CSharp_core
C#核心篇
面向对象的概念
封装(类)、继承,多态
类
基本概念
- 具有相同特征、相同行为、一类事物的抽象
- 类是对象的模板,可以通过类创建出对象
- 关键词class
类的申明
申明在nameplace语句块中——也就是要写在class Program 的外面,如果在类(class)里面申明类,那就是内部类
语法
namespace 面向对象;
#region 类申明语法
// 命名:帕斯卡命名法
// 同一个语句块中的不同类不能重名
//访问修饰符 class 类名{
// //特征——成员变量
// //行为——成员方法(函数)
// //保护特征——成员属性
// //构造函数、析构函数
// //索引器
// //运算符重载
// //静态成员
// }
#endregion
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
}
}
使用
namespace 面向对象;
class Person{
}
class Machine{
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
#region 实例化对象示例(类创建对象)
//类对象都是引用类型的
//语法: 类名 对象名 = new 类名();
//在栈上开辟了一个空间存放地址,但是不开辟 堆内存空间,也就是null
Person p;
Person p1 = null;
//分配堆内存空间
//创建的每个对象只是模板都是同一个类,但是里面的信息都是不同的————类似造人
Person p2 = new Person();
Person p3 = new Person();
#endregion
}
}
习题

namespace 类和对象习题;
class Person{
}
class Animal{
}
class Machine{
}
class Plant{
}
class Astro{
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 1
Machine robot = new Machine();
Machine machine = new Machine();
Person people = new Person();
Animal cat = new Animal();
Person aunt = new Person();
Person uncle_Wang = new Person();
Machine car = new Machine();
Machine plane = new Machine();
Plant sunflower = new Plant();
Plant chrysanthemum = new Plant();
Astro sun = new Astro();
Astro star = new Astro();
Plant lotus = new Plant();
}
}
A指向一个地址指向一块堆内存
B指向一个地址,地址拷贝自A的地址,所以也指向A的堆内存
B = null :把B的地址与堆内存之间的指向关系断开
所以,A的堆内存没变
A和B没关系
成员变量——类的特征
- 申明在类语句块中
- 用来描述对象的特征
- 任意变量类型
- 数量不限
- 赋不赋值都行
namespace 成员变量;
//性别枚举
enum E_SexType{
Male,
Female,
}
//位置结构体
struct Position{
}
//宠物类
class Pet{
}
class Person{
//特征——成员变量
public string name = "Eano";//可以初始化也可以不初始化
public int age;
public E_SexType sex;
public Position position;
//可以申明任意类的对象,包括自身类
// (这点和结构体就不同,结构体如果申明自身结构体的变量就会无限循环导致报错
// 而在类里申明自身类的对象则没有问题,因为类是引用类型,只是声明一个对该对象的引用,也就是开辟了一个地址空间
// 不能实例化自身类的对象,因为这样的话在后面创建对象的时候就会陷入无限循环)
public Person girlfriend; //不能实例化自身类的对象,初始化为null是可以的
public Person[] friends;
public Pet pet; //可以实例化其他类的对象
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//创建对象
Person p = new Person();
#region 成员变量的使用与初始值
//值类型的默认值 都是0
// 相应的bool——false , char——'' ,string——""
//引用类型的默认值 都是null
//调用defalut()方法可以查看默认值
Console.WriteLine(default(int));
Console.WriteLine(default(bool));
Console.WriteLine(default(char));
//如果不申明,那么这个成员变量就是默认值
Console.WriteLine(p.age);
p.age = 25;
Console.WriteLine(p.age);
#endregion
}
}
总结:
- 访问修饰符——3P
- 在类里面申明自身类的对象的时候,不能实例化
- defalut()方法得到数据类型的默认值
习题

3P:
private
public
protected
namespace 成员变量习题;
class Student{
public string name;
public int age;
public string num;
public Student deskmate;
}
class Classroom{
public string major;
public int capacity;
public Student[] students;
public Classroom(int capacity)
{
this.capacity = capacity;
students = new Student[capacity];
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//3
Student s1 = new Student();
Student s2 = new Student();
//4
Classroom c1 = new Classroom(5);
}
}
p.age = 10
p2.age 是引用类型,拷贝的时候拷贝的是p.age的地址,改变p2.age的值,p.age也会改变
p.age = 20
age是值类型,只是拷贝了s.age的值,不指向同一地址,所以s.age不变
s.age = 10
s.deskmate.age = 20
成员方法——类的行为
不要加static关键字
namespace 成员方法;
class Person{
//成员方法
public void Speak(string message){
Console.WriteLine("{0}说{1}",name,message);
}
public bool IsAdult(){
return age>=18;
}
public void AddFriend(Person p){
if(friends==null) friends = new Person[]{p};
else{
Person[] temp = new Person[friends.Length+1];
for(int i=0;i<friends.Length;i++){
temp[i] = friends[i];
}
friends = temp;
friends[friends.Length-1] = p;
}
}
//成员变量
public Person[] friends;
public string name;
public int age;
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Person p = new Person();
p.Speak("Hello");
p.name = "Tom";
p.age = 20;
Console.WriteLine(p.IsAdult());
Person p2 = new Person(){name="Jerry",age=25};
p.AddFriend(p2);
Console.WriteLine(string.Join(",",p.friends.Select(f=>f.name)));
}
}
习题

namespace 成员方法习题;
class Student{
public void Speak(string message){
Console.WriteLine("{0} says: {1}",name,message);
}
public void Eat(Food food){
Console.WriteLine("{0} is eating {1},calories: {2}",name,food.name,food.calories);
}
public string name;
}
class Food{
public string name;
public int calories;
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student student = new Student(){name="Alice"};
Food apple = new Food(){name="apple",calories=50};
student.Eat(apple);
}
}
构造、析构函数、垃圾回收机制
构造函数——初始化时调用
- 在类里面用于调用时快速初始化的函数
- 没有构造函数的时候默认存在一个无参构造函数
也就是Person p = new Person();
写法:
和结构体一样,构造函数名要和类名相同
namespace 构造_析构函数;
class Person{
public string name;
public int age;
//构造函数
//类中允许申明无参构造函数,结构体则不允许
public Person(){
name = "eano";
age = 18;
}
//构造函数可以被重载
public Person(string name, int age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//现在有了3种申明并初始化对象的方式
Person p = new Person();
Console.WriteLine("Name: " + p.name);
Person p2 = new Person("eano", 18);
Console.WriteLine("Name: " + p2.name);
Person p3 = new Person(){name = "eano", age = 18};
Console.WriteLine("Name: " + p3.name);
}
}
注意:
- 如果不申明无参构造函数而申明了有参构造函数,那么这个默认的无参构造函数会被顶掉。
- this用来区分类内成员变量和外部传入参数
构造函数的特殊写法
:this(可选参数)复用代码
先进入无参构造函数
作用:复用先进入的构造函数代码
class Person{
public string name;
public int age;
//构造函数
//类中允许申明无参构造函数,结构体则不允许
public Person(){
name = "eano";
age = 18;
}
// //构造函数可以被重载
// public Person(string name, int age){
// this.name = name;
// this.age = age;
// }
//构造函数的特殊写法,在构造函数后:this(可选参数)
public Person(string name, int age) : this(){
Console.WriteLine("先进入无参构造函数");
}
}
:this(可选参数)可以指定先进入的构造函数
可选参数可以写死,比如
:this(18)就是先进入参数为int类型的构造函数
:this("eano")就是先进入参数为string类型的构造函数
习题

namespace 构造_析构函数习题;
class Person{
public string name;
public int age;
//构造函数
public Person(){
name = "eano";
age = 25;
}
//重载
public Person(string name, int age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
//特殊的构造函数
public Person(string name):this(){
Console.WriteLine("有参构造函数里的name:"+name);
}
}
class Ticket{
uint distance;
float price;
//构造函数
public Ticket(uint distance){
this.distance = distance;
//price是通过GetPrice()方法计算出来的
price = GetPrice();
}
//成员方法
public float GetPrice(){
if(distance > 300){
return distance * 0.8f;
}
else if(distance > 200){
return distance * 0.9f;
}
else if(distance > 100){
return distance * 0.95f;
}
else{
return distance * 1.0f;
}
}
public void PrintPrice(){
Console.WriteLine("距离{0}的票价为:{1}",distance,GetPrice());
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//1
//先进入无参构造函数,再进入有参构造函数
Person p1 = new Person("John");
Console.WriteLine(p1.name+" "+p1.age);
//3
Ticket t1 = new Ticket(250);
t1.PrintPrice();
}
}
析构函数——释放时调用
当引用类型的堆内存真正被回收时,调用析构函数
C++需要手动管理内存,所以才需要在析构函数中做内存回收处理
C#有自带的自动垃圾回收机制,所以不太需要析构函数,除非想在某个对象被垃圾回收时做一些特殊处理
要写在类里面
~类名(){
}
垃圾回收机制GC
原理:遍历堆(Heap)上动态分配的所有对象,通过识别是否被引用来确定哪些对象是垃圾,然后回收释放
垃圾回收的算法:
- 引用计数
- 标记清除
- 标记整理
- 复制集合
堆(Heap)内存由GC垃圾回收,引用类型
栈(Stack)内存由系统自动管理,值类型在栈中分配内存,有自己的申明周期,自动分配和释放
C#中内存回收机制的原理:
分代算法
0代内存 1代内存 2代内存
新分配的对象都被配置在0代内存中,(0代内存满时)触发垃圾回收
在一次内存回收过程开始时,垃圾回收器会认为堆中全是垃圾,进行以下两步:
- 标记对象:从根(静态字段、方法参数)开始检查引用对象,标记后为可达对象,被标记的为不可达对象——不可达对象就是垃圾
- 搬迁对象压缩堆:(挂起执行托管代码线程)释放未标记的对象,搬迁可达对象到一代内存中,修改可达对象的引用地址为连续的地址
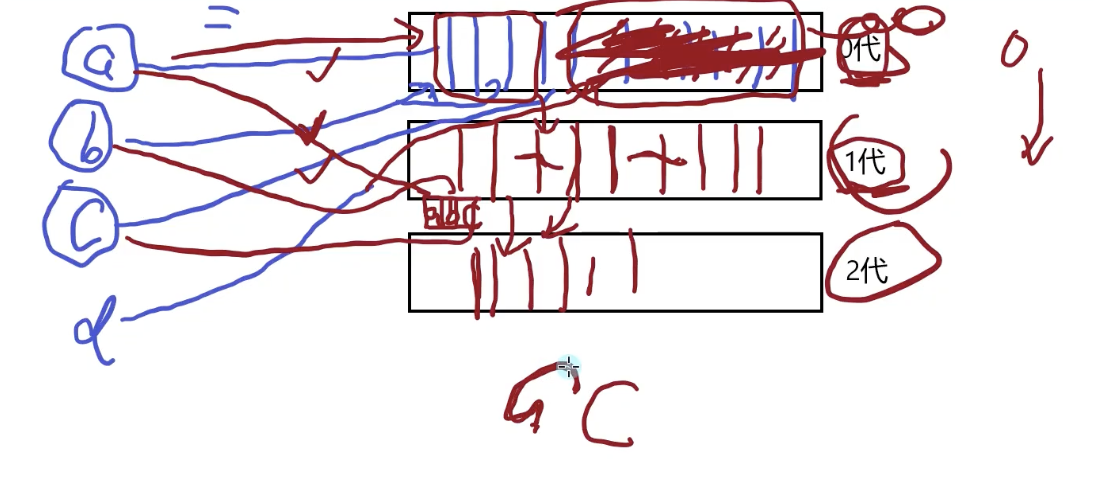
大对象:
大对象是第二代内存,目的是减少性能损耗以提高性能
不会对大对象进行搬迁压缩,85000字节(83kb)以上的对象是大对象
这个机制有点像三级缓存
速度:0 > 1 > 2
容量:0 < 1 < 2
手动进行GC
GC.Collect()
一般在Loading过场动画的时候调用
小节
class 类名{
//特征——成员变量
//行为——成员的方法
//初始化时调用——构造函数
//释放时调用——析构函数
}
成员属性——保护成员变量
- 通过在get和set里面写逻辑,来保护成员变量
- 解决3p的局限性
- 用来让成员变量在外部:只能获取不能修改 / 只能修改不能获取
语法:
//访问修饰符 属性类型 属性名{
// get{}
// set{}
//}
使用:
namespace 成员属性;
//访问修饰符 属性类型 属性名{
// get{}
// set{}
//}
class Person{
private string name;
private int age;
private int money;
private bool sex;
//成员属性
public string Name{
get{
//返回之前可以写逻辑规则
return name;
}
set{
//设置之前可以写逻辑规则
//value用来接收外部传入的值
name = value;
}
}
public int Money{
get{
//加密处理
return money - 5;
}
set{
//逻辑处理
if(value < 0){
value = 0;
Console.WriteLine("金额不能为负数");
}
//加密处理
//这一部分涉及到加密算法,这里省略
money = value + 5;
}
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Person p = new Person();
p.Name = "eano";//调用的是set语句块
Console.WriteLine(p.Name);//调用的是get语句块
p.Money = -999;
Console.WriteLine(p.Money);
p.Money = 1000;
Console.WriteLine(p.Money);
}
}
get和set前可以加访问修饰符
#region get和set前可以加访问修饰符
//1. 默认不加,会使用成员属性的访问修饰符(这里就是public)
//2. 加的修饰符要低于成员属性的访问修饰符,否则会报错
//3. 不能让get和set的访问权限都低于成员属性的权限
public int Age{
private get{
return age;
}
set{
age = value;
}
}
#endregion
get和set可以只有一个
#region get和set可以只有一个
//一般只会出现 只有get的情况,只能获取值,不能修改值————只读属性
//只有一个的时候,不要加修饰符
public bool Sex{
get{
return sex;
}
}
#endregion
自动属性
#region 自动属性
//作用:外部只读不写的特性
//使用场景:一个特征是只希望外部只读不可写,也不加别的特殊处理
public float Height { get; private set; }
//只可以在类内部set
#endregion
习题

namespace 成员属性习题;
class Student{
private string name;
private string sex;
private int age;
private int csGrade;
private int unityGrade;
public string Name{get; private set;}
public string Sex{
get{
return sex;
}
private set{
if(value != "男" && value != "女") sex = "unknown";
else sex = value;
}
}
public int Age{
get{
return age;
}
private set{
if(value < 0) age = 0;
else if(value > 150) age = 150;
else age = value;
}
}
public int CsGrade{get; private set;}
public int UnityGrade{
get{
return unityGrade;
}
private set{
if(value < 0) unityGrade = 0;
else if(value > 120) unityGrade = 120;
else unityGrade = value;
}
}
public Student(string name, string sex, int age, int csGrade, int unityGrade){
Name = name;
Sex = sex;
Age = age;
CsGrade = csGrade;
UnityGrade = unityGrade;
}
public void Saymyself(){
Console.WriteLine("My name is {0}, I am {1} years old, a {2}.", Name, Age, Sex);
}
public void SayGrade(){
int sum = CsGrade + UnityGrade;
float average = (float)sum / 2;
Console.WriteLine("My sum grade is {0}, my average grade is {1}.", sum, average);
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student student1 = new Student("Tom", "男", 18, 90, 80);
student1.Saymyself();
student1.SayGrade();
Student student2 = new Student("Jerry", "女", 160, 100, 90);
student2.Saymyself();
student2.SayGrade();
}
}
索引器——像数组一样访问元素
让对象可以像数组一样通过索引访问元素
注意:结构体中也支持索引器
语法
class Person{
private string name;
private int age;
private Person[] friends;
#region 索引器语法
//访问修饰符 返回值 this[数据类型 参数名1,数据类型 参数名2,...]{
// 和属性的写法相同:
// get{
// }
// set{
// }
// }
public Person this[int index]{
get{
return friends[index];
}
set{
friends[index] = value;
}
}
#endregion
}
用法
namespace 索引器;
class Person{
private string name;
private int age;
private Person[] friends;
private int[,] array;
public string Name{get;private set;}
public int Age{get;private set;}
public Person[] Friends{get;private set;}
public int[,] Array{get;private set;}
public Person(string name, int age){
Name = name;
Age = age;
friends = new Person[5];
Friends = friends;
array = new int[3, 4];
Array = array;
}
#region 索引器语法
//访问修饰符 返回值 this[数据类型 参数名1,数据类型 参数名2,...]{
// 和属性的写法相同:
// get{
// }
// set{
// }
// }
public Person this[int index]{
get{
#region 索引器里也能写逻辑
if(friends == null || index < 0 || index >= friends.Length){
return null;
}
else{
return friends[index];
}
#endregion
}
set{
if(friends == null){
friends = new Person[]{value};
}
//如果越界,顶掉最后一个元素
else if(index < 0 || index >= friends.Length){
friends[friends.Length - 1] = value;
}
else friends[index] = value;
}
}
#endregion
#region 索引器可以重载
//参数不同
public int this[int row, int col]{
get{
return array[row, col];
}
set{
array[row, col] = value;
}
}
public string this[string str]{
get{
switch(str){
case "name":
return Name;
case "age":
return Age.ToString();
default:
return "Invalid index";
}
}
}
#endregion
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Person p1 = new Person("Alice", 25);
p1.Friends[0] = new Person("Bob", 20);
p1[1] = new Person("Charlie", 22);
Console.WriteLine(p1[0].Name);
p1[2, 3] = 10;
Console.WriteLine(p1[2, 3]);
Console.WriteLine("{0}的年龄是{1}, 朋友是{2}", p1["name"],p1["age"],p1[0]["name"]);
}
}
索引器就相当于给对象加一个属性,用中括号[参数]调用这个属性的内容
习题

namespace 索引器习题;
class IntArray{
public int[] arr;
public int length;
public IntArray(int size){
length = 0;
arr = new int[size];
}
//增
public void Add(int index, int value){
if(index < 0 || index > length){
Console.WriteLine("索引超出范围");
return;
}
else{
if(length < arr.Length){
arr[length] = value;
length++;
}
else{
int[] newArr = new int[arr.Length + 1];
for(int i=0;i<arr.Length;i++){
newArr[i] = arr[i];
}
arr = newArr;
//后面元素后移
for(int i = length-1;i>=index;i--){
arr[i+1] = arr[i];
}
arr[index] = value;
length++;
}
}
}
//删
public void Remove(int index){
if(index > length-1 || index < 0){
Console.WriteLine("索引超出范围");
return;
}
else{
//后面元素前移
for(int i = index;i<length-1;i++){
arr[i] = arr[i+1];
}
length--;
}
}
//索引器
//查
//改
public int this[int index]{
get{
return arr[index];
}
set{
arr[index] = value;
}
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
IntArray arr = new IntArray(5);
arr.Add(0,1);
arr.Add(1,2);
arr.Add(2,3);
arr.Add(3,4);
arr.Add(4,5);
arr.Add(5,6);
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
Console.Write(arr[i] + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine(arr.length);
arr.Remove(2);
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
Console.Write(arr[i] + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine(arr.length);
arr[0] = 10;
Console.WriteLine(arr[0]);
}
}
静态成员——类名.出来使用
静态关键字 static
修饰成员变量、方法、属性
静态成员可以用 类名.静态成员名直接调用
一般写成public公共的
申明与使用
namespace 静态成员;
class Test{
static public float PI = 3.14f;
public int testInt = 10;
static public float CircleArea(float r){
#region 静态函数不能访问非静态成员
// 非静态成员只能在实例化对象后调用
Test t = new Test();
Console.WriteLine(t.testInt);
#endregion
return PI * r * r;
}
public void TestFunc(){
Console.WriteLine("This is a test function");
#region 非静态函数可以使用静态成员
Console.WriteLine(PI);
Console.WriteLine(CircleArea(5));
#endregion
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
#region 静态成员的使用
Console.WriteLine(Test.PI);
// Console.WriteLine(Test.testInt); // 不能直接类名.调用
// 非静态成员只能在实例化对象后调用
Test t = new Test();
Console.WriteLine(t.testInt);
Console.WriteLine(Test.CircleArea(5));
//Console.WriteLine(Test.TestFunc());// 不能直接类名.调用
t.TestFunc();
#endregion
}
}
为什么可以类名.静态成员名使用
程序开始运行的时候,就会给静态成员分配内存空间
静态成员与程序共生死
每个静态成员都会有一个唯一的内存空间
直到程序结束,静态成员的内存空间才会被释放
作用
- 申明唯一变量
- 方便在其他地方获取的对象的申明
- 申明唯一方法——相同规则的数学计算
问题
长期占用内存空间,其他非静态成员gc的阈值变小,程序性能降低
常态和静态变量
相同点:
- 都可以通过类名.出来使用
不同点:
- const修饰常量,必须初始化,不能修改
- const要直接写在变量的前面,也就是访问修饰符的后面
- const只能修饰变量,static还可以修饰方法、属性
习题

namespace 静态成员习题;
//单例模式
class Test{
private static Test t = new Test();
public int testInt = 10;
public static Test T{
get{
return t;
}
}
private Test(){
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine(Test.T.testInt);
Test.T.testInt = 20;
// Test t1 = new Test(); //外部无法实例化
Console.WriteLine(Test.T.testInt);
}
}
静态类和静态构造函数
作为工具使用,就像Console类一样,直接类名.出来使用静态成员
静态类
static修饰的类
- 只能包含静态成员
- 不能被实例化
作用:
- 将常用的静态成员写在静态类中
- 静态类不能被实例化,体现工具类的唯一性
静态构造函数
static修饰的构造函数
- 静态类和非静态类都可以用静态构造函数
- 静态构造函数不能使用访问修饰符
- 不能有参数
- 只会调用一次
静态构造函数只会在第一次使用类的时候调用一次,与类是否是静态类无关
普通构造函数每次实例化类的对象都会调用一次
using System.Runtime.CompilerServices;
namespace 静态类和静态构造函数;
#region 静态类
static class TestStatic{
public static void TestFunc(){
}
//静态类只能包含静态成员
// public void Say(){
// }
public static int TestIndex{get;set;}
}
#endregion
#region 静态构造函数
//1. 静态类中的静态构造函数
static class StaticClass{
public static int testInt = 10;
//静态构造函数不能加访问修饰符
//无参
static StaticClass(){
Console.WriteLine("静态类中的静态构造函数执行");
//在静态构造函数里初始化成员变量
testInt = 20;
}
}
//2. 普通类中的静态构造函数
class NormalClass{
public static int testInt = 10;
static NormalClass(){
Console.WriteLine("普通类中的静态构造函数执行");
//在静态构造函数里初始化成员变量
testInt = 20;
}
public NormalClass(){
Console.WriteLine("普通类中的普通构造函数执行");
}
}
#endregion
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//调用两次静态成员,但只执行一次静态构造函数
Console.WriteLine(StaticClass.testInt);
Console.WriteLine(StaticClass.testInt);
//普通类中的静态构造函数也只执行一次
Console.WriteLine(NormalClass.testInt);
Console.WriteLine(NormalClass.testInt);
//普通类中的普通构造函数每次实例化都会执行
NormalClass nc = new NormalClass();
NormalClass nc2 = new NormalClass();
}
}
习题

namespace 静态类和静态构造函数习题;
static class MathCalc{
const float pi = 3.14f;
public static float CircleArea(float r){
Console.WriteLine("半径为{0}的圆的面积为{1}", r, pi * r * r);
return pi * r * r;
}
public static float CirclePerimeter(float r){
Console.WriteLine("半径为{0}的圆的周长为{1}", r, 2 * pi * r);
return 2 * pi * r;
}
public static float RectangleArea(float a, float b){
Console.WriteLine("长为{0}宽为{1}的矩形的面积为{2}", a, b, a * b);
return a * b;
}
public static float RectanglePerimeter(float a, float b){
Console.WriteLine("长为{0}宽为{1}的矩形的周长为{2}", a, b, 2 * (a + b));
return 2 * (a + b);
}
public static float Abs(float n){
float n1 = (n > 0)?n:-n;
Console.WriteLine("{0}绝对值为{1}", n, n1);
return n1;
}
static MathCalc(){
Console.WriteLine("静态构造函数执行");
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
MathCalc.CircleArea(5);
MathCalc.CirclePerimeter(5);
MathCalc.RectangleArea(5, 10);
MathCalc.RectanglePerimeter(5, 10);
MathCalc.Abs(-5);
}
}
拓展方法
为现有非静态变量类型 添加新方法
作用:
- 提升程序拓展性
- 不需要在对象中重新写方法
- 不需要继承来添加方法
- 为别人封装的类写额外的方法
特点:
- 一定写在静态类中
- 一定是一个静态函数
- 第一个参数是拓展目标(想要拓展方法的类型),要用this修饰
语法
访问修饰符 static 返回值类型 函数名(this 拓展类名 参数名,参数数据类型 参数, ...){
}
namespace 拓展方法;
#region 语法
//访问修饰符 static 返回值类型 函数名(this 拓展类名 参数名,参数数据类型 参数, ...){
//
//}
#endregion
#region 示例
static class Tools{
public static void Print(this string str){
Console.WriteLine("为string拓展方法:"+str);
}
}
#endregion
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string str = "Hello World";
str.Print(); //调用拓展方法
}
}
使用
namespace 拓展方法;
#region 语法
//访问修饰符 static 返回值类型 函数名(this 拓展类名 参数名,参数数据类型 参数, ...){
//
//}
#endregion
#region 示例
static class Tools{
public static void Print(this string str){
Console.WriteLine("为string拓展方法:"+str);
}
public static void PrintInfo(this string str, string str1, int num){
Console.WriteLine("拓展方法的对象:"+str);
Console.WriteLine("传入的参数:"+str1 + " " + num);
}
public static void PrintInfo(this Test t){
Console.WriteLine("为Test类拓展方法:"+t.i);
}
//如果拓展的方法名和类里面的方法重名,优先使用类的方法
public static void Func(this Test t){
Console.WriteLine("为Test类拓展同名方法:");
}
}
#endregion
#region 为自定义的类型拓展方法
class Test{
public int i = 10;
public void Func(){
Console.WriteLine("Test类自己的Func方法");
}
}
#endregion
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string str = "Hello World";
str.Print(); //调用拓展方法
str.PrintInfo("你好", 123); //调用拓展方法
//为自定义的类型拓展方法
Test t = new Test();
t.PrintInfo(); //调用拓展方法
t.Func(); //重名,优先调用类自己的方法
}
}
注意:
如果拓展的方法名和类里面的方法重名,优先使用类的方法
习题

namespace 拓展方法习题;
//1
//平方
static class Test{
public static int Square(this int n){
Console.WriteLine("Square of " + n + " is " + (n*n));
return n*n;
}
public static void Suicide(this Player player){
Console.WriteLine("Player " + player.name + " is suiciding!");
}
}
//2
//玩家
class Player{
public string name;
public int hp;
public int atk;
public int def;
public Player(string name, int hp, int atk, int def){
this.name = name;
this.hp = hp;
this.atk = atk;
this.def = def;
}
public void Attack(Player target){
Console.WriteLine(this.name + " attacks " + target.name + "!");
target.hp -= this.atk - target.def;
Console.WriteLine(target.name + " now has " + target.hp + " HP.");
if(this.atk - target.def > 0){
Hurted(target);
}
}
public void Move(int x, int y){
Console.WriteLine(this.name + " moves to (" + x + ", " + y + ").");
}
public void Hurted(Player target){
Console.WriteLine(target.name + " is hurt!");
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//1
int num = 3;
num.Square();
//2
Player player1 = new Player("player1", 100, 10, 5);
Player player2 = new Player("player2", 100, 13, 2);
player1.Attack(player2);
player1.Move(1, 2);
player1.Suicide();
player2.Attack(player1);
player2.Suicide();
}
}
运算符重载——自定义对象能够运算
让自定义的类和结构体对象 能够使用运算符
关键字: operator
特点:
- 必须是公共的静态方法
- 返回值写在operator前
注意:
- 条件运算符需要成对实现
- 一个符号可以多个重载
- 不能使用ref和out
语法
//语法
//public static 类名 返回类型 operator 运算符(参数类型1 参数名1, 参数类型2 参数名2){
//}
用法实例
namespace 运算符重载;
class Program
{
//语法
//public static 类名 返回类型 operator 运算符(参数类型1 参数名1, 参数类型2 参数名2){
//}
//实例
class Point {
public int x, y;
public static Point operator +(Point p1, Point p2) {
Point p = new Point();
p.x = p1.x + p2.x;
p.y = p1.y + p2.y;
return p;
}
//重载
public static Point operator +(Point p1, int num) {
Point p = new Point();
p.x = p1.x + num;
p.y = p1.y + num;
return p;
}
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Point p1 = new Point();
p1.x = 1;
p1.y = 2;
Point p2 = new Point();
p2.x = 3;
p2.y = 4;
Point p3 = p1 + p2;
Console.WriteLine("p3.x = " + p3.x);
Point p4 = p1 + 2;
Console.WriteLine("p4.x = " + p4.x);
//可以连续使用
p4 = p1 + p2 + 3;
Console.WriteLine("p4.x = " + p4.x);
}
}
可重载和不可重载的运算符
#region 可重载的运算符
//算数运算符:+ - * / % ++ --
// (自增自减的参数只有一个)
//逻辑运算符:!
// ( &&和||不能重载 )
//位运算符:~ & | ^ << >>
// (~只有一个参数)
// (左移右移的参数Point p,int num)
//条件运算符:> < >= <= == !=
//条件运算符需要成对实现
// 也就是>和<需要成对重载,>=和<=需要成对重载,==和!=需要成对重载
#endregion
#region 不可重载的运算符
//逻辑运算符:&& ||
//索引符:[]
//强转运算符:()
//特殊运算符:点. 三目运算符的? 赋值符号=
#endregion
习题

namespace 运算符重载习题;
//1
class Position{
public int x;
public int y;
public static bool operator ==(Position p1, Position p2){
if(p1.x == p2.x && p1.y == p2.y){
return true;
}
return false;
}
public static bool operator !=(Position p1, Position p2){
if(p1.x!= p2.x || p1.y!= p2.y){
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
//2
class Vector3{
public int x;
public int y;
public int z;
public static Vector3 operator +(Vector3 v1, Vector3 v2){
Vector3 result = new Vector3();
result.x = v1.x + v2.x;
result.y = v1.y + v2.y;
result.z = v1.z + v2.z;
return result;
}
public static Vector3 operator -(Vector3 v1, Vector3 v2){
Vector3 result = new Vector3();
result.x = v1.x - v2.x;
result.y = v1.y - v2.y;
result.z = v1.z - v2.z;
return result;
}
public static Vector3 operator *(Vector3 v1, int n){
Vector3 result = new Vector3();
result.x = v1.x * n;
result.y = v1.y * n;
result.z = v1.z * n;
return result;
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//1
Position a = new Position();
a.x = 1;
a.y = 2;
Position b = new Position();
b.x = 1;
b.y = 2;
Console.WriteLine(a == b); // True
Console.WriteLine(a!= b); // False
//2
Vector3 v1 = new Vector3();
v1.x = 1;
v1.y = 2;
v1.z = 3;
Vector3 v2 = new Vector3();
v2.x = 2;
v2.y = 3;
v2.z = 4;
Vector3 v3 = v1 + v2;
Console.WriteLine("(v3.x, v3.y, v3.z) = ({0}, {1}, {2})", v3.x, v3.y, v3.z);
Vector3 v4 = v1 - v2;
Console.WriteLine("(v4.x, v4.y, v4.z) = ({0}, {1}, {2})", v4.x, v4.y, v4.z);
Vector3 v5 = v1 * 2;
Console.WriteLine("(v5.x, v5.y, v5.z) = ({0}, {1}, {2})", v5.x, v5.y, v5.z);
}
}
内部类和分部类
内部类——在一个类中申明一个类
要用包裹者点出这个内部类
作用:亲密关系的体现,有点像继承
注意:访问修饰符作用很大
namespace 内部类和分部类;
#region 内部类
class Person{
public string name;
public int age;
public Body body;
public class Body{
Arm leftArm;
Arm rightArm;
class Arm{
}
}
}
#endregion
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Person person = new Person();
person.body = new Person.Body();
//访问修饰符的作用,不写public,则无法访问
// person.body.leftArm = new Person.Body.Arm();
}
}
分部类——一个类分成几部分申明
关键字:partial
作用:分部描述一个类,增加程序的可拓展性
注意:
- 分部类可以写在多个脚本文件中
- 分部类的访问修饰符要一致
- 分部类中不能有重复的成员
namespace 内部类和分部类;
#region 内部类
class Person{
public string name;
public int age;
public Body body;
public class Body{
Arm leftArm;
Arm rightArm;
class Arm{
}
}
}
#endregion
#region 分部类
partial class Student{
public bool sex;
public string name;
}
partial class Student{
public int age;
//注意不要重复成员名
// public string name;
public void SayHello(){
Console.WriteLine("Hello,I'm {0},age is {1}",name,age);
}
}
#endregion
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//内部类
Person person = new Person();
person.body = new Person.Body();
//访问修饰符的作用,不写public,则无法访问
// person.body.leftArm = new Person.Body.Arm();
//分部类
Student student = new Student();
student.age = 18;
student.name = "Tom";
student.sex = true;
student.SayHello();
}
}
分部方法——将方法的申明和实现分离
注意:
- 不能加访问修饰符,默认私有
- 只能在分部类里申明
- 返回值只能是void
- 参数不能用out关键字
namespace 内部类和分部类;
#region 内部类
class Person{
public string name;
public int age;
public Body body;
public class Body{
Arm leftArm;
Arm rightArm;
class Arm{
}
}
}
#endregion
#region 分部类
partial class Student{
public bool sex;
public string name;
public partial void SayHello();
}
partial class Student{
public int age;
//注意不要重复成员名
// public string name;
public partial void SayHello(){
Console.WriteLine("I'm {0},age:{1}", name, age);
}
}
#endregion
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//内部类
Person person = new Person();
person.body = new Person.Body();
//访问修饰符的作用,不写public,则无法访问
// person.body.leftArm = new Person.Body.Arm();
//分部类
Student student = new Student();
student.age = 18;
student.name = "Tom";
student.sex = true;
student.SayHello();
}
}
CSharp_core的更多相关文章
- .net core 2.x - ids4 - identity - two factory 登录认证
本片内容使用到ids4+ids4.Entityframework持久化表单,以及core的identity相关表的一并持久化,然后就是登录认证,认证使用email发送邮件的方式.所以这里涉及到四块内容 ...
随机推荐
- Linux 部署DVWA靶场
Linux 部署DVWA靶场 DVWA是一款开源的网络安全漏洞实践平台,专为安全学习者设计.它涵盖了XXS.SQL注入.文件上传.文件包含.CSRF和暴力破解等多种安全漏洞环境,每个漏洞都有从简单到复 ...
- FLink参数pipeline.operator-chaining介绍
1.当使用flink提交一个任务,没有给算子设置并行度情况下,默认所有算子会chain在一起,整个DAG图只会显示一个算子,虽然有利于数据传输,提高程序性能,但是无法看到数据的输入和疏忽,业绩反压相关 ...
- 深入浅出理解Continuous Queries和Cypher Query Language
1. 什么是Continuous Queries? 连续查询是 Drasi 最重要的组件.它们是您告诉 Drasi 要在源系统中检测哪些更改以及检测到更改时要分发的数据的机制.源为订阅的 Contin ...
- ssh远程连接linux服务器
Linux,ssh远程连接 一. linux端配置 1.安装ssh服务 sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install openssh-client sudo apt ...
- FormCreate设计器v5.6发布—AI加持的低代码表单设计器正式上线!
近期DeepSeek可谓是刷遍全网,当然,在DeepSeek等AI技术的推动下,人工智能正以惊人的速度改变着各行各业.AI不仅是一种技术趋势,更是未来生产力的核心驱动力. 如今,FormCreate设 ...
- RealityCapture重建试验
一.使用已有数据集 (一)小型物件(官网) 输入:Camera_Lubitel2_studio "Lubitel Camera" consisting of 72 images 地 ...
- golang结构体判断是否为空
前言 使用任何编程语言都会遇到判空的问题,那么Golang对于自定义的结构体类型如何判空呢? 其实空结构体可不是简单的与nil做比较哦.请看下面两种方法: package main import ( ...
- 『Plotly实战指南』--折线图绘制进阶篇
上一篇介绍了Plotly绘制折线图的基础知识和数据预处理的技巧, 本文将重点探讨如何利用Plotly实现多线折线图的布局设计以及动态折线图的实现, 让我们一起掌握进阶的折线图绘制技巧. 1. 多折线图 ...
- docker搭建本地仓库
环境准备: 服务器:9.134.130.35 私有仓库服务器,运行registry容器 客户端:9.208.244.175 测试客户端,用于上传.下载镜像文件 测试搭建本地仓库 mkdir /dock ...
- 项目实战 TS
项目实战 TS 通用技巧 新手先 any 再填坑,老手先定义数据结构写逻辑 遇到新场景,没把握快速,先用 any 再填坑,填坑的过程也是 TS 技能满满提升的过程. TS 发现潜在问题 1)复杂逻辑, ...
