Mybatis源码之StatementType
在mybatis中StatementType的值决定了由什么对象来执行我们的SQL语句。本文来分析下在mybatis中具体是怎么处理的。
StatementType
1.StatementType枚举
StatementType是一个枚举类型。如下:
/**
* @author Clinton Begin
*/
public enum StatementType {
STATEMENT, PREPARED, CALLABLE
}
| 选项 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| STATEMENT | 对应于Statement对象,有SQL注入的风险 |
| PREPARED | PreparedStatement,预编译处理 |
| CALLABLE | CallableStatement一般调用存储过程的时候使用 |
2.设置StatementType
我们可以在映射文件中通过‘statementType’属性设置,如下:
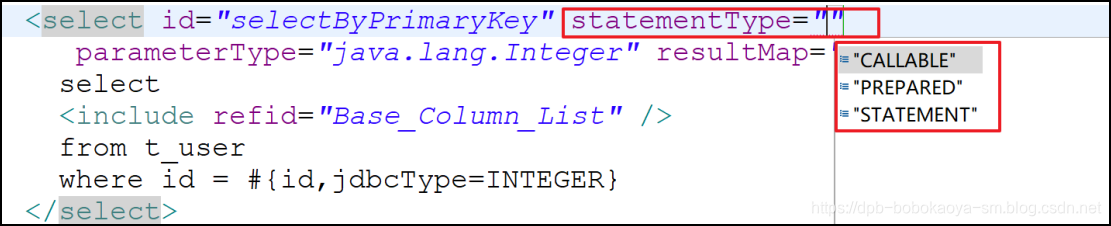
注意默认是'PREPARED ',通过源码分析我们可以查看到。
3.源码跟踪查看
我们要从源码中发现StatementType的处理,应该是从加载配置文件的地方开始查看,所以我们从'new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(in);'这行代码入手
//InputStream in = Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml");
InputStream in = TestMybatis.class.getResourceAsStream("/mybatis-config.xml");
// 获取SqlSessionFactory对象
SqlSessionFactory factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(in);
进入build方法中查看
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties properties) {
try {
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(inputStream, environment, properties);
// 配置文件解析的重点是 'parser.parse()'这行代码
return build(parser.parse());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// Intentionally ignore. Prefer previous error.
}
}
}
进入parse方法中
public Configuration parse() {
if (parsed) {
throw new BuilderException("Each XMLConfigBuilder can only be used once.");
}
parsed = true;
// 进入
parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration"));
return configuration;
}
private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) {
try {
//issue #117 read properties first
propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties"));
Properties settings = settingsAsProperties(root.evalNode("settings"));
loadCustomVfs(settings);
typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases"));
pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins"));
objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory"));
objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory"));
reflectorFactoryElement(root.evalNode("reflectorFactory"));
settingsElement(settings);
// read it after objectFactory and objectWrapperFactory issue #631
environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments"));
databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider"));
typeHandlerElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers"));
// 上面都是解析主配置文件中子节点,直接进入本方法
mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
mapperElement方法,该方法会根据我们在mappers中不同的配置做出不同的处理。我们直接看resource的方式
private void mapperElement(XNode parent) throws Exception {
if (parent != null) {
for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) {
if ("package".equals(child.getName())) {
String mapperPackage = child.getStringAttribute("name");
configuration.addMappers(mapperPackage);
} else {
String resource = child.getStringAttribute("resource");
String url = child.getStringAttribute("url");
String mapperClass = child.getStringAttribute("class");
if (resource != null && url == null && mapperClass == null) {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(resource);
// 加载配置文件
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, resource, configuration.getSqlFragments());
// 解析配置文件的方法 进入
mapperParser.parse();
} else if (resource == null && url != null && mapperClass == null) {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(url);
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getUrlAsStream(url);
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, url, configuration.getSqlFragments());
mapperParser.parse();
} else if (resource == null && url == null && mapperClass != null) {
Class<?> mapperInterface = Resources.classForName(mapperClass);
configuration.addMapper(mapperInterface);
} else {
throw new BuilderException("A mapper element may only specify a url, resource or class, but not more than one.");
}
}
}
}
}
进入 mapperParser.parse() 方法查看
public void parse() {
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {
// 解析根节点
configurationElement(parser.evalNode("/mapper"));
configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);
// 绑定名称空间
bindMapperForNamespace();
}
parsePendingResultMaps();
parsePendingCacheRefs();
// 重点本方法,解析未处理的Statements
parsePendingStatements();
}
进入parsePendingStatements方法:
private void parsePendingStatements() {
Collection<XMLStatementBuilder> incompleteStatements = configuration.getIncompleteStatements();
synchronized (incompleteStatements) {
Iterator<XMLStatementBuilder> iter = incompleteStatements.iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
try {
// 解析我们的select|update|insert|delete节点
iter.next().parseStatementNode();
iter.remove();
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
// Statement is still missing a resource...
}
}
}
}
进入parseStatementNode 方法
public void parseStatementNode() {
String id = context.getStringAttribute("id");
String databaseId = context.getStringAttribute("databaseId");
if (!databaseIdMatchesCurrent(id, databaseId, this.requiredDatabaseId)) {
return;
}
Integer fetchSize = context.getIntAttribute("fetchSize");
Integer timeout = context.getIntAttribute("timeout");
String parameterMap = context.getStringAttribute("parameterMap");
String parameterType = context.getStringAttribute("parameterType");
Class<?> parameterTypeClass = resolveClass(parameterType);
String resultMap = context.getStringAttribute("resultMap");
String resultType = context.getStringAttribute("resultType");
String lang = context.getStringAttribute("lang");
LanguageDriver langDriver = getLanguageDriver(lang);
Class<?> resultTypeClass = resolveClass(resultType);
String resultSetType = context.getStringAttribute("resultSetType");
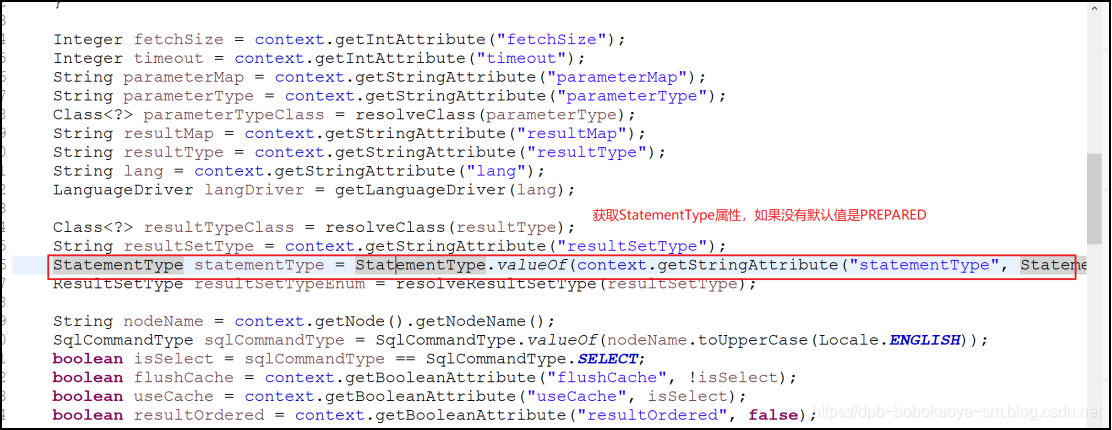
// 重点代码,看截图
StatementType statementType = StatementType.valueOf(context.getStringAttribute("statementType", StatementType.PREPARED.toString()));
ResultSetType resultSetTypeEnum = resolveResultSetType(resultSetType);
String nodeName = context.getNode().getNodeName();
SqlCommandType sqlCommandType = SqlCommandType.valueOf(nodeName.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH));
boolean isSelect = sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT;
boolean flushCache = context.getBooleanAttribute("flushCache", !isSelect);
boolean useCache = context.getBooleanAttribute("useCache", isSelect);
boolean resultOrdered = context.getBooleanAttribute("resultOrdered", false);
// Include Fragments before parsing
XMLIncludeTransformer includeParser = new XMLIncludeTransformer(configuration, builderAssistant);
includeParser.applyIncludes(context.getNode());
// Parse selectKey after includes and remove them.
processSelectKeyNodes(id, parameterTypeClass, langDriver);
// Parse the SQL (pre: <selectKey> and <include> were parsed and removed)
SqlSource sqlSource = langDriver.createSqlSource(configuration, context, parameterTypeClass);
String resultSets = context.getStringAttribute("resultSets");
String keyProperty = context.getStringAttribute("keyProperty");
String keyColumn = context.getStringAttribute("keyColumn");
KeyGenerator keyGenerator;
String keyStatementId = id + SelectKeyGenerator.SELECT_KEY_SUFFIX;
keyStatementId = builderAssistant.applyCurrentNamespace(keyStatementId, true);
if (configuration.hasKeyGenerator(keyStatementId)) {
keyGenerator = configuration.getKeyGenerator(keyStatementId);
} else {
keyGenerator = context.getBooleanAttribute("useGeneratedKeys",
configuration.isUseGeneratedKeys() && SqlCommandType.INSERT.equals(sqlCommandType))
? Jdbc3KeyGenerator.INSTANCE : NoKeyGenerator.INSTANCE;
}
builderAssistant.addMappedStatement(id, sqlSource, statementType, sqlCommandType,
fetchSize, timeout, parameterMap, parameterTypeClass, resultMap, resultTypeClass,
resultSetTypeEnum, flushCache, useCache, resultOrdered,
keyGenerator, keyProperty, keyColumn, databaseId, langDriver, resultSets);
}
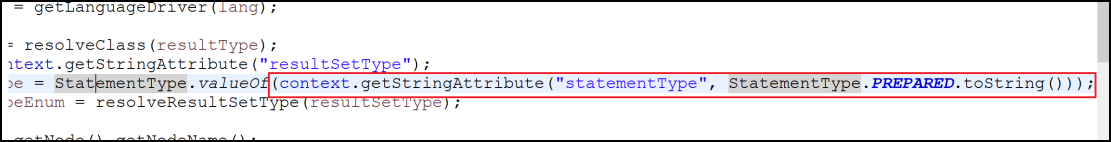
最后解析完这个select|insert|update|delete节点的信息被封装到了一个MapperedStatement对象中。

至此StatementType解析阶段的内容分析完了~
Mybatis源码之StatementType的更多相关文章
- MyBatis源码分析-SQL语句执行的完整流程
MyBatis 是支持定制化 SQL.存储过程以及高级映射的优秀的持久层框架.MyBatis 避免了几乎所有的 JDBC 代码和手动设置参数以及获取结果集.MyBatis 可以对配置和原生Map使用简 ...
- 【MyBatis源码分析】select源码分析及小结
示例代码 之前的文章说过,对于MyBatis来说insert.update.delete是一组的,因为对于MyBatis来说它们都是update:select是一组的,因为对于MyBatis来说它就是 ...
- Spring mybatis源码篇章-MybatisDAO文件解析(二)
前言:通过阅读源码对实现机制进行了解有利于陶冶情操,承接前文Spring mybatis源码篇章-MybatisDAO文件解析(一) 默认加载mybatis主文件方式 XMLConfigBuilder ...
- Spring mybatis源码篇章-MybatisDAO文件解析(一)
前言:通过阅读源码对实现机制进行了解有利于陶冶情操,承接前文Spring mybatis源码篇章-SqlSessionFactory 加载指定的mybatis主文件 Mybatis模板文件,其中的属性 ...
- Mybatis源码分析-BaseExecutor
根据前文Mybatis源码分析-SqlSessionTemplate的简单分析,对于SqlSession的CURD操作都需要经过Executor接口的update/query方法,本文将分析下Base ...
- Mybatis源码分析-StatementHandler
承接前文Mybatis源码分析-BaseExecutor,本文则对通过StatementHandler接口完成数据库的CRUD操作作简单的分析 StatementHandler#接口列表 //获取St ...
- mybatis源码分析(一)
mybatis源码分析(sqlSessionFactory生成过程) 1. mybatis框架在现在各个IT公司的使用不用多说,这几天看了mybatis的一些源码,赶紧做个笔记. 2. 看源码从一个d ...
- Mybatis源码分析之存储过程调用
这一篇博客我们学习一下Mybatis调用存储过程的使用和运行流程.首先我们先创建一个简单的存储过程 DELIMITER $ CREATE PROCEDURE mybatis.ges_user_coun ...
- MyBatis 源码分析 - 缓存原理
1.简介 在 Web 应用中,缓存是必不可少的组件.通常我们都会用 Redis 或 memcached 等缓存中间件,拦截大量奔向数据库的请求,减轻数据库压力.作为一个重要的组件,MyBatis 自然 ...
随机推荐
- 类型后面加问号 int?
类型后面加问号 int? 单问号---用于给变量设初值的时候,给变量(int类型)赋值为null,而不是0! 双问号---用于判断并赋值,先判断当前变量是否为null,如果是就可以赋一个新值,否则跳过 ...
- IaaS,PaaS和SaaS
云计算的三种服务模式:IaaS,PaaS和SaaS IaaS: Infrastructure-as-a-Service(基础设施即服务)是第一层. PaaS: Platform-as-a-Servic ...
- Spring SpringMVC SpringBoot SpringCloud概念、关系及区别
一.正面解读: Spring主要是基于IOC反转Beans管理Bean类,主要依存于SSH框架(Struts+Spring+Hibernate)这个MVC框架,所以定位很明确,Struts主要负责表示 ...
- 2.9 linux学习(1)
2019-2-9 16:07:44 学一下Linux,多学一点东西 新认识个老师,超哥 很牛逼感觉! https://www.cnblogs.com/pyyu/p/9276851.html 这是入门参 ...
- Codeforces Round #555 (Div. 3) AB
A: http://codeforces.com/contest/1157/problem/A 题意:每次加到10的整数倍之后,去掉后面的0,问最多有多少种可能. #include <io ...
- Redis安装及使用
1.我们可以通过在官网下载tar.gz的安装包,或者通过wget的方式下载 进入要下载到的文件夹: wget http://download.redis.io/releases/redis-4.0.1 ...
- 使用jQuery.form库中ajaxSubmit提交表单时遇到的一些问题
初入前端,网上找的很多资料都不够详细,导致遇到很多问题,现记录如下: 1.首先引入 <script src="~/Scripts/jquery-1.10.2.js">& ...
- changXY
changXY <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <link rel="shortcut icon" href= ...
- 大数据与云计算的关系是什么,Hadoop又如何参与其中?Nosql在什么位置,与BI又有什么关系?
大数据与云计算的关系是什么,Hadoop又如何参与其中,Nosql在什么位置,与BI又有什么关系?以下这篇文字讲他们的关系讲的非常清楚. 在谈大数据的时候,首先谈到的就是大数据的4V特性,即类型复杂 ...
- [Swift]LeetCode483. 最小好进制 | Smallest Good Base
For an integer n, we call k>=2 a good base of n, if all digits of n base k are 1. Now given a str ...
