = 0; // us
double dbTotalTimes = 0.0; // s
long nReadTotal = 0;
struct timeval timeStart, timeEnd;
int main()
{
int memfd;
void *mapped_base, *mapped_dev_base;
off_t dev_base = CDMA_BASE_ADDRESS; int memfd_2;
void *mapped_base_2, *mapped_dev_base_2;
off_t dev_base_2 = DDR_BASE_WRITE_ADDRESS; unsigned int TimeOut =5;
unsigned int ResetMask;
unsigned int RegValue;
unsigned int DestArray[BUFFER_BYTESIZE ];
unsigned int Index; for (Index = 0; Index < (BUFFER_BYTESIZE/2); Index++)
{ DestArray[Index] = 0x12345678+Index;
} memfd = open("/dev/mem", O_RDWR | O_SYNC);
if (memfd == -1)
{
printf("Can't open /dev/mem.\n");
exit(0);
}
printf("/dev/mem opened.\n"); // Map one page of memory into user space such that the device is in that page, but it may not
// be at the start of the page.
mapped_base = mmap(0, MAP_SIZE, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED, memfd, dev_base & ~MAP_MASK);
if (mapped_base == (void *) -1)
{
printf("Can't map the memory to user space.\n");
exit(0);
} // get the address of the device in user space which will be an offset from the base
// that was mapped as memory is mapped at the start of a page
mapped_dev_base = mapped_base + (dev_base & MAP_MASK);
//Reset CDMA
do{
ResetMask = (unsigned long )XAXICDMA_CR_RESET_MASK;
*((volatile unsigned long *) (mapped_dev_base + XAXICDMA_CR_OFFSET)) = (unsigned long)ResetMask;
/* If the reset bit is still high, then reset is not done */
ResetMask = *((volatile unsigned long *) (mapped_dev_base + XAXICDMA_CR_OFFSET));
if(!(ResetMask & XAXICDMA_CR_RESET_MASK))
{
break;
}
TimeOut -= 1;
}while (TimeOut);
//enable Interrupt
RegValue = *((volatile unsigned long *) (mapped_dev_base + XAXICDMA_CR_OFFSET));
RegValue = (unsigned long)(RegValue | XAXICDMA_XR_IRQ_ALL_MASK );
*((volatile unsigned long *) (mapped_dev_base + XAXICDMA_CR_OFFSET)) = (unsigned long)RegValue;
// Checking for the Bus Idle
RegValue = *((volatile unsigned long *) (mapped_dev_base + XAXICDMA_SR_OFFSET));
if(!(RegValue & XAXICDMA_SR_IDLE_MASK))
{
printf("BUS IS BUSY Error Condition \n\r");
return 1;
}
// Check the DMA Mode and switch it to simple mode
RegValue = *((volatile unsigned long *) (mapped_dev_base + XAXICDMA_CR_OFFSET));
if((RegValue & XAXICDMA_CR_SGMODE_MASK))
{
RegValue = (unsigned long)(RegValue & (~XAXICDMA_CR_SGMODE_MASK));
printf("Reading \n \r");
*((volatile unsigned long *) (mapped_dev_base + XAXICDMA_CR_OFFSET)) = (unsigned long)RegValue ; }
//Set the Source Address
*((volatile unsigned long *) (mapped_dev_base + XAXICDMA_SRCADDR_OFFSET)) = (unsigned long)PL_BRAM_SRC_ADDRESS;
//Set the Destination Address
*((volatile unsigned long *) (mapped_dev_base + XAXICDMA_DSTADDR_OFFSET)) = (unsigned long)DDR_BASE_WRITE_ADDRESS;
RegValue = (unsigned long)(BUFFER_BYTESIZE);
// write Byte to Transfer
*((volatile unsigned long *) (mapped_dev_base + XAXICDMA_BTT_OFFSET)) = (unsigned long)RegValue;
/*======================================================================================
STEP 6 : Wait for the DMA transfer Status
========================================================================================*/
gettimeofday(&timeStart, NULL);
do
{
RegValue = *((volatile unsigned long *) (mapped_dev_base + XAXICDMA_SR_OFFSET));
}while(!(RegValue & XAXICDMA_XR_IRQ_ALL_MASK));
gettimeofday(&timeEnd, NULL); times = 1000000*(timeEnd.tv_sec - timeStart.tv_sec) + timeEnd.tv_usec - timeStart.tv_usec; if(BUFFER_BYTESIZE == 32768)
printf("Read 32 Lines * 512 Dots :\n\r");
else
printf("Read 128 Lines * 512 Dots :\n\r");
printf("Xilinx AXI-CDMA Read %d Byte = %d us \n", BUFFER_BYTESIZE,times); if((RegValue & XAXICDMA_XR_IRQ_IOC_MASK))
{
printf("Transfer Completed \n\r ");
}
if((RegValue & XAXICDMA_XR_IRQ_DELAY_MASK))
{
printf("IRQ Delay Interrupt\n\r ");
}
if((RegValue & XAXICDMA_XR_IRQ_ERROR_MASK))
{
printf("Transfer Error Interrupt\n\r ");
} /*======================================================================================
STEP 7 : Un-map the AXI CDMA memory from the User layer.
========================================================================================*/
if (munmap(mapped_base, MAP_SIZE) == -1)
{
printf("Can't unmap memory from user space.\n");
exit(0);
} close(memfd); /*======================================================================================
STEP 8 : Map the kernel memory location starting from 0x30000000 to the User layer
========================================================================================*/
memfd_2 = open("/dev/mem", O_RDWR | O_SYNC);
if (memfd_2 == -1)
{
printf("Can't open /dev/mem.\n");
exit(0);
}
printf("/dev/mem opened.\n");
// Map one page of memory into user space such that the device is in that page, but it may not
// be at the start of the page.
mapped_base_2 = mmap(0, DDR_MAP_SIZE, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED, memfd_2, dev_base_2 & ~DDR_MAP_MASK);
if (mapped_base_2 == (void *) -1)
{
printf("Can't map the memory to user space.\n");
exit(0);
}
printf("Memory mapped at address %p.\n", mapped_base_2);
// get the address of the device in user space which will be an offset from the base
// that was mapped as memory is mapped at the start of a page
mapped_dev_base_2 = mapped_base_2 + (dev_base_2 & DDR_MAP_MASK); /*======================================================================================
STEP 9 : Copy the Data from DDR Memory location 0x20000000 to Destination Buffer
========================================================================================*/
memcpy(DestArray, mapped_dev_base_2, (BUFFER_BYTESIZE ));
/*======================================================================================
STEP 10 : Un-map the Kernel memory from the User layer.
========================================================================================*/
if (munmap(mapped_base_2, DDR_MAP_SIZE) == -1)
{
printf("Can't unmap memory from user space.\n");
exit(0);
} close(memfd_2); /*======================================================================================
STEP 11 : Compare Source Buffer with Destination Buffer.
========================================================================================*/
for(i=0; i<4; i++)
{
k = DestArray[i];
printf("The AXI-CDMA read from address = %4d, the read value = 0x0%7x, MSB value=%5d, LSB value=%5d-----\n\r",i,k,k >> 16,k & 0x0000FFFF);
}
for(i=8188; i<8192; i++)
{
k = DestArray[i];
printf("The AXI-CDMA read from address = %4d, the read value = 0x%8x, MSB value=%5d, LSB value=%5d-----\n\r",i,k,k >> 16,k & 0x0000FFFF);
} return 0;
}
测试结果可参见:
https://www.cnblogs.com/ifpga/p/7859068.html
[原创]Zynq AXI-CDMA的使用的更多相关文章
- [原创]Zynq SDIO WIFI SotfAP调试
编译好kernel和driver 加载firmware后,运行下述命令. mkdir /var/run/ mkdir /var/run/hostapd ifconfig -a ...
- [原创]Zynq AXI-CDMA测试结果
经过研究与demo,在zynq上使用axi-cmda效率还是很高,测试报告如下所示 对于读取32KB,GP0和HP0的测试结果如下:
- 原创zynq文章整理(MiZ702教程+例程)
MiZ702教程+例程 网盘链接: http://pan.baidu.com/s/1sj23yxv 不时会跟新版本,增加勘误之类的,请关注--
- ZYNQ笔记(7):AXI从口自定义IP封装
使用 AXI_Lite 从口实现寄存器列表的读写,并且自己封装为一个自定义 IP,以便以后使用.本次记录的是 M_AXI_GP0 接口,此接口是 ARM 作为主机,FPGA 作为从机,配置 FPGA ...
- Xilinx DMA的几种方式与架构
DMA是direct memory access,在FPGA系统中,常用的几种DMA需求: 1. 在PL内部无PS(CPU这里统一称为PS)持续干预搬移数据,常见的接口形态为AXIS与AXI,AXI与 ...
- Learn ZYNC (2)
AXI HP接口的DMA+GIC编程(参照博客) 参照文档:UG873,博客文档 参考设计代码文件:ug873源码 我的Vivado+SDK工程文件打包(60+M) 我的DMA驱动程序(已完成) Vi ...
- 一步一步学ZedBoard & Zynq(四):基于AXI Lite 总线的从设备IP设计
本帖最后由 xinxincaijq 于 2013-1-9 10:27 编辑 一步一步学ZedBoard & Zynq(四):基于AXI Lite 总线的从设备IP设计 转自博客:http:// ...
- 利用ZYNQ SOC快速打开算法验证通路(6)——利用AXI总线实时配置sysGen子系统
利用ZYNQ验证算法的一大优势在于,可以在上位机发送指令借助CPU的控制能力和C语言易开发特点,实时配置算法模块的工作模式.参数等对来对其算法模块性能进行全面的评估.最重要的是无需重新综合硬件模块. ...
- 利用ZYNQ SOC快速打开算法验证通路(4)——AXI DMA使用解析及环路测试
一.AXI DMA介绍 本篇博文讲述AXI DMA的一些使用总结,硬件IP子系统搭建与SDK C代码封装参考米联客ZYNQ教程.若想让ZYNQ的PS与PL两部分高速数据传输,需要利用PS的HP(高性能 ...
随机推荐
- HDU 1757 A Simple Math Problem (矩阵快速幂)
题目 A Simple Math Problem 解析 矩阵快速幂模板题 构造矩阵 \[\begin{bmatrix}a_0&a_1&a_2&a_3&a_4&a ...
- 【转】C语言堆栈入门——堆和栈的区别
@2019-04-25 [小记] C语言堆栈入门——堆和栈的区别
- [GoogleBlog]new-approach-to-china
https://googleblog.blogspot.com/2010/01/new-approach-to-china.html
- django 2.接口之工作原理
1.创建应用程序有两种方法,第一种就是在新建项目的时候,在最初使的时填入应用程序名称,第二种就是进入目录下面,输入 python manage.py startapp appName 就会自动生成一个 ...
- linux下python安装
下载包: wget https://www.python.org/ftp/python/3.6.3/Python-3.6.3.tar.gz 解压安装: tar -zvxf Python-3.6.3. ...
- Android防止手动添加的本地库文件被NDK工具清理掉
比如要添加一个名为libocr的本地库,先将libocr.so文件拷贝到jni目录下,然后在Android.mk文件中添加以下语句即可. 例: LOCAL_PATH := $(call my-dir) ...
- 转化.vdi到.vmdk
OracleVirtualBox转化.vdi到.vmdk E:\Genymotion-deployed\CentOS_7_64>"D:/Program Files/Oracle/Vir ...
- QMQTT简单介绍(2)
QMQTT mqtt client for Qt Please compile the library with Qt >= 5.3 version. On Windows you need t ...
- Nodejs一键实现微信内打开网页url自动跳转外部浏览器访问的功能
前言 现如今微信对第三方推广链接的审核是越来越严格了,域名在微信中分享转发经常会被拦截,一旦被拦截用户就只能复制链接手动打开浏览器粘贴才能访问,要不然就是换个域名再推,周而复始.无论是哪一种情况都会面 ...
- BMCP位图图片压缩算法
什么是位图?位图也称像素图像或点阵图像,是由多个点组成的,这些点被称为像素.位图可以模仿照片的真实效果,具有表现力强.细腻.层次多和细节多等优点. 图片的压缩格式:在Windows系统中,我们常见的b ...
