05--STL序列容器(List)
补充:
注意:list和forward_list都有自己的sort排序方法,所以排序时最好使用自带的sort方法,节省时间
一:List
(一):List双向链表简介
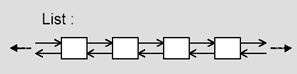
list是一个双向链表容器,可高效地进行插入删除元素。
list不可以随机存取元素,所以不支持at.(pos)函数与[]操作符。It++(ok) it+5(err)
list不支持任意存取迭代

(二):list默认构造函数
list采用采用模板类实现,对象的默认构造形式:list<T> lstT; 如: list<int> lstInt; //定义一个存放int的list容器。 list<float> lstFloat; //定义一个存放float的list容器。 list<string> lstString; //定义一个存放string的list容器。 //尖括号内还可以设置指针类型或自定义类型。
(三):list的带参构造函数
list(beg,end); //构造函数将[beg, end)区间中的元素拷贝给本身。注意该区间是左闭右开的区间。
list(n,elem); //构造函数将n个elem拷贝给本身。
list(const list &lst); //拷贝构造函数。
(四):list头尾添加删除操作
list.push_back(elem); //在容器尾部加入一个元素
list.pop_back(); //删除容器中最后一个元素
list.push_front(elem); //在容器开头插入一个元素
list.pop_front(); //从容器开头移除第一个元素
(五):list头尾数据获取
list.front(); //返回第一个元素。
list.back(); //返回最后一个元素。
(六):list迭代器相关
list.begin(); //返回容器中第一个元素的迭代器。
list.end(); //返回容器中最后一个元素之后的迭代器。
list.rbegin(); //返回容器中倒数第一个元素的迭代器。
list.rend(); //返回容器中倒数最后一个元素的后面的迭代器。
(七):list赋值操作
list.assign(beg,end); //将[beg, end)区间中的数据拷贝赋值给本身。注意该区间是左闭右开的区间。
list.assign(n,elem); //将n个elem拷贝赋值给本身。
list& operator=(const list &lst); //重载等号操作符
list.swap(lst); // 将lst与本身的元素互换。
(八):list大小获取
list.size(); //返回容器中元素的个数
list.empty(); //判断容器是否为空
list.resize(num); //重新指定容器的长度为num,若容器变长,则以默认值填充新位置。如果容器变短,则末尾超出容器长度的元素被删除。
list.resize(num, elem); //重新指定容器的长度为num,若容器变长,则以elem值填充新位置。如果容器变短,则末尾超出容器长度的元素被删除。
(九):list插入操作
list.insert(pos,elem); //在pos位置插入一个elem元素的拷贝,返回新数据的位置。
list.insert(pos,n,elem); //在pos位置插入n个elem数据,无返回值。
list.insert(pos,beg,end); //在pos位置插入[beg,end)区间的数据,无返回值。
同链表一样,先是查找位置,耗时。后是插入数据,快速
(十):list删除区间数据
list.clear(); //移除容器的所有数据
list.erase(beg,end); //删除[beg,end)区间的数据,返回下一个数据的位置。 //使用迭代器删除较快,不需要查找
list.erase(pos); //删除pos位置的数据,返回下一个数据的位置。
lst.remove(elem); //删除容器中所有与elem值匹配的元素。
(十一):list数据序列翻转《重点》
lst.reverse(); //反转链表,比如lst包含1,3,5元素,运行此方法后,lst就包含5,3,1元素。
只动指针,不动数据
(十二)性能测试
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <cstring> #if _MSC_VER
#define snprintf _snprintf
#endif using namespace std; long get_a_target_long()
{
/******变量声明********/
long target = ;
/**********************/ cout << "targer (0~" << RAND_MAX << "):";
cin >> target;
return target;
} string get_a_target_string()
{
/******变量声明********/
long target = ;
char buf[];
/**********************/ cout << "targer (0~" << RAND_MAX << "):";
cin >> target; snprintf(buf, , "%d", target);
return string(buf);
} //与后面的比较函数中回调参数对应
int compareLongs(const void* l1, const void* l2)
{
return (*(long*)l1 - *(long*)l2);
} int compareStrings(const void* s1, const void* s2)
{
if (*(string*)s1 > *(string*)s2)
return ;
if (*(string*)s1 < *(string*)s2)
return -;
return ;
}
公共函数
#include <list>
namespace jj03
{
void test_list(long& l_size)
{
cout << "\ntest_list()*******" << endl; /******变量声明:数组初始********/
char buf[]; /******变量声明:list初始********/
list<string> lt; /******变量声明:记录时间********/
clock_t timeStart = clock(); //开始时间
for (long i = ; i < l_size; i++)
{
try
{
snprintf(buf, , "%d", rand());
lt.push_back(string(buf));
}
catch (exception& e)
{
cout << e.what() << endl;
cout << "Max_size:" << i << endl;
abort(); //终止
}
} cout << "inti vector use milli-seconds:" << (clock() - timeStart) << endl; //获取初始化数组耗时
cout << "list.size:" << lt.size() << endl; //获取list大小
cout << "list.max_size:" << lt.max_size() << endl; //获取list所允许的最大长度
cout << "list.front:" << lt.front() << endl; //获取list首元素
cout << "list.back:" << lt.back() << endl; //获取list尾元素 /******变量声明:获取我们要查询的数********/
string target = get_a_target_string(); //注意list是链表实现,算法中sort不能使用,sort用在顺序表中 //qsort和bsearch是C编译器自带的快速排序和二分查找算法
//但是list不维护data首地址(一直变),所以这个查找方法不能使用 //使用find方法进行查找:find不需要进行排序,查找时间可能较短<因为是迭代查找>(若是一次查找的话,耗时少,但是多次查找,那么先排序效率更好)
timeStart = clock(); auto pItem = find(lt.begin(), lt.end(), target); //auto变量用得好 cout << "::find(),milli-seconds:" << clock() - timeStart << endl;
if (pItem != lt.end())
cout << "found:" << *pItem << endl;
else
cout << "not found!" << endl; //使用list自带sort方法进行排序,节省时间 需要排序,所以耗时长于find
timeStart = clock(); lt.sort(); //使用list自带sort方法进行排序,节省时间
cout << "list.sort(),milli-seconds:" << clock() - timeStart << endl; timeStart = clock();
/******变量声明:flag布尔型判断是否找到数据********/
bool flag =
binary_search(lt.begin(), lt.end(), target); cout << "binary_search(),milli-seconds:" << clock() - timeStart << endl;
if (flag != false)
cout << "found:" << target << endl;
else
cout << "not found!" << endl;
}
}

数据量大时destroy销毁内存时,耗时太长
二:Forward_list
(一)forward_list简介
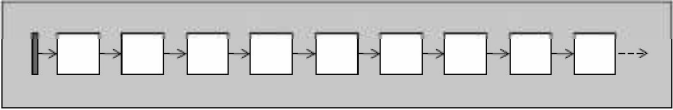
单向列表,但实际上它是一种单向列表,只能从单一方向遍历
(二)单链表的实现
forward_list内部是用单向列表实现的,并且为了保证该库的运行效率(时间上和空间上)。
它是唯一一个C++标准库容器中没有size成员函数的容器, 因为维护这样一个信息会造成效率上的轻微损失。
和list双向链表相比,forward_list类只有一个结点只有一个指针,节省4字节相比于list
若是数据太多,若是可以,尽可能选择forward_list可以节省大量空间
和其他的标准序列容器(array,vector,deque)相比较的话,forward_list在任何位置的插入,删除和移动操作会更快。因此在诸如sorting算法中会更倾向于使用它。
(三)forward_list构造方法
forward_list<int> first; // 默认构造:为空
forward_list<int> second (,); // fill填充 3 个 77
forward_list<int> third (second.begin(), second.end()); // range initialization
forward_list<int> fourth (third); // 拷贝构造
forward_list<int> fifth= {, , , }; // 列表赋值
(四)forward_list赋值操作
assign:
forward_list<int> first;
forward_list<int> second;
first.assign (4,15); // 15 15 15 15 second.assign (first.begin(),first.end()); // 15 15 15 15 first.assign ( {77, 2, 16} ); // 77 2 16
swap:
forward_list<int> first = {, , };
forward_list<int> second = {, };
first.swap(second);
operator=:相同
(五) forward_list插入操作push_front《含有头结点》
forward_list<int> mylist = {, , };
mylist.push_front ();
mylist.push_front ();
由于为了效率,forward_list连size函数都不要了,当然不会要尾指针。因为维护尾指针比维护头指针复杂多了
(六)forward_list删除操作pop_front和front
forward_list<int> mylist = {, , , };
cout << "Popping out the elements in mylist:";
while (!mylist.empty())
{
cout << ' ' << mylist.front(); //获取开始结点数据
mylist.pop_front(); //删除开始结点
}
(七)更多方法参考:http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/forward_list/forward_list/pop_front/
(八)性能测试
#include <forward_list>
namespace jj04
{
void test_flist(long& l_size)
{
cout << "\ntest_list()*******" << endl; /******变量声明:数组初始********/
char buf[]; /******变量声明:forward_list初始********/
forward_list<string> fl; /******变量声明:记录时间********/
clock_t timeStart = clock(); //开始时间
for (long i = ; i < l_size; i++)
{
try
{
snprintf(buf, , "%d", rand());
fl.push_front(string(buf));
}
catch (exception& e)
{
cout << e.what() << endl;
cout << "Max_size:" << i << endl;
abort(); //终止
}
} cout << "inti vector use milli-seconds:" << (clock() - timeStart) << endl; //获取初始化数组耗时
cout << "list.max_size:" << fl.max_size() << endl; //获取forward_list所允许的最大长度
cout << "list.front:" << fl.front() << endl; //获取forward_list首元素
//为了效率,forward_list并不维护size和back /******变量声明:获取我们要查询的数********/
string target = get_a_target_string(); //注意forward_list是链表实现,算法中sort不能使用,sort用在顺序表中 //qsort和bsearch是C编译器自带的快速排序和二分查找算法
//但是forward_list不维护data首地址(一直变),所以这个查找方法不能使用 //使用find方法进行查找:find不需要进行排序,查找时间可能较短<因为是迭代查找>(若是一次查找的话,耗时少,但是多次查找,那么先排序效率更好)
timeStart = clock(); auto pItem = find(fl.begin(), fl.end(), target); //auto变量用得好 cout << "::find(),milli-seconds:" << clock() - timeStart << endl;
if (pItem != fl.end())
cout << "found:" << *pItem << endl;
else
cout << "not found!" << endl; //使用forward_list自带sort方法进行排序,节省时间 需要排序,所以耗时长于find
timeStart = clock(); fl.sort(); //使用list自带sort方法进行排序,节省时间
/******变量声明:flag布尔型判断是否找到数据********/
cout << "list.sort()milli-seconds:" << clock() - timeStart << endl; timeStart = clock();
bool flag =
binary_search(fl.begin(), fl.end(), target); cout << "binary_search(),milli-seconds:" << clock() - timeStart << endl;
if (flag != false)
cout << "found:" << target << endl;
else
cout << "not found!" << endl;
}
}
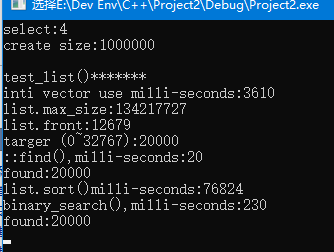
链表销毁耗时都较长
05--STL序列容器(List)的更多相关文章
- STL 序列容器
转自时习之 STL中大家最耳熟能详的可能就是容器,容器大致可以分为两类,序列型容器(SequenceContainer)和关联型容器(AssociativeContainer)这里介绍STL中的各种序 ...
- STL List容器
转载http://www.cnblogs.com/fangyukuan/archive/2010/09/21/1832364.html 各个容器有很多的相似性.先学好一个,其它的就好办了.先从基础开始 ...
- STL序列式容器学习总结
STL序列式容器学习总结 参考资料:<STL源码剖析> 参考网址: Vector: http://www.cnblogs.com/zhonghuasong/p/5975979.html L ...
- STL常用序列容器
这里简要的记述一下STL常用容器的实现原理,要点等内容. vector vector是比较常用的stl容器,用法与数组是非类似,其内部实现是连续空间分配,与数组的不同之处在于可弹性增加空间,而arra ...
- C++ STL基本容器的使用
C++中有两种类型的容器:顺序容器和关联容器.顺序容器主要有vector.list.deque等.其中vector表示一段连续的内存,基于数组实现,list表示非连续的内存,基于链表实现,deque与 ...
- STL基础--容器
容器种类 序列容器(数组,链表) Vector, deque, list, forward list, array 关联容器(二叉树),总是有序的 set, multiset根据值排序,元素值不能修改 ...
- c++复习:STL之容器
1 STL的string 1 String概念 string是STL的字符串类型,通常用来表示字符串.而在使用string之前,字符串通常是用char*表示的.string与char*都可以用来表示字 ...
- string基本字符序列容器(竞赛时常用的使用方法总结)
C语言只提供了一个char类型用来处理字符,而对于字符串,只能通过字符串数组来处理,而C++STL提供了string基本字符序列容器来处理字符串,可以将其理解为字符串类,它提供了添加,删除,替换.查找 ...
- 【C++】STL常用容器总结之五:双端队列deque
6.双端队列deque 所谓的deque是”double ended queue”的缩写,双端队列不论在尾部或头部插入元素,都十分迅速.而在中间插入元素则会比较费时,因为必须移动中间其他的元素.双端队 ...
- [C++ STL] 各容器简单介绍
什么是STL? 1.STL(Standard Template Library),即标准模板库,是一个高效的C++程序库. 2.包含了诸多常用的基本数据结构和基本算法.为广大C++程序员们提供了一个可 ...
随机推荐
- vue的表单编辑删除,保存取消功能
过年回来第一篇博客,可能说的不是很清楚,而且心情可能也不是特别的high,虽然今天是元宵,我还在办公室11.30在加班,但就是想把写过的代码记下来,怕以后可能真的忘了.(心将塞未塞,欲塞未满) VUE ...
- 重庆3Shape CAMbridge都有哪些功能
三维打印技术创新领导者Objet Geometries公司和牙科领域三维扫描仪.CAD/CAM软件解决方案供应商3Shape A/S公司日前宣布两家公司合作研发的牙科领域三维修复解决方案已付诸实施.此 ...
- 查看CPU使用率
rem 如果wmi服务(服务名为Winmgmt)坏掉了,需要到system32\webm目录下执行如下注释的命令 rem for %i in (*.dll) do RegSvr32 -s %i rem ...
- qt5.11.2+vs2017环境下配置pcl1.8.1以及第三方依赖库vtk的编译
1.准备工作 我所用的开发环境是win10下的qt5.11.2配置了vs2017的编译器,根据自己所用的VS的版本去官网下载对应版本的pcl库,如下 PCL-1.8.1-AllInOne-msvc20 ...
- Facebook 广告投放相关概念简介(1)
本文不涉及具体代码实现,仅对开发API的前置内容做简单介绍,想参考代码请绕行! 广告主(广告管理工具) ·需要推广自己的应用.网站.主页,所以有了广告管理工具 . ·一个广告主仅可拥有一个广告账户(可 ...
- 关于Net core 的https 设置小知识
今天我是遇到了一个蛋疼的问题, 就是https 协议, 在创建项目的时候, 我勾选了for https (如下图), 然后我就在startup.cs 和Kestrel 各种设置还是全部走https ...
- JS 设计模式六 -- 代理模式
概念 为一个对象提供一个代用品或占位符,以便控制对它的访问. 当客户不方便直接访问一个对象的时候,需要提供一个替身对象来控制对这个对象的访问. 替身对象对请求做出一些处理之后, 再把请求转交给本体对象 ...
- 03SpringBoot用JdbcTemplates访问Mysql
03SpringBoot用JdbcTemplates访问Mysql 文章指导 学习笔记 学习代码 初始化mysql -- create table `account` DROP TABLE `acco ...
- nodejs部署方式-pm2
目前Nodejs开发中有很多痛点,其中有一个是修改完代码以后需要我们重启服务才能看到效果.这样一次次的杀进程.重启,杀进程.重启很让人头大.程序员是最痛恨重复工作的物种,之前有了解过的同学可能知道 f ...
- AngularJS路由变化 监听方法
#使用AngularJS时,当路由发生改变时,我们需要做某些处理,此时可以监听路由事件,常用的是$routeStartChange, $routeChangeSuccess ##使用场景:在路由配置文 ...
