小洋的Python入门笔记😀
小洋的python入门笔记
起因:发现自己前三年做的Python项目很多都是现做先学的,修改理解语法错误多依仗对C/C++的理解,对python缺乏一个系统的学习。趁此有空,补上!
特别鸣谢:B站找到的“Python课程推荐”UP主的1039.8万播放量的课程《【2025】Python小白零基础如何正确入门?这期视频手把手教你从零开始,入门到起飞!》;以及原作者Mosh Hamedani的课程《[Complete Python Mastery](Complete Python Mastery)》;还有Python 3的官方文档《[Python Documentation contents](Python Documentation contents — Python 3.13.0 documentation)》
运行环境:pycharm + python 3.8(conda自建的虚拟环境)
1.输出
print("He Yang")#里面是单引号也可以!
输出结果:
He Yang
2.变量
变量定义:
price = 10 #全局变量,也是整数
rating = 4.9#float型浮点数
name = 'HeYang'#字符串
is_published = False#bool型,注意python是大小写敏感的
#尤其是bool变量对应的值,它是关键字,有“False”和“True”两种类型
print(price)#10
练习:
age = 20
name = "John"
new_or_not = True
print(age,name,new_or_not)
输出结果:
20 John True
3.输入接收
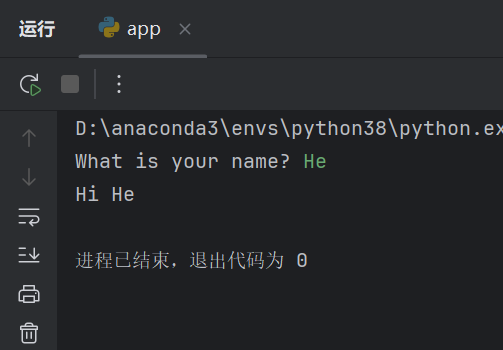
name = input('What is your name? ')
print('Hi '+ name)#表达式:使用一个变量的代码
#上面这串代码连接了两个字符串
PS:注意上面的?后面加了一个“ ”,便于让终端中我们的输入不和问题挨在一起
输出结果:
练习:
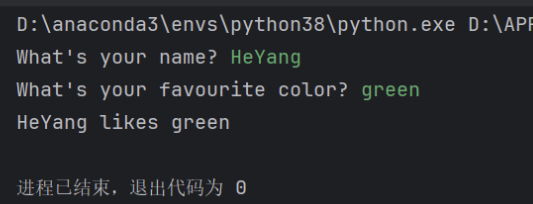
person_name = input("What's your name? ")
fav_color = input("What's your favourite color? ")
print(person_name +" likes "+fav_color)
输出结果:
4.型号转换
birth_year = input('Birth year: ')#注意birth_year是字符串
print(type(birth_year))
age = 2019 - int(birth_year)
#下面是其他类型变量转换为相应类型变量的函数
#int()
#float()
#bool()
print(type(age))
print(age)
练习:
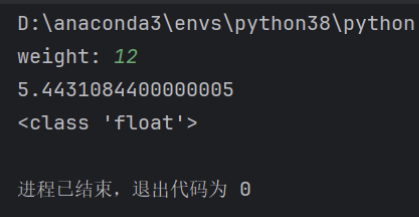
pounds=input('weight: ')
kilograms=int(pounds)*0.45359237
print(kilograms)
print(type(kilograms))
输出结果:
5.字符串
#假如你想打出不换行的内部带引号的内容
course = "Python's Course for Beginners"#内部只有单引号
print(course)#Python's Course for Beginners
course = 'Python for "Beginners"'
print(course)#Python for "Beginners"
#假如你想打内部跨越多行的
course='''
Hi John,
Here is our first email to you.
Thank you,
The support team
'''
print(course)
#
#Hi John,
#
#Here is our first email to you.
#
#Thank you,
#The support team
#
#
#
#python的索引
course = 'Python for Beginners'
print(course[0])#P
print(course[1])#y
print(course[-1])#s
print(course[-2])#r
print(course[0:3])#包含前,不包含后#Pyt
print(course[0:])#等价于print(course[0:字符串的长度值])#Python for Beginners
print(course[1:])#ython for Beginners
print(course[:5])#等价于print(course[0:5])#Pytho
print(course[:])#Python for Beginners
another = course[:]#等价于复制
print(another)#Python for Beginners
name = 'Jennifer'
print(name[1:-1])#ennife
6.格式化字符串
#用文本变量动态生成某些字符串
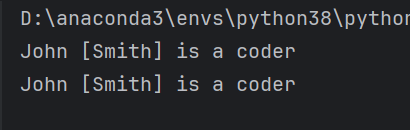
#生成目标:John [Smith] is a coder
first = 'John'
last = 'Smith'
message = first + ' [' + last + '] is a coder'#不适用于复杂文本
print(message)
msg = f'{first} [{last}] is a coder'
print(msg)
输出结果:
7.字符串方法
1)len函数
course = 'Python for Beginner'
print(len(course))#len不仅仅用于字符串,传说还可以用于计算列表中项目的个数
#19
我们还有专门用于字符串的函数
当一个函数针对某种特定的类型或对象,就是方法
下面的方法特定于字符串,上面的函数len,print是通用方法
2)全部转换为大写/小写方法
course.upper()不会改变原有字符串,会创造一个新字符串并返回它
course = 'Python for Beginner'
print(course.upper())#PYTHON FOR BEGINNER
print(course.lower())#python for beginner
print(course)#Python for Beginner
3)find方法
course = 'Python for Beginner'
print(course.find('P'))#会返回P在这个字符串中第一次出现的索引#0
print(course.find('o'))#会返回o在这个字符串中第一次出现的索引#4
#find方法是大小写敏感的,如果找不到对应字母会返回-1
#比如找大写O
print(course.find('O'))#-1
#我们还可以找字符串
print(course.find('Beginner'))#返回11,因为Beginner是从第11个索引开始的#11
4)replace方法
course = 'Python for Beginner'
#我们还能替换字符/字符串
print(course.replace('Beginner','Absolute Beginners'))
#Python for Absolute Beginners
#但是如果被替换的部分找不到,就会返回原字符串,replace方法也是大小写敏感的
print(course.replace('beginner','Absolute Beginners'))
#Python for Beginner
print(course.replace('P','J'))
#Jython for Beginner
5)in函数
course = 'Python for Beginner'
#当我们查找原字符串中是否包含某字符串时,我们用in它会返回bool值
print('python' in course)
#False
8.算术运算
#算术运算
print(10+3)
print(10-3)
print(10*3)
print(10/3)#3.3333333333333335
print(10//3)#3
print(10%3)#1,表示取余
print(10**3)#指数运算,1000
#增广赋值运算符
x=10
x=x+2#等价于x+=2
x-=3#等价于x=x-3
print(x)#9
9.运算符优先级
x=10+3*2**2
print(x)#22
#先是括号
#接着是指数 eg.2**3
#然后是乘法/除法
#最后是加减法
x=(2+3)*10-3
print(x)#47
10.数学函数
x=2.9
print(round(x))#四舍五入函数#3
print(abs(-2.9))#绝对值#2.9
import math
print(math.ceil(2.9))#上限函数#3
print(math.floor(2.9))#下限函数#2
round函数还可以指定四舍五入的位数,
# 四舍五入到小数点后两位
print(round(3.14159, 2)) # 输出: 3.14
所有数学函数 math — 数学函数 — Python 3.13.0 文档,如下:
数论和表示函数
| 函数 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| ceil(x) | x 的上限,大于或等于 x 的最小整数 |
| comb(n,k) | 从 n 个项目中选择 k 个项目的方法数,不重复且无序 |
| copysign(x,y) | x 的绝对值,带有 y 的符号 |
| fabs(x) | x 的绝对值 |
| factorial(n) | n 的阶乘 |
| floor(x) | x 的下限,小于或等于 x 的最大整数 |
| fma(x,y,z) | 融合乘加操作:(x*y)+z |
| fmod(x,y) | x 除以 y 的余数 |
| frexp(x) | x 的尾数和指数 |
| fsum(iterable) | 输入可迭代对象中值的总和 |
| gcd(*integers) | 整数参数的最大公约数 |
| isclose(a,b, rel_tol, abs_tol) | 检查 a 和 b 的值是否彼此接近 |
| isfinite(x) | 检查 x 是否既不是无穷大也不是 NaN |
| isinf(x) | 检查 x 是否是正无穷或负无穷大 |
| isnan(x) | 检查 x 是否是 NaN(不是一个数字) |
| isqrt(n) | 非负整数 n 的整数平方根 |
| lcm(*integers) | 整数参数的最小公倍数 |
| ldexp(x,i) | x*(2**i),frexp() 函数的逆函数 |
| modf(x) | x 的小数部分和整数部分 |
| nextafter(x,y, steps) | 用于计算浮点数x之后朝向y的下一个浮点数 |
| perm(n,k) | 从 n 个项目中选择 k 个项目的方法数,不重复且有序 |
| prod(iterable, start) | 输入可迭代对象中元素的乘积,具有起始值 |
| remainder(x,y) | x 相对于 y 的余数 |
| sumprod(p,q) | 两个可迭代对象 p 和 q 的乘积之和 |
| trunc(x) | x 的整数部分 |
| ulp(x) | x 的最低有效位的值 |
幂函数和对数函数
| 函数 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| cbrt(x) | x 的立方根 |
| exp(x) | e 的 x 次幂 |
| exp2(x) | 2 的 x 次幂 |
| expm1(x) | e 的 x 次幂减去 1 |
| log(x, base) | 以给定底数(默认为 e)计算 x 的对数 |
| log1p(x) | 1+x 的自然对数(底数为 e) |
| log2(x) | 以 2 为底数计算 x 的对数 |
| log10(x) | 以 10 为底数计算 x 的对数 |
| pow(x, y) | x 的 y 次幂 |
| sqrt(x) | x 的平方根 |
三角函数
| 函数 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| acos(x) | x 的反余弦 |
| asin(x) | x 的反正弦 |
| atan(x) | x 的反正切 |
| atan2(y, x) | atan(y / x) |
| cos(x) | x 的余弦 |
| dist(p, q) | 两点 p 和 q 之间的欧几里得距离,给定为一个坐标可迭代对象 |
| hypot(*coordinates) | 一个坐标可迭代对象的欧几里得范数 |
| sin(x) | x 的正弦 |
| tan(x) | x 的正切 |
其他函数
| 函数分类 | 函数名称 | 描述/定义 |
|---|---|---|
| 角度转换 | degrees(x) | 将角度x从弧度转换为度数 |
| radians(x) | 将角度x从度数转换为弧度 | |
| 双曲函数 | acosh(x) | x的反余弦双曲函数 |
| asinh(x) | x反正弦双曲函数 | |
| atanh(x) | x反切线双曲函数 | |
| cosh(x) | x的双曲余弦函数 | |
| sinh(x) | x的双曲正弦函数 | |
| tanh(x) | x的双曲正切函数 | |
| 特殊函数 | erf(x) | x处的误差函数 |
| erfc(x) | x处的补误差函数 | |
| gamma(x) | x处的伽马函数 | |
| lgamma(x) | 伽马函数在x处绝对值的自然对数 | |
| 常数 | pi | π = 3.141592... |
| e | e = 2.718281... | |
| tau | τ = 2π = 6.283185... | |
| inf | 正无穷大 | |
| nan | "Not a number" (NaN) |
11.if条件分支
is_hot = False
is_cold = True
if is_hot:
print("It's a hot day")
print("Drink plenty of water")
elif is_cold:
print("It's a cold day")
print("Wear warm clothes")
else:
print("It's a lovely day!")
print("Enjoy your day!")
输出结果:
练习:
price=1000000#1M
good_credict = False
if good_credict:
down_payment = price * 0.1
print(price*0.1)
else:
down_payment = price * 0.2
print(price*0.2)
print(f"Down payment: ${down_payment}")#down_payment意为首付
输出结果:
12.逻辑运算符
and or not
has_high_income = True
has_good_credict = True
if has_high_income and has_good_credict:#and:both
print("Eligible for loan")
if has_high_income or has_good_credict:#or:at least one
print("Eligible for loan 2")
has_criminal_record = True
if has_good_credict and not has_criminal_record:#not
print("Eligible for loan 3")
输出结果:
13.比较运算符
#比较运算符
temperature = 30
if temperature>30:#> < >= <= == != 没有=,因为赋值不会生成bool值
print("It's a hot day")
else:
print("It's not a hot day")
输出结果:

练习:
name = input("your name: ")
if len(name)<3:
print("name must be at least 3 characters")
elif len(name)>50:
print("name can be a maxinum of 50 characters")
else:
print("name looks good!")
输出结果:
14.重量转换器
weight = input("Weight: ")#也可以直接float(input("……"))
danwei = input("(L)bs or (K)g: ")
if danwei == "L" or danwei == "l":#磅转KG,也可以 if danwei.upper()=="L"
ans = float(weight)*0.45
print(f"You are {ans} KG")
elif danwei == "K" or danwei == "k":#KG转磅
ans = float(weight)*2.20#也可以ans=float(weight)/0.45
print(f"You are {ans} pounds")
输出结果:
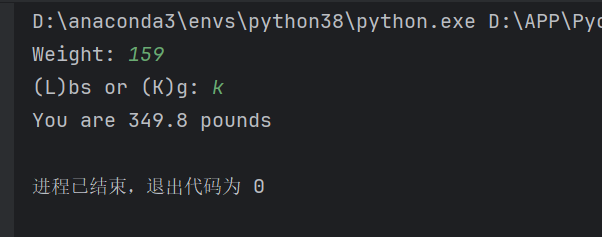
15.while循环
i = 1
while i<=5:
print('*'* i)
i = i + 1
print("Done")
输出结果:
小技巧:变量的重命名方法
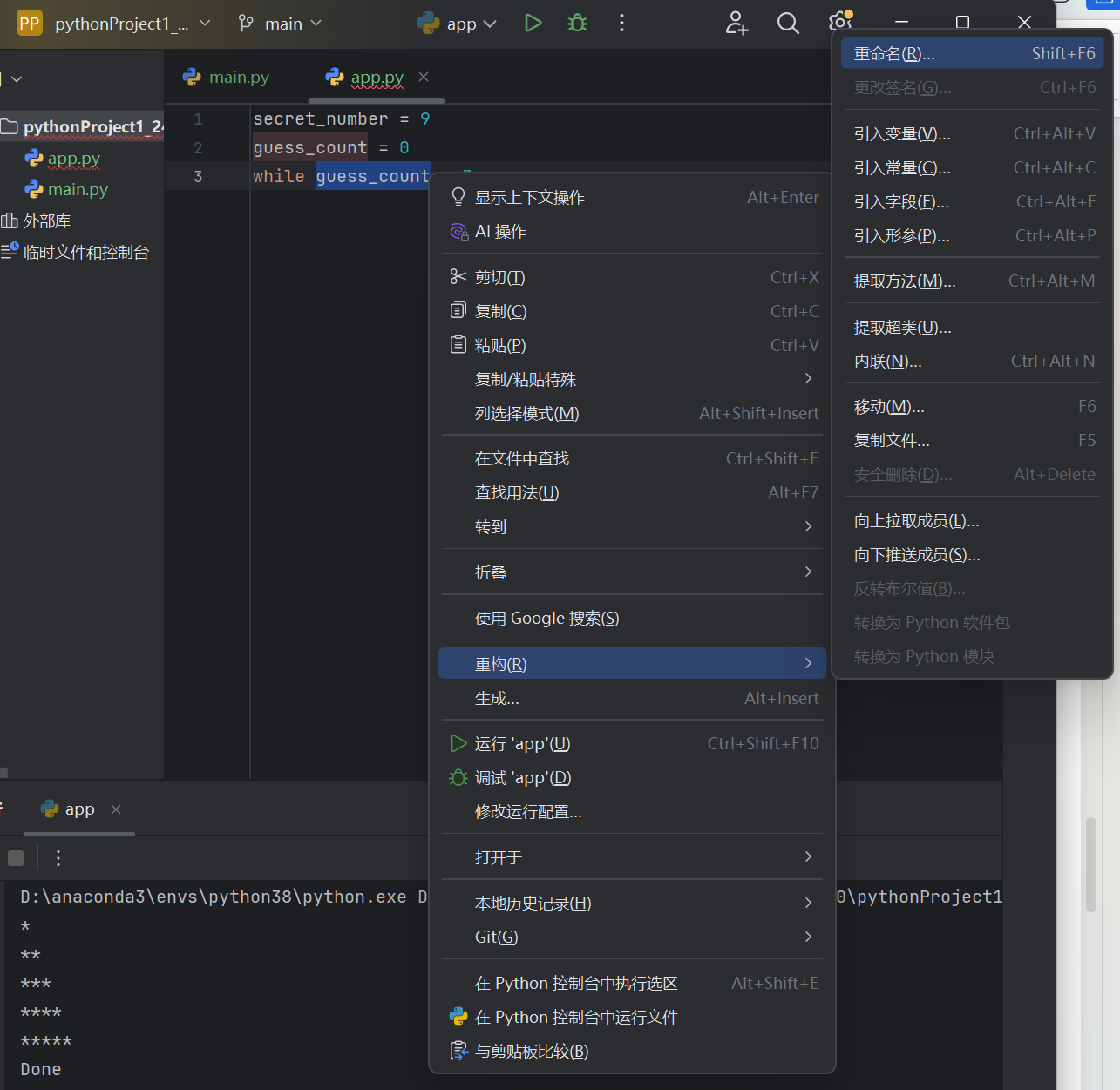
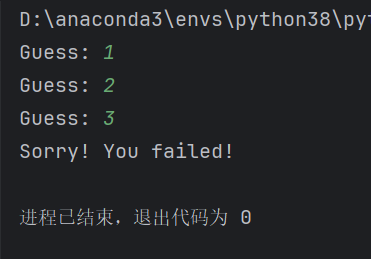
1)猜谜游戏
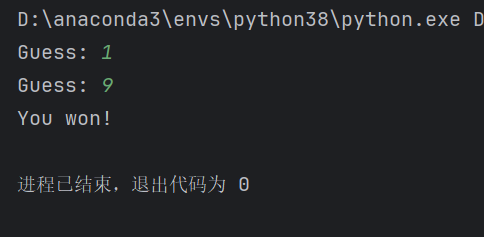
secret_number = 9
guess_count = 0
guess_limit = 3
while guess_count < guess_limit:
guess = int(input('Guess: '))
guess_count += 1
if guess == secret_number:
print('You won!')
break
else:#在while循环中,可以选择性含有else部分,当while循环中的条件不被满足时会执行它
print('Sorry! You failed!')
输出结果:
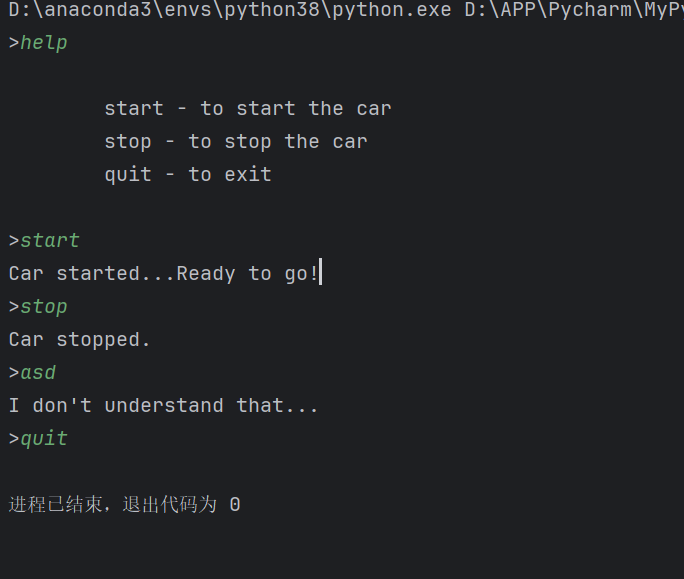
2)汽车游戏
promot = input(">")
while promot.lower() != "quit":
if promot.lower() == "help":
print('''
start - to start the car
stop - to stop the car
quit - to exit
''')
elif promot.lower() == "start":
print("Car started...Ready to go!")
elif promot.lower() == "stop":
print("Car stopped.")
else:
print("I don't understand that...")
promot = input(">")
输出结果:
改进一:简化指令版
promot = input(">").lower()
while promot!= "quit":
if promot == "help":
print('''
start - to start the car
stop - to stop the car
quit - to exit
''')
elif promot == "start":
print("Car started...Ready to go!")
elif promot == "stop":
print("Car stopped.")
else:
print("I don't understand that...")
promot = input(">").lower()#也可以提前把promot定义为空字符串"",然后把这个判断条件放在循环最前面
改进二:缩进调整版
command = ""#定义为空字符串
started = False
while True:#这表示如果我们不主动break,循环会一直执行
command = input("> ").lower()
if command == "start":
if started:
print("Car is already started!")
else:
started = True
print("Car started...")
elif command == "stop":
if not started:
print("Car is already stopped!")
else:
started = False
print("Car stopped.")
elif command == "help":
print('''
start - to start the car
stop - to stop the car
quit - to exit
''')#当我们输入三引号时,输出会完全按照原样打印,所以会多出缩进
elif command == "quit":
break
else:
print("Sorry,I don't understand that...")
16.for循环
for 用于迭代集合中的项目
1)迭代字符串
for item in 'Python':
print(item)
输出
P
y
t
h
o
n
2)迭代列表元素
列表中元素为字符串:
for item in ['Mosh','John','Sarah']:
print(item)
输出
Mosh
John
Sarah
列表中元素为数字:
for item in [1,2,3,4]:
print(item)
输出
1
2
3
4
3)迭代range
for item in range(10):#从0开始,到10(但是不含10)
print(item)
#0
#1
#...
#8
#9
for item in range(5,10):#从5开始,到10(但是不含10)
print(item)
#5
#6
#7
#8
#9
for item in range(5,10,2):#这里还设置了step
print(item)
#5
#7
#9
练习:
prices = [10,20,30]
sum = 0
for price in prices:
sum += price
print(f"sum:{sum}")
输出:

17.嵌套循环
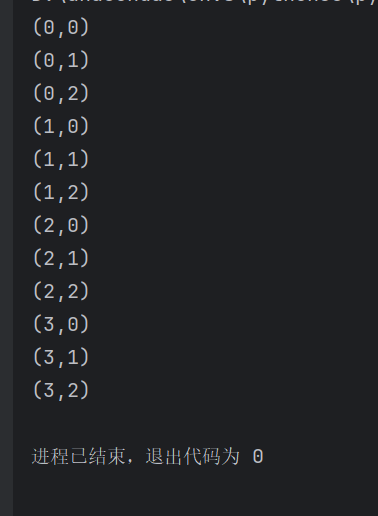
#嵌套循环
for x in range(4):
for y in range(3):
print(f"({x},{y})")
输出:
练习(输出F):
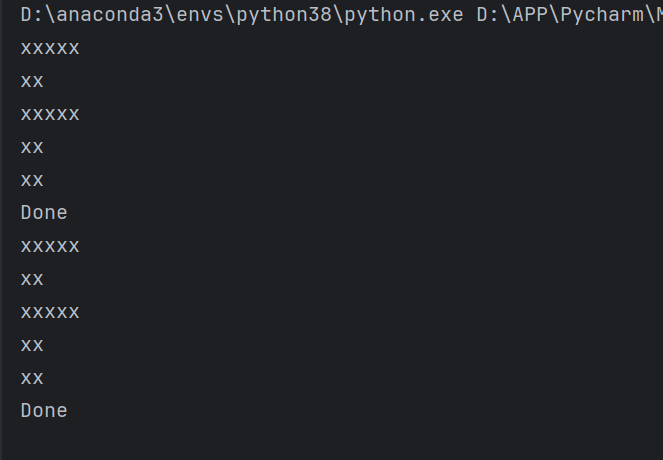
#在python中,可以拿数字×一个字符串
numbers = [5,2,5,2,2]
for number in numbers:
print('x'* number )
print("Done")
#方法二:(需要定义一个空字符串)
for number in numbers:
output = ''
for item in range(number):
output += 'x'#这个补充字符串的方法好奇妙!
print(output)
print("Done")
在python中,可以拿数字×一个字符串,字符串=字符串+字符串
输出:
18.列表方法
names = ['John','Bob','Mosh','Sarah','Mary']
print(names[0])
print(names[2])
print(names[-1])
print(names[-2])
print("Done")
print(names[2:])
print(names[2:4])#含前不含后
print(names[0:])#等价于names[:]
#另外,这个就像字符串一样,这个的方括号不会修改最初的列表,他们只是返回一个新的列表
print(names)
print("lalala")
#当然,我们也能轻而易举修改列表中的内容
names[0] = 'Jon'
print(names)
输出:
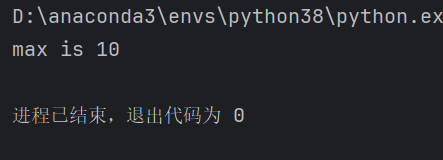
练习(找到列表中最大的元素):
numbers = [3,6,2,8,4,10]
max = numbers[0]
for number in numbers:
if number > max :
max = number
print(f"max is {max}")
输出:
19.二维列表
1)访问
matrix = [
[1,2,3],
[4,5,6],
[7,8,9]
]
#访问
print(matrix[0][1])
#2
2)修改
matrix = [
[1,2,3],
[4,5,6],
[7,8,9]
]
matrix[0][1]=20
print(matrix[0][1])
#20
3)遍历
for row in matrix:
for item in row:
print(item)
输出:

网址:Code with Mosh讲真好!( ω )
20.列表方法
1)尾部加数
numbers = [5,2,1,7,4]
numbers.append(20)
print(numbers)#[5, 2, 1, 7, 4, 20]
2)中间加数
numbers = [5,2,1,7,4]
numbers.insert(0,10)
print(numbers)#[10, 5, 2, 1, 7, 4]
3)列表删数
numbers = [5,2,1,7,4]
numbers.remove(5)#这个remove每次只能删一个
print(numbers)#[2, 1, 7, 4]
4)清空列表
numbers = [5,2,1,7,4]
numbers.clear()
print(numbers)#[]
5)弹出最后一个元素
numbers = [5,2,1,7,4]
numbers.pop()
print(numbers)#[5, 2, 1, 7]
6)查找元素是否在某个列表中,在则返回索引
numbers = [5,2,1,7,4]
print(numbers.index(5))#0
#print(numbers.index(50))#ValueError: 50 is not in list
#返回bool值的方法,in,和字符串中的用法差不多
print(50 in numbers)#False
7)你想知道一个元素在里面的个数
numbers = [5,2,1,5,7,4]
print(numbers.count(5))#2
print(numbers.count(0))#0
8)列表排序
numbers = [5,2,1,5,7,4]
#print(numbers.sort())#None
#升序
numbers.sort()
print(numbers)#[1, 2, 4, 5, 5, 7]
#降序
numbers.reverse()
print(numbers)#[7, 5, 5, 4, 2, 1]
9)独立复制列表
numbers = [5,2,1,5,7,4]
numbers2 = numbers.copy()
numbers.append(10)
print(numbers)#[5, 2, 1, 5, 7, 4, 10]
print(numbers2)#[5, 2, 1, 5, 7, 4]
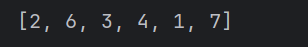
练习(移除列表中的重复项)
我的方法:
numbers = [2,2,4,6,3,4,1,7]
for number in numbers:
if numbers.count(number)>1:
numbers.remove(number)
print(numbers)
输出:
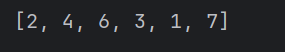
老师的方法:
numbers = [2,2,4,6,3,4,1,7]
uniques = []
for number in numbers:
if number not in uniques:
uniques.append(number)
print(uniques)
输出:
21.元组
元组与列表不同的点在于,我们不能修改它们,这意味着我们不能添加新项目/删除现有项目,或者弹出。
numbers = (1,2,3,1)
print(numbers.count(1))#返回此元素的个数#2
print(numbers.index(1))#返回此元素第一次出现时的索引#0
#其他有两个下划线的方法叫做魔术方法
#另外,元组不支持元素修改
#numbers[0]=10#'tuple' object does not support item assignment
#仅支持访问
print(numbers[0])#1
22.拆包
不仅适用于元组,还适用于列表。
1)元组
coordinates = (1,2,3)
x = coordinates[0]
y = coordinates[1]
z = coordinates[2]
#上面三行等价于
x, y, z = coordinates
print(x)#1
print(y)#2
2)列表
coordinates = [1,2,3]
x, y, z = coordinates
print(y)#2
23.字典
注意字典中的键都应该是唯一的。
1)元素访问
customer = {
"name": "John Smith",
"age":30,
"is_verified":True
}
#键除了字符串还可以是数字
#但是值可以是任何东西,比如字符串、数字、布尔值、列表...
print(customer["name"])#John Smith
#如果使用不存在的键
#print(customer["birthdate"]) #KeyError: 'birthdate'
#同样,字典也是大小写敏感的
#print(customer["Name"])#KeyError: 'Name'
#get方法:不会在一个键不存在时向我们警告
print(customer.get("name"))#John Smith
print(customer.get("birthdate"))#None
#也可若未查到则返回默认值
print(customer.get("birthdate","Jan 1 1980"))#Jan 1 1980
2)元素更新
#另外,也可以更新字典中键对应的值
customer = {
"name": "John Smith",
"age":30,
"is_verified":True
}
customer["name"] = "Jack Smith"
print(customer["name"])#Jack Smith
#当然,我们还能添加新的键值对
customer["birthdate"] = "Jan 1 1980"
print(customer["birthdate"])#Jan 1 1980
练习(电话号码翻译):
phone_number = {
'0':"Zero",
'1':"One",
'2':"Two",
'3':"Three",
'4':"Four",
'5':"Five",
'6':"Six",
'7':"Seven",
'8':"Eight",
'9':"Nine"
}
output = ''
phone = input("Phone: ")
for item in phone:
#output += phone_number[item] + " "
#为了避免用户输入字典中没有的键程序警告,我们使用get方法会更好
output +=phone_number.get(item,"!") + " "
print(output)
输出1:
输出2:
!正在更新中...
小洋的Python入门笔记😀的更多相关文章
- Python入门笔记(13):列表解析
一.列表解析 列表解析来自函数式编程语言(haskell),语法如下: [expr for iter_var in iterable] [expr for iter_var in iterable i ...
- 小甲鱼:Python学习笔记001_变量_分支_数据类型_运算符等基础
1.下载并安装Python 3.5.0 Python是一个跨平台语言,Python从3.0的版本的语法很多不兼容2版本,官网找到最新的版本并下载:http://www.python.org 2.IDL ...
- [Python]Python入门笔记:语法基础
Python笔记 一.基本语法 1.1 注释 文档注释: """contents""" 多行注释: ''' contents ''' 单行注 ...
- python 入门笔记
1.pip包安装 pip install *** pip 中http和https代理设置(/etc/profile) 2.强制保存 :w !sudo tee % 3.cffi是python调用C的包 ...
- python入门笔记
创建变量 python的变量不需要声明数据类型. >>> fred=100 >>> print (fred) 100 >>> fred 100 创 ...
- Python入门笔记(26):Python执行环境
一.python特定的执行环境 在当前脚本继续进行 创建和管理子进程 执行外部命令或程序 执行需要输入的命令 通过网络来调用命令 执行命令来创建需要处理的输出 动态生成Python语句 导入Pytho ...
- Python入门笔记(25):Python面向对象(2)
一.类 类就是一个数据结构,封装了数据和操作. 类的声明与函数的声明十分类似: class newClass(object): """class documentatio ...
- Python入门笔记(24):Python面向对象(1)速成
一.Python经典类与新类 经典类:如果没有直接或间接的子类化一个对象,也就是说如果没有指定一个父类,或者是如果子类化的基本类没有父类,那么就定义了经典类: class classics: 'def ...
- Python入门笔记(23):模块
一.模块基础 1.模块 自我包含,且有组织的代码片段就是模块 模块是Pyhon最高级别的程序组织单元,它将程序代码和数据封装起来以便重用.实际的角度,模块往往对应Python程序文件. 每个文件都是一 ...
- Python入门笔记(22):Python函数(5):变量作用域与闭包
一.全局变量与局部变量 一个模块中,最高级别的变量有全局作用域. 全局变量一个特征就是:除非被删除,否则他们存活到脚本运行结束,且对于所有的函数都可访问. 当搜索一个标识符(也称变量.名字等),Pyt ...
随机推荐
- jenkins Publish over SSH 的配置与使用
一.安装Publish over SSH 插件 二.在Configure System 配置Publish over SSH属性 Passphrase:如果私钥设置了密码就是私钥的密码,私钥没设置密码 ...
- AOT漫谈专题(第三篇): 如何获取C#程序的CPU利用率
一:背景 1. 讲故事 上篇聊到了如何对AOT程序进行轻量级的APM监控,有朋友问我如何获取AOT程序的CPU利用率,本来我觉得这是一个挺简单的问题,但一研究不是这么一回事,这篇我们简单的聊一聊. 二 ...
- 【2024】所有人都能看懂的 Win 11 安装/重装教程,跟着我一遍包成功
无论你因为系统坏掉想重装一下 Windows,或者只是想升级一下 Windows 都可以.虽然标题写的是 Win 11,不过实际上对于任何 Windows 系统都适用,不过现在 Win 11 已经相当 ...
- MongoDB mongod.log "connection refused because too many open connections" 处理方法
一.MongoDB副本集 副本集名称 角色 IP地址 端口号 优先级 CCTV-test Primary 192.168.1.21 27017 10 Secondary 192.168.1.21 27 ...
- 出现负载均衡问题IP端口不通的紧急处理
出现负载均衡IP不能用的处理方案,重启这个服务. 命令: systemctl stop keepalived systemctl start keepalived
- SSIS作业提示所请求的 OLE DB 访问接口 Microsoft.ACE.OLEDB.12.0 尚未注册
没有跨不过的坎,也没有解决不了的问题,那些曾经没有把我们打死的困难,最终都会让我们变得更加强大 最近在使用ETL获取Excel数据时,在本地运行没有任何问题,部署到服务器后,使用作业运行时便一直提示以 ...
- centos7系统安装部署zabbix5.0
一.简介 zabbix是一个基于[WEB]界面的提供分布式[系统监视]以及网络监视功能的企业级的开源解决方案.zabbix能监视各种网络参数,保证[服务器系统]的安全运营:并提供灵活的通知机制以让[系 ...
- Shell之根据关键字符串替换文件中的行
KEY="所要搜索的关键字符串"FullPath=所要搜索的文件的路径str="要替换行的字符串" 根据关键字符串定位行号:line=`sed -n ' ...
- awk优化钉钉通知测试报告
一.背景 在之前的博客 Go服务自动触发单元测试覆盖率 中钉钉通知的效果实现如下图: 最近RD提出对本次和上次覆盖率的比对需求,并把比对结果也显示在钉钉通知上. 二.实现思路 要实现数据比对,就需要对 ...
- CF207C3 Game with Two Trees
CF207C3 Game with Two Trees 妙到家的树上字符串问题. 约定 树 \(1\):\(t_1\). 树 \(2\):\(t_2\). \(S_{1/2}(i,l)\) 为树 \( ...
