条件概率:{乘法公式•全概率公式•Bayes公式}_Bayes: PosteriorP(A|B)=PriorP(A)•Likelihood:(P(B|A)/P(B))
条件概率的三种形式
乘法公式Multiplication formula: P(AB) = P(A)•P(B|A)
全概率公式: P(A) = P(Aω)=P(AB1)+P(AB2)+…P(ABn) = Sum( P(A)•P(Bi|A) ), i=1,2…,n
Bayes Formula(theorem): Posterior = Prior * Likelihood, P(A | B) = P(A) • ( P (B | A) / P(B) )
https://www.oreilly.com/library/view/machine-learning-with/9781785889936/ff082869-751b-4de3-9a59-edff60ad4e94.xhtml#:~:text=Prior%2C likelihood%2C and posterior Bayes theorem states the,probability of A given B%2C also called posterior.Prior, likelihood, and posterior
Bayes theorem: Posterior = Prior * Likelihood
This can also be stated as P (A | B) = P(A) • (P (B | A) / P(B) , where P(A|B) is the probability of A given B, also called posterior
- Prior: Probability distribution representing knowledge or uncertainty of a data object prior or before observing it
- Posterior: Conditional probability distribution representing what parameters are likely after observing the data object
- Likelihood: The probability of falling under a specific category or class.
P(Y|X) = P(YX) / P(X):
条件概率P(Y|X) 是集合 X与Y的交集XY占条件集X的比例。P(X)P(Y|X) = P(Y)P(X|Y) = P(XY)
Y、X 是两个事件,存在某种程度上的相互联系:
则由 Whole总体-Part局部、History历史-Current现在 的客观规律性;P(Y): Empirical Info.( History/Whole ):
经验概率, 来自理论, 总体普遍规律, 既有经验, 大范围统计, 历史时序数据)P(X|Y): Likelihood Probability:
似然概率(经验概率为前提, 普遍总体->群/样本集,历史->当前, 甚至是主观预估)P(X):Practical Sampling Info. 样本概率(标准化常量: 因样本概率可处理成标准化常量)
来源于 practice真实实践, sampling抽样得到Part局部/Current当前批次/时刻的样本P(Y|X):后验概率(practical info.为前提)
在实践得到的样本之上,以 计数原理/统计采样, 得到 P(Y|X)后验概率。
条件概率应用之分类器:
要从概率的角度处理分类器的问题:
把 Y, X 视为随机变量(随机事件的结果集合),
features: X =(X1, X2,…,Xn), 有 n 个特征的向量;
label: Y 属于结果集合{y1, y2, …, yn}
则有条件概率(X为给定集合时, Y = y 的概率)表示为:
P(Y=y | X=(x1, x2, …, xn))
Hypothesis:
for what value of y,
P(Y=y|X=(x1,x2,…,xn)) is maximum.
But …, P(Y|X) is hard to find.
To address it, here we introduce Bayes Theorem.
P(Y|X) = P(Y)•P(X|Y)/P(X)
where the right side is our dataset .
Application of Bayes' Theorem: Naive Bayes Classifiers and their implementation
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/naive-bayes-classifiers/
Naive Bayes classifiers are a collection of classification algorithms,
based on Bayes’ Theorem. It is not a single algorithm but a family of algorithms where all of them share a common principle, i.e. every pair of features being classified is independent of each other.
To start with, let us consider a dataset.
Consider a fictional dataset that describes the weather conditions for playing a game of golf.
Given the weather conditions, each tuple classifies the conditions as fit(“Yes”) or unfit(“No”) for playing golf.

The dataset is divided into two parts, namely, feature matrix and the response vector:
- Feature matrix contains all the vectors(rows) of dataset in which each vector consists of the value of dependent features. In above dataset, features are ‘Outlook’, ‘Temperature’, ‘Humidity’ and ‘Windy’.
- Response vector contains the value of class variable(prediction or output) for each row of feature matrix. In above dataset, the class variable name is ‘Play golf’.
Assumption:
The fundamental Naive Bayes assumption is that each feature makes an:
- independent
- equal
contribution to the outcome.
With relation to our dataset, this concept can be understood as:
- We assume that no pair of features are dependent. For example, the temperature being 'Hot' has nothing to do with the 'Humidity' or the 'Outlook' being "Rainy" has no effect on the 'Windy'. Hence, the features are assumed to be independent.
- Secondly, each feature is given the same weight(or importance). For example, knowing only temperature and humidity alone can’t predict the outcome accurately. None of the attributes is irrelevant and assumed to be contributing equally to the outcome.
Note: The assumptions made by Naive Bayes are not generally correct in real-world situations. In-fact, the independence assumption is never correct but often works well in practice.
Now, before moving to the formula for Naive Bayes, it is important to know about Bayes’ theorem.
Bayes’ Theorem:
Bayes’ Theorem finds the probability of an event occurring given the probability of another event that has already occurred. Bayes’ theorem is stated mathematically as the following equation:
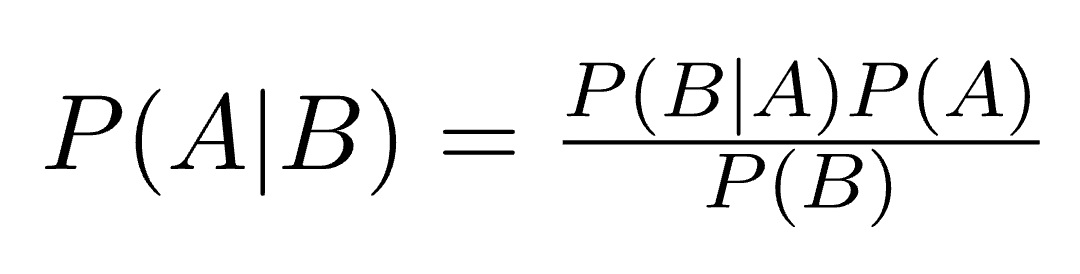
where A and B are events and P(B) ≠ 0.
Basically, we are trying to find probability of event A, given the event B is true.
- P(A) is the priori of A (the prior probability, i.e. Probability of event before evidence is seen).
- Event B is also termed as evidence. The evidence is an attribute value of an unknown instance(here, it is event B).
- P(A|B) is a posteriori probability of B, i.e. probability of event after evidence is seen.
Now, with regards to our dataset, we can apply Bayes’ theorem in following way:
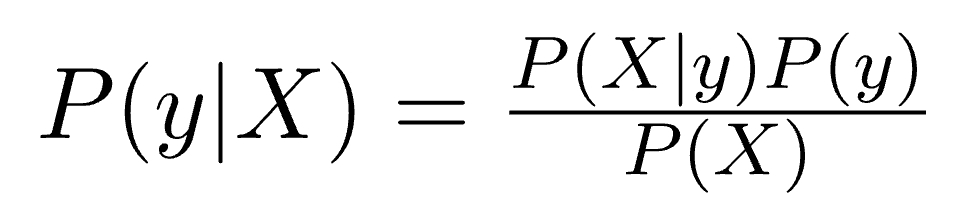
where, y is class variable and X is a dependent feature vector (of size n) where:
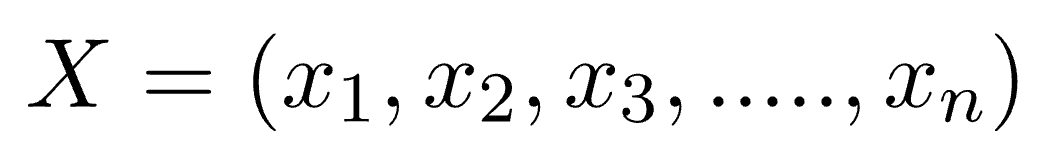
Just to clear, an example of a feature vector and corresponding class variable can be: (refer 1st row of dataset)
X = (Rainy, Hot, High, False)
y = No
So basically, P(y|X) here means, the probability of “Not playing golf” given that the weather conditions are “Rainy outlook”, “Temperature is hot”, “high humidity” and “no wind”.
Naive assumption
Now, its time to put a naive assumption to the Bayes’ theorem, which is, independence among the features. So now, we split evidence into the independent parts.
Now, if any two events A and B are independent, then,
P(A,B) = P(A)P(B)
Hence, we reach to the result:

which can be expressed as:
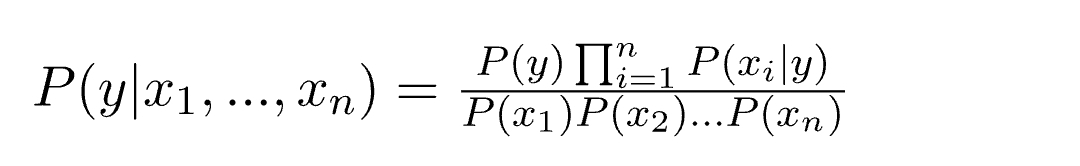
Now, as the denominator remains constant for a given input, we can remove that term:
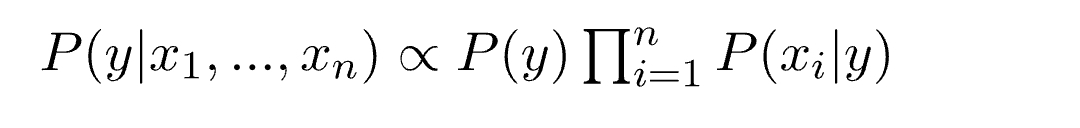
Now, we need to create a classifier model. For this, we find the probability of given set of inputs for all possible values of the class variable y and pick up the output with maximum probability. This can be expressed mathematically as:

So, finally, we are left with the task of calculating P(y) and P(xi | y).
Please note that P(y) is also called class probability and P(xi | y) is called conditional probability.
The different naive Bayes classifiers differ mainly by the assumptions they make regarding the distribution of P(xi | y).
Let us try to apply the above formula manually on our weather dataset. For this, we need to do some precomputations on our dataset.
We need to find P(xi | yj) for each xi in X and yj in y. All these calculations have been demonstrated in the tables below:
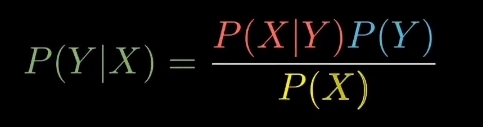
条件概率:{乘法公式•全概率公式•Bayes公式}_Bayes: PosteriorP(A|B)=PriorP(A)•Likelihood:(P(B|A)/P(B))的更多相关文章
- 用bayes公式进行机器学习的经典案例
用bayes公式进行机器学习的经典案例 从本科时候(大约9年前)刚接触Bayes公式,只知道P(A|B)×P(B) = P(AB) = P(B|A)×P(A) 到硕士期间,机器学习课上对P(B|A)P ...
- bayes公式 - 再从零开始理解
bayes公式与机器学习 - 再从零开始理解 从本科时候(大约9年前)刚接触Bayes公式,只知道P(A|B)×P(B) = P(AB) = P(B|A)×P(A) 到硕士期间,机器学习课上对P(B| ...
- 最大似然判别法和Bayes公式判别法
最大似然判别法 Bayes公式判别法
- EXCEL 如何实现下拉填充公式,保持公式部分内容不变,使用绝对引用
EXCEL 如何实现下拉填充公式,保持公式部分内容不变,使用绝对引用 在不想变的单元格前加$符号(列标和列数,两个都要加$),变成绝对引用,默认情况是相对引用 L4固定不变的方式:$L$4 M4固定不 ...
- latex:在公式之中和公式之间插入说明文字和标点符号
在公式之中和公式之间插入说明文字和标点符号,主要使用 \intertext{文本} \shortintertext{文本} \text{文本} 这三个命令 代码: \begin{align*}x^{2 ...
- 51Nod 1013 3的幂的和 快速幂 | 乘法逆元 | 递归求和公式
1.乘法逆元 直接使用等比数列求和公式,注意使用乘法逆元 ---严谨,失细节毁所有 #include "bits/stdc++.h" using namespace std; #d ...
- POI单元格添加公式以及读取公式结果的值
POI提供了为单元格添加条件样式的方法,但是我并没有找到获取单元格改变后样式的方法,获取到样式依旧是没有改变之前的. 比如为单元格添加条件样式用于监听单元格值是否被修改,如果单元格值被修改那么字体颜色 ...
- 个人整理方幂和公式(∑i^k 公式)
有个Oier小学妹问了我一个Σi^k,i<=1e8 ,k<=1e6的问题,我认为这个用伯努利数列可能可以解决他的问题,所以整理了以下文章,给学弟学习学习~~~本人水平有限,也只能帮到这里了 ...
- latex之行内公式与行间公式
1.行内公式 我是对行内公式的测试$f(x)=1+x+x^2$ 2.行间公式 单行不编号 \begin{equation} \int_0^1(1+x)dx \end{equation} 结果为: 单行 ...
- Word中MathType公式与LaTeX公式的转换
1. 对Word文档中用MathType输入的公式,在word中,选中mathtype公式,按住“Alt+\”键,可以将MathType公式转换成Latex格式. 2. 同样,将Latex格式的公式代 ...
随机推荐
- 微信小程序 6/12 的坑
配置 小程序的时候配置请求的是 https://xxx 不是http://xxx 前端请求的链接都是https
- 一款Windows平台上的开源Ark工具——OpenArk
简介 OpenArk是一款Windows平台上的开源Ark工具. Ark是Anti-Rootkit(对抗恶意程序)的简写, OpenArk目标成为逆向工程师.编程人员的工具,同时也能为那些希望清理恶意 ...
- 代码随想录第二十二天 | Leecode 77. 组合、216. 组合总和 III、17. 电话号码的字母组合
Leecode 77. 组合 题目描述 给定两个整数 n 和 k,返回范围 [1, n] 中所有可能的 k个数的组合. 你可以按 任何顺序 返回答案. 示例 1: 输入:n = 4, k = 2 输出 ...
- 通过 aqtinstall 安装 Qt5 的库
Qt Maintenance Tool (Qt Online Installer)可能没有 Qt5 的安装选项了,但是从 Qt 官网下载的qt-opensource-windows-x86-5.14. ...
- 探索Rust:所有权和借用的魅力与应用
@charset "UTF-8"; .markdown-body { line-height: 1.75; font-weight: 400; font-size: 15px; o ...
- 通过COM,用Python调用C#库
1.C#配置 (1)类库 (2)COM互操作打勾 (3)代码中类必须要有无参构造函数,否则不会注册成功!!! using System; using System.Runtime.InteropSer ...
- 2003 can't connect to mysql server on
把配置文件my.ini换成如下所示: mysql和mysql数据存放路径都是加双斜线 [mysql] # 设置mysql客户端默认字符集 default-character-set=utf8 [mys ...
- 一个基于 C# 编写的事件驱动、具备专业水准的算法交易平台(量化交易引擎)
前言 今天大姚给大家分享一个基于 C# 编写的事件驱动.采用模块化设计.具备专业水准的算法交易平台(量化交易引擎):Lean. 项目介绍 Lean 是由 QuantConnect 提供的一个基于 C# ...
- 「Note」POI 套题
POI 2011 \(\color{limegreen}{P3524}\) 此题是奇妙题. 每次删两个不连通的点,最多删掉 \(\frac{n}{3}\) 个点, 剩下的点一定都在团内,选 \(\fr ...
- 「Note」数论方向 - 数论基础
0. 前置知识 0.1. 费马小定理 \[a ^{p-1}\equiv1\pmod p(p\in\mathbb P,a\perp p) \] 由此可以推出模意义下乘法逆元: \[a ^{-1}\equ ...
