java_List集合及其实现类
第一章:List集合_List接口介绍
1).特点
1).有序的;
2).可以存储重复元素;
3).可以通过索引访问;
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("张无忌");
list.add("张三丰");
list.add("章子怡");
list.add("章子怡");//OK的,可以添加
for(String s : list){
System.out.println(s);//有序的
}
2).方法
继承了Collection接口的所有方法,并且又有很多自己的方法
void add(String item)
向滚动列表的末尾添加指定的项。
void add(String item, int index)
向滚动列表中索引指示的位置添加指定的项。
void addActionListener(ActionListener l)
添加指定的动作侦听器以从此列表接收动作事件。
void addItemListener(ItemListener l)
添加指定的项侦听器以接收此列表的项事件。
void addNotify()
创建列表的同位体。
void deselect(int index)
取消选择指定索引处的项。
AccessibleContext
getAccessibleContext()
获取与此 List 关联的 AccessibleContext。
ActionListener[]
getActionListeners()
返回已在此列表上注册的所有动作侦听器的数组。
String
getItem(int index)
获取与指定索引关联的项。
int getItemCount()
获取列表中的项数。
ItemListener[]
getItemListeners()
返回已在此列表上注册的所有项侦听器的数组。
String[]
getItems()
获取列表中的项。
<T extends EventListener>
T[]
getListeners(Class<T> listenerType)
返回目前已在此 List 上注册为 FooListener 的所有对象的数组。
Dimension
getMinimumSize()
确定此滚动列表的最小大小。
Dimension
getMinimumSize(int rows)
获取具有指定行数的列表的最少维数。
Dimension
getPreferredSize()
获取此滚动列表的首选大小。
Dimension
getPreferredSize(int rows)
获取具有指定行数的列表的首选维数。
int getRows()
获取此列表中的可视行数。
int getSelectedIndex()
获取列表中选中项的索引。
int[] getSelectedIndexes()
获取列表中选中的索引。
String
getSelectedItem()
获取此滚动列表中选中的项。
String[]
getSelectedItems()
获取此滚动列表中选中的项。
Object[]
getSelectedObjects()
获取对象数组中此滚动列表的选中项。
int getVisibleIndex()
获取上次由 makeVisible 方法使其可视的项的索引。
boolean isIndexSelected(int index)
确定是否已选中此滚动列表中的指定项。
boolean isMultipleMode()
确定此列表是否允许进行多项选择。
void makeVisible(int index)
使指定索引处的项可视。
protected String
paramString()
返回表示此滚动列表状态的参数字符串。
protected void processActionEvent(ActionEvent e)
处理发生在此列表上的动作事件,方法是将这些事件指派给所有已注册的 ActionListener 对象。
protected void processEvent(AWTEvent e)
此滚动列表的进程事件。
protected void processItemEvent(ItemEvent e)
处理发生在此列表上的项事件,方法是将这些事件指派给所有已注册的 ItemListener 对象。
void remove(int position)
从此滚动列表中移除指定位置处的项。
void remove(String item)
从列表中移除项的第一次出现。
void removeActionListener(ActionListener l)
移除指定的动作侦听器,以便不再从此列表接收动作事件。
void removeAll()
从此列表中移除所有项。
void removeItemListener(ItemListener l)
移除指定的项侦听器,以便不再从此列表接收项事件。
void removeNotify()
移除此列表的同位体。
void replaceItem(String newValue, int index)
使用新字符串替换滚动列表中指定索引处的项。
void select(int index)
选择滚动列表中指定索引处的项。
void setMultipleMode(boolean b)
设置确定此列表是否允许进行多项选择的标志。
api
3).常用方法(以下几个方法都是List接口中特有的方法)
1).增:public void add(int index,E e):将e添加到当前集合的index位置。
2).删:public E remove(int index):删除index位置上的元素,并将删除的元素返回。
3).改:public E set(int index,E element):将element替换index位置上的元素,并将原index位置上的元素返回。
4).查:public E get(int index):获取index位置上的元素。
示例代码:
public static void main(String[] args) {
//List集合中增加自己的add方法,add(int index,E e);
List<String> list=new ArrayList<>();
list.add("aaaa");
list.add("bbbb");
list.add("cccc");
list.add(1,"dddd");
System.out.println(list);
//删除指定索引的元素,并将删除的元素返回
String removeStr=list.remove(2);
System.out.println(removeStr);
System.out.println(list);
//修改指定索引位置上的元素set(int index,E e),并将原index位置上的元素返回
String setStr=list.set(2,"ffff");
System.out.println(setStr);
System.out.println(list);
//通过索引获取指定索引上的元素
String getStr=list.get(2);
System.out.println("索引为3的元素为:"+getStr);
System.out.println(list);
}
第二章.实现List接口的常用类_ArrayList
1).list接口常用实现类

2).ArrayList
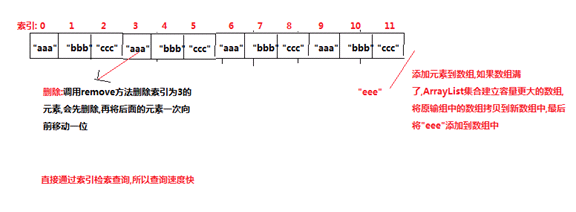
特点:
查询快----使用索引
增删慢---需要扩容,移位
图解:
方法:
无特有方法
案例
public static void main(String[] args) {
//List集合中增加自己的add方法,add(int index,E e);
ArrayList<String> list=new ArrayList<>();
list.add("aaaa");
list.add("hhhh");
list.add("cccc");
list.add(1,"dddd");
System.out.println(list);
//删除指定索引的元素,并将删除的元素返回
String removeStr=list.remove(2);
System.out.println(removeStr);
System.out.println(list);
//修改指定索引位置上的元素set(int index,E e),并将原index位置上的元素返回
String setStr=list.set(2,"ffff");
System.out.println(setStr);
System.out.println(list);
//通过索引获取指定索引上的元素
String getStr=list.get(2);
System.out.println("索引为3的元素为:"+getStr);
System.out.println(list);
}
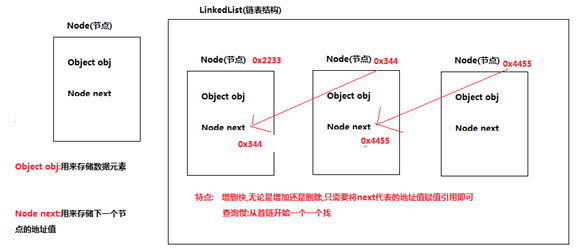
3).LinkedList
特点
使用链表实现
增删快,查询慢
图解
方法
新增了一些方法,可以模拟栈、队列:
1).public void push(Object o):压栈 等同于addFirst(E e) ,将指定元素添加到此集合的开头
2).public
E pop():弹栈--如果没有元素,会抛异常;
public E poll():弹栈--如果没有元素,会返回null【建议使用】
案例:
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList<String> list = new LinkedList<>();
list.push("孙悟空");
list.push("猪八戒");
list.push("沙和尚");
System.out.println(list);
while (list.size() > 0) {
System.out.println("弹出一个:" + list.poll());
System.out.println("集合大小:" + list.size());
}
}
}
java_List集合及其实现类的更多相关文章
- 操作集合的工具类:Collections
Java提供了一个操作Set.List和Map等集合的工具类:Collections,该工具类提供了大量方法对集合进行排序.查询和修改等操作,还提供了将集合对象置为不可变.对集合对象实现同步控制等方法 ...
- JAVA基础学习之 Map集合、集合框架工具类Collections,Arrays、可变参数、List和Set集合框架什么时候使用等(4)
package com.itcast.test20140113; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Arrays; import java.ut ...
- 线程高级应用-心得8-java5线程并发库中同步集合Collections工具类的应用及案例分析
1. HashSet与HashMap的联系与区别? 区别:前者是单列后者是双列,就是hashmap有键有值,hashset只有键: 联系:HashSet的底层就是HashMap,可以参考HashSe ...
- 操作集合的工具类Collections
1 操作集合的工具类Collections Java提供了一个操作Set.List和Map等集合的工具类:Collections,该工具类里提供了大量方法对集合元素进行排序.查询和修改等操 ...
- Java集合概述、Set集合(HashSet类、LinkedHashSet类、TreeSet类、EnumSet类)
Java集合概述.Set集合(HashSet类.LinkedHashSet类.TreeSet类.EnumSet类) 1.Java集合概述1)数组可以保存多个对象,但数组长度不可变,一旦在初始化数组时指 ...
- JAVA中的集合容器操作类
目录 JAVA中的集合容器操作类 List集合 ArrayList的操作方法说明 LinkedList Stack Set Map Queue 总结 JAVA中的集合容器操作类 Java容器类库总共分 ...
- 转:C#常用的集合类型(ArrayList类、Stack类、Queue类、Hashtable类、Sort)
C#常用的集合类型(ArrayList类.Stack类.Queue类.Hashtable类.Sort) .ArrayList类 ArrayList类主要用于对一个数组中的元素进行各种处理.在Array ...
- 集合框架的类和接口均在java.util包中。 任何对象加入集合类后,自动转变为Object类型,所以在取出的时候,需要进行强制类型转换。
集合框架的类和接口均在java.util包中. 任何对象加入集合类后,自动转变为Object类型,所以在取出的时候,需要进行强制类型转换.
- Java中各种集合(字符串类)的线程安全性!!!
Java中各种集合(字符串类)的线程安全性!!! 一.概念: 线程安全:就是当多线程访问时,采用了加锁的机制:即当一个线程访问该类的某个数据时,会对这个数据进行保护,其他线程不能对其访问,直到该线程读 ...
随机推荐
- PyCharm下载及使用
PyCharm教育版是一款能够对你编写Python程序的工作有所帮助的免费编译器. PyCharm-community下载链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1Hwd_TOVA3en ...
- 手动安装composer详细教学
1.下载compser.phar 地址 https://getcomposer.org/download/ 2.新建composer.bat 文件,写入“@php "%~dp0compose ...
- C#相对路径
1. 根目录 .\\ 或者直接给出文件名称,是找根目录的路径. 如:path = "gs.mdb" 与 path = ".\\gs.mdb"是一个意思. 2. ...
- nmon监控分析
一.下载软件安装 wget http://sourceforge.net/projects/nmon/files/nmon_linux_14i.tar.gz tar xf nmon_linux_14i ...
- 请输入一个大于7的整数,输出小于k并且至少满足下面2个条件中的1个条件的所有正整数
import java.util.Scanner; /** * @author:(LiberHome) * @date:Created in 2019/3/6 22:06 * @description ...
- truffle unbox react 出坑指南
最近几天差点就被这鬼东西给逼疯了,truffle init .truffle unbox webpack 不管我怎么运行都是对的,唯独truffle unbox react 不管在哪个windows都 ...
- 两层fragment嵌套时出现空白,(收藏别人的)
完美解决 两层Fragment,内层空白 转载:http://blog.csdn.net/bingospunky/article/details/51352400 目录(?)[+] 前言 两层Frag ...
- 微服务(Microservices)和服务网格(Service Mesh)架构概念整理
注:文章内容为摘录性文字,自己阅读的一些笔记,方便日后查看. 微服务(Microservices) 在过去的 2016 年和 2017 年,微服务技术迅猛普及,和容器技术一起成为这两年中最吸引眼球的技 ...
- 使用BurpSuite进行双文件上传拿Webshell
首先进入网站后台:(后台界面应该是良精CMS) <ignore_js_op> 在 添加产品 这一栏有个上传文件: <ignore_js_op> 选择一个*.jpg格式的图片进行 ...
- Python网络爬虫与如何爬取段子的项目实例
一.网络爬虫 Python爬虫开发工程师,从网站某一个页面(通常是首页)开始,读取网页的内容,找到在网页中的其它链接地址,然后通过这些链接地址寻找下一个网页,这样一直循环下去,直到把这个网站所有的网页 ...
