set用法小结
set本质上是一棵红黑树,用法也就那么几个,插入删除lowerbound,再就是迭代器之类的
基本用法
begin()--返回指向第一个元素的迭代器
#include<cstdio>
#include<set>
int main()
{
std::set<int>s;
s.insert();
s.insert();
s.insert();
printf("%d",*s.begin());
//输出4
return ;
}
begin()
end()--返回指向最后一个元素的迭代器
#include<cstdio>
#include<set>
int main()
{
std::set<int>s;
s.insert();
s.insert();
s.insert();
printf("%d",*s.end());
//注意这里的跌倒器指向的是一个空位置!
//所以最好不要输出end() //输出末尾元素可以用下面的方法
//std::set<int>::iterator it=s.end();
//printf("%d",*--it);
return ;
}
end()
rbegin()--返回指向集合中最后一个元素的反向迭代器
rend()--返回指向集合中第一个元素的反向迭代器
find()--返回一个指向被查找到元素的迭代器
insert()--在集合中插入元素
size()--集合中元素的数目
clear()--清除所有元素
#include<cstdio>
#include<set>
int main()
{
std::set<int>s;
s.insert();
s.insert();
s.insert();
printf("%d\n",s.size());
s.clear();
printf("%d\n",s.size());
return ;
}
clear()
count()--返回某个值元素的个数//主要应用于multiset
#include<cstdio>
#include<set>
int main()
{
std::multiset<int>s;
s.insert();
s.insert();
s.insert();
printf("%d",s.count());
return ;
}
count
empty()--如果集合为空,返回true
erase()--删除集合中的元素
erase可以删除给定的元素,也可以删除迭代器
在multiset中,删除给定的元素是全部删除,而删除迭代器只会删除一次,下面还会讲到
#include<cstdio>
#include<set>
int main()
{
std::set<int>s;
s.insert();
s.insert();
s.insert();
s.erase();
s.erase(s.find());
if(s.find()==s.end()) printf("5 is not found\n");
if(s.find()==s.end()) printf("4 is not found\n");
if(s.find()!=s.end()) printf("6 is found");
return ;
}
erase()
lower_bound()--返回指向大于(或等于)某值的第一个元素的迭代器
#include<cstdio>
#include<set>
int main()
{
std::set<int>s;
s.insert();
s.insert();
s.insert();
printf("%d",*s.lower_bound());
//输出为4
return ;
}
lower_bound()
upper_bound()--返回大于某个值元素的迭代器
#include<cstdio>
#include<set>
int main()
{
std::set<int>s;
s.insert();
s.insert();
s.insert();
printf("%d",*s.upper_bound());
//输出为4
return ;
}
upper_bound()
swap()--交换两个集合变量
#include<cstdio>
#include<set>
int main()
{
std::set<int>s;
std::set<int>a;
s.insert();
s.insert();
a.insert();
s.swap(a);
printf("%d",s.size());
//输出为1
return ;
}
swap()
几个常用操作
正序遍历所有元素
这个需要借助迭代器来实现
set中是重载了迭代器的++和--运算符的,所以直接使用就可以了
#include<cstdio>
#include<set>
#define sit set<int>::iterator
using namespace std;
int main()
{
set<int>s;
for(int i=;i<=;i++)
s.insert(i);
for(sit i=s.begin();i!=s.end();i++)
printf("%d ",*i);
//输出1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
return ;
}
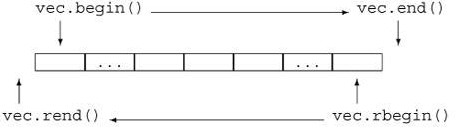
倒序遍历所有元素
可以使用rbegin和rend实现,他们与begin和end的关系如下图所示
#include<cstdio>
#include<set>
#define rsit set<int>::reverse_iterator
using namespace std;
int main()
{
set<int>s;
for(int i=;i<=;i++)
s.insert(i);
rsit it=s.rbegin();
for(rsit i=s.rbegin();i!=s.rend();i++)
printf("%d ",*i);
//输出10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
return ;
}
multiset中删除元素
在multiset中,如果仅仅用erase($x$)来删除$x$元素,那么$x$的出现次数会变为$0$
解决方法是先找到$x$对应的迭代器,然后将迭代器删除,这样就可以使$x$只删除一次
#include<cstdio>
#include<set>
#define sit set<int>::iterator
using namespace std;
int main()
{
multiset<int>s;
s.insert();
s.insert();
s.insert();
s.erase();
printf("%d\n",s.count()); s.insert();
s.insert();
s.insert();
s.erase(s.find());
printf("%d\n",s.count());
//输出0 2
return ;
}
自定义排序规则
如果元素不在结构体中,需要自定义结构体并重载“$()$”运算符
#include<cstdio>
#include<set>
#define sit set<int>::iterator
using namespace std;
struct comp
{
bool operator ()(const int &a,const int &b)
{
return a>b;
}
};
int main()
{
set<int,comp>s;
for(int i=;i<=;i++)
s.insert(i);
for(sit i=s.begin();i!=s.end();i++)
printf("%d ",*i);
//输出10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
return ;
}
若元素在结构体中,则需要重载$<$运算符
#include<cstdio>
#include<set>
#define sit set<node>::iterator
using namespace std;
struct node
{
int l,r;
node(int l=,int r=):l(l),r(r){};
bool operator < (const node &a) const
{
return r==a.r?l<a.l:r<a.r;
}
};
int main()
{
set<node>s;
for(int i=;i<=;i++)
s.insert(node(i,-i+));
for(sit i=s.begin();i!=s.end();i++)
printf("%d %d\n",i->l,i->r); //输出
/*
10 1
9 2
8 3
7 4
6 5
5 6
4 7
3 8
2 9
1 10
*/
return ;
}
在结构体中二分
只要重载了$<$,就可以在结构体中二分了
#include<cstdio>
#include<set>
#define sit set<node>::iterator
using namespace std;
struct node
{
int l,r;
node(int l=,int r=):l(l),r(r){};
bool operator < (const node &a) const
{
return r==a.r?l<a.l:r<a.r;
}
};
int main()
{
set<node>s;
for(int i=;i<=;i++)
s.insert(node(i,i));
sit it=s.lower_bound(node(,));
printf("%d %d",it->l,it->r); //输出 2 2
return ;
}
题目
都是可以用set水的大水题
set用法小结的更多相关文章
- 转载:Hadoop排序工具用法小结
本文转载自Silhouette的文章,原文地址:http://www.dreamingfish123.info/?p=1102 Hadoop排序工具用法小结 发表于 2014 年 8 月 25 日 由 ...
- [No000010]Ruby 中一些百分号(%)的用法小结
#Ruby 中一些百分号(%)的用法小结 #这篇文章主要介绍了Ruby 中一些百分号(%)的用法小结,需要的朋友可以参考下 what_frank_said = "Hello!"#% ...
- C++ typedef用法小结 (※不能不看※)
C++ typedef用法小结 (※不能不看※) 第一.四个用途 用途一: 定义一种类型的别名,而不只是简单的宏替换.可以用作同时声明指针型的多个对象.比如:char* pa, pb; // 这多数不 ...
- 函数fgets和fputs、fread和fwrite、fscanf和fprintf用法小结 (转)
函数fgets和fputs.fread和fwrite.fscanf和fprintf用法小结 字符串读写函数fgets和fputs 一.读字符串函数fgets函数的功能是从指定的文件中读一个字符串到字符 ...
- 1:CSS中一些@规则的用法小结 2: @media用法详解
第一篇文章:@用法小结 第二篇文章:@media用法 第一篇文章:@用法小结 这篇文章主要介绍了CSS中一些@规则的用法小结,是CSS入门学习中的基础知识,需要的朋友可以参考下 at-rule ...
- 英语语法最终珍藏版笔记- 21it 用法小结
it 用法小结 it 在英语中的意思较多,用法较广,现总结如下. 一.it作句子的真正主语 1.it 指前面已经提到过的人或事物,有时指心目中的或成为问题的人或事物,作真正主语. 例如: What’s ...
- [转]ssh常用用法小结
ssh常用用法小结 1.连接到远程主机: 命令格式 : ssh name@remoteserver 或者 ssh remoteserver -l name 说明:以上两种方式都可以远程登录到远程主机, ...
- 结构体定义 typedef struct 用法详解和用法小结
typedef是类型定义的意思.typedef struct 是为了使用这个结构体方便.具体区别在于:若struct node {}这样来定义结构体的话.在申请node 的变量时,需要这样写,stru ...
- typedef用法小结
typedef用法小结- - 注意:本文转自网络,版权归原作者所有. typedef typedef用法小结- - 这两天在看程序的时候,发现很多地方都用到typedef,在结构体定义,还有一些数组等 ...
- NSEnumerator用法小结
NSEnumerator 3)枚举 (NSEnumerator)遍历数组每个索引处的对象,你可以编写一个0到[array count]的循环,而NSEnumerator用来描述这种集合迭代运算的方 ...
随机推荐
- SSIS - 10.执行过程任务
一.创建批处理文件 在SSIS包中,执行过程任务可以用来运行应用程序或批处理文件.它执行时用到的输入.输出和参数可以在任务编辑器中进行设置. 在使用执行过程任务之前,我们需要先创建一个批处理文件,实现 ...
- ubuntu 16.04卸载不必要默认安装软件
两个办法,一个在ubuntu软件里一个一个删,明显的windows下做法. 还有一个通过终端来删除.ctrl+alt+t打开终端. 1.卸载libreoffices(要删一起删了,然后去装office ...
- 回顾4180天在腾讯使用C#的历程,开启新的征途
今天是2018年8月8日,已经和腾讯解除劳动关系,我的公司正式开始运营,虽然还有很多事情需要理清,公司官网也没有做,接下来什么事情都需要自己去完成了,需要一步一个脚印去完善,开启一个新的征途,我将在博 ...
- Java线程和进程相关面试题与答案总结
有几天没有写一写博客了,今天就带给大家一些面试题和参考答案吧! 这些都是上海尚学堂Java培训的学员去面试时遇到的问题,今天总结出来的是Java线程相关类的面试题.把参考答案和解析也发布出来,供大家学 ...
- JDK设计模式之——装饰者模式
假定已经有三个类A,B和C他们的继承关系如下 ClassA Class B extends A Class C extends A 想进一步扩展类B和类C的功能,新增三个方法 m ...
- Node.js 种子下载器
Node.js 种子下载器 庆祝 2018 国庆,制作了一个 Node.js 的种子下载器.爬取页面,根据页面的链接,破解另外一个网站,下载种子文件.项目比较简单,爬取页面没有使用任何爬虫框架.项目源 ...
- python网络-Socket之udp编程(24)
一.udp简介 udp --- 用户数据报协议,是一个无连接的简单的面向数据报的运输层协议. udp不提供可靠性,它只是把应用程序传给IP层的数据报发送出去,但是并不能保证它们能到达目的地. udp在 ...
- 10.Git分支-分支管理(git branch命令)、分支开发工作流
1.分支管理 git branch 不仅可以创建和删除分支,还可以做一些其他工作. 1.不带参数的 git branch ,得到本地仓库当前的分支列表.并且会显示,当期所在的分支,也就是HEAD所指 ...
- .NET Core实战项目之CMS 第十三章 开发篇-在MVC项目结构介绍及应用第三方UI
作为后端开发的我来说,前端表示真心玩不转,你如果让我微调一个位置的样式的话还行,但是让我写一个很漂亮的后台的话,真心做不到,所以我一般会选择套用一些开源UI模板来进行系统UI的设计.那如何套用呢?今天 ...
- .NET Core实战项目之CMS 第十七章 CMS网站系统的部署
目前我们的.NET Core实战项目之CMS系列教程基本走到尾声了,通过这一系列的学习你应该能够轻松应对.NET Core的日常开发了!当然这个CMS系统的一些逻辑处理还需要优化,如没有引入日志组件以 ...
